JDBC详解——增删改查(CRUD)、sql注入、事务、连接池
1. 概念:
-
Java DataBase Connectivity, Java 数据库连接, Java语言操作数据库
-
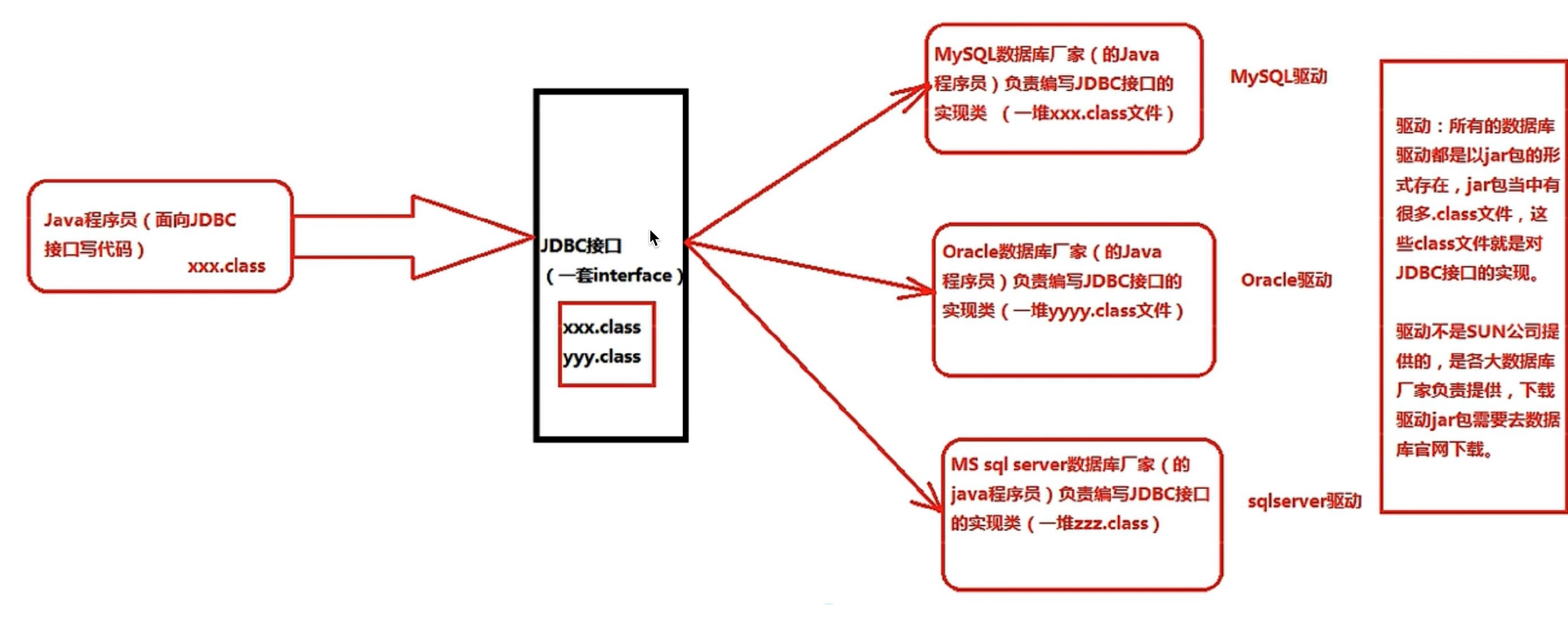
JDBC本质:其实是官方(sun公司)定义的一套操作所有关系型数据库的规则,即接口。各个数据库厂商去实现这套接口,提供数据库驱动jar包。我们可以使用这套接口(JDBC)编程,真正执行的代码是驱动jar包中的实现类。
-
接口都有调用者和实现者,面向接口调用,面向接口写实现类,这都属于面向接口编程。
-
为什么要面向接口编程?
