[VUE]3-路由
?🍃作者介绍:双非本科大三网络工程专业在读,阿里云专家博主,专注于Java领域学习,擅长web应用开发、数据结构和算法,初步涉猎Python人工智能开发和前端开发。
🦅主页:@逐梦苍穹
📕所属专栏:前端(专栏的其他文章,详见文末?)
🍔您的一键三连,是我创作的最大动力🌹
路由 Vue-Router
1、Vue-Router 介绍
vue 属于单页面应用,所谓路由,就是根据浏览器路径不同,用不同的视图组件替换这个页面内容。
不同的访问路径,对应不同的页面展示。
在vue应用中使用路由功能,需要安装Vue-Router:
注:创建完带有路由功能的前端项目后,在工程中会生成一个路由文件,如下所示: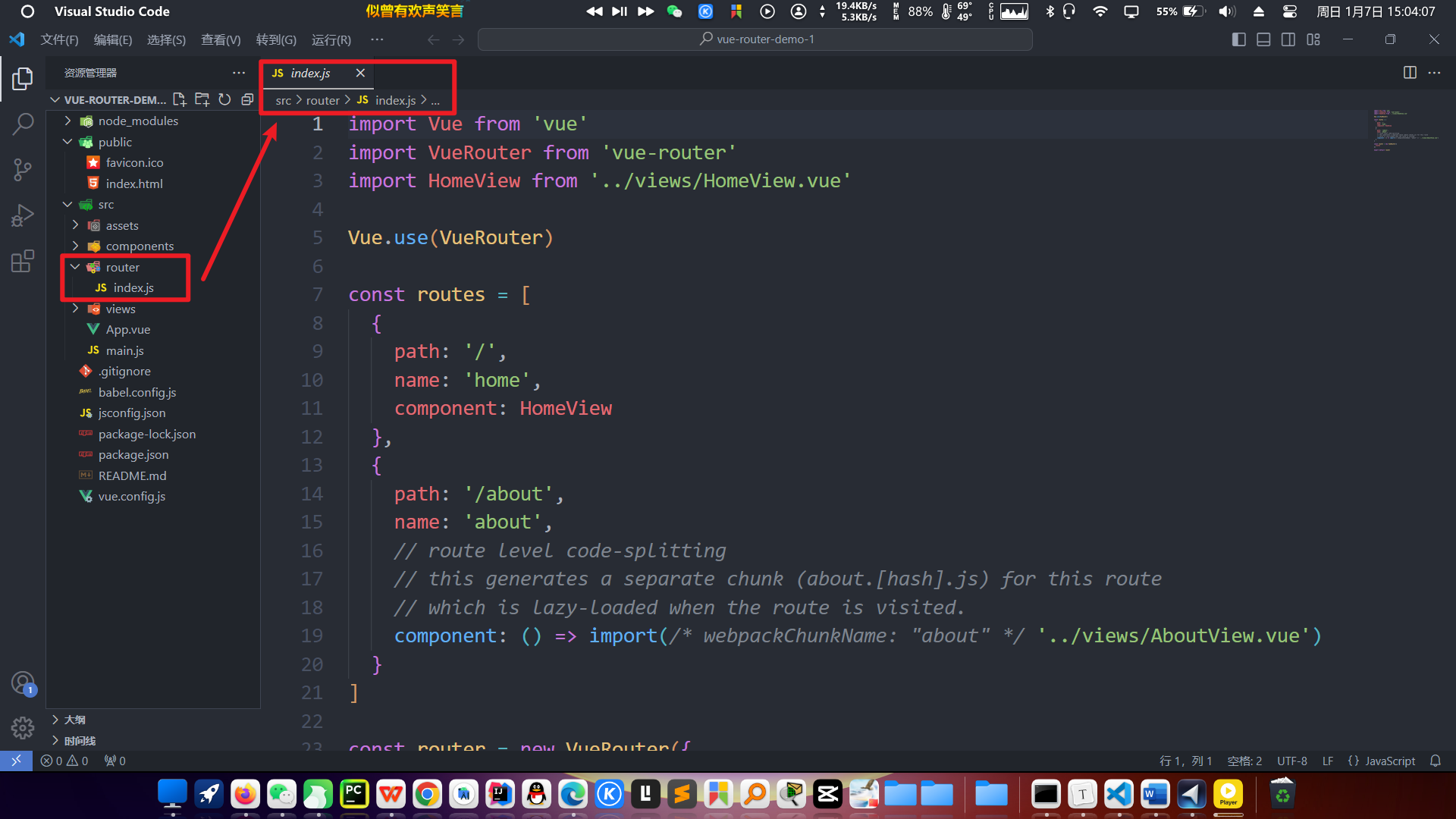
关于路由的配置,主要就是在这个路由文件中完成的。
为了能够使用路由功能,在前端项目的入口文件main.js中,创建Vue实例时需要指定路由对象: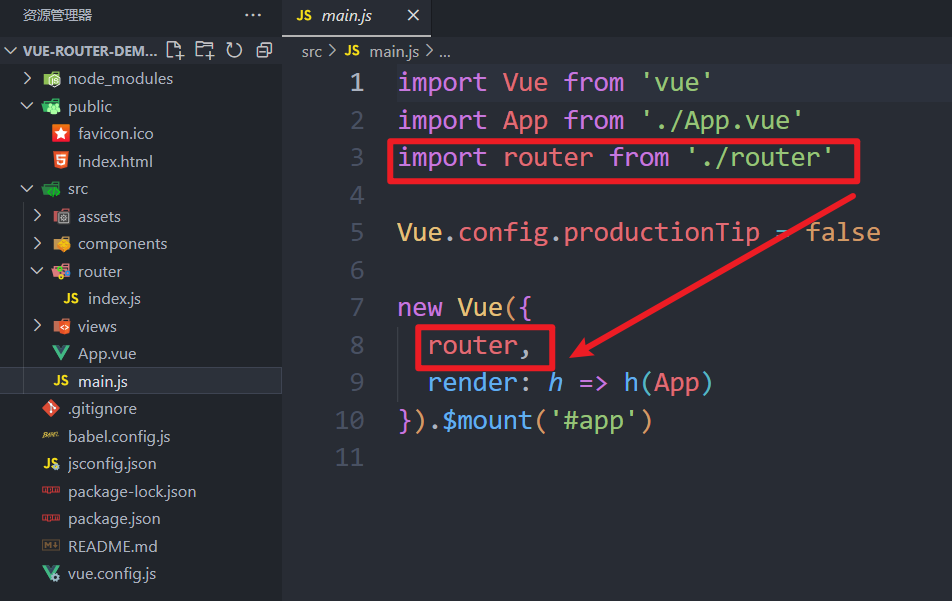
