Python接单亲身经历,学会爬虫来钱能有多爽?
今天给大家是Python接单的一个副业机会,文末有福利!
上周末接到一个单1200,客服抽了百分之十的提成,到手1000,两个小时就完成了,心里美滋滋的,这样的单其实平常不多,技术难度低但是价格高,我们俗称“捡鱼单”。想着赚钱了请女神吃饭,竟被无情拒绝。
效果展示

工具准备
-
数据来源: https://maoyan.com/board/4?offset=1
-
开发环境:win10、python3.7
-
开发工具:pycharm、Chrome
项目思路解析
首先将猫眼电影的所以的电影信息采集下来。
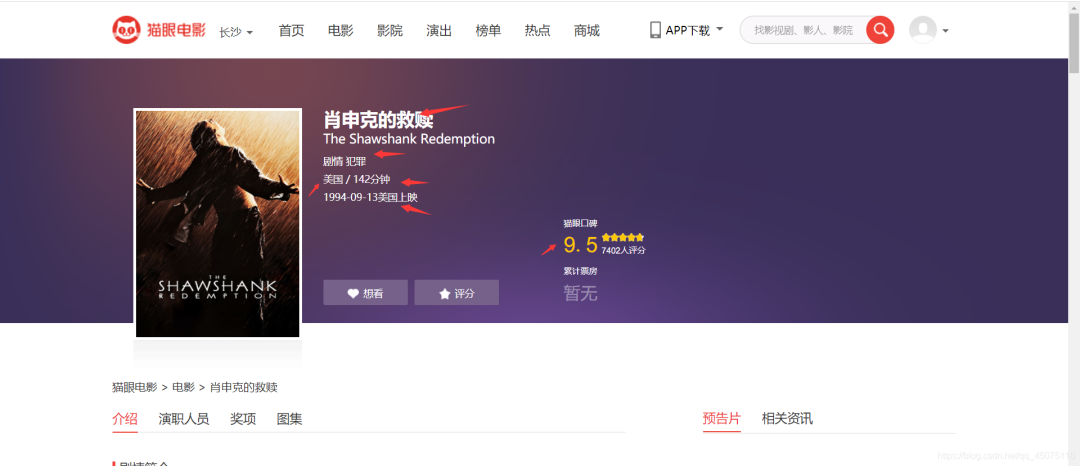
这里以猫眼的top100榜为例。
获取到电影信息:
-
电影名称
-
电影评分
-
电影链接
-
电影类型
-
电影上映地点
-
地点
-
电影时长
-
电影时长
解析网页数据信息,解析首页的跳转链接。
猫眼详情页面的评分是有加密的,所以我们直接重主页提取评分信息。
在详情页面提取数据。
将数据保存在csv表格,方便之后做数据可视化。

数据可视化需要用到的工具
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get\_ipython().run\_line\_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
效果图展示


源码展示
爬虫代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -\*- coding: utf-8 -\*-
# @Time : 2021年06月05日
# @File : demo4.py
import requests
from fake\_useragent import UserAgent
from lxml import etree
import time
# 随机请求头
ua = UserAgent()
# 构建请求 需要自己去网页上面换一下 请求不到了就 去网页刷新 把验证码弄了
headers = {
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,\*/\*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9',
'Cookie': '\_\_mta=244176442.1622872454168.1622876903037.1622877097390.7; uuid\_n\_v=v1; uuid=6FFF6D30C5C211EB8D61CF53B1EFE83FE91D3C40EE5240DCBA0A422050B1E8C0; \_csrf=bff9b813020b795594ff3b2ea3c1be6295b7453d19ecd72f8beb9700c679dfb4; Hm\_lvt\_703e94591e87be68cc8da0da7cbd0be2=1622872443; \_lxsdk\_cuid=1770e9ed136c8-048c356e76a22b-7d677965-1fa400-1770e9ed136c8; \_lxsdk=6FFF6D30C5C211EB8D61CF53B1EFE83FE91D3C40EE5240DCBA0A422050B1E8C0; ci=59; recentCis=59; \_\_mta=51142166.1622872443578.1622872443578.1622876719906.2; Hm\_lpvt\_703e94591e87be68cc8da0da7cbd0be2=1622877097; \_lxsdk\_s=179dafd56bf-06d-403-d81%7C%7C12',
'User-Agent': str(ua.random)
}
def RequestsTools(url):
'''
爬虫请求工具函数
:param url: 请求地址
:return: HTML对象 用于xpath提取
'''
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers).content.decode('utf-8')
html = etree.HTML(response)
return html
def Index(page):
'''
首页函数
:param page: 页数
:return:
'''
url = 'https://maoyan.com/board/4?offset={}'.format(page)
html = RequestsTools(url)
# 详情页地址后缀
urls\_text = html.xpath('//a\[@class="image-link"\]/@href')
# 评分
pingfen1 = html.xpath('//i\[@class="integer"\]/text()')
pingfen2 = html.xpath('//i\[@class="fraction"\]/text()')
for i, p1, p2 in zip(urls\_text, pingfen1, pingfen2):
pingfen = p1 + p2
urs = 'https://maoyan.com' + i