-
解耦合:降低程序的耦合性,提高程序的扩展力,多态就是典型的面向接口(面向抽象)编程,而不是面向具体编程。
-
2. 快速入门:
-
步骤:
-
导入驱动jar包 mysql-connector-java-8.0.w-bin.jar 1.复制mysql-connector-java-8.0.22-bin.jar到项目的lib目录下 2.右键-->Add As Library
-
注册驱动
-
获取数据库连接对象 Connection
-
定义sql
-
获取执行sql语句的对象 Statement
-
执行sql,接受返回结果
-
处理结果
-
释放资源
代码示例:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
?
public class Simple01 {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
? ? ? ?// 1. 导入驱动jar包 mysql-connector-java-8.0.w-bin.jar
? ? ? ?// ? ? 1.复制mysql-connector-java-8.0.22-bin.jar到项目的lib目录下
? ? ? ?// ? ? 2.右键-->Add As Library
? ? ? ?// 2. 注册驱动
? ? ? ?Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ?//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ?// 3. 获取数据库连接对象 Connection
? ? ? ?Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
? ? ? ?//Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo?user=root&password=root");
? ? ? ?//Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///jdbcDemo?user=root&password=root");
?
? ? ? ?// 4. 定义sql
? ? ? ?String sql = "insert into student values (null,'赵六')";
? ? ? ?// 5. 获取执行sql语句的对象 Statement
? ? ? ?Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
? ? ? ?// 6. 执行sql,接受返回结果
? ? ? ?int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
? ? ? ?// 7. 处理结果
? ? ? ?System.out.println(count > 0 ? "插入成功" : "插入失败");
? ? ? ?// 8. 释放资源
? ? ? ?statement.close();
? ? ? ?connection.close();
? }
}3. 详解各个对象:
3.1 DriverManager:驱动管理对象
-
功能:
-
注册驱动:告诉程序该使用哪一个数据库驱动jar static void registerDriver(Driver driver) :注册与给定的驱动程序 DriverManager 。 写代码使用: Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
查看源码发现:在com.mysql.jdbc.Driver类中存在静态代码块
static { ? ? ? ?try { ? ? ? ? ? ?java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); ? ? ? } catch (SQLException E) { ? ? ? ? ? ?throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!"); ? ? ? } } //注意:mysql5之后的驱动jar包可以省略注册驱动的步骤。 //8.022数据库驱动程序改为:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver -
获取数据库连接:
-
方法
static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password) -
参数:
-
url:指定连接的路径
-
语法:jdbc:mysql://ip地址(域名):端口号/数据库名称
-
例子:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo
-
细节:如果连接的是本机mysql服务器,并且mysql服务默认端口是3306,则url可以简写为:jdbc:mysql:///数据
-
库名称,例子:jdbc:mysql:///jdbcDemo
-
-
-
-
user:用户名
-
password:密码
3.2 Connection:数据库连接对象
-
功能:
-
获取执行sql 的对象
-
Statement createStatement()
-
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql)
-
-
管理事务:
-
开启事务:setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) :调用该方法设置参数为false,即开启事务
-
提交事务:commit()
-
回滚事务:rollback()
-
3.3 Statement:数据库连接对象
-
执行sql
-
boolean execute(String sql) :可以执行任意的sql 这个不常用 了解
-
int executeUpdate(String sql) :
执行DML(insert、update、delete)语句、
执行DDL (create,alter、drop)语句,很少用,都用sql语句创建。
返回值:int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
count是影响的行数,可以通过这个影响的行数判断DML语句是否执行成功 返回值>0 的则执行成功,反之,则失败。
-
-
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) :
执行DQL(select)语句
3.4 执行DML语句
-
Account表 添加一条记录
-
Account表 修改一条记录
-
Account表 删除一条记录
3.5 添加一条记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
?
public class SimpleInsert {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?Connection connection = null;
? ? ? ?Statement statement = null;
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 注册驱动
? ? ? ? ? ?Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取数据库连接对象
? ? ? ? ? ?connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取执行sql语句对象 Statement
? ? ? ? ? ?statement = connection.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 定义sql 执行并接收返回结果
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "insert into account values(null,'王五' , 23000)";
? ? ? ? ? ?int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// 处理结果
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(count > 0 ? "插入成功" : "插入失败");
? ? ? } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 释放资源
? ? ? ? ? ?if (statement != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?statement.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?if (connection != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?connection.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}3. 6 修改一条记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
?
