2024.1.1 hive_sql 题目练习,开窗,行列转换
?
重点知识:
在使用group by时,select之后的字段要么包含在聚合函数里,要么在group by 之后
进行行转列,行转列的核心就是使用concat_ws函数拼接(分隔符,内容),
-- 以及collect_list函数进行收集,list不去重, set去重无序列转行,核心就是使用炸裂函数把东西炸开,然后使用侧视图做成新表
目录
?
行列转换
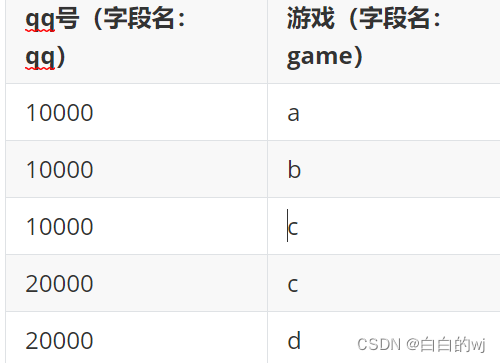
表table如下:
| DDate | shengfu |
|---|---|
| 2015-05-09 | 胜 |
| 2015-05-09 | 胜 |
| 2015-05-09 | 负 |
| 2015-05-09 | 负 |
| 2015-05-10 | 胜 |
| 2015-05-10 | 负 |
| 2015-05-10 | 负 |
如果要生成下列结果, 该如何写sql语句?
| DDate | 胜 | 负 |
|---|---|---|
| 2015-05-09 | 2 | 2 |
| 2015-05-10 | 1 | 2 |
--解题 ,当为胜时,就显示1,否则就0,最后使用求和函数来记
select DDate,
sum(case when shengfu = '胜' then 1 else 0 end) win ,
sum(case when shengfu = '负' then 1 else 0 end) lose
from test5_4
group by DDate
;行列互转2?
请写出以下sql逻辑:
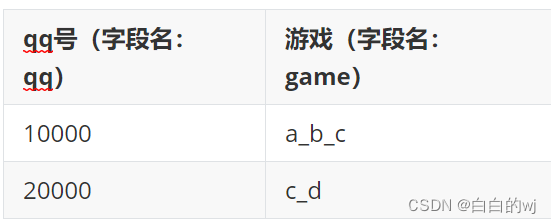
a, 将tableA输出为tableB的格式; 【行转列】
--题目5
--清空表
drop table test5_5;
--建表
create table test5_5 (
qq int,
game string
)comment 'Table A'
;
--插入数据
insert into test5_5 values
(10000,'a'),
(10000,'b'),
(10000,'c'),
(20000,'c'),
(20000,'d')
;
-- 解题 进行行转列,行转列的核心就是使用concat_ws函数拼接(分隔符,内容),
-- 以及collect_list函数进行收集,list不去重, set去重无序
select * from test5_5;
select qq,concat_ws('-',collect_list(game)) as game from test5_5
group by qq
;b, 将tableB输出为tableA的格式; 【列转行】
--解题 列转行,核心就是使用炸裂函数把东西炸开,然后使用侧视图做成新表
select * from test5_6;
select explode(split(game,'_')) from test5_6 ;
select (split(game,'-'))from test5_6;
--已经炸开,接下来弄成新的列
select qq,new_table.Game
from test5_6
lateral view
explode(split(game,'_')) new_table as Game;
需求1:
题干
有一个账号表字段信息如下,请写出SQL语句,查询各自区组的money排名前十的账号 (分组取前10)
dist_id string '区组id',
account string '账号',
gold int '金币'
数据准备:
-- 电商分组TopK实战 CREATE TABLE test_sql.test10( `dist_id` string COMMENT '区组id', `account` string COMMENT '账号', `gold` int COMMENT '金币' ); -- 插入数据 INSERT INTO TABLE test_sql.test10 VALUES ('1','77',18),('1','88',106),('1','99',10),('1','12',13),('1','13',14), ('1','14',25),('1','15',36),('1','16',12),('1','17',158), ('2','18',12),('2','19',44),('2','10',66), ('2','45',80),('2','78',98); -- 验证 select * from test_sql.test10;
解题:
--解题 select * from (select *,row_number() over (partition by dist_id order by gold desc ) as top from test10) as table2 where table2.top <=10 ;?
