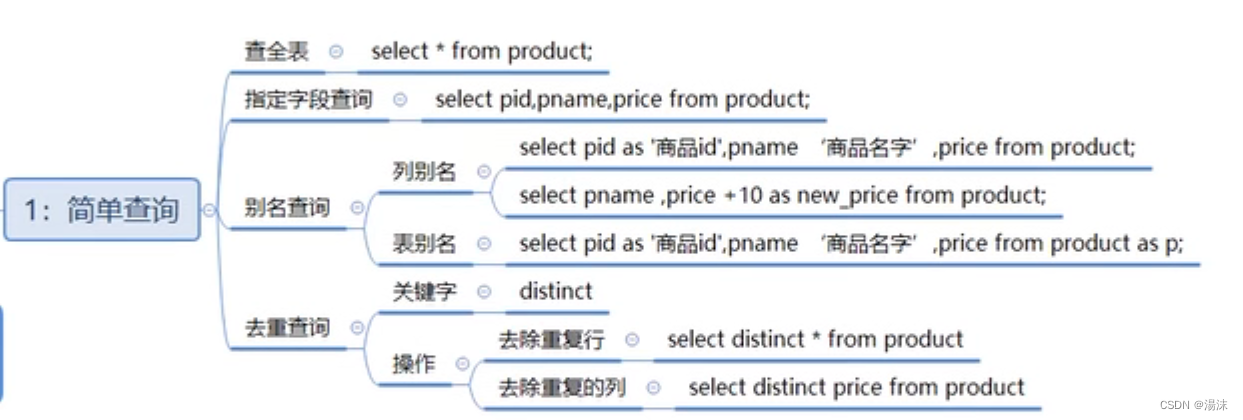
DQL-基本查询
概念:
1,数据库管理系统一个重要功能就是数据查询,数据查询不应只是简单返回数据库中存储的数据,还应该根据需要对数据进行筛选以及确定数据以什么样的格式显示
2,MySQL提供了功能强大、灵活的语句来实现这些操作
3,MySQL数据库使用select语句来查询数据
查询格式:
select
[all|distinct]
<目标列的表达式1>[别名],
<目标列的表达式2>[别名]...
from <表名或视图名> [别名],<表名或视图名> [别名]...
[where<条件表达式>]
[group by<列名>]
[having<条件表达式>]
[order by <列名>[asc|desc]]
[limit<数字或者列表>];简化版语法:
select *|列名 from 表 where 条件1,查询
(1)数据准备
创建数据库和表:

?添加数据:
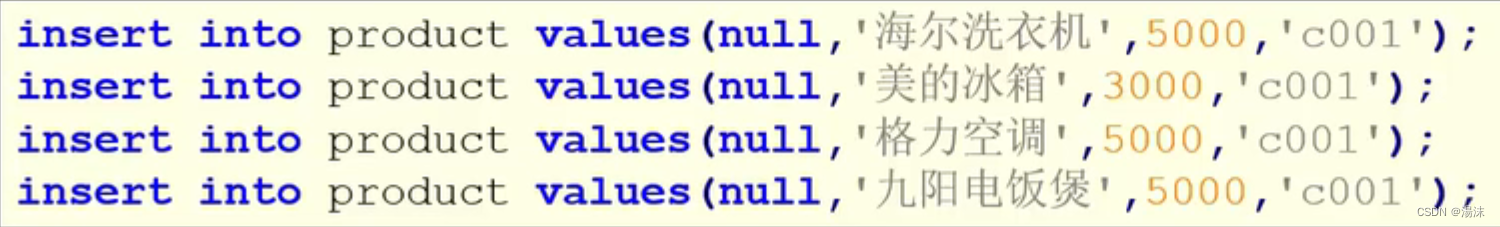
?(2)简单查询
select pid,pname,price,category_id from product;
select * from product;--查询所有商品
select pname,price from product;--查询商品名和商品价格
--别名查询,使用的关键字是as(as可以省略)
--1,表别名
select *from product as p;
select *from product p;
--2,列别名
select pname as '商品名',price '商品价格' from product;
--3,去掉重复值
select distinct price from product;
select distinct * from product;--去除所有列都一样的
--5,查询结果是表达式:将所有商品都加价10元进行显示
select pname,price+10 new_price from product;2,运算符
简介:
数据库中的表结构确立后,表中的数据代表的意义就已经确定。通过MySQL运算符进行运算,就可以获取到表结构以外的另一种数据
例如,学生表中存在一个bith字段,这个字段表示学生的出生年份。而运用MySQL的算术运算符用当前的年份减学生出生的年份,那么得到的就是这个学生的实际年龄数据
MySQL支持4种运算符
算术运算符,比较运算符,逻辑运算符,位运算符
(1)算数运算符
| 算术运算符 | 说明 |
| + | 加法运算 |
| - | 减法运算 |
| * | 乘法运算 |
| /或 DIV | 除法运算,返回商 |
| %或 MOD | 求余运算,返回余数 |
(2)比较运算符
| 比较运算符 | 说明 |
| = | 等于 |
| <和<= | 小于和小于等于 |
| >和>= | 大于和大于等于 |
| <=> | 安全的等于,两个操作码均为NULL时,其所得值为1;而当一个操作码为NULL时,其所得值为0 |
| <>或!= | 不等于 |
| IS NULL 或 ISNULL | 判断一个值是否为NULL |
| IS NOT NULL | 判断一个值是否不为NULL |
| LEAST | 当有两个或多个参数时,返回最小值 |
| GREATEST | 当有两个或多个参数时,返回最大值 |
| BETWEEN AND | 判断—个值是否落在两个值之间 |
| IN | 判断一个值是IN列表中的任意一个值 |
| NOT IN | 判断一个值不是IN列表中的任意一个值 |
| LIKE | 通配符匹配 |
| REGEXP | 正则表达式匹配 |
(3)逻辑运算符
| 逻辑运算符 | 说明 |
| NOT或者! | 逻辑非 |
| AND或者&& | 逻辑与 |
| OR或者 || | 逻辑或 |
| XOR | 逻辑异或 |
(4)位运算符
| 位运算符 | 说明 |
| | | 按位或 |
| & | 按位与 |
| ^ | 按位异或 |
| << | 按位左移 |
| >> | 按位右移 |
| ~ | 按位取反,反转所有比特 |
位运算符是在二进制数上进行计算的运算符。位运算会先将操作数变成二进制数,进行位运算。然后再将计算结果从二进制数变回十进制数
3,运算符操作
(1)算术运算符
select 6+2;
select 6-2;
select 6*2;
select 6/2;
select 6%2;
select pname,price+10 new_price from product;