public class SimpleUpdate {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?Connection connection = null;
? ? ? ?Statement statement = null;
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 注册驱动
? ? ? ? ? ?Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取数据库连接对象
? ? ? ? ? ?connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取执行sql语句对象 Statement
? ? ? ? ? ?statement = connection.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 定义sql 执行并接收返回结果
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "update account set balance = 20000 where id = 2";
? ? ? ? ? ?int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// 处理结果
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(count > 0 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
? ? ? } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 释放资源
? ? ? ? ? ?if (statement != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?statement.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?if (connection != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?connection.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}3.7 删除一条记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
?
public class SimpleDelete {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?Connection connection = null;
? ? ? ?Statement statement = null;
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 注册驱动
? ? ? ? ? ?Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取数据库连接对象
? ? ? ? ? ?connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取执行sql语句对象 Statement
? ? ? ? ? ?statement = connection.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 定义sql 执行并接收返回结果
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "delete from account where id = 3";
? ? ? ? ? ?int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// 处理结果
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(count > 0 ? "删除成功" : "删除失败");
? ? ? } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 释放资源
? ? ? ? ? ?if (statement != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?statement.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?if (connection != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?connection.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}3.8 执行DDL语句
代码示例:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
?
public class CreateTable05 {
? ?// DDL:数据定义语言:创建一个表、视图、操作列
? ?// DML:数据操作语言:对表进行增 删 改。insert delete update
? ?// DQL:数据查询语言:对表进行查询 select from where
? ?// DCL:数据控制语言:对数据库进行授权或者控制
?
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?Statement stmt = null;
? ? ? ?Connection conn = null;
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 1.注册驱动
? ? ? ? ? ?// 2.定义sql
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "create table student(id int , name varchar(20))";
? ? ? ? ? ?// 3.获取连接数据库的对象 Connection
? ? ? ? ? ?conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///DB_JDBC_01", "root", "root1234");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 4.获取操作sql的对象 Statement
? ? ? ? ? ?stmt = conn.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 5.执行sql影响的行数
? ? ? ? ? ?int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// 6.处理结果
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(count);// DDL 返回结果就是0 不需要判断
?
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 7.释放资源
? ? ? ? ? ?// stmt.close();
? ? ? ? ? ?if (stmt != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stmt.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?if (conn != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?conn.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}4 ResultSet:结果集对象,封装查询结果
4.1 ResultSet概述
-
boolean next(): 游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否是最后一行末尾(是否有数据),
-
如果是最后一行末尾,则返回false,如果不是最后一行末尾则返回true
* getXxx(参数):获取数据
* Xxx:代表数据类型 如: int getInt() , String getString()
* 参数:
1. int:代表列的编号,从1开始 如: getString(1) getString(“name”)
2. String:代表列名称。 如: getDouble("balance") getDouble(1)
* 注意:
* 使用步骤:
1. 游标向下移动一行
2. 判断是否有数据
3. 获取数据
//循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while(rs.next()){
//获取数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}4.2 执行DQL语句:
代码示例:
import java.sql.*;
?
public class SimpleSelect {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?Connection connection = null;
? ? ? ?Statement statement = null;
? ? ? ?ResultSet resultSet = null;
? ? ? ?try {
?
? ? ? ? ? ?// 注册驱动
? ? ? ? ? ?Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 建立连接
? ? ? ? ? ?connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
? ? ? ? ? ?// 获取操作sql的对象 Statement
? ? ? ? ? ?statement = connection.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 定义sql
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "select * from account ";
?
? ? ? ? ? ?// 执行sql影响的行数
? ? ? ? ? ?resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(resultSet.next());
? ? ? ? ? ?// 处理结果
? ? ? ? ? ?// 循环判断游标是否是最后一行
? ? ? ? ? ?while (resultSet.next()) {
// ? ? ? ? ? ? ? int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
// ? ? ? ? ? ? ? String name = resultSet.getString("name");
// ? ? ? ? ? ? ? double balance = resultSet.getDouble("balance");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?String name = resultSet.getString(2);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?double balance = resultSet.getDouble(3);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("id:" + id + " ? " + "name:" + name + " ? ? " + "balance:" + balance);
? ? ? ? ? }
?