# 反正请求太过于频繁
time.sleep(2)
Details(urs, pingfen)
def Details(url, pingfen):
html = RequestsTools(url)
dianyan = html.xpath('//h1\[@class="name"\]/text()') # 电影名称
leixing = html.xpath('//li\[@class="ellipsis"\]/a/text()') # 类型
diqu = html.xpath('/html/body/div\[3\]/div/div\[2\]/div\[1\]/ul/li\[2\]/text()') # 读取总和
timedata = html.xpath('/html/body/div\[3\]/div/div\[2\]/div\[1\]/ul/li\[3\]/text()') # 时间
for d, l, b, t in zip(dianyan, leixing, diqu, timedata):
countyr = b.replace('\\n', '').split('/')\[0\] # 地区
shichang = b.replace('\\n', '').split('/')\[1\] # 时长
f = open('猫眼.csv', 'a')
f.write('{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}\\n'.format(d, pingfen, url, l, countyr, shichang, t))
print(d, pingfen, url, l, countyr, shichang, t )
for page in range(0, 11):
page \*= 10
Index(page)
可视化
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# 加载数据分析常用库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get\_ipython().run\_line\_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
# In\[3\]:
path='./maoyan.csv'
df=pd.read\_csv(path,sep=',',encoding='utf-8',index\_col=False)
df.drop(df.columns\[0\],axis=1,inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
df.drop\_duplicates(inplace=True)
df.head(10)
#查看数据的结构
df.info()
print(df.columns)
# In\[11\]:
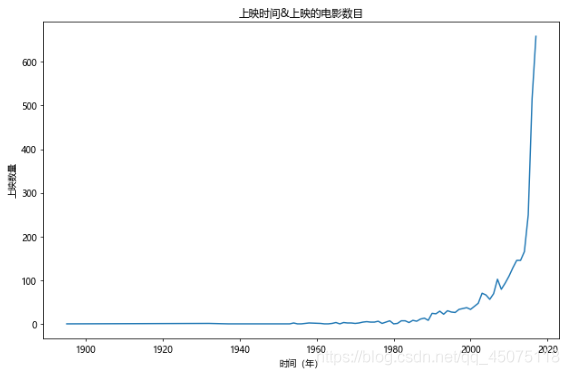
#年份&上映电影的数目 2018及以后的上映数目只是目前猫眼上公布的,具有不确定性,就先把2018及之后的剔除
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=70)
df\[df\[u'上映时间'\]<2018\]\[u'上映时间'\].value\_counts().sort\_index().plot(kind='line',ax=ax)
ax.set\_xlabel(u'时间(年)')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'上映数量')
ax.set\_title(u'上映时间&上映的电影数目')
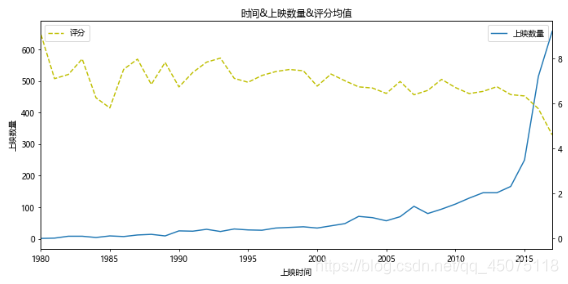
#基于上图,再弄一个上映时间&上映数量&评分的关系图
#但是由于1980年以前的数据量较少,评分不准确,将主要的分析区域集中在1980-2017
x=df\[df\[u'上映时间'\]<2018\]\[u'上映时间'\].value\_counts().sort\_index().index
y=df\[df\[u'上映时间'\]<2018\]\[u'上映时间'\].value\_counts().sort\_index().values
y2=df\[df\[u'上映时间'\]<2018\].sort\_values(by=u'上映时间').groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].values
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5),dpi=70)
ax.plot(x,y,label=u'上映数量')
ax.set\_xlim(1980,2017)
ax.set\_xlabel(u'上映时间')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'上映数量')
ax.set\_title(u'时间&上映数量&评分均值')
ax2=ax.twinx()
ax2.plot(x,y2,c='y',ls='--',label=u'评分')
ax.legend(loc=1)
ax2.legend(loc=2)
