DOM and XPATH
2023-12-26 14:40:18
DOM
-
Originally developed for HTML. Supported by most browsers.
-
Represents the content of the XML or HTML document as a tree structure.
-
Using DOM, we can easily read and update the contents of the document.
D: Document —> file
O: Object —> tags elements
M: Model —> layout structure
Online DOM viewer:
XPATH
-
Allows us to use path expressions to navigate an XML document.
-
It allow us to select only the nodes we're interested in.
its :
-
Expression language.
-
Contains some standard functions.
-
Non-XML
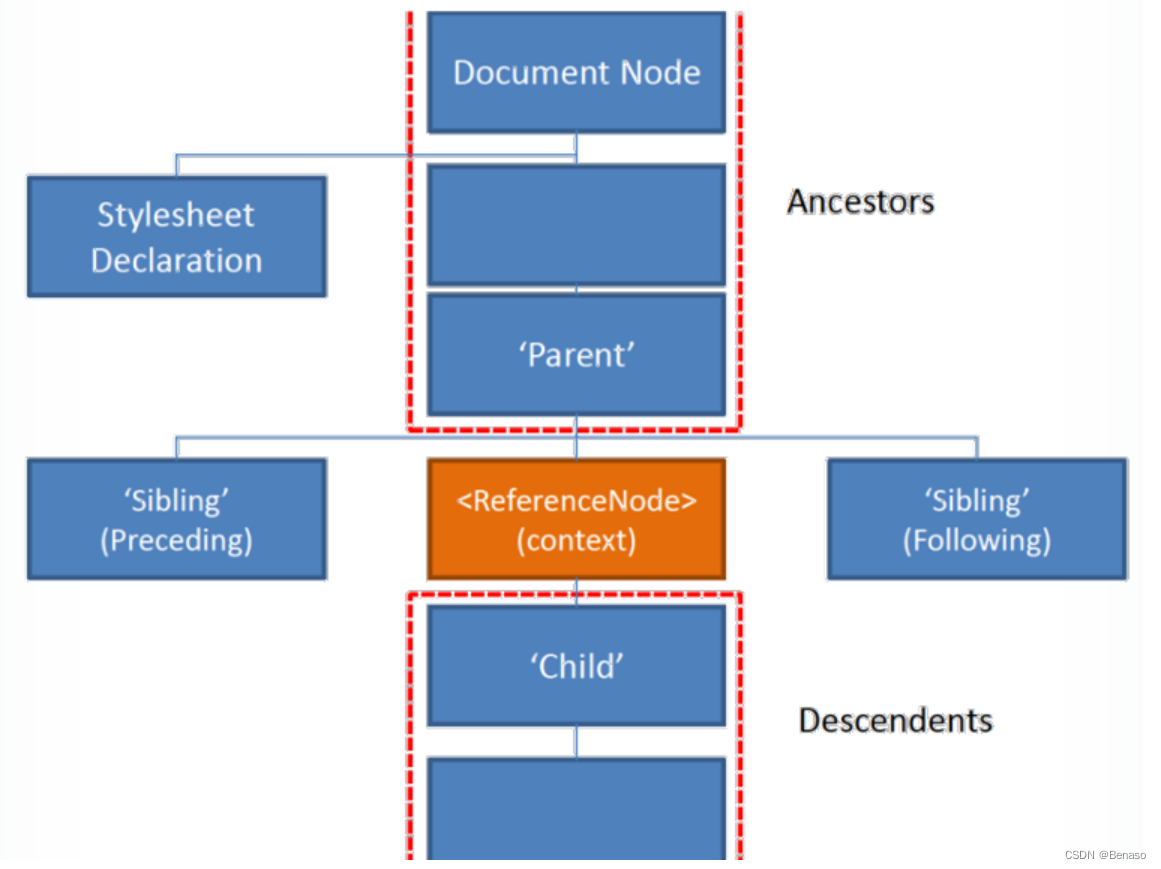
XPATH works on the following kinds of nodes:
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| nodename | Selects all nodes with the name"nodename" |
| / | Selects from the root node |
| // | Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection no matter where they are |
| . | Selects the value of the current node |
| .. | Selects the parent of the current node |
| @ | Selects attributes |
Predicates
-
similar to filters
-
They always appear in[]
-
They appear after the axis and node text
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| /bookstore/book[1] | Selects the first book element that is the child of the bookstore element. |
| /bookstore/book[last()] | Selects the last book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| /bookstore/book[last()-1] | Selects the last but one book element that is the child of the bookstore element |
| /bookstore/book[position()<3] | Selects the first two book elements that are children of the bookstore element |
| //title[@lang] | Selects all the title elements that have an attribute named lang |
| //title[@lang='en'] | Selects all the title elements that have a "lang" attribute with a value of "en" |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00] | Selects all the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element |
| /bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title | Selects all the title elements of the book elements of the bookstore element that have a price element with a value greater than 35.00 |
XPATH Axes
an Axes represents a relationship to the current node on the tree.
| AxisName | Result |
|---|---|
| ancestor | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node |
| ancestor-or-self | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node and the current node itself |
| attribute | Selects all attributes of the current node |
| child | Selects all children of the current node |
| descendant | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node |
| descendant-or-self | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node and the current node itself |
| following | Selects everything in the document after the closing tag of the current node |
| following-sibling | Selects all siblings after the current node |
| namespace | Selects all namespace nodes of the current node |
| parent | Selects the parent of the current node |
| preceding | Selects all nodes that appear before the current node in the document, except ancestors, attribute nodes and namespace nodes |
| preceding-sibling | Selects all siblings before the current node |
| self | Selects the current node |
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_74783792/article/details/135220370
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!