?
? ? ? } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 释放资源
? ? ? ? ? ?if (connection != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?connection.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ? ? ?if (statement != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?statement.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ? ? ?if (resultSet != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?resultSet.close();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
?
? ? ? }
? }
?
}4. 3 查询练习:
-
定义一个方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
1. 定义Emp类
2. 定义方法 public List<Emp> findAll(){}
3. 实现方法 select * from emp;
代码示例:
-- 员工表
CREATE TABLE emp (
id INT PRIMARY KEY, -- 员工id
ename VARCHAR(50), -- 员工姓名
job_id INT, -- 职务id
mgr INT , -- 上级领导
joindate DATE, -- 入职日期
salary DECIMAL(7,2) -- 工资
?
);
-- 添加员工
INSERT INTO emp(id,ename,job_id,mgr,joindate,salary) VALUES
(1001,'孙悟空',4,1004,'2000-12-17','8000.00'),
(1002,'卢俊义',3,1006,'2001-02-20','16000.00'),
(1003,'林冲',3,1006,'2001-02-22','12500.00'),
(1004,'唐僧',2,1009,'2001-04-02','29750.00'),
(1005,'李逵',4,1006,'2001-09-28','12500.00'),
(1006,'宋江',2,1009,'2001-05-01','28500.00'),
(1007,'刘备',2,1009,'2001-09-01','24500.00'),
(1008,'猪八戒',4,1004,'2007-04-19','30000.00');
?
SELECT * FROM emp;package com.whitecamellia.entity;
?
import java.util.Date;
?
public class Emp {
? ?private Integer id;
? ?private String eName;
? ?private Integer jobId;
? ?private Integer mgr;
? ?private Date joinDate;
? ?private Double salary;
?
? ?public Integer getId() {
? ? ? ?return id;
? }
?
? ?public void setId(Integer id) {
? ? ? ?this.id = id;
? }
?
? ?public String geteName() {
? ? ? ?return eName;
? }
?
? ?public void seteName(String eName) {
? ? ? ?this.eName = eName;
? }
?
? ?public Integer getJobId() {
? ? ? ?return jobId;
? }
?
? ?public void setJobId(Integer jobId) {
? ? ? ?this.jobId = jobId;
? }
?
? ?public Integer getMgr() {
? ? ? ?return mgr;
? }
?
? ?public void setMgr(Integer mgr) {
? ? ? ?this.mgr = mgr;
? }
?
? ?public Date getJoinDate() {
? ? ? ?return joinDate;
? }
?
? ?public void setJoinDate(Date joinDate) {
? ? ? ?this.joinDate = joinDate;
? }
?
? ?public Double getSalary() {
? ? ? ?return salary;
? }
?
? ?public void setSalary(Double salary) {
? ? ? ?this.salary = salary;
? }
?
? ?@Override
? ?public String toString() {
? ? ? ?return "Emp{" +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?"id=" + id +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", eName='" + eName + '\'' +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", jobId=" + jobId +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", mgr=" + mgr +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", joinDate=" + joinDate +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", salary=" + salary +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?'}';
? }
}package com.whitecamellia;
import com.whitecamellia.entity.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FindAllEmp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Emp> all = findAll();
for (Emp emp : all) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
public static List<Emp> findAll() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
List<Emp> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcDemo", "root", "root");
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from emp";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
Integer id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String eName = resultSet.getString(2);
Integer jobId = resultSet.getInt(3);
Integer mgr = resultSet.getInt(4);
Date joinDate = resultSet.getDate(5);
Double salary = resultSet.getDouble(6);
Emp emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(id);
emp.seteName(eName);
emp.setJobId(jobId);
emp.setMgr(mgr);
emp.setJoinDate(joinDate);
emp.setSalary(salary);
list.add(emp);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
}5. JDBC工具类
5.1 JDBCUtils
-
抽取JDBC工具类 : JDBCUtils
* 目的:简化书写
* 分析:
1. 注册驱动也抽取
2. 抽取一个方法获取连接对象
* 需求:不想传递参数(麻烦),还得保证工具类的通用性。
* 解决:配置文件
jdbc.properties
url=
?
user=
?