# 解决中文乱码,坐标轴显示不出负值的问题
plt.rcParams\['font.sans-serif'\] =\['Microsoft YaHei'\]
plt.rcParams\['axes.unicode\_minus'\] = False
# In\[12\]:
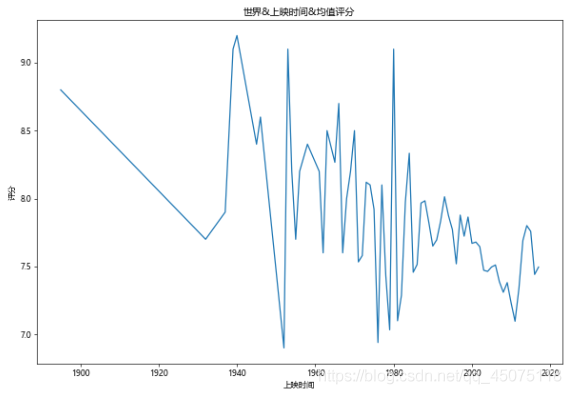
#世界&上映时间&均值评分
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7),dpi=60)
df\[df\[u'评分'\]>0\].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].plot(kind='line',ax=ax)
ax.set\_ylabel(u'评分')
ax.set\_title(u'世界&上映时间&均值评分')
# In\[13\]:
#世界各类型影片所占的数目
#对类型进行切割成最小单位,然后统计
types=\[\]
for tp in df\[u'类型'\]:
ls=tp.split(',')
for x in ls:
types.append(x)
tp\_df=pd.DataFrame({u'类型':types})
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=60)
tp\_df\[u'类型'\].value\_counts().plot(kind='bar',ax=ax)
ax.set\_xlabel(u'类型')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'数量')
ax.set\_title(u'世界&类型&数目')
# In\[14\]:
#影片时长与评分的分布
#有个问题:其实有一些影片未进行评分,在这里要将这些给取缔
x=df\[df\[u'评分'\]>0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'时长(min)'\].values
y=df\[df\[u'评分'\]>0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'评分'\].values
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6),dpi=70)
ax.scatter(x,y,alpha=0.6,marker='o')
ax.set\_xlabel(u'时长(min)')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'数量')
ax.set\_title(u'影片时长&评分分布图')
#可以看出评分
i=0
c0=\[\]
c1=\[\]
c2=\[\]
c3=\[\]
c4=\[\]
c5=\[\]
c6=\[\]
c7=\[\]
for x in df\[u'地区'\]:
if u'中国大陆' in x:
c0.append(df.iat\[i, 0\])
c1.append(df.iat\[i, 1\])
c2.append(df.iat\[i, 2\])
c3.append(df.iat\[i, 3\])
c4.append(df.iat\[i, 4\])
c5.append(df.iat\[i, 5\])
c6.append(df.iat\[i, 6\])
c7.append(df.iat\[i, 7\])
i=i+1
china\_df=pd.DataFrame({u'电影':c0, u'评分':c1,u'链接':c2, u'类型':c3,u'地区':c4, u'上映地点':c5,u'时长(min)':c6,u'上映时间':c7})
# In\[16\]:
#中国&世界均值评分比较 时间范围在1980-2017
x1 = df\[df\[u'评分'\]>0\].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].index
y1 = df\[df\[u'评分'\]>0\].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].values
x2 = china\_df\[china\_df\[u'评分'\]>0\].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].index
y2 = china\_df\[china\_df\[u'评分'\]>0\].groupby(u'上映时间').mean()\[u'评分'\].values
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,9),dpi=60)
ax.plot(x1,y1,ls='-',c='DarkTurquoise',label=u'世界')
ax.plot(x2,y2,ls='--',c='Gold',label=u'中国')
ax.set\_title(u'中国&世界均值评分')
ax.set\_xlabel(u'时间')
ax.set\_xlim(1980,2017)
ax.set\_ylabel(u'评分')
ax.legend()
