【数据结构第 6 章 ②】- 用 C 语言实现邻接矩阵
2023-12-13 04:33:32
目录
由于图的结构比较复杂,任意两个顶点之间都可能存在联系,因此无法以数据元素在存储区中的物理位置来表示元素之间的关系,即图没有顺序存储结构,但可以借助二维数组来表示元素之间的关系,即邻接矩阵表示法。另一方面,由于图的任意两个顶点间都可能存在关系,因此,用链式存储表示图是很自然的事,图的链式存储有多种,有邻接表、十字链表和邻接多重表,应根据实际需要的不同,选择不同的存储结构。
一、邻接矩阵表示法
邻接矩阵(Adjacency Matrix)是表示顶点之间相邻关系的矩阵。设 G(V, E) 是具有 n 个顶点的图,则 G 的邻接矩阵是具有如下性质的 n 阶方阵:

例如,图一中的 G1 和 G2 的邻接矩阵如下所示:
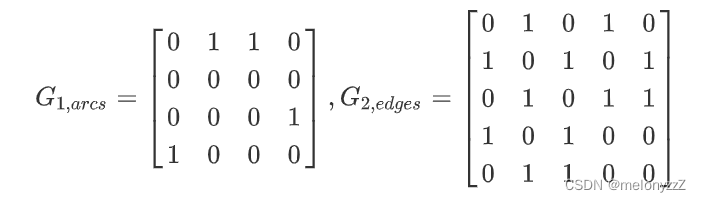
若 G 是网,则邻接矩阵可以定义为:

其中??表示边上的权值;?
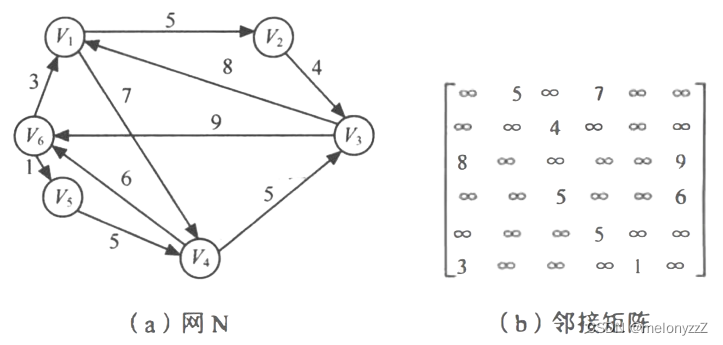
?表示计算机允许的,大于所有边上权值的数。例如,下图所示为一个有向网和它的邻接矩阵。
二、AMGraph.h
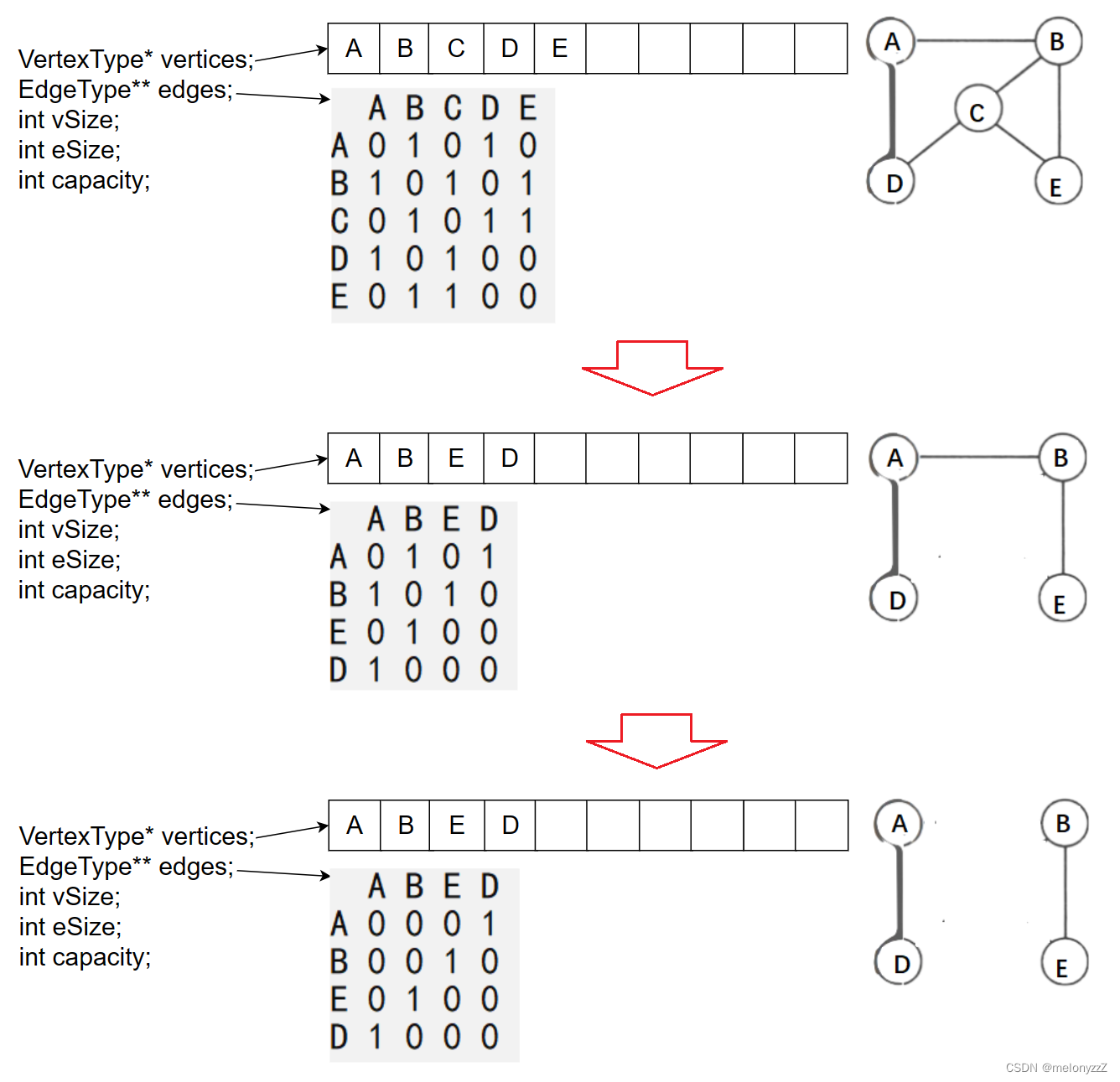
用邻接矩阵表示法表示图,除了一个用于存储邻接矩阵的二维数组外,还需要用一个一维数组来存储顶点信息。
注意:下面是以无向图为例的。
#pragma once
#define DEFAULT_CAPACITY 10
typedef char VertexType; // 假定顶点的数据类型为 char
typedef int EdgeType; // 假定边的权值的数据类型为 int
typedef struct AMGraph
{
VertexType* vertices; // 顶点表(vertices 是 vertex 的复数)
EdgeType** edges; // 邻接矩阵
int vSize; // 当前图中的顶点数
int eSize; // 当前图中的边数
int capacity; // 容量
}AMGraph;
// 基本操作
void AMGraphInit(AMGraph* pg); // 初始化
void ShowAdjMatrix(AMGraph* pg); // 显示邻接矩阵
int GetVetexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v); // 获取顶点的位置
void InsertVertex(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v); // 插入顶点
void InsertEdge(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2); // 插入边
void EraseVertex(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v); // 删除顶点
void EraseEdge(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2); // 删除边
int GetFirstAdjVexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v); // 获取 v 的第一个邻接顶点的位置
int GetNextAdjVexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v, VertexType w);
// 获取 v 的(相对于 w 的)下一个邻接顶点的位置
void AMGraphDestroy(AMGraph* pg); // 销毁三、AMGraph.c
-
初始化:
void AMGraphInit(AMGraph* pg) { assert(pg); pg->vSize = pg->eSize = 0; pg->capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY; pg->vertices = (VertexType*)malloc(sizeof(VertexType) * pg->capacity); assert(pg->vertices); pg->edges = (EdgeType**)malloc(sizeof(EdgeType*) * pg->capacity); assert(pg->edges); for (int i = 0; i < pg->capacity; ++i) { pg->edges[i] = (EdgeType*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeType) * pg->capacity); assert(pg->edges[i]); for (int j = 0; j < pg->capacity; ++j) { pg->edges[i][j] = 0; } } } -