password=3. 抽取一个方法释放资源
代码示例:
package com.whitecamellia.util;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
/**
* 文件读取 只需要读取一次 即可 使用静态代码块
*/
static {
// 1.创建Properties集合类
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 获取src路径下的文件的方式--->ClassLoader 类加载器
// 获取字符串的路径
String path = jdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResource("jdbc.properties").getPath();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(path));
// System.out.println(path);
// 获取数据 赋值
url = properties.getProperty("url");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
// 获取驱动
Class.forName(driver);
// System.out.println(url);
// System.out.println(user);
// System.out.println(password);
// System.out.println(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 释放资源*
*
* @param resultSet
* @param connection
* @param statement
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 释放资源*
*
* @param connection
* @param statement
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}5.2 用户登入练习:
-
需求:
1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
2. 判断用户是否登录成功
* select * from user where username = "" and password = "";
* 如果这个sql有查询结果,则成功,反之,则失败
代码示例:
-- 创建数据库表 user
?
CREATE TABLE USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32),
password VARCHAR(32)
);
?
INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL,'zhangsan','123');
INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL,'lisi','1234');package com.whitecamellia;
?
import com.whitecamellia.util.JdbcUtils;
?
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
?
/**
* 练习: 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class Login {
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?// 1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
? ? ? ?Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
? ? ? ?System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
? ? ? ?String username = sc.nextLine();
? ? ? ?System.out.println("请输入密码:");
? ? ? ?String password = sc.nextLine();
? ? ? ?// 2.调用方法
? ? ? ?boolean flag = new Login().login(username, password);
? ? ? ?// 3.判断结果,输出不同语句
? ? ? ?if (flag)
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("登录成功!");
? ? ? ?else
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
?
? }
?
? ?/**
? ? * 登入方法
? ? *
? ? * @param username
? ? * @param password
? ? * @return
? ? */
? ?public boolean login(String username, String password) {
? ? ? ?if (username == null || password == null)
? ? ? ? ? ?return false;
? ? ? ?Connection conn = null;
? ? ? ?Statement stmt = null;
? ? ? ?ResultSet rs = null;
? ? ? ?// 和数据库进行验证
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?// 1.建立连接
? ? ? ? ? ?conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 2.定义sql
? ? ? ? ? ?String sql = "select * from user where username ='" + username + "' and password= '" + password + "' ";
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("sql:" + sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// select * from user where username ='s' and password = 'a' or 'a' = 'a'
? ? ? ? ? ?// 3.获取执行sql的对象
? ? ? ? ? ?stmt = conn.createStatement();
? ? ? ? ? ?// 4.执行查询
? ? ? ? ? ?rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
? ? ? ? ? ?// 5.判断
? ? ? ? ? ?return rs.next();
? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? } finally {
? ? ? ? ? ?JdbcUtils.close(conn, stmt, rs);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return false;
? }
}5.3 SQL注入问题
-
PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement:执行sql的对象
1. SQL注入问题:在拼接sql时,有一些sql的特殊关键字参与字符串的拼接。会造成安全性问题
1. 输入用户随便,输入密码:a' or 'a' = 'a
2. sql:select * from user where username = 'fhdsjkf' and password = a' or 'a' = 'a
由于前面的用户名和密码不匹配结果是false 但是后面的or 是true,结果就是true
2. 解决sql注入问题:使用PreparedStatement对象来解决
3. 预编译的SQL:参数使用?作为占位符
4. 步骤:
1. 导入驱动jar包 mysql-connector-java-8.0.22-bin.jar
2. 注册驱动
3. 获取数据库连接对象 Connection
4. 定义sql
注意:sql的参数使用?作为占位符。
如:select * from user where username = ? and password = ?;
5. 获取执行sql语句的对象 PreparedStatement Connection.prepareStatement(String sql)
6. 给?赋值:
* 方法: setXxx(参数1,参数2)
* 参数1:?的位置编号 从1 开始
* 参数2:?的值
7. 执行sql,接受返回结果,不需要传递sql语句
8. 处理结果
9. 释放资源
代码示例:
package com.whitecamellia;
import com.whitecamellia.util.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习: 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class LoginOk {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
// 2.调用方法
boolean flag = new LoginOk().login(username, password);
// 3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag)
System.out.println("登录成功!");
else
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
/**
* 登入方法
*
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null)
return false;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
// 和数据库进行验证
try {
// 1.建立连接
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 2.定义sql 参数赋值修改成?