?需求2:
题干
有个京东店铺 ,每个顾客访客访问任何一个店铺的任何一个商品时都会产生一条访问日志,访问日志存储的表名为Visit ,访客的用户id为user_id ,被访问的店铺名称为shop ,数据如下:
请统计:
(1) 每个店铺的UV(访客数)
(2)每个店铺访问次数top3的访客信息。输出店铺名称、访客id、访问次数
?数据准备:
--题目2 -- 第2题:电商场景TopK统计 CREATE TABLE test_sql.test2 ( user_id string, shop string ) ROW format delimited FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t'; INSERT INTO TABLE test_sql.test2 VALUES ( 'u1', 'a' ), ( 'u2', 'b' ), ( 'u1', 'b' ), ( 'u1', 'a' ), ( 'u3', 'c' ), ( 'u4', 'b' ), ( 'u1', 'a' ), ( 'u2', 'c' ), ( 'u5', 'b' ), ( 'u4', 'b' ), ( 'u6', 'c' ), ( 'u2', 'c' ), ( 'u1', 'b' ), ( 'u2', 'a' ), ( 'u2', 'a' ), ( 'u3', 'a' ), ( 'u5', 'a' ), ( 'u5', 'a' ), ( 'u5', 'a' ); --验证数据 select * from test2;
解题:
?
--解题1:每个店铺的访客数 select count(user_id) as user_count,shop from test2 group by shop; --解题2:每个店铺访问次数top3的访客信息 with t1 as (select shop,user_id,count(1)as cnt from test2 group by shop, user_id), t2 as ( select * ,row_number() over (partition by shop order by cnt desc) as top from t1) select * from t2 where t2.top<=3 ;
?
进阶题
题干
已知一个订单表,有如下字段:dt ,order_id ,user_id ,amount。
请给出sql进行统计:
(1)给出2017年每个月的订单数、用户数、总成交金额
(2)给出2017年11月的新客数(指在11月才有第一笔订单)
数据准备:
-- 建表 CREATE TABLE test_sql.test3 ( dt string, order_id string, user_id string, amount DECIMAL ( 10, 2 ) )ROW format delimited FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t'; -- 插入数据 INSERT INTO TABLE test_sql.test3 VALUES ('2017-01-01','10029028','1000003251',33.57), ('2017-01-01','10029029','1000003251',33.57), ('2017-01-01','100290288','1000003252',33.57), ('2017-02-02','10029088','1000003251',33.57), ('2017-02-02','100290281','1000003251',33.57), ('2017-02-02','100290282','1000003253',33.57), ('2017-11-02','10290282','100003253',234), ('2018-11-02','10290284','100003243',234);?
?
解题:
--解题1:2017年每个月的订单数,用户数,总成交金额 select date_format(dt,'yyyy-MM') as month1, count(distinct order_id) as cnt_oid, count(distinct user_id) as cnt_uid, sum(amount) as sum_amount from test3 where year(dt) == 2017 group by date_format(dt,'yyyy-MM') ; --解题2 给出2017年11月的新客数(指在11月才有第一笔订单) --这个min(date_format)是为了group by才加的, --在使用group by时,select之后的字段要么包含在聚合函数里,要么在group by 之后 select count(user_id) cnt_uid from( select user_id,min(date_format(dt,'yyyy-MM'))min_month from test3 group by user_id) as new_table where new_table.min_month =='2017-11' ;?
行列存储的特点?
?? ?行存储的特点:?查询满足条件的一整行数据的时候,列存储则需要去每个聚集的字段找到对应的每个列的值,行存储只需要找到其中一个值,其余的值都在相邻地方,所以此时行存储查询的速度更快。
?? ?列存储的特点:?因为每个字段的数据聚集存储,在查询只需要少数几个字段的时候,能大大减少读取的数据量;每个字段的数据类型一定是相同的,列式存储可以针对性的设计更好的设计压缩算法。行存储: textfile和squencefile
?? ?优点: 每行数据连续存储 ? ? ? ? ? ? ?select * from 表名; 查询速度相对较快
?? ?缺点: 每列类型不一致,空间利用率不高 ? select 列名 from 表名; 查询速度相对较慢
列存储: orc和parquet
?? ?优点: 每列数据连续存储 ? ? ? ? select 列名 from 表名; ?查询速度相对较快
?? ?缺点: 因为每行数据不是连续存储 ?select * from 表名;查询速度相对较慢
?? ?
注意: ORC文件格式的数据, 默认内置一种压缩算法:zlib , 在实际生产中一般会将ORC压缩算法替换为 snappy使用,格式为: STORED AS orc tblproperties ("orc.compress"="SNAPPY")
HIVE调优的手段
Hive数据压缩
Hive数据存储格式
fetch抓取策略
本地模式
join优化操作
SQL优化(列裁剪,分区裁剪,map端聚合,count(distinct),笛卡尔积)
动态分区
MapReduce并行度调整
并行执行严格模式 ??
JVM重用
推测执行
执行计划explain?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!