2、路由配置
首先了解一下路由组成:
- VueRouter:路由器,根据路由请求在路由视图中动态渲染对应的视图组件
- <router-link>:路由链接组件,浏览器会解析成
- <router-view>:路由视图组件,用来展示与路由路径匹配的视图组件
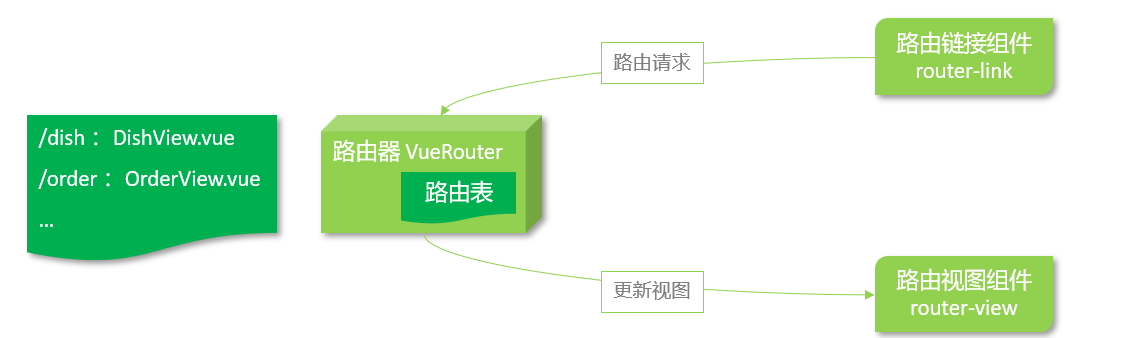
具体配置方式:
1、在路由文件/router/index.js中配置路由路径和视图的对应关系:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
//维护路由表,某个路由路径对应哪个视图组件
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
}
,
{
path: '/404',
component: () => import('../views/404View.vue')