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ? ";
System.out.println("sql:" + sql);
// 3.获取执行sql的对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.1 依次给 ?号赋值 先执行sql对象再赋值
ps.setString(1, username);
ps.setString(2, password);
// 4.执行查询
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 5.判断
return rs.next();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return false;
}
}6 JDBC控制事务:
概念:
-
事务:
一个包含多个步骤的业务操作,如果这个业务操作被事务管理,则这多个步骤要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
-
操作:
1. 开启事务
2. 提交事务
3. 回滚事务
-
使用Connection对象来管理事务
* 开启事务:setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) :调用该方法设置参数为false,即开启事务
* 在执行sql之前开启事务
* 提交事务:commit()
* 当所有sql都执行完提交事务
* 回滚事务:rollback()
* 在catch中回滚事务
代码示例:
-- 举例:
CREATE TABLE account1 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR (10),
balance DOUBLE
);
-- 添加数据
INSERT INTO account1 (NAME, balance) VALUES ('zhangsan', 1000), ('lisi', 1000);
?
SELECT * FROM account1;
?
-- 恢复默认
UPDATE account1 set balance = 1000;package com.whitecamellia;
import com.whitecamellia.util.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TransAction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement ps1 = null;
PreparedStatement ps2 = null;
try {
// 1.数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//2. 开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql1 = "update account1 set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";
String sql2 = "update account1 set balance = balance + ? where id = ?";
// 4.获取执行sql语句对象
ps1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps2 = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
// 5.设置参数
ps1.setDouble(1, 500);
ps1.setInt(2, 1);
ps2.setDouble(1, 500);
ps2.setInt(2, 2);
// 6. 执行sql语句
ps1.executeUpdate();
// int a = 3 / 0;// 模拟异常
ps2.executeUpdate();
connection.commit(); // 事务提交
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.rollback(); // 事务回滚
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7. 释放连接
JdbcUtils.close(connection, ps1);
JdbcUtils.close(null, ps2);
}
}
}7 数据库连接池
7.1 概念:
-
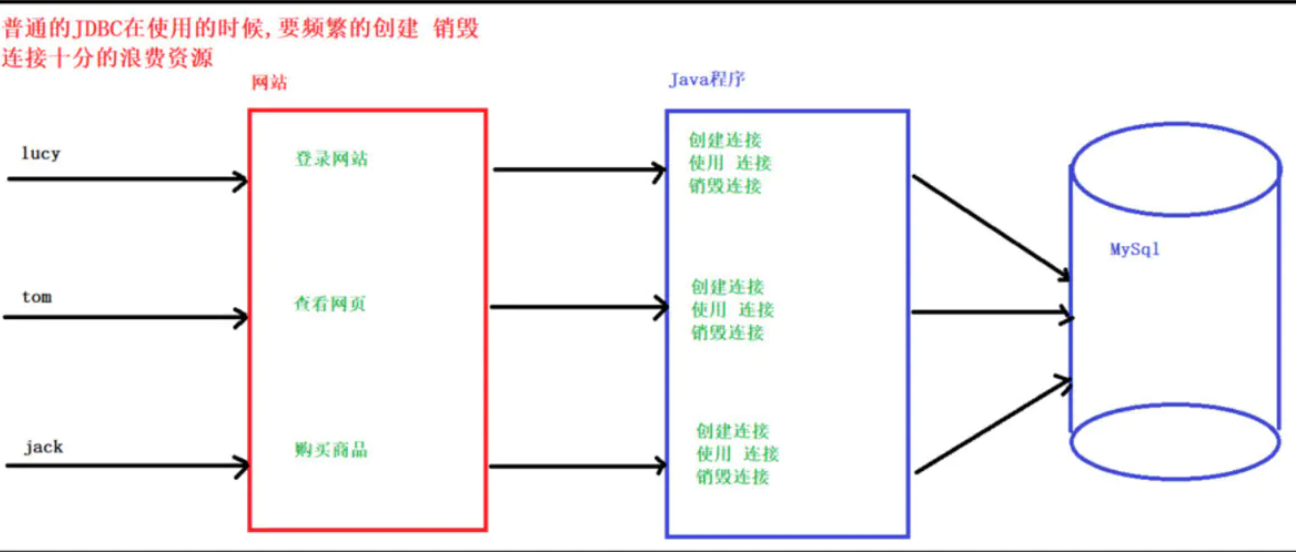
其实就是一个容器(集合),存放数据库连接的容器。当系统初始化好后,容器被创建,容器中会申请一些连接对象,当用户来访问数据库时,从容器中获取连接对象,用户访问完之后,会将连接对象归还给容器。
