Redis-内存模型
参考资料: 极客时间 Redis 亚风
内存管理
从两个问题入手:
1 Redis是如何知道?个key是否过期呢?
2 是不是TTL到期就?即删除了呢?
Redis是K-V内存数据库,所有的K、V都保存在Dict中。不过在其db结构体中有5个Dict,我们只用关注两个Dict 和 Expires:?个?来记录K-V,另?个?来记录K-TTL。
// 6.2的源码
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* 数据存储dict, ALLKEYS*/
dict *expires; /* 上面的keys如果设置了过期时间则会存储到这里*/
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
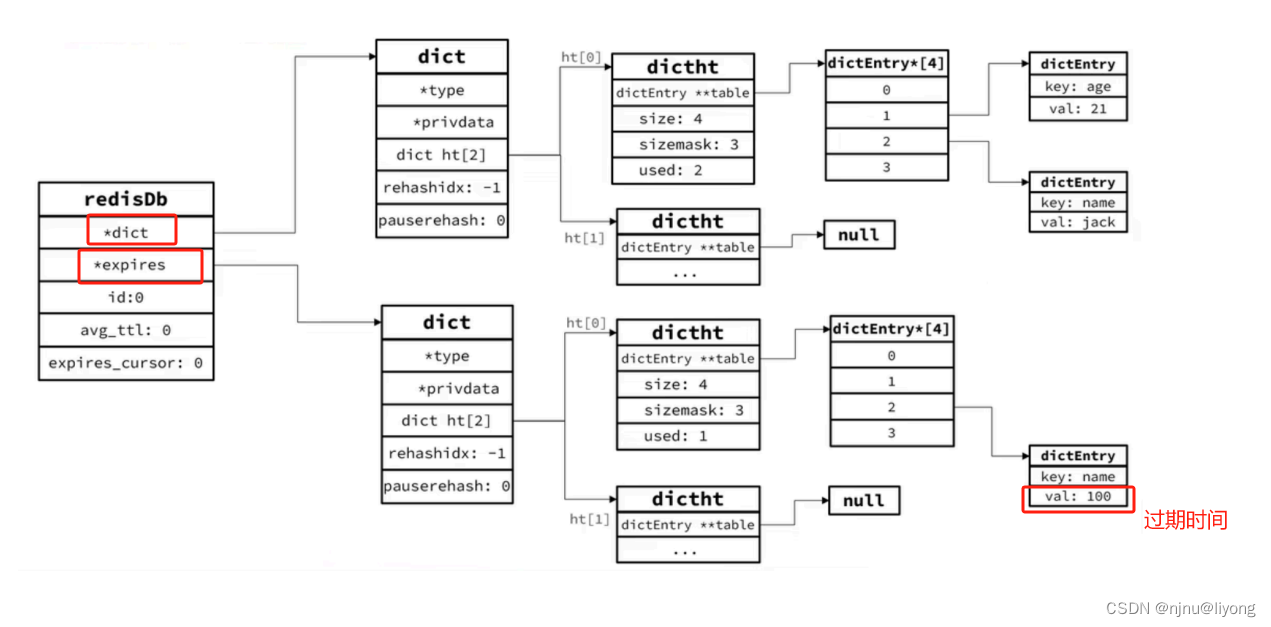
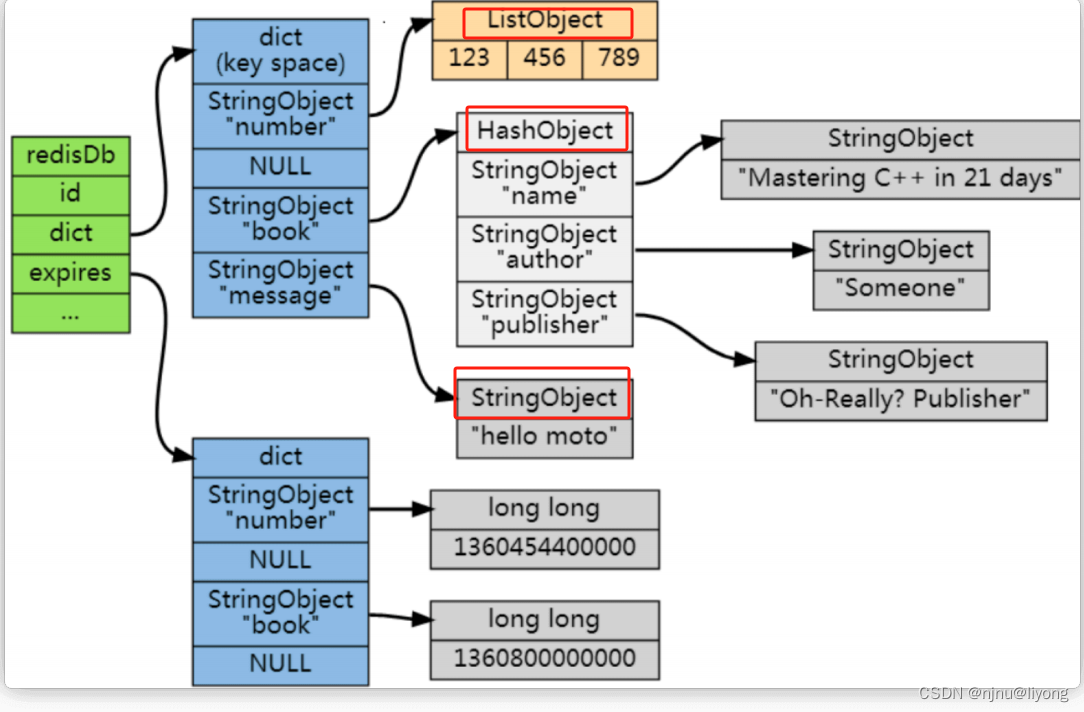
怎么真正的删除Key呢?
