代码随想录刷题题Day13
刷题的第十三天,希望自己能够不断坚持下去,迎来蜕变。😀😀😀
刷题语言:C++
Day13 任务
● 104.二叉树的最大深度 559.n叉树的最大深度
● 111.二叉树的最小深度
● 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
1 二叉树的最大深度 && n叉树的最大深度
根据上一篇实现层序遍历的模板,用迭代法解决了这两道题
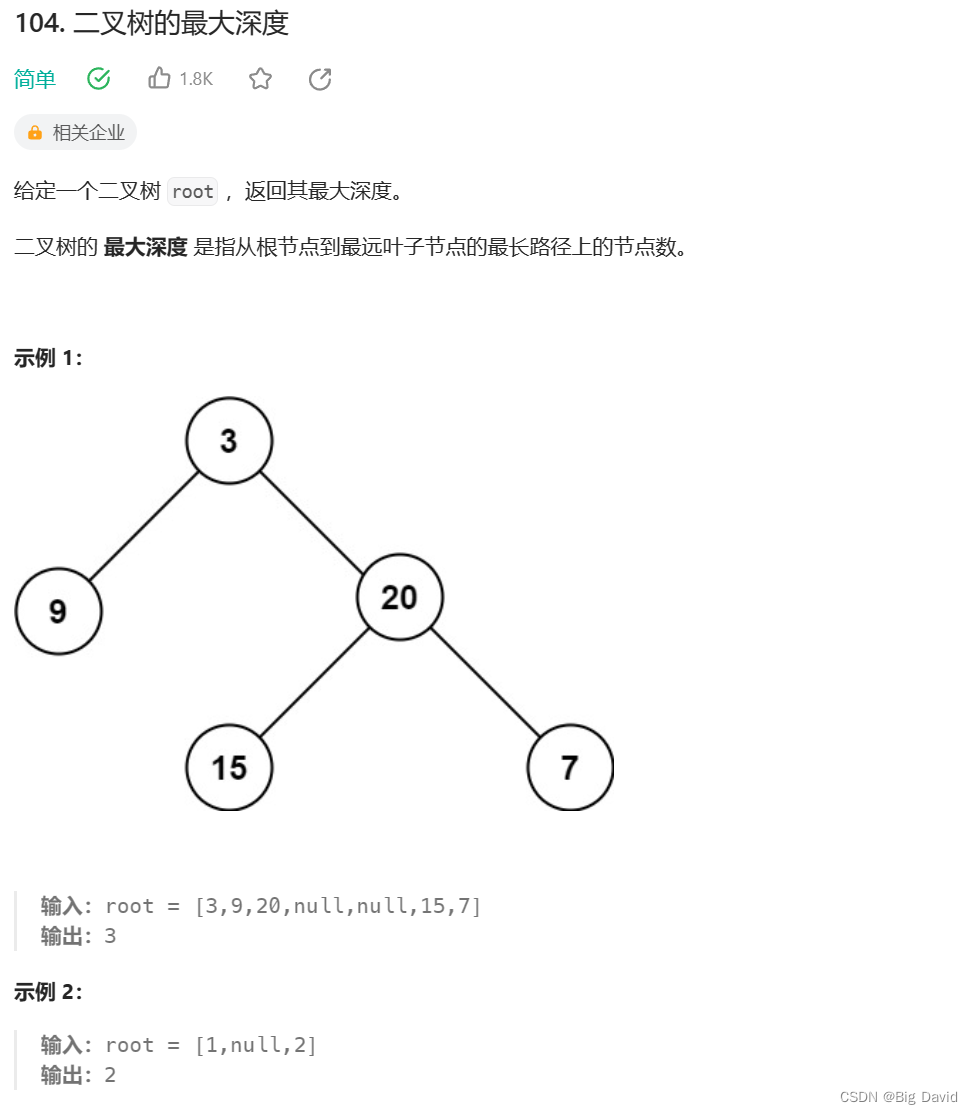
递归法:
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),
前序遍历求的是深度,后序遍历求得是高度
(1)确定递归函数得参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型
int getheight(TreeNode* node)
(2)确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0
if (node == NULL) return 0;
(3)确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度
int leftheight = getheight(node->left);
int rightheight = getheight(node->right);
int height = 1 + max(leftheight, rightheight);
return height;
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftheight = maxDepth(root->left); // 左
int rightheight = maxDepth(root->right); // 右