-
普通方式
-
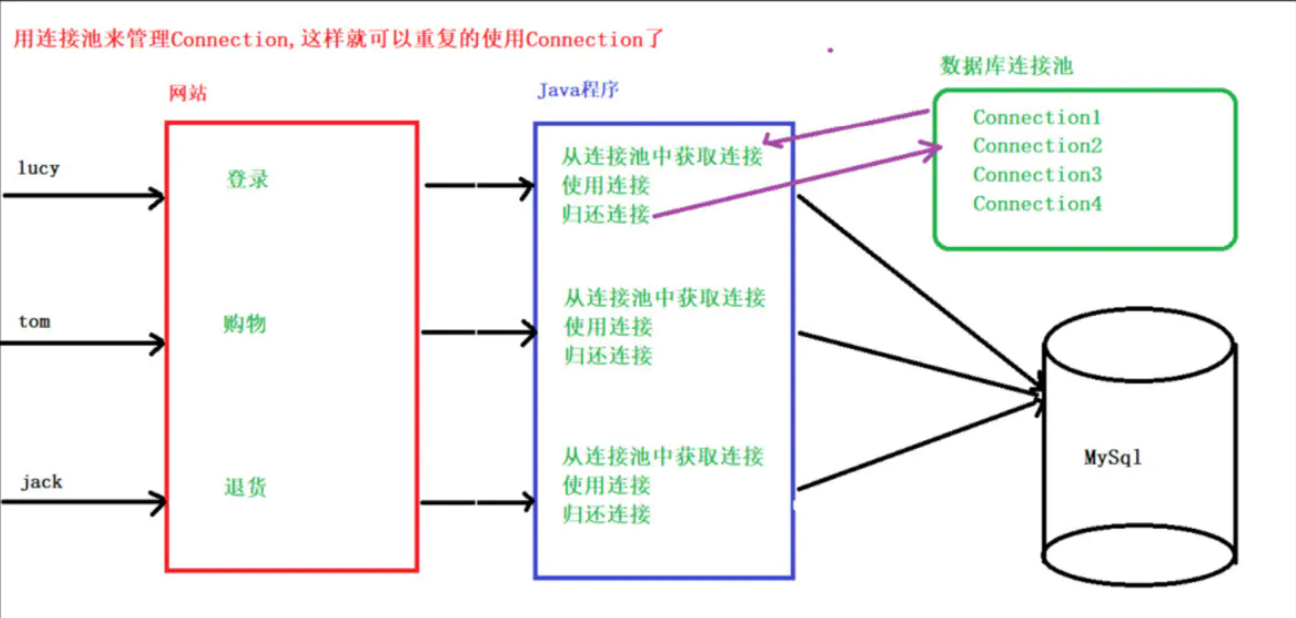
使用连接池
-
好处:
-
节约资源
-
用户访问高效
-
-
可以用数据库连接池来管理Connection,这可以重复使用Connection。
有了池,所以我们就不用自己来创建Connection,而是通过池来获取Connection对象。
当使用完Connection后,调用Connection的close()方法也不会真的关闭Connection,而是把Connection“归还”给连接池,池就可以再利用这个Connection对象了。
池参数(所有池参数都有默认值):
-
初始大小
-
最小空闲连接数
-
增量:一次创建的最小单位
-
最大空闲连接数
-
最大连接数
-
最大的等待时间
-
……
四大连接参数:
-
Driver
-
url
-
用户名
-
密码
常见的开源连接池:
-
DBCP
-
C3P0
-
Druid
-
7.2 实现:
-
标准接口:
-
标准接口:DataSource javax.sql包下的,这是官方提供的,提供了获取数据库连接的方法
-
-
方法
获取连接:getConnection()
归还连接:Connection.close()。
如果连接对象Connection是从连接池中获取的,那么调用Connection.close()方法,
则不会再关闭连接了。而是归还连接
-
数据库厂商实现
-
一般我们不去实现它,有数据库厂商来实现
-
C3P0:数据库连接池技术,相对比较老旧
-
Druid:数据库连接池实现技术,由阿里巴巴提供的
-
7.3 C3P0
-
C3P0数据库连接池技术
步骤:
-
导入jar包 (两个) c3p0-0.9.5.2.jar和mchange-commons-java-0.2.12.jar ,
不要忘记导入数据库驱动jar包,mysql-connector-java-8.0.22-bin
-
定义配置文件:
名称: c3p0.properties 或者 c3p0-config.xml,二者都可以
路径:直接将文件放在src目录下即可。
-
创建核心对象 数据库连接池对象 ComboPooledDataSource
-
获取连接:getConnection
代码示例:
package com.whitecamellia;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class C3P0Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
// test1();// 使用方式
test2();//测试
}
public static void test1() throws SQLException {
//1.创建数据库连接池对象
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//2.获取连接对象
Connection connection = ds.getConnection();
//3.输出打印
System.out.println(connection);
//4.归还连接对象
connection.close();// c3p0默认不会把连接回收到连接池中,需要手动归还close
}
public static void test2() throws SQLException {
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
for (int i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {
Connection connection = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println(i + " : " + connection);
if (i == 5) {
connection.close();
}
// connection.close();//c3p0默认不会把连接回收到连接池中,需要手动归还close
}
}
}7.4 Druid
-
Druid:数据库连接池实现技术,由阿里巴巴提供的
-
步骤:
-
导入jar包 druid-1.0.9.jar
-
定义配置文件:
-
是properties形式的
-
可以叫任意名称,可以放在任意目录下
-
-
加载配置文件 Properties
-
获取数据库连接池对象:通过工厂来来获取 DruidDataSourceFactory
-
获取连接:getConnection
代码示例:
package com.whitecamellia;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DruidTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.导入jar包
