LeGO-LOAM 几个特有函数的分析(2)
2024-01-09 00:56:59
接上回LeGO-LOAM 几个特有函数的分析(1)
二、广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历(Breadth-First Search, BFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。这种算法从树的根(或图的某一指定节点)开始,然后探索邻近的节点,之后对每一个邻近的节点,它再去探索它们各自相邻的节点,这个过程持续进行直到访问所有可达的节点。
广度优先遍历的主要特点是它按照距离起始点的“层次”来遍历。首先访问距离起点最近的节点,然后是它们的邻居,如此类推。
2.1 广度优先遍历的步骤:
-
初始化:首先将起始节点放入队列中。
-
遍历:
- 从队列中弹出一个节点。
- 检查该节点是否为目标节点。如果是,则完成搜索。
- 将该节点的所有未访问过的邻居节点加入队列。
-
重复:重复步骤2,直到队列为空或找到目标节点。
-
结束:当队列为空且目标未找到,或已找到目标节点时,算法结束。
2.2基于 BFS 的点云聚类和外点剔除
2.2.1原理

?
?2.2.2源码注释
void labelComponents(int row, int col){
// use std::queue std::vector std::deque will slow the program down greatly
// 声明所需的变量,输入的ROW和col是单帧点云第几行第几列的点
// 用于存储距离和角度计算的临时变量
float d1, d2, alpha, angle;
// 用于存储索引的变量
int fromIndX, fromIndY, thisIndX, thisIndY;
// 标记是否每个扫描线都至少有一个点被添加
bool lineCountFlag[N_SCAN] = {false};
//用两个数组分别保存x,y
queueIndX[0] = row;
queueIndY[0] = col;
//算法标志
int queueSize = 1;
// 队列开始的索引
int queueStartInd = 0;
// 队列结束的索引
int queueEndInd = 1;
// 初始化聚类数组
allPushedIndX[0] = row;
allPushedIndY[0] = col;
//计数
int allPushedIndSize = 1;
//很巧妙,有有效邻点就加一,每次循环减1,实现bfs广度优先遍历关键
while(queueSize > 0){
// Pop point
// 取出当前点x,y坐标
fromIndX = queueIndX[queueStartInd];
fromIndY = queueIndY[queueStartInd];
//队列大小减一
--queueSize;
//索引加一
++queueStartInd;
// Mark popped point
// 标记该点为一类,聚类就是给点加标签,标签一致的就是一类
labelMat.at<int>(fromIndX, fromIndY) = labelCount;
// Loop through all the neighboring grids of popped grid
// 检查所有邻点
for (auto iter = neighborIterator.begin(); iter != neighborIterator.end(); ++iter){
// new index
// 计算邻点的索引,其实就是上下左右四个点
thisIndX = fromIndX + (*iter).first;
thisIndY = fromIndY + (*iter).second;
// index should be within the boundary
// 如果raw为0或者15,上或者下没有邻点,跳过
if (thisIndX < 0 || thisIndX >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// at range image margin (left or right side)
//设置矩阵最两边的点也为邻点,因为VLP16是360度
//在cow为0时左边的邻点,在1799
if (thisIndY < 0)
thisIndY = Horizon_SCAN - 1;
//在cow为1799时左边的邻点,在0
if (thisIndY >= Horizon_SCAN)
thisIndY = 0;
// prevent infinite loop (caused by put already examined point back)
// 如果该点已被标记,则跳过
if (labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) != 0)
continue;
// 计算角度差以决定是否将邻点加入到当前区域
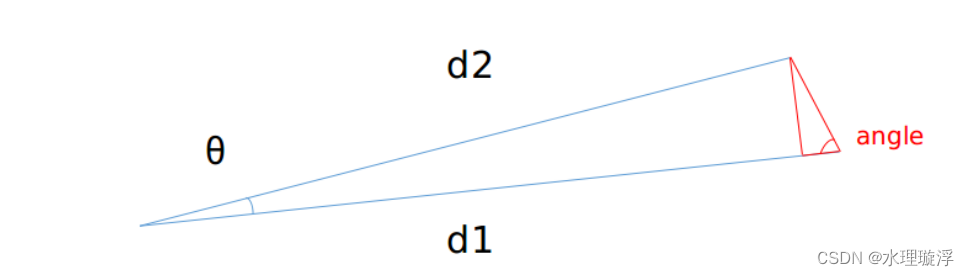
// 距离雷达远的是D1,近的是D2
d1 = std::max(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
d2 = std::min(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
//(0,-1),(0,1),意味着是一条线上的点,角度是360/1800*3.14/180=0.0035
if ((*iter).first == 0)
alpha = segmentAlphaX;
else
//(1,0),(-1,0),意味着是上下两条线上的点,角度是30/(16-1)*3.14/180=0.035
alpha = segmentAlphaY;
//计算图中angle角度
angle = atan2(d2*sin(alpha), (d1 -d2*cos(alpha)));
//如果角度大于60度
if (angle > segmentTheta){
//把此邻点放入队列
queueIndX[queueEndInd] = thisIndX;
queueIndY[queueEndInd] = thisIndY;
//增加size
++queueSize;
//末尾索引右移
++queueEndInd;
//把此邻点赋上和之前取出来的点一样的标签
labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) = labelCount;
//这行有点被标记过
lineCountFlag[thisIndX] = true;
//保存聚类结果
allPushedIndX[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndX;
allPushedIndY[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndY;
++allPushedIndSize;
}
}
}
// check if this segment is valid
bool feasibleSegment = false;
//如果聚类大于30则认为是一个好的聚类
if (allPushedIndSize >= 30)
feasibleSegment = true;
//如果大于5,而且都是竖着的超过3个,也认为是一个好聚类,可能是树,电线杆
else if (allPushedIndSize >= segmentValidPointNum){
int lineCount = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
if (lineCountFlag[i] == true)
++lineCount;
if (lineCount >= segmentValidLineNum)
feasibleSegment = true;
}
// segment is valid, mark these points
//如果聚类成功,标签加一
if (feasibleSegment == true){
++labelCount;
}else{ // segment is invalid, mark these points
for (size_t i = 0; i < allPushedIndSize; ++i){
//不成功,则标记为999999,代表依托答辩
labelMat.at<int>(allPushedIndX[i], allPushedIndY[i]) = 999999;
}
}
}?需要注意的点:
一是 邻点的定义,就是代表取当前点上下左右四个点
std::pair<int8_t, int8_t> neighbor; neighbor.first = -1; neighbor.second = 0; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor); neighbor.first = 0; neighbor.second = 1; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor); neighbor.first = 0; neighbor.second = -1; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor); neighbor.first = 1; neighbor.second = 0; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor);
?二是 巧妙的通过queueSize 实现广度优先遍历算法的核心
开始是int queueSize =1,让其进入循环
while(queueSize > 0){
//队列大小减一
--queueSize;
for (auto iter = neighborIterator.begin(); iter != neighborIterator.end(); ++iter){
//如果角度大于60度
if (angle > segmentTheta){
//增加size
++queueSize;
}
}
}
三是 聚类时候,大于30个点,或者大于5个点,但是有三个竖着的聚为一类
我觉得原因是考虑到竖着的点距离远的因素
四是 通过计算角度来判断是否是邻点
想象一下,是不是D1越长,angle越小
2.3函数的调用
用此种方式实现了一帧雷达所有点的聚类
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
//上一个函数说过地面点label被置为1
//如果这个点既不是地面点也没有聚类过,开始聚类
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 0)
labelComponents(i, j);
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44760904/article/details/135412032
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!