int height = 1 + max(leftheight, rightheight); // 中
return height;
}
};
精简之后的代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
迭代法
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int depth = 0;
if (root == NULL) return 0;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
depth++;
while (size--)
{
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
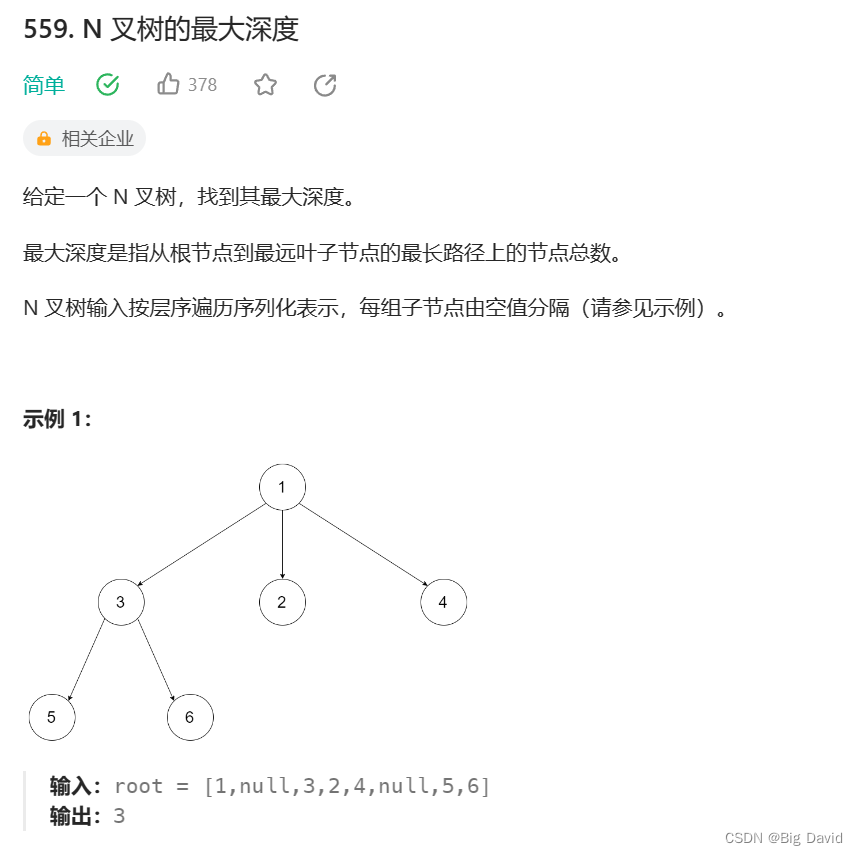
和二叉树求最大深度思路是一样的
递归法:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
int depth = 0;
if (root == NULL) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++)
{
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};
迭代法
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
int depth = 0;
if (root == NULL) return 0;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
depth++;// 记录深度
while (size--)
{