1 惰性删除
访问key的时候,检查该key的存活时间,如果过期才执?删除。也就是用户发起一个查询的时候来检查如果过期就删除。
robj *lookupKeyWriteWithFlags(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
expireIfNeeded(db,key); // 过期删除KEY
return lookupKey(db,key,flags);
}
2 周期删除
顾明思议是通过?个定时任务,周期性的抽样部分过期的key,然后执?删除。执?周期有两种:
? Redis会设置?个定时任务serverCron(),按照server.hz的频率来执?过期key清理,模式为SLOW
? Redis的每个事件循环前会调?beforesleep()函数,执?过期key清理,模式为FAST
initServer 是时候会创建一个serverCron定时任务
/* Create the timer callback, this is our way to process many background
* operations incrementally, like clients timeout, eviction of unaccessed
* expired keys and so forth. */
if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers.");
exit(1);
}
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
// 更新lruclock 到当前时间 为后期的LRU和LFU做准备
unsigned int lruclock = getLRUClock();
/* for debug purposes: skip actual cron work if pause_cron is on */
if (server.pause_cron) return 1000/server.hz;
/* We need to do a few operations on clients asynchronously. */
clientsCron();
/* 数据清理. */
databasesCron();
return 1000/server.hz; // 返回时间间隔 执行是时候和上一次返回值做比较
}
// databasesCron 的逻辑
void databasesCron(void) {
/* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves
* as master will synthesize DELs for us. */
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (iAmMaster()) {
// 采用的是 Slow模式
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
}
// beforesleep 里面的逻辑
if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL)
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST); // Fast模式
SLOW模式规则:
1 执?频率受server.hz影响,默认为10,即每秒执?10次,每个执?周期100ms。
2 执?清理耗时不超过?次执?周期的25%。
3 逐个遍历db,逐个遍历db中的bucket,抽取20个key判断是否过期
4 如果没达到时间上限(25ms)且过期key?例?于10%,再进??次抽样,否则结束。
FAST模式规则(过期key?例?于10%不执?):
1 执?频率受beforeSleep()调?频率影响,但两次FAST模式间隔不低于2ms
2 执?清理耗时不超过1ms
3 逐个遍历db,逐个遍历db中的bucket,抽取20个key判断是否过期
4 如果没达到时间上限(1ms)并且过期key?例?于10%,再进??次抽样,否则结束
总结
RedisKey的TTL记录?式:在RedisDB中通过?个Dict记录每个Key的TTL时间过期key的删除策略:
? 惰性清理:每次查找key时判断是否过期,如果过期则删除
? 定期清理:定期抽样部分key,判断是否过期,如果过期则删除。
定期清理的2种模式:
? SLOW模式执?频率默认为10,每次不超过25ms
? FAST模式执?频率不固定,但两次间隔不低于2ms,每次耗时不超过1ms
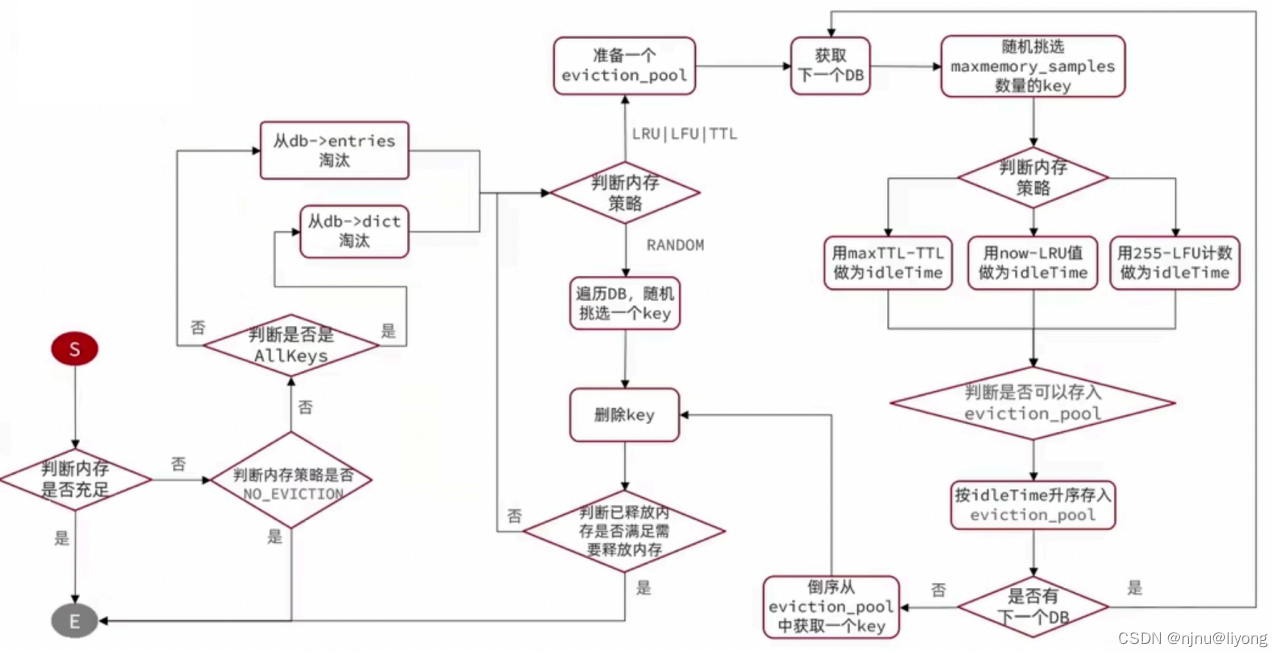