},
{
path: '*',
redirect: '/404'
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
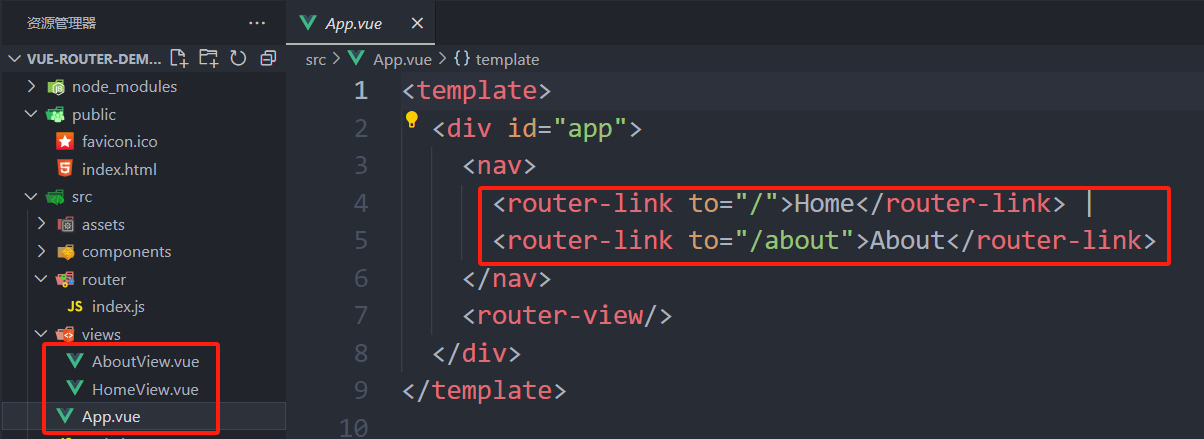
2、在视图组件中配置 router-link标签,用于生成超链接
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link> |
<router-link to="/test">Test</router-link> |
3、在视图组件汇总配置router-view标签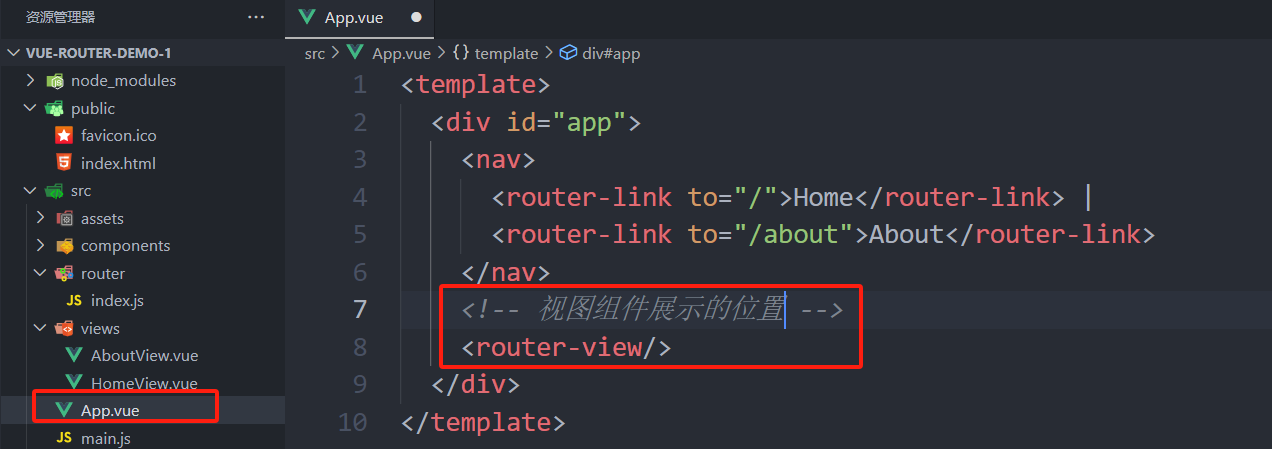
要实现路由跳转,可以通过标签式和编程式两种:
- 标签式:About
- 编程式:this.$router.push(‘/about’)
问题思考: 如果用户访问的路由地址不存在,该如何处理?