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < node->children.size(); i++)
{
que.push(node->children[i]);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
2 二叉树的最小深度

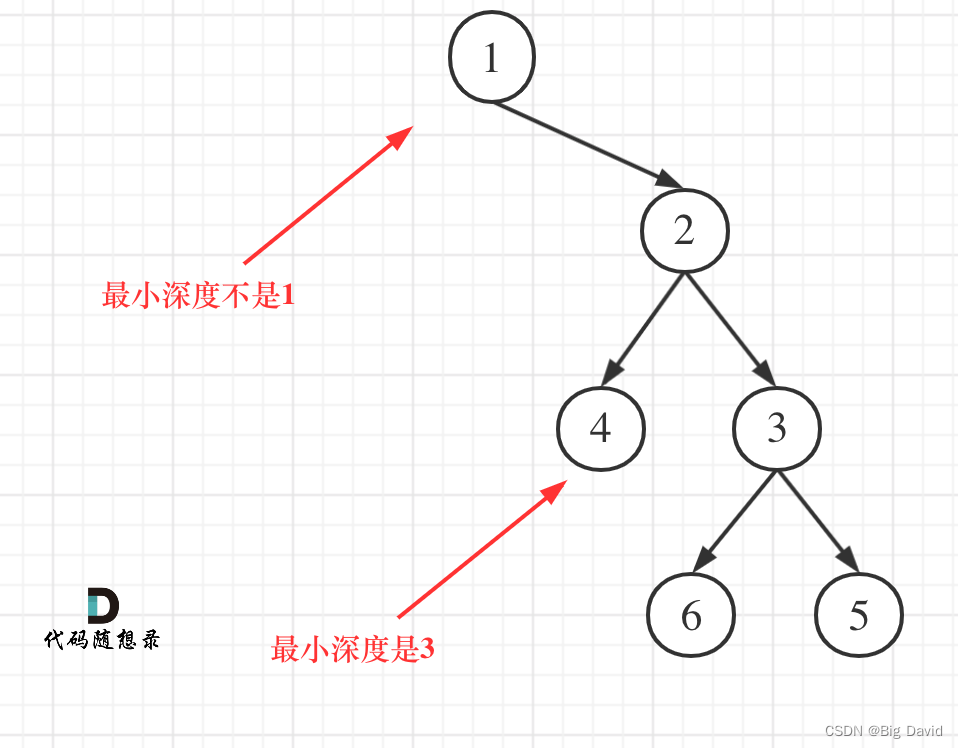
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量,注意是叶子节点(左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点)
递归法:
(1)确定递归函数的参数和返回值
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
(2)确定终止条件
终止条件也是遇到空节点返回0,表示当前节点的高度为0
if (node == NULL) return 0;
(3)确定单层递归的逻辑
- 如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
- 右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。
- 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑
递归法
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftheight = minDepth(root->left);// 左
int rightheight = minDepth(root->right);// 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (root->left != NULL && root->right == NULL) return 1 + leftheight;