//2.导入配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
String path = DruitTest.class.getClassLoader().getResource("druid.properties").getPath();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(path));
//3.加载配置文件
DataSource ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
//4.测试
for (int i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {
Connection connection = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println(i + " : " + connection);
if (i == 5) {
connection.close();
}
// 5. 归还连接对象 connection.close();
}
}
}7.5 定义工具类
-
定义一个类 JDBCUtils
-
提供静态代码块加载配置文件,初始化连接池对象
-
提供方法
-
获取连接方法:通过数据库连接池获取连接
-
释放资源
-
获取连接池的方法
-
代码示例:
package com.util;
?
?
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
?
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
?
/**
* 连接池JDBCUtils工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
?
? ?//1.定义成员变量 DataSource
? ?private static DataSource ds;
?
? ?static {
? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ?//1.加载配置文件
? ? ? ? ? ?Properties pro = new Properties();
? ? ? ? ? ?InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
? ? ? ? ? ?pro.load(is);
? ? ? ? ? ?//2.获取DateSource
? ? ? ? ? ?ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
? ? ? } catch (Exception e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? }
? }
?
? ?/**
? ? * 获取连接
? ? */
? ?public static Connection getConnections() throws SQLException {
? ? ? ?return ds.getConnection();
? }
?
?
? ?/**
? ? * 释放资源
? ? *
? ? * @param stmt
? ? * @param conn
? ? */
? ?public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
? ? ? ?close(null, stmt, conn);
? }
?
? ?/**
? ? * 释放资源
? ? *
? ? * @param rs
? ? * @param stmt
? ? * @param conn
? ? */
? ?public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
? ? ? ?if (rs != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?rs.close();
? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ?if (stmt != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stmt.close();
? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ?if (conn != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?conn.close();//归还连接
? ? ? ? ? } catch (SQLException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!