获取顶点的位置:
int GetVetexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v) { assert(pg); for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i) { if (pg->vertices[i] == v) return i; } return -1; } -
显示邻接矩阵:
void ShowAdjMatrix(AMGraph* pg) { assert(pg); printf(" "); // 输出两个空格 for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i) { printf("%c ", pg->vertices[i]); } printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i) { printf("%c ", pg->vertices[i]); for (int j = 0; j < pg->vSize; ++j) { printf("%d ", pg->edges[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } } -
插入顶点:
void InsertVertex(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v) { assert(pg); // 考虑是否需要扩容 if (pg->vSize == pg->capacity) { VertexType* tmp1 = (VertexType*)realloc(pg->vertices, sizeof(VertexType) * 2 * pg->capacity); assert(tmp1); pg->vertices = tmp1; EdgeType** tmp2 = (EdgeType**)realloc(pg->edges, sizeof(EdgeType*) * 2 * pg->capacity); assert(tmp2); pg->edges = tmp2; for (int i = 0; i < pg->capacity; ++i) { EdgeType* tmp3 = (EdgeType*)realloc(pg->edges[i], sizeof(EdgeType) * 2 * pg->capacity); assert(tmp3); pg->edges[i] = tmp3; for (int j = pg->capacity; j < 2 * pg->capacity; ++j) { pg->edges[i][j] = 0; } } for (int i = pg->capacity; i < 2 * pg->capacity; ++i) { pg->edges[i] = (EdgeType*)malloc(sizeof(EdgeType) * 2 * pg->capacity); assert(pg->edges[i]); for (int j = 0; j < 2 * pg->capacity; ++j) { pg->edges[i][j] = 0; } } pg->capacity *= 2; } // 插入顶点 pg->vertices[pg->vSize++] = v; } -
插入边:
void InsertEdge(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2) { assert(pg); int pos1 = GetVetexPos(pg, v1); int pos2 = GetVetexPos(pg, v2); if (pos1 == -1 || pos2 == -1) return; if (pg->edges[pos1][pos2] != 0) return; pg->edges[pos1][pos2] = pg->edges[pos2][pos1] = 1; ++pg->eSize; } -
删除顶点:
void EraseVertex(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v) { assert(pg); int pos = GetVetexPos(pg, v); if (pos == -1) return; // cnt 为和 v 相关联的边的数目 int cnt = 0; for (int j = 0; j < pg->vSize; ++j) { if (pg->edges[pos][j] != 0) ++cnt; } pg->vertices[pos] = pg->vertices[pg->vSize - 1]; for (int j = 0; j < pg->vSize; ++j) { pg->edges[pos][j] = pg->edges[pg->vSize - 1][j]; } for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i) { pg->edges[i][pos] = pg->edges[i][pg->vSize - 1]; } --pg->vSize; pg->eSize -= cnt; } -