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) return 1 + rightheight;
int result = 1 + min(leftheight, rightheight);
return result;
}
};
迭代法
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录最小深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
if (!node->left && !node->right)
{
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
3 完全二叉树的节点个数
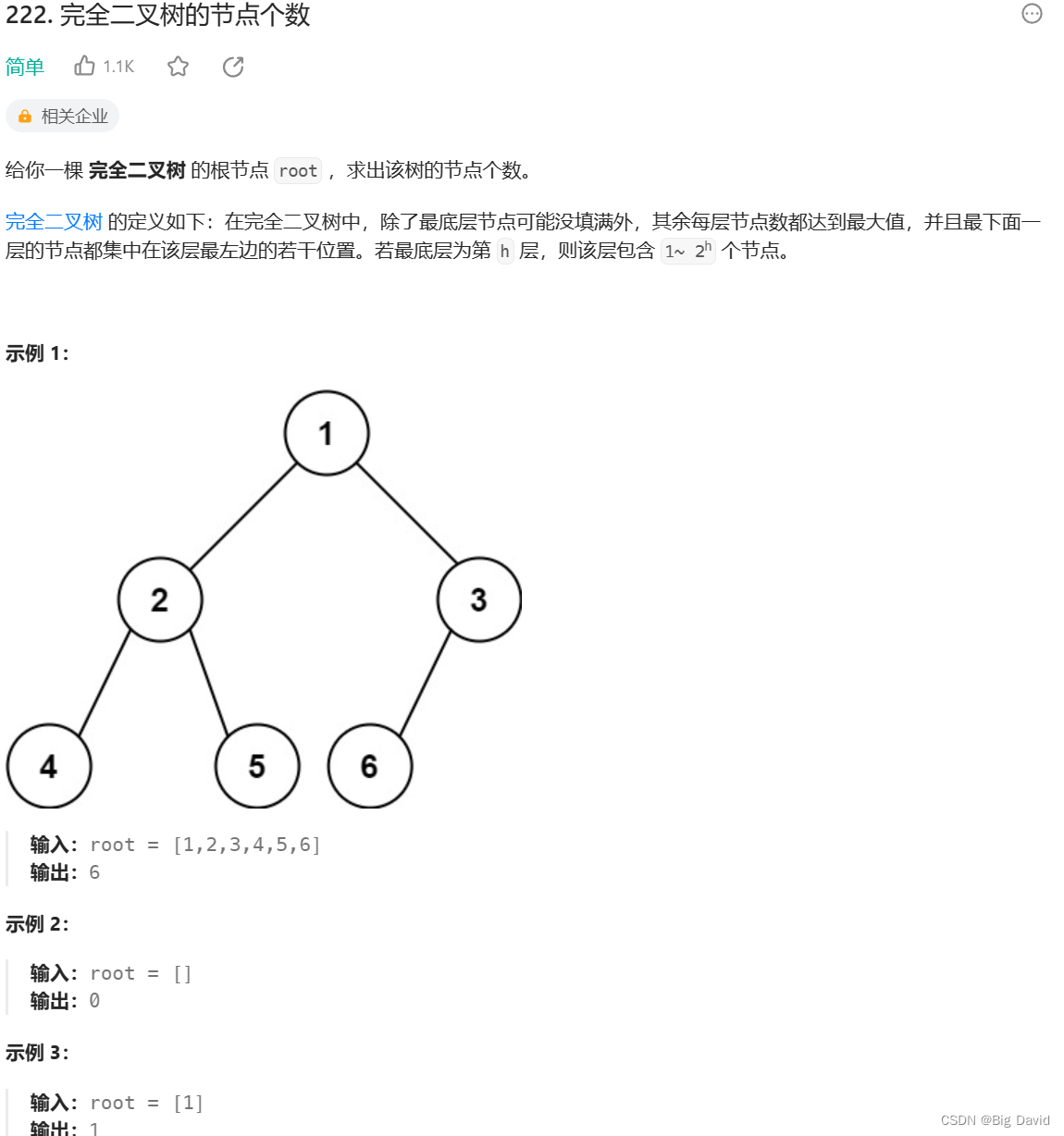
思路:
普通二叉树的求法以及利用完全二叉树的求法
普通二叉树:
递归法
遍历顺序:左右中
(1)确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型
int getNodeNum(TreeNode* cur)
(2)确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示节点数为0。
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
(3)确定单层递归的逻辑:
先求它的左子树的节点数量,再求右子树的节点数量,最后取总和再加一 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的节点数量。
int leftNum = getNodeNum(cur->left);
