Opencv_CUDA实现推理图像前处理与后处理
2023-12-25 23:21:32
Opencv_CUDA实现推理图像前处理与后处理
- 通过trt 或者 openvino部署深度学习算法时,往往会通过opencv的Mat及算法将图像转换为固定的格式作为输入
- openvino图像的前后处理后边将在单独的文章中写出
- 今晚空闲搜了一些opencv_cuda的使用方法,在此总结一下
- 前提是已经通过CMake将cuda和opencv重新编译好了C++库
1.前处理
// -------------- opencv ----------------------- #
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
// ---------------- opencv-cuda ---------------- #
#include <opencv2/cudawarping.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudaarithm.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudaimgproc.hpp>
// ------------ cuda ------------------------- #
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
// ------------------- nvinfer1 ------------------ #
#include "NvInfer.h"
// ------------ standard libraries --------------- #
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
// ---------------------------------------------- #
void preprocessImage(const std::string& image_path, float* gpu_input,
nvinfer1::Dims3& dims)
{
// read image
cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(image_path);
if(frame.empty())
{
std::cerr << "failed to load image: " << image_path << "!" << std::endl;
return;
}
// upload
cv::cuda::GpuMat gpu_frame;
gpu_frame.upload(frame);
// resize
// CHW order
auto input_width = dims.d[2];
auto input_height = dims.d[1];
auto channels = dims.d[0];
auto input_size = cv::Size(input_width, input_height);
cv::cuda::GpuMat resized;
cv::cuda::resize(gpu_frame, resized, input_size, 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
//* ------------------------ Pytorch ToTensor and Normalize ------------------- */
cv::cuda::GpuMat flt_image;
resized.convertTo(flt_image, CV_32FC3, 1.f/255.f);
cv::cuda::subtract(flt_image, cv::Scalar(0.485f, 0.346f, 0.406f), flt_image,
cv::noArray(), -1);
cv::cuda::divide(flt_image, cv::Scalar(0.229f, 0.224f, 0.225f), flt_image, 1, -1);
//* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /
// BGR To RGB
cv::cuda::GpuMat rgb;
cv::cuda::cvtColor(flt_image, rgb, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
// toTensor(copy data to input float pointer channel by channel)
std::vector<cv::cuda::GpuMat> rgb_out;
for(size_t i=0; i<channels; ++i)
{
rgb_out.emplace_back(cv::cuda::GpuMat(cv::Size(input_width, input_height), CV_32FC1, gpu_input + i * input_width * input_height));
}
cv::cuda::split(flt_image, rgb_out); // opencv HWC order -> CHW order
}
// calculate size of tensor
size_t getSizeByDim(const nvinfer1::Dims& dims)
{
size_t size = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < dims.nbDims; ++i)
{
size *= dims.d[i];
}
return size;
}
int main()
{
std::string image_path = "./turkish_coffee.jpg";
// CHW order
nvinfer1::Dims3 input_dim(3, 640, 640);
auto input_size = getSizeByDim(input_dim) * sizeof(float);
// allocate gpu memory for network inference
// 此处的buffer可以认为是TensorRT engine推理时在GPU上分配的输入显存
std::vector<void*> buffers(1);
cudaMalloc(&buffers[0], input_size);
// preprocess