# In\[17\]:
#类型上映数目 中国&世界对比
#因为类型是混合的,为了方便统计 先写一个函数用来对类型进行分割
# In\[18\]:
#写分割的函数 传入一个Sreies 类型对象 返回一个类型分割的DataFrame
#这里传入的是一个 类型的Series
def Cuttig\_type(typeS):
types=\[\]
types1=\[\]
for x in typeS:
if len(x)<4:
# print x
types1.append(x)
ls=x.split(',')
for i in ls:
types.append(i)
types.extend(types1)
df=pd.DataFrame({u'类型':types})
return pd.DataFrame(df\[u'类型'\].value\_counts().sort\_values(ascending=False))
# In\[19\]:
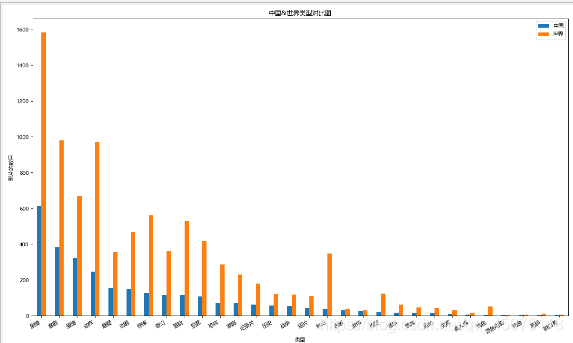
#中国&世界影片类型比较
df1=Cuttig\_type(china\_df\[u'类型'\])
df2=Cuttig\_type(df\[u'类型'\])
trans=pd.concat(\[df1,df2\],axis=1)
trans.dropna(inplace=True)
trans.columns=\[u'中国',u'世界'\]
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(15,9),dpi=80)
trans.plot(kind='bar',ax=ax)
fig.autofmt\_xdate(rotation=30)
ax.set\_title(u'中国&世界类型对比图')
ax.set\_xlabel(u'类型')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'影片的数目')
# In\[20\]:
#然后就是散点分布了,中国&世界&时长&评分分布
y = df\[df\[u'评分'\] > 0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'评分'\].values
x = df\[df\[u'评分'\] > 0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'时长(min)'\].values
y2 = china\_df\[china\_df\[u'评分'\] > 0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'评分'\].values
x2 = china\_df\[china\_df\[u'评分'\] > 0\].sort\_values(by=u'时长(min)')\[u'时长(min)'\].values
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7), dpi=80)
ax.scatter(x, y, c='DeepSkyBlue', alpha=0.6, label=u'世界')
ax.scatter(x2, y2, c='Salmon', alpha=0.7, label=u'中国')
ax.set\_title(u'中国&世界评分分布情况')
ax.set\_xlabel(u'时长(min)')
ax.set\_ylabel(u'评分')
ax.legend(loc=4)
# In\[25\]:
dfs=df\[(df\[u'上映时间'\]>1980)&(df\[u'上映时间'\]<2019)\]
# for x in range(0,len(dfs)):
# print(dfs.iat\[x,0\],dfs.iat\[x,-1\])
df666 = dfs\['电影'\]\[:15\]
wl = ",".join(df666.values)
# 把分词后的txt写入文本文件
# fenciTxt = open("fenciHou.txt","w+")
# fenciTxt.writelines(wl)
# fenciTxt.close()
# 设置词云l
wc = WordCloud(background\_color="white", #设置背景颜色
# mask=imread('shen.jpg'), #设置背景图片
# max\_words=2000, #设置最大显示的字数
font\_path="C:\\\\Windows\\\\Fonts\\\\simkai.ttf", # 设置为楷体 常规
#设置中文字体,使得词云可以显示(词云默认字体是“DroidSansMono.ttf字体库”,不支持中文)
max\_font\_size=60, #设置字体最大值
random\_state=30, #设置有多少种随机生成状态,即有多少种配色方案
)
myword = wc.generate(wl) #生成词云
wc.to\_file('result.jpg')
# 展示词云图
plt.imshow(myword)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
这里先给大家展示一下我进的兼职群和最近接单的截图,小伙伴有需要也可继续往下看.