int rightNum = getNodeNum(cur->right);
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1;
return treeNum;
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftNum = countNodes(root->left);// 左
int rightNum = countNodes(root->right);// 右
int result = leftNum + rightNum + 1;// 中
return result;
}
};
时间复杂度:
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O
(
l
o
g
n
)
O(log n)
O(logn),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间
迭代法
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int result = 0;
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
result++;// 记录节点数量
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
时间复杂度:
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
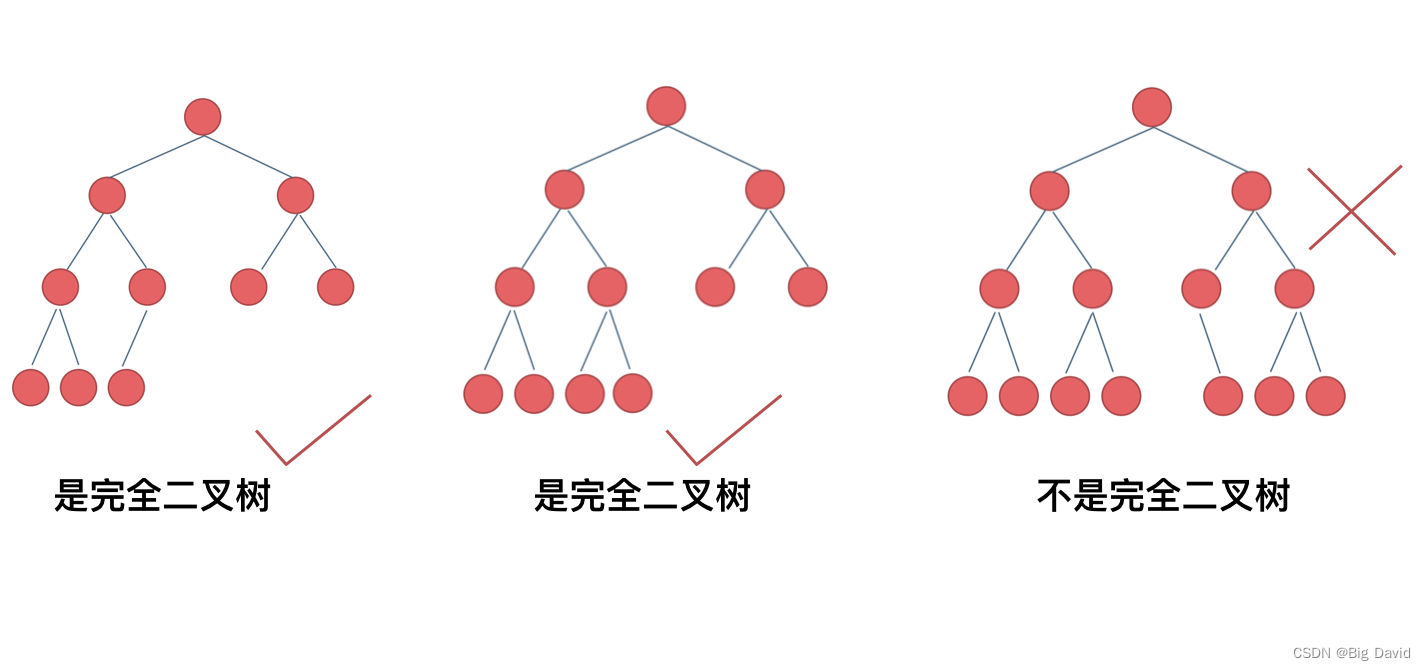
完全二叉树
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2 h ? 1 2^{h-1} 2h?1 个节点
思路:
