json Deserialization of Python Objects
2023-12-14 23:51:53
openweathermap.json
{
"coord": {
"lon": 114.0683, "lat":22.5455
}
,
"weather":[ {
"id": 803, "main":"Clouds", "description":"多云", "icon":"04d"
}
],
"base":"stations",
"main": {
"temp": 299.1, "feels_like":299.1, "temp_min":296.39, "temp_max":300.29, "pressure":1018, "humidity":79, "sea_level":1018, "grnd_level":1017
}
,
"visibility":10000,
"wind": {
"speed": 2.73, "deg":137, "gust":3.32
}
,
"clouds": {
"all": 82
}
,
"dt":1702530001,
"sys": {
"type": 2, "id":2031340, "country":"CN", "sunrise":1702508106, "sunset":1702546869
}
,
"timezone":28800,
"id":1795565,
"name":"Shenzhen",
"cod":200
}
# encoding: utf-8
# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司
# 许可信息查看:
# 描述:
# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.
# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 3.11
# Datetime : 2023/12/14 22:14
# User : geovindu
# Product : PyCharm
# Project : pyBaiduAi
# File : Clouds.py
# explain : 学习
import json
import pickle
from typing import List
from typing import Any
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Clouds:
all: int
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Clouds':
_all = int(obj.get("all"))
return Clouds(_all)
@dataclass
class Coord:
lon: float
"""
经度
"""
lat: float
"""
纬度
"""
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Coord':
_lon = float(obj.get("lon"))
_lat = float(obj.get("lat"))
return Coord(_lon, _lat)
@dataclass
class Main:
"""
"""
temp: float
"""
温度
"""
feels_like: float
temp_min: float
"""
最低温
"""
temp_max: float
"""
最高温
"""
pressure: int
humidity: int
"""
湿魔
"""
sea_level: int
grnd_level: int
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Main':
_temp = float(obj.get("temp"))
_feels_like = float(obj.get("feels_like"))
_temp_min = float(obj.get("temp_min"))
_temp_max = float(obj.get("temp_max"))
_pressure = int(obj.get("pressure"))
_humidity = int(obj.get("humidity"))
_sea_level = int(obj.get("sea_level"))
_grnd_level = int(obj.get("grnd_level"))
return Main(_temp, _feels_like, _temp_min, _temp_max, _pressure, _humidity, _sea_level, _grnd_level)
@dataclass
class Sys:
"""
系统信息
"""
type: int
id: int
country: str
"""
所属国家
"""
sunrise: int
"""
日出时间戳
"""
sunset: int
"""
日落时间戳
"""
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Sys':
_type = int(obj.get("type"))
_id = int(obj.get("id"))
_country = str(obj.get("country"))
_sunrise = int(obj.get("sunrise"))
_sunset = int(obj.get("sunset"))
return Sys(_type, _id, _country, _sunrise, _sunset)
@dataclass
class Weather:
"""
天气情况
"""
id: int
main: str
description: str
"""
天气
"""
icon: str
"""
图标ID
"""
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Weather':
_id = int(obj.get("id"))
_main = str(obj.get("main"))
_description = str(obj.get("description"))
_icon = str(obj.get("icon"))
return Weather(_id, _main, _description, _icon)
@dataclass
class Wind:
"""
风况
"""
speed: float
"""
风速
"""
deg: int
gust: float
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Wind':
_speed = float(obj.get("speed"))
_deg = int(obj.get("deg"))
_gust = float(obj.get("gust"))
return Wind(_speed, _deg, _gust)
@dataclass
class OpenWeather:
""""
天气类
"""
coord: Coord
weather: List[Weather]
base: str
main: Main
visibility: int
wind: Wind
clouds: Clouds
dt: int
sys: Sys
timezone: int
id: int
name: str
cod: int
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'OpenWeather':
_coord = Coord.from_dict(obj.get("coord"))
_weather = [Weather.from_dict(y) for y in obj.get("weather")]
_base = str(obj.get("base"))
_main = Main.from_dict(obj.get("main"))
_visibility = int(obj.get("visibility"))
_wind = Wind.from_dict(obj.get("wind"))
_clouds = Clouds.from_dict(obj.get("clouds"))
_dt = int(obj.get("dt"))
_sys = Sys.from_dict(obj.get("sys"))
_timezone = int(obj.get("timezone"))
_id = int(obj.get("id"))
_name = str(obj.get("name"))
_cod = int(obj.get("cod"))
return OpenWeather(_coord, _weather, _base, _main, _visibility, _wind, _clouds, _dt, _sys, _timezone, _id, _name, _cod)调用:
import Model.Clouds
def print_hi(name):
# Use a breakpoint in the code line below to debug your script.
print(f'Hi, {name} world,geovindu,涂聚文') # Press Ctrl+F8 to toggle the breakpoint.
# Press the green button in the gutter to run the script.
if __name__ == '__main__':
print_hi('PyCharm,geovindu')
#deserialization process:
with open('openweathermap.json',encoding='utf-8') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
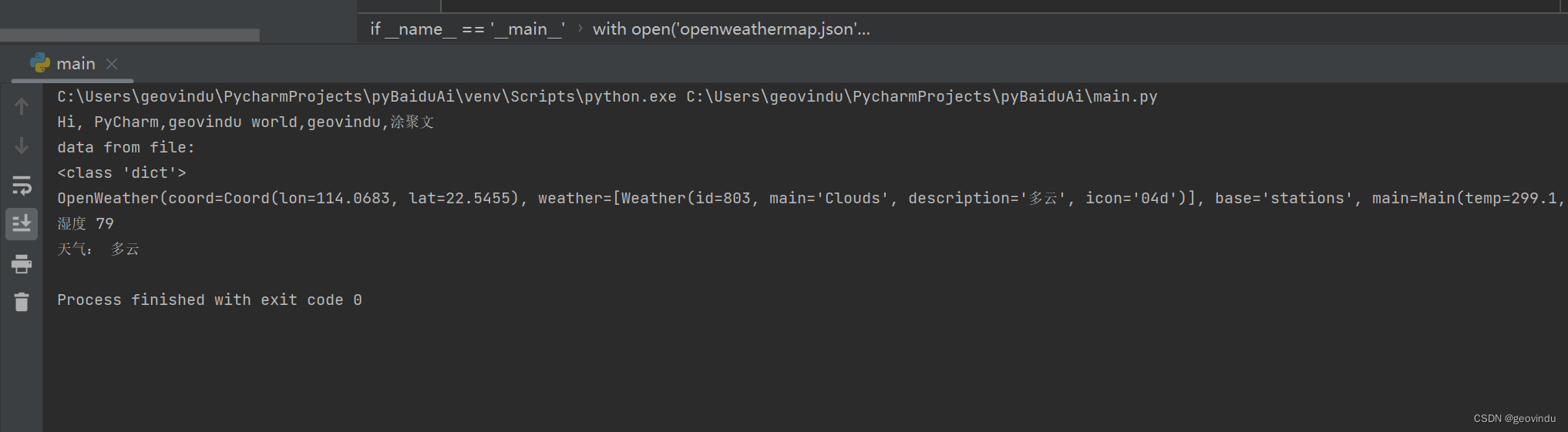
print("data from file:")
print(type(data))
root=Model.Clouds.OpenWeather.from_dict(data)
print(root)
print("湿度",root.main.humidity)
print("天气:", root.weather[0].description)
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/geovindu/article/details/135005825
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!