有需要Python兼职爬虫资料和兼职内推的小伙伴可点下方链接
👉CSDN大礼包🎁:全网最全《Python学习资料》免费赠送🆓!(安全链接,放心点击)
题外话
感谢你能看到最后,给大家准备了一些福利!
感兴趣的小伙伴,赠送全套Python学习资料,包含面试题、简历资料等具体看下方。
👉CSDN大礼包🎁:全网最全《Python学习资料》免费赠送🆓!(安全链接,放心点击)
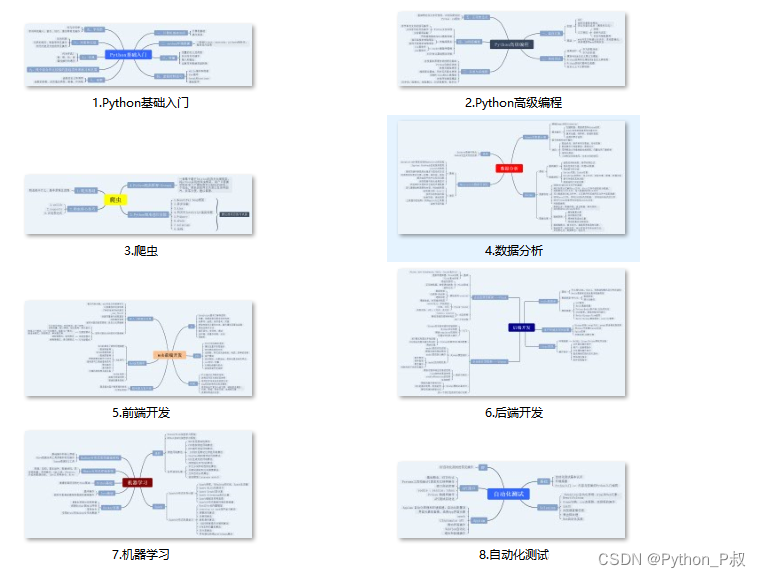
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照下面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
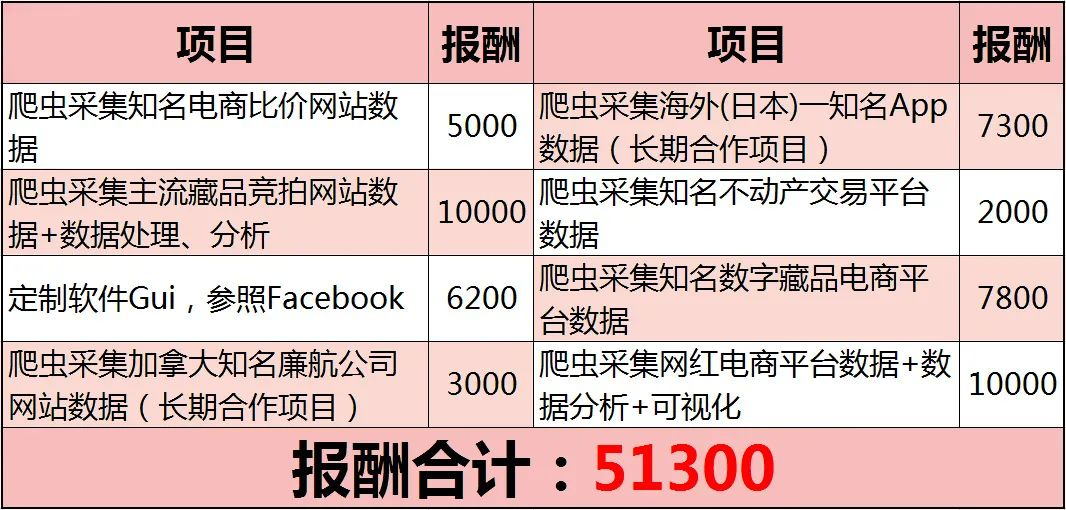
二、Python兼职渠道推荐*
学的同时助你创收,每天花1-2小时兼职,轻松稿定生活费.
三、最新Python学习笔记
当我学到一定基础,有自己的理解能力的时候,会去阅读一些前辈整理的书籍或者手写的笔记资料,这些笔记详细记载了他们对一些技术点的理解,这些理解是比较独到,可以学到不一样的思路。
四、实战案例
纸上得来终觉浅,要学会跟着视频一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
👉CSDN大礼包🎁:全网最全《Python学习资料》免费赠送🆓!(安全链接,放心点击)
若有侵权,请联系删除
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!