删除边:
void EraseEdge(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2) { assert(pg); int pos1 = GetVetexPos(pg, v1); int pos2 = GetVetexPos(pg, v2); if (pos1 == -1 || pos2 == -1) return; if (pg->edges[pos1][pos2] == 0) return; pg->edges[pos1][pos2] = pg->edges[pos2][pos1] = 0; --pg->eSize; } -
获取 v 的第一个邻接顶点:
int GetFirstAdjVexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v) { assert(pg); int pos = GetVetexPos(pg, v); if (pos == -1) return -1; for (int j = 0; j < pg->vSize; ++j) { if (pg->edges[pos][j] != 0) return j; } return -1; } -
获取 v 的(相对于 w 的)下一个邻接顶点:
int GetNextAdjVexPos(AMGraph* pg, VertexType v, VertexType w) { assert(pg); int pos1 = GetVetexPos(pg, v); int pos2 = GetVetexPos(pg, w); if (pos1 == -1 || pos2 == -1) return -1; for (int j = pos2 + 1; j < pg->vSize; ++j) { if (pg->edges[pos1][j] != 0) return j; } return -1; } -
销毁:
void AMGraphDestroy(AMGraph* pg) { assert(pg); free(pg->vertices); pg->vertices = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < pg->capacity; ++i) { free(pg->edges[i]); pg->edges[i] = NULL; } free(pg->edges); pg->edges = NULL; pg->vSize = pg->eSize = pg->capacity = 0; }
四、Test.c
#include "AMGraph.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
AMGraph g;
AMGraphInit(&g);
InsertVertex(&g, 'A');
InsertVertex(&g, 'B');
InsertVertex(&g, 'C');
InsertVertex(&g, 'D');
InsertVertex(&g, 'E');
InsertEdge(&g, 'A', 'B');
InsertEdge(&g, 'A', 'D');
InsertEdge(&g, 'B', 'C');
InsertEdge(&g, 'B', 'E');
InsertEdge(&g, 'C', 'D');
InsertEdge(&g, 'C', 'E');
ShowAdjMatrix(&g);
printf("\n");
EraseVertex(&g, 'C');
ShowAdjMatrix(&g);
printf("\n");
EraseEdge(&g, 'A', 'B');
ShowAdjMatrix(&g);
printf("\n");
printf("%d\n", GetFirstAdjVexPos(&g, 'A')); // 3
printf("%d\n", GetNextAdjVexPos(&g, 'A', 'D')); // -1
AMGraphDestroy(&g);
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/melonyzzZ/article/details/134890233
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!