【源码解析】Semaphore角度聊聊AQS
2023-12-19 00:18:21
案例
Semaphore,俗称信号量,它是操作系统中PV操作的原语在java的实现,它也是基于 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer实现的
private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for ( ; ; ) {
threadPool.execute(()-> exec());
}
}
public static void exec() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " before");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("执行任务");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " after");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
从执行结果来看的话,先是2个线程获取到凭证,然后执行完毕。后续两个线程才开始获取凭证。
pool-1-thread-1 before
pool-1-thread-2 before
执行任务
执行任务
pool-1-thread-2 after
pool-1-thread-1 after
pool-1-thread-3 before
pool-1-thread-4 before
执行任务
执行任务
pool-1-thread-3 after
pool-1-thread-4 after
应用场景
Semaphore的使用场景主要用于一些中间件的时候,进行限流使用。
源码解析
构造方法
默认是非公平锁,可以通过构造参数进行设置。本篇主要介绍非公平锁的实现方式。
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
// 非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
}
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
// 设置state为构造方法的数值
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
获取凭证
semaphore.acquire();
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
//是否中断
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 线程等待
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
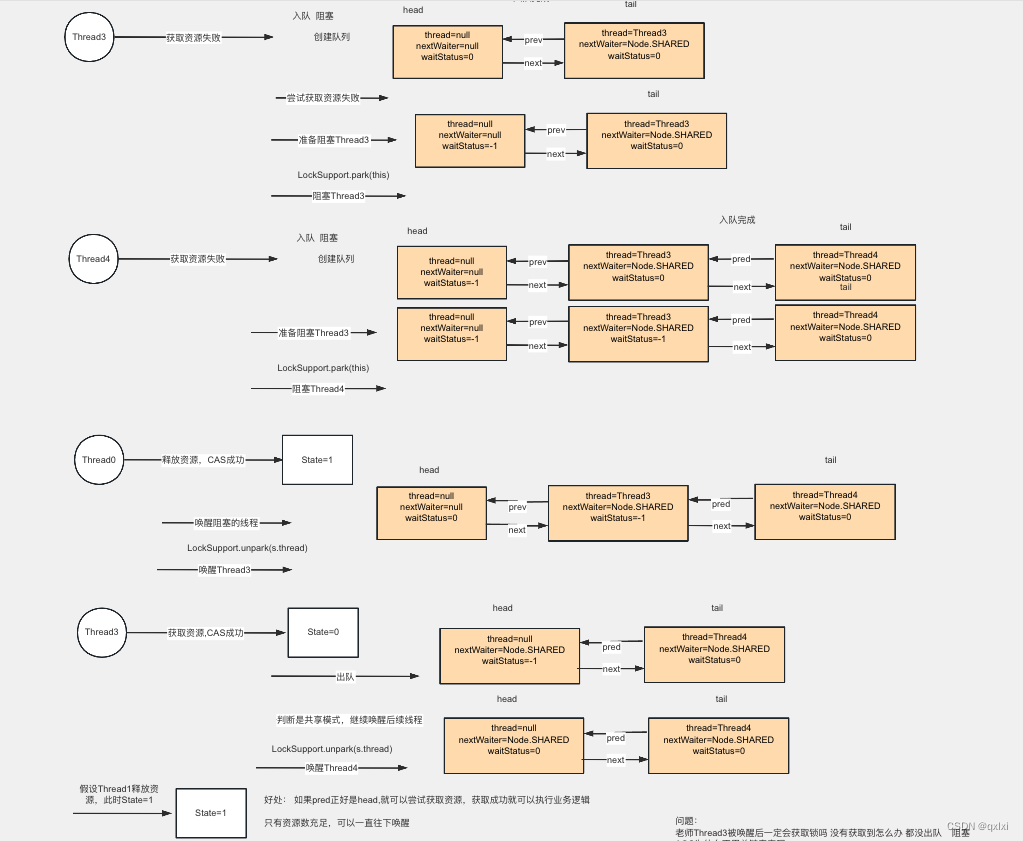
T1线程直接获取锁,返回。T2线程也可以获取,但是T3线程进入的时候 state=0,获取不到锁。就会进入到 doAcquireSharedInterruptibly 这个逻辑中
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
获取当前state的值
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
// //cas操作
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly 其实就是将当前线程封装成一个Node节点,添加到AQS队列中。 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 会进行阻塞。
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// 封装成一个node 加入AQS队列中 共享模式
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
//自选锁
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// state 不等于0 返回-1
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
// 第一次不会进入
if (r >= 0) {
// // 2. 这里将唤醒t3的后续节点t4,以此类推,t4被唤醒后,会在t4的await中唤醒t4的后续节点
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
// t3节点删除
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 修改前驱节点waitstate = -1 挂起当前线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
释放凭证
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
获取当前state的值,然后将state+=1 操作。
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
释放资源。 unparkSuccessor(h); 会将T3线程进行唤醒。然后T3线程会尝试唤醒T4 (共享模式)。如果有资源的话,就获取锁,没有的话就会阻塞。
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 自选锁
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
// 前面已经将pre节点 设置为-1
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// 设置为0
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
// 唤醒head的后继节点
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
小结
通过代码进一步分析 可以更加了解Semaphore的原理。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/jia970426/article/details/135072194
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!