可以通过配置一个404视图组件,当访问的路由地址不存在时,则重定向到此视图组件,具体配置如下:
{
path: '/404',
component: () => import('../views/404View.vue')
},
{
path: '*',
redirect: '/404' //重定向
}
3、嵌套路由
3.1、简介
嵌套路由:组件内要切换内容,就需要用到嵌套路由(子路由),效果如下:
在App.vue视图组件中有标签,其他视图组件可以展示在此 ContainerView.vue组件可以展示在App.vue视图组件的位置
ContainerView.vue组件可以展示在App.vue视图组件的位置
ContainerView.vue组件进行了区域划分(分为上、左、右),在右边编写了标签,点击左侧菜单时,可以将对应的子视图组件展示在此
3.2、实现步骤
第一步:安装并导入 elementui,实现页面布局(Container 布局容器)—ContainerView.vue:
<template>
<el-container>
<el-header>Header</el-header>
<el-container>
<el-aside width="200px">
</el-aside>
<el-main>
</el-main>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.el-header, .el-footer {
background-color: #B3C0D1;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
}
.el-aside {
background-color: #D3DCE6;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
}
.el-main {
background-color: #E9EEF3;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 160px;
}
body > .el-container {
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(5) .el-aside,
.el-container:nth-child(6) .el-aside {
line-height: 260px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(7) .el-aside {
line-height: 320px;
}
</style>
第二步:提供子视图组件,用于效果展示 ->P1View.vue、P2View.vue、P3View.vue:
<template>
<div>
这是P1 View
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.el-header, .el-footer {
background-color: #B3C0D1;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
}
.el-aside {
background-color: #D3DCE6;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
}
.el-main {
background-color: #E9EEF3;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 160px;
}
body > .el-container {
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(5) .el-aside,
.el-container:nth-child(6) .el-aside {
line-height: 260px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(7) .el-aside {
line-height: 320px;
}
</style>
第三步:在 src/router/index.js 中配置路由映射规则(嵌套路由配置)
{
path: '/c',
component: () => import('../views/container/ContainerView.vue'),
//嵌套路由(子路由),对应的组件会展示在当前组件内部
children: [//通过children属性指定子路由相关信息(path、component)
{
path: '/c/p1',
component: () => import('../views/container/P1View.vue')
},
{
path: '/c/p2',
component: () => import('../views/container/P2View.vue')
},
{
path: '/c/p3',
component: () => import('../views/container/P3View.vue')
}
]
}
第四步:在ContainerView.vue 布局容器视图中添加,实现子视图组件展示
<el-main>
<router-view/>
</el-main>
第五步:在ContainerView.vue 布局容器视图中添加,实现路由请求
<el-aside width="200px">
<router-link to="/c/p1">P1</router-link><br>
<router-link to="/c/p2">P2</router-link><br>
<router-link to="/c/p3">P3</router-link><br>
</el-aside>
注意:子路由变化,切换的是【ContainerView 组件】中 部分的内容
问题思考:
1.对于前面的案例,如果用户访问的路由是 /c,会有什么效果呢?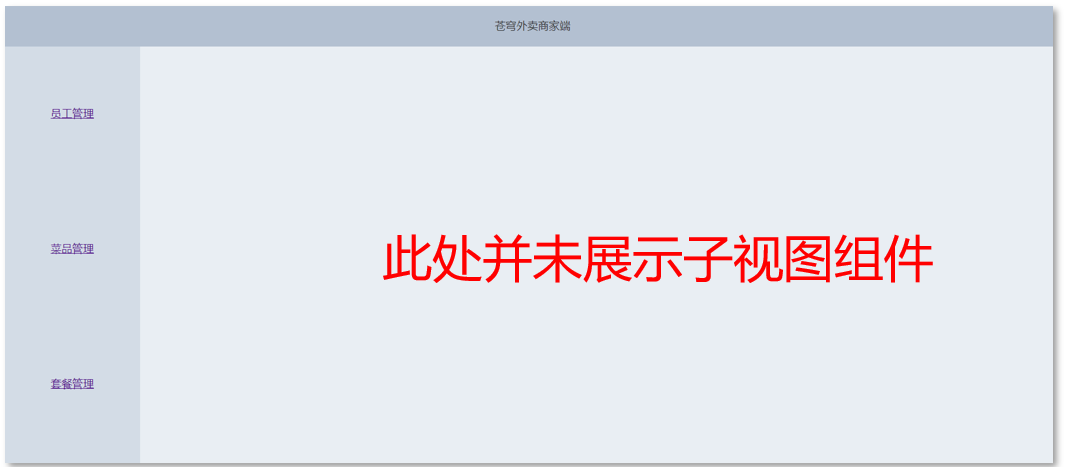
如何实现在访问 /c 时,默认就展示某个子视图组件呢?