内存淘汰:就是当Redis内存使?达到设置的阈值时,Redis主动挑选部分key删除以释放更多内存的流程。
内存淘汰入口:
processCommand
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = (performEvictions() == EVICT_FAIL);
/* performEvictions may evict keys, so we need flush pending tracking
* invalidation keys. If we don't do this, we may get an invalidation
* message after we perform operation on the key, where in fact this
* message belongs to the old value of the key before it gets evicted.*/
trackingHandlePendingKeyInvalidations();
/* performEvictions may flush slave output buffers. This may result
* in a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */
if (server.current_client == NULL) return C_ERR;
int reject_cmd_on_oom = is_denyoom_command;
/* If client is in MULTI/EXEC context, queuing may consume an unlimited
* amount of memory, so we want to stop that.
* However, we never want to reject DISCARD, or even EXEC (unless it
* contains denied commands, in which case is_denyoom_command is already
* set. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand) {
reject_cmd_on_oom = 1;
}
if (out_of_memory && reject_cmd_on_oom) {
rejectCommand(c, shared.oomerr);
return C_OK;
}
Redis?持8种不同策略来选择要删除的key:
noeviction:不淘汰任何key,但是内存满时不允许写?新数据,默认就是这种策略。
volatile-ttl:对设置了TTL的key,?较key的剩余TTL值,TTL越?越先被淘汰
allkeys-random:对全体key,随机进?淘汰。也就是直接从dict中随机挑选
volatile-random:对设置了TTL的key,随机进?淘汰。也就是从expires中随机挑选。
allkeys-lru:对全体key,基于LRU算法进?淘汰
volatile-lru:对设置了TTL的key,基于LRU算法进?淘汰
allkeys-lfu: 对全体key,基于LFU算法进?淘汰
volatile-lfu:对设置了TTL的key,基于LFU算法进?淘汰
?较容易混淆的有两个:
LRU (Least Recently Used),最少最近使?。?当前时间减去最后?次访问时间,这个值越?则淘汰优先级越?。
LFU (Least Frequently used),最少频率使?。会统计每个key的访问频率,值越?淘汰优先级越?。
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
// LRU 以毫秒为单位记录最近一次访问时间,长度24bit
// LFU 高16位以分钟为单位记录最近一次访问时间,低8位记录逻辑访问次数
int refcount; // 引用计数
void *ptr; // 数据指针 指向真实数据
} robj;
LFU的访问次数之所以叫做逻辑访问次数,是因为并不是每次key被访问都计数,?是通过运算:
1 ?成0~1之间的随机数R。
2 计算1/(旧次数 x Ifu_log_factor +1),记录为P,lfu_log_factor默认为10。
3 如果R < P,则计数器 +1,且最?不超过255。
4 访问次数会随时间衰减,距离上?次访问时间每隔 Ifu_decay_time 分钟(默认1),计数器 -1。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!