select pname,price*1.1 new_price from product;(2)比较运算符
(3)逻辑运算符
select pname,price+10 new_price from product;
select pname,price*1.1 new_price from product;
--查询海尔洗衣机商品的所有信息
select * from product where pname='海尔洗衣机';
--查询价格为800的商品
select *from product where price=800;
--查询价格不是800的所有商品
select *from product where price!=800;
select *from product where price<>800;
select *from product where not (price=800);
--查询价格大于等于60的所有商品
select *from product where price>=60;
--查询价格在200到1000的所有商品
select *from product where price between 200 and 1000;
select *from product where price>=200 and price<=1000;
select *from product where price>=200 && price<=1000;
--查询价格是200或者1000的所有商品
select *from product where price in(200,800);
select *from product where price=200 or price=1000;
select *from product where price=200 || price=1000;
--插叙包含‘裤’字所有的商品
select *from product where pname like '裤';
select *from product where pname like '%裤';
select *from product where pname like '%裤&';--&用来匹配任意字符
--查询以‘海’字开头的商品
select *from product where pname like '海%';
--查询第二个字为‘蔻’的所有商品
select *from product where pname like '_蔻%';--下划线匹配单个字符
--查询category_id为null的商品
select *from product where category_id is null;
--查询category_id不为null的商品
select *from product where category_id is not null;
--使用least求最小值
select least (10,2,20) as small_number;
select least (10,null,20) as small_number;--如果求最小值时,有一个为null,不会进行比较,结果直接为null
--使用greatest求最大值
select greatest (10,20,30) as big_number;
select greatest (10,null,20) as big_number;--null(4)位运算符
位运算符是在二进制数上进行计算的运算符。位运算会先将操作数变成二进制数,进行位运算。然后再将计算结果从二进制数变回十进制数
select 3&5; --位与 1
0011
0101
----
0001 --都为1则为1
select 3|5;--位或 7
0011
0101
----
0111 --有一个为1就为1
select 3^5;--位异或 6
0011
0101
----
0110 --相同为0,不同为1
select 3>>1;--位右移 1
0011 >> 1----->0001
select 3<<1;--位左移 6
0011 << 6----->0110
select ~3;--位取反 18446744073709551612
000000000000000000011->1111111111111111111100 --0变1,1变04,排序查询
介绍:
如果我们需要对读取的数据进行排序,我们就可以使用MySQL的order by子句来设定你想按哪个字段哪种方式来进行排序,再返回搜索结果
select
字段名1,字段名2,.....