preprocessImage(image_path, (float*)buffers[0], input_dim);
// download
cv::cuda::GpuMat gpu_output;
std::vector<cv::cuda::GpuMat> resized;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
resized.emplace_back(cv::cuda::GpuMat(cv::Size(input_dim.d[2], input_dim.d[1]), CV_32FC1, (float*)buffers[0] + i * input_dim.d[2] * input_dim.d[1]));
}
cv::cuda::merge(resized, gpu_output);
cv::cuda::GpuMat image_out;
// normalize
gpu_output.convertTo(image_out, CV_32FC3, 1.f * 255.f);
// download
cv::Mat dst;
image_out.download(dst);
cv::imwrite("../01_test_demo.jpg", dst);
for(void* buf:buffers)
{
cudaFree(buf);
}
return 0;
}
- 原图与结果图:
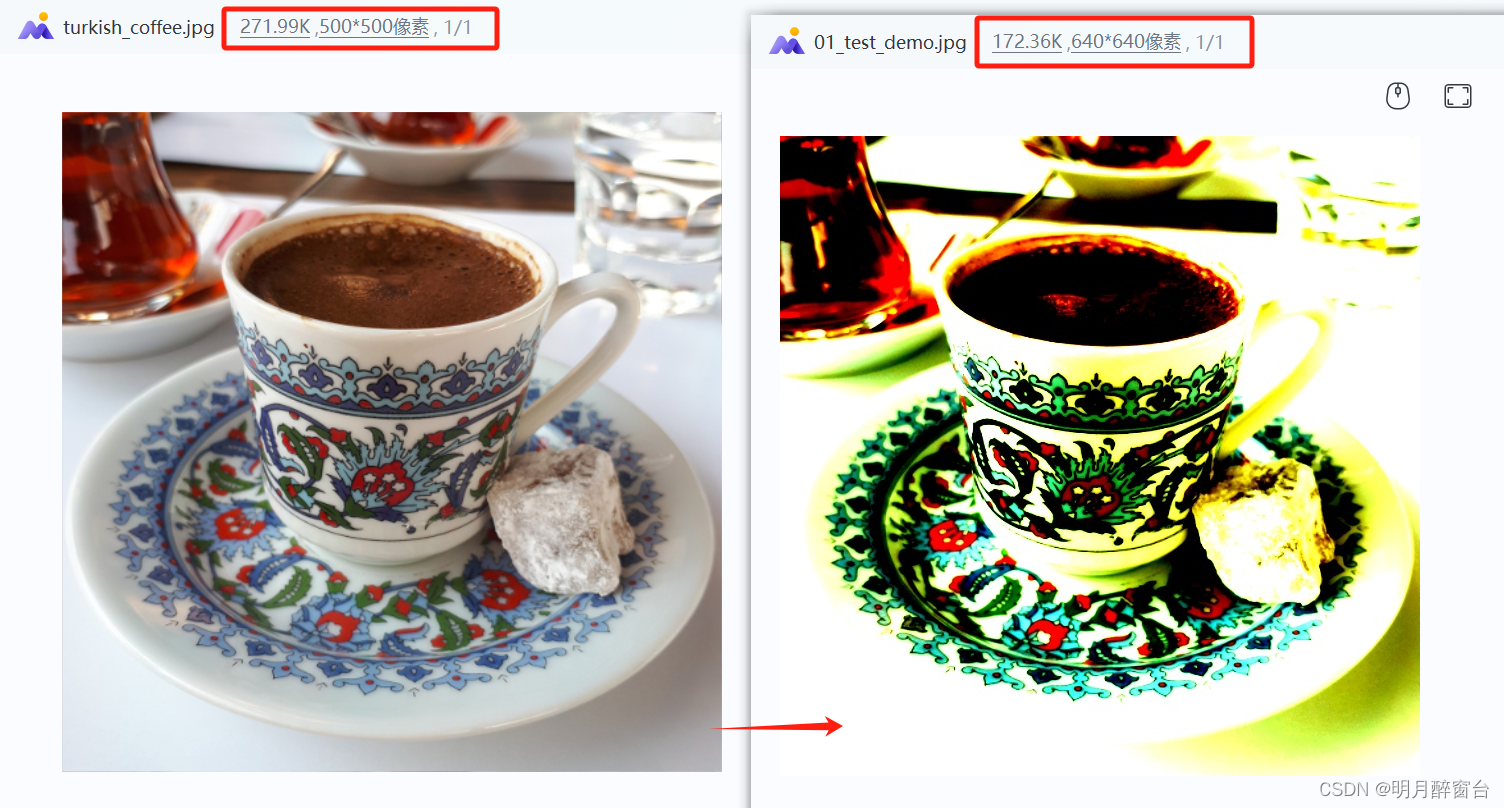
2. 输出后处理
- 下边通过一个trt demo展示一下后处理操作
- 源码实现如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <NvInfer.h>
#include <memory>
#include <NvOnnxParser.h>
#include <vector>
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/cuda.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudawarping.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudaarithm.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
// destroy TensorRT objects if something goes wrong
struct TRTDestroy
{
template <class T>
void operator()(T* obj) const
{
if (obj)
{
obj->destroy();
}
}
};
template <class T>
using TRTUniquePtr = std::unique_ptr<T, TRTDestroy>;
// calculate size of tensor
size_t getSizeByDim(const nvinfer1::Dims& dims)
{
size_t size = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < dims.nbDims; ++i)
{
size *= dims.d[i];
}
return size;
}
// get classes names
std::vector<std::string> getClassNames(const std::string& imagenet_classes)
{
std::ifstream classes_file(imagenet_classes);
std::vector<std::string> classes;
if (!classes_file.good())
{
std::cerr << "ERROR: can't read file with classes names.\n";
return classes;
}
std::string class_name;
while (std::getline(classes_file, class_name))
{
classes.push_back(class_name);
}
return classes;
}
// preprocessing stage ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void preprocessImage(const std::string& image_path, float* gpu_input, const nvinfer1::Dims& dims)
{
// read input image
cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(image_path);
if (frame.empty())
{
std::cerr << "Input image " << image_path << " load failed\n";
return;
}
cv::cuda::GpuMat gpu_frame;
// upload image to GPU
gpu_frame.upload(frame);
auto input_width = dims.d[2];
auto input_height = dims.d[1];
auto channels = dims.d[0];
auto input_size = cv::Size(input_width, input_height);
// resize
cv::cuda::GpuMat resized;
cv::cuda::resize(gpu_frame, resized, input_size, 0, 0, cv::INTER_NEAREST);
// normalize
cv::cuda::GpuMat flt_image;
resized.convertTo(flt_image, CV_32FC3, 1.f / 255.f);
cv::cuda::subtract(flt_image, cv::Scalar(0.485f, 0.456f, 0.406f), flt_image, cv::noArray(), -1);
cv::cuda::divide(flt_image, cv::Scalar(0.229f, 0.224f, 0.225f), flt_image, 1, -1);
// to tensor
std::vector<cv::cuda::GpuMat> chw;
for (size_t i = 0; i < channels; ++i)
{