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
(1)对于情况一,可以直接用 2 树深度 ? 1 2^{树深度 - 1} 2树深度?1 来计算,注意这里根节点深度为1。
(2)对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算
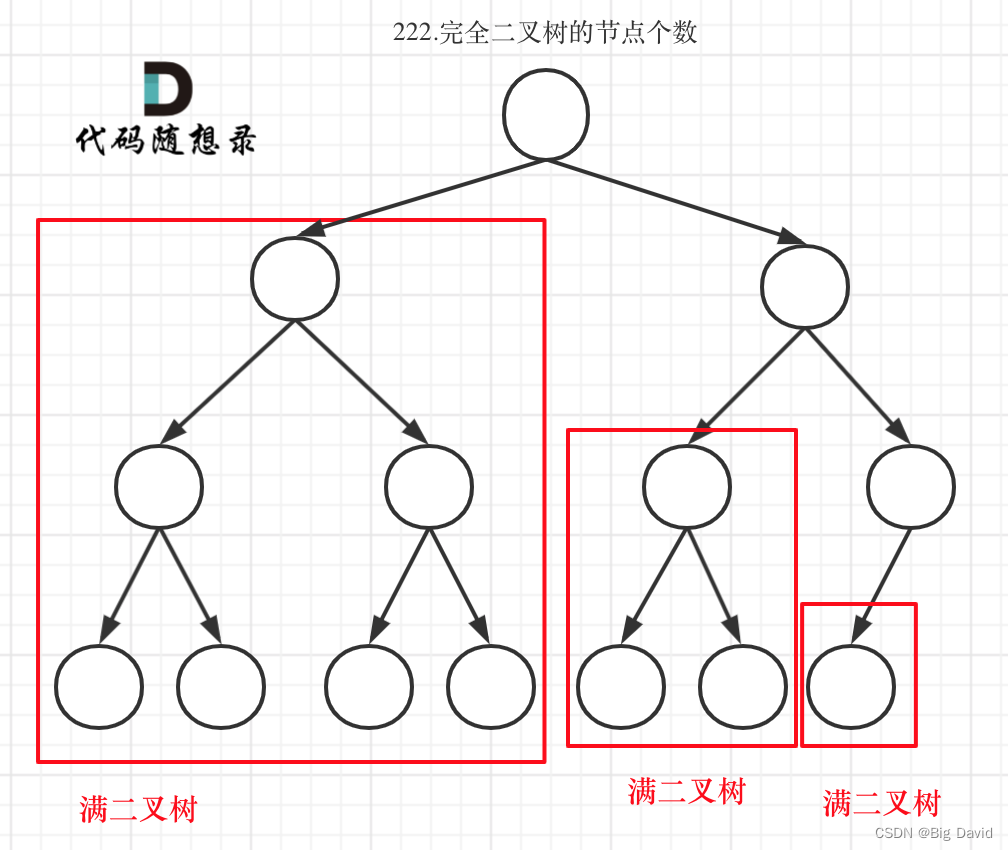
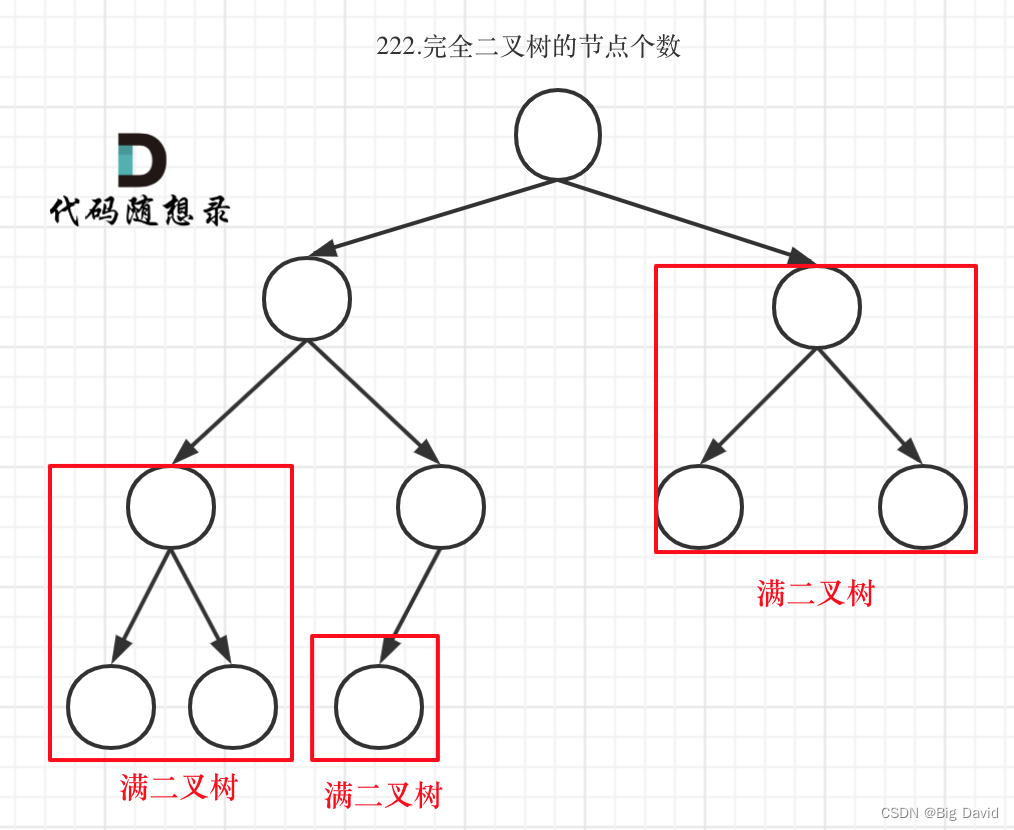
如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量
关键在于如何去判断一个左子树或者右子树是不是满二叉树
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树
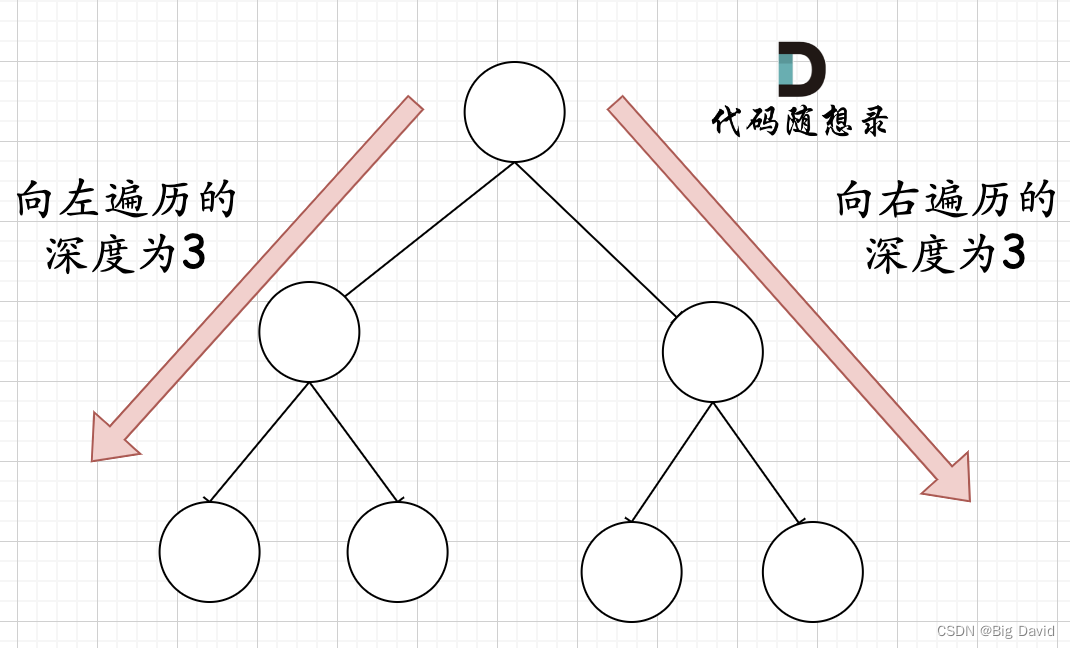
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度不等于递归向右遍历的深度,则说明不是满二叉树
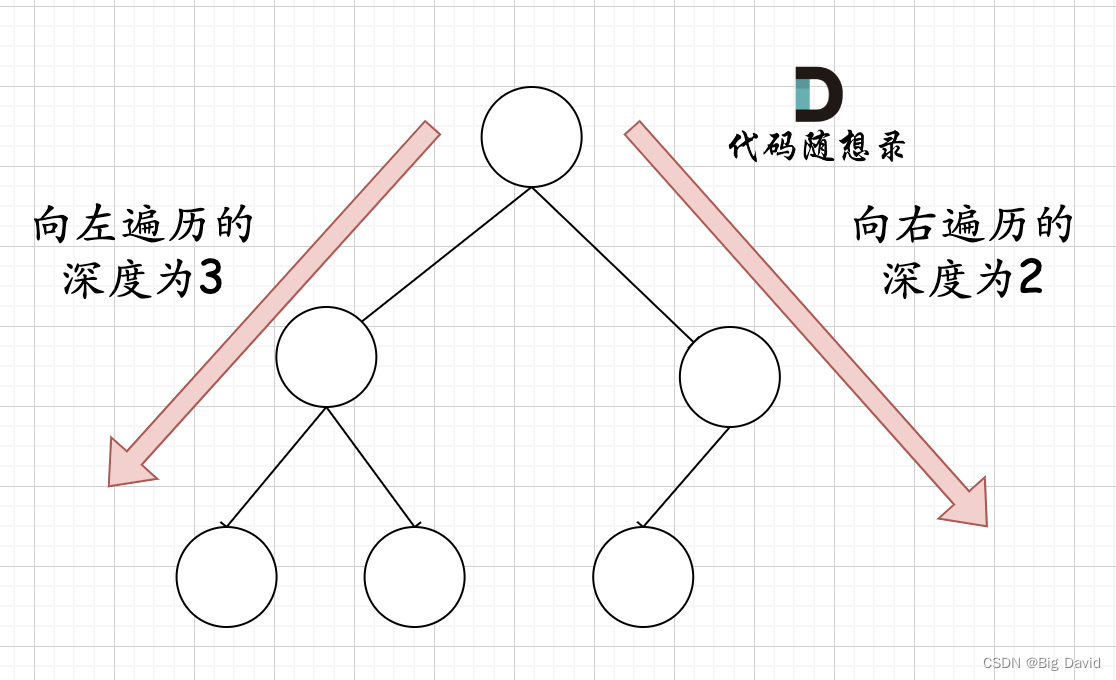
(1)确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型
int getNodeNum(TreeNode* cur)
(2)确定终止条件
if (root == NULL) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0;
while (left)
{
left = left->left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right)
{
right = right->right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth)
{
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1;
}
(3)单层递归的逻辑
int leftTreeNum = countNodes(root->left);
int rightTreeNum = countNodes(root->right);
int result = leftTreeNum + rightTreeNum + 1;
return result;
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0;// 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
while (left)// 求左子树深度
{
left = left->left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right)// 求右子树深度
{
right = right->right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth)
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1;// 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1; // 左 右 中
}
};
时间复杂度:
O
(
l
o
g
n
×
l
o
g
n
)
O(log n × log n)
O(logn×logn)
空间复杂度:
O
(
l
o
g
n
)
O(log n)
O(logn)
鼓励坚持十四天的自己😀😀😀
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!