配置重定向,当访问/c时,直接重定向到/c/p1即可,如下配置: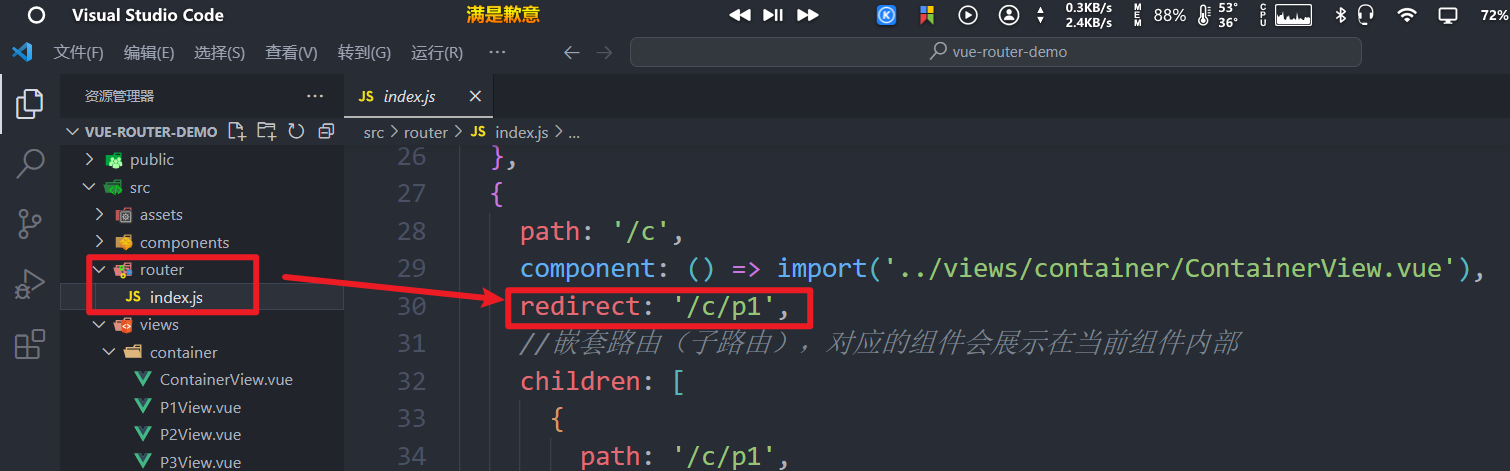
3.3、?注意事项
- 子路由的路径不需要以 / 开头。因为以 / 开头的路径将会被视为根路径。
- 子路由的完整路径是由其所有的祖先路由的路径和自己的路径拼接而成的。例如,/user/:id/profile 路径是由 /user/:id 和 profile 拼接而成的。
- 子路由的写法,要么"/父/子",要么"子":
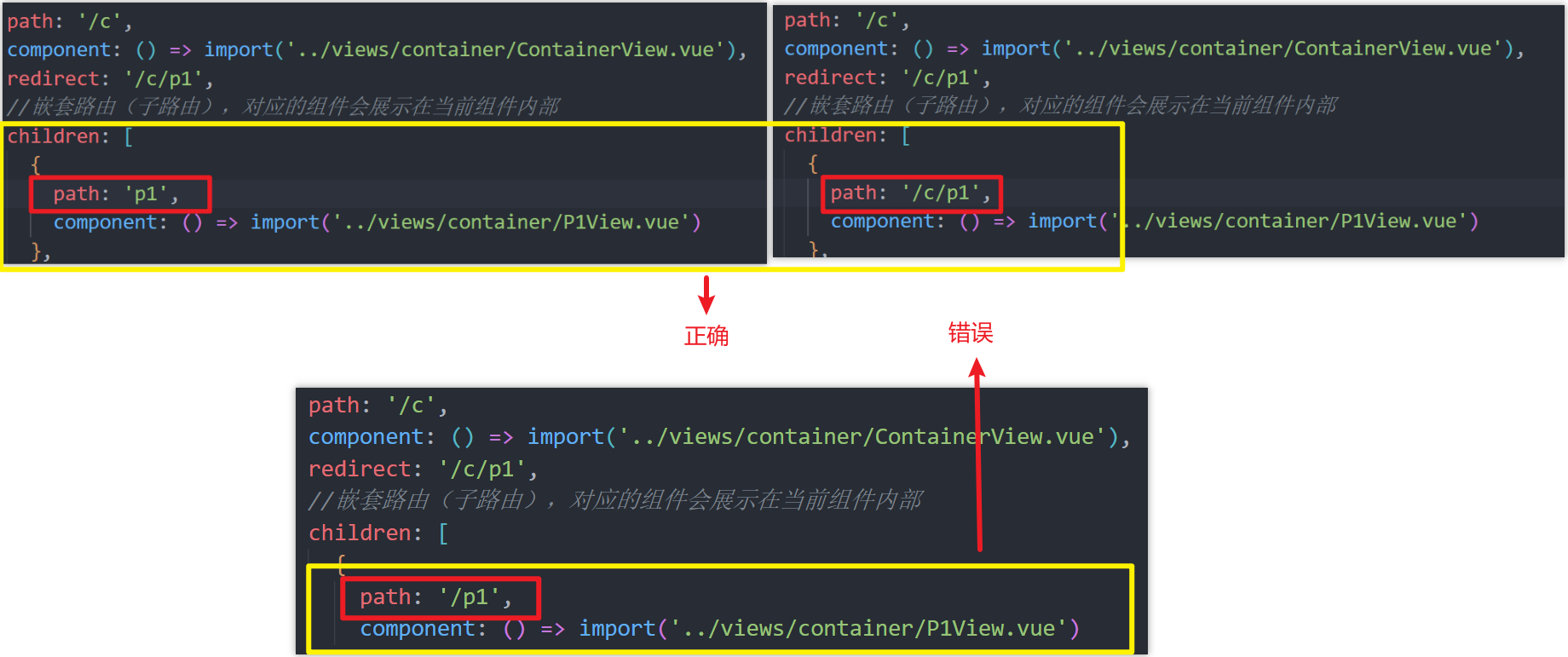
更多关于嵌套路由的信息,你可以查阅Vue Router官方文档。
4、?router-view标签详解
<router-view/> 是 Vue Router 的一个核心组件,它是一个功能性的组件,用于渲染匹配的路由组件。
当你的应用访问一个路由路径时,Vue Router 会查找与该路径匹配的路由配置,然后将该路由配置中的组件渲染到 <router-view/> 所在的位置。
例如,假设你有以下的路由配置:
const routes = [
{ path: '/home', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About }
]
当你访问 /home 路径时,Home 组件会被渲染到 <router-view/> 所在的位置;当你访问 /about 路径时,About 组件会被渲染到 <router-view/> 所在的位置。
此外,<router-view/> 还可以嵌套使用,以支持显示嵌套路由。在嵌套路由的配置中,子路由的组件将会被渲染到父路由组件内部的 <router-view/> 中。
例如,假设你有以下的嵌套路由配置:
const routes = [
{
path: '/user',
component: User,
children: [
{
path: 'profile',
component: UserProfile
},
{
path: 'posts',
component: UserPosts
}
]
}
]
当你访问 /user/profile 路径时,User 组件会被渲染到最外层的 <\router-view/> 中,而 UserProfile 组件会被渲染到 User 组件内部的 <router-view/> 中。
?
????????????????????前端的其他文章:
📕 1-创建vue工程
📕 2-vue的基本使用
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!