chw.emplace_back(cv::cuda::GpuMat(input_size, CV_32FC1, gpu_input + i * input_width * input_height));
}
cv::cuda::split(flt_image, chw);
}
// post-processing stage ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void postprocessResults(float *gpu_output, const nvinfer1::Dims &dims, int batch_size)
{
// get class names
auto classes = getClassNames("imagenet_classes.txt");
// copy results from GPU to CPU
std::vector<float> cpu_output(getSizeByDim(dims) * batch_size);
cudaMemcpy(cpu_output.data(), gpu_output, cpu_output.size() * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// calculate softmax
std::transform(cpu_output.begin(), cpu_output.end(), cpu_output.begin(), [](float val) {return std::exp(val);});
auto sum = std::accumulate(cpu_output.begin(), cpu_output.end(), 0.0);
// find top classes predicted by the model
std::vector<int> indices(getSizeByDim(dims) * batch_size);
std::iota(indices.begin(), indices.end(), 0); // generate sequence 0, 1, 2, 3, ..., 999
std::sort(indices.begin(), indices.end(), [&cpu_output](int i1, int i2) {return cpu_output[i1] > cpu_output[i2];});
// print results
int i = 0;
while (cpu_output[indices[i]] / sum > 0.005)
{
if (classes.size() > indices[i])
{
std::cout << "class: " << classes[indices[i]] << " | ";
}
std::cout << "confidence: " << 100 * cpu_output[indices[i]] / sum << "% | index: " << indices[i] << "\n";
++i;
}
}
// main pipeline ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < 3)
{
std::cerr << "usage: " << argv[0] << " model.onnx image.jpg\n";
return -1;
}
std::string model_path(argv[1]);
std::string image_path(argv[2]);
int batch_size = 1;
// initialize TensorRT engine and parse ONNX model
TRTUniquePtr<nvinfer1::ICudaEngine> engine{nullptr};
//初始化engine.........省略
// get sizes of input and output and allocate memory required for input data and for output data
std::vector<nvinfer1::Dims> input_dims; // we expect only one input
std::vector<nvinfer1::Dims> output_dims; // and one output
std::vector<void*> buffers(engine->getNbBindings()); // buffers for input and output data
for (size_t i = 0; i < engine->getNbBindings(); ++i)
{
auto binding_size = getSizeByDim(engine->getBindingDimensions(i)) * batch_size * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&buffers[i], binding_size);
if (engine->bindingIsInput(i))
{
input_dims.emplace_back(engine->getBindingDimensions(i));
}
else
{
output_dims.emplace_back(engine->getBindingDimensions(i));
}
}
if (input_dims.empty() || output_dims.empty())
{
std::cerr << "Expect at least one input and one output for network\n";
return -1;
}
// preprocess input data
preprocessImage(image_path, (float *) buffers[0], input_dims[0]);
// inference
context->enqueue(batch_size, buffers.data(), 0, nullptr);
// postprocess results
postprocessResults((float *) buffers[1], output_dims[0], batch_size);
for (void* buf : buffers)
{
cudaFree(buf);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/yohnyang/article/details/135209572
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!