from表名
order by字段名1 [asc|desc],字段名2[asc|desc].....特点:
1.asc代表升序,desc代表降序,如果不写默认升序
2.order by用于子句中可以支持单个字段,多个字段,表达式,函数,别名
3.order by子句,放在查询语句的最后面。LIMIT子句除外
select * from product order by price ;
select * from product order by price desc;
select * from product order by price desc,category_id desc;
select distinct price from product order by price desc;--去重并降序5,聚合查询
简介:
之前我们做的查询都是横向查询,它们都是根据条件一行一行的进行判断,而使用聚合函数查询是纵向查询,它是对一列的值进行计算,然后返回一个单一的值;另外聚合函数会忽略空值
| 聚合函数 | 作用 |
| count() | 统计指定列不为NULL的记录行数; |
| sum() | 计算指定列的数值和,如果指定列类型不是数值类型,那么计算结果为0 |
| max() | 计算指定列的最大值,如果指定列是字符串类型,那么使用字符串排序运算; |
| min() | 计算指定列的最小值,如果指定列是字符串类型,那么使用字符串排序运算; |
| avg() | 计算指定列的平均值,如果指定列类型不是数值类型,那么计算结果为o |
select count(pid) from product;--商品总条目
select count(pid) from product where price >200;--商品大于200
select sum(price) from product where category_id='c001';--为c001商品的总和
select max(price) from product;--商品最大价格
select min(price) from product;--商品最小价格
select max(price),min(price) from product;
select avg(price) from product where category_id='c002';--c002的平均价格(1)聚合查询-NULL值的处理
1、count函数对null值的处理
如果count函数的参数为星号(*),则统计所有记录的个数。而如果参数为某字段,不统计含null值的记录个数
2、sum和avg函数对null值的处理
这两个函数忽略null值的存在,就好象该条记录不存在一样
3、max和min函数对null值的处理
max和min两个函数同样忽略null值的存在
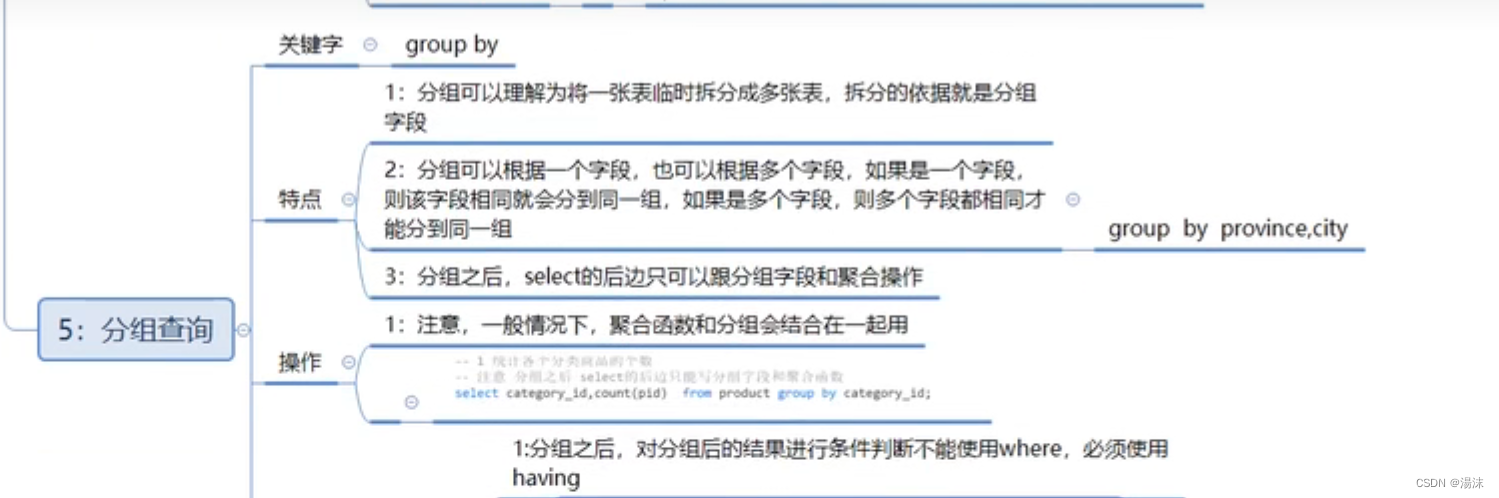
6,分组查询
(1)group by
简介:
分组查询是指使用group by字句对查询信息进行分组
格式:
select? 字段1,字段2....? ?from? 表名? group by? 分组字段? having? 分组条件;
如果要进行分组的话,则SELECT子句之后,只能出现分组的字段和统计函数,其他的字段不能出现;
注意分组之后select的后边只能写分组字段和聚合函数
select category_id,count(pid) from product group by category_id;--统计各个分类商品的个数(2)分组之后的条件筛选-having
分组之后对统计结果进行筛选的话必须使用having,不能使用where
where子句用来筛选FROM子句中指定的操作所产生的行
group by 子句用来分组WHERE子句的输出
having子句用来从分组的结果中筛选行
格式:
select 字段1,字段2... from 表名 group by 分组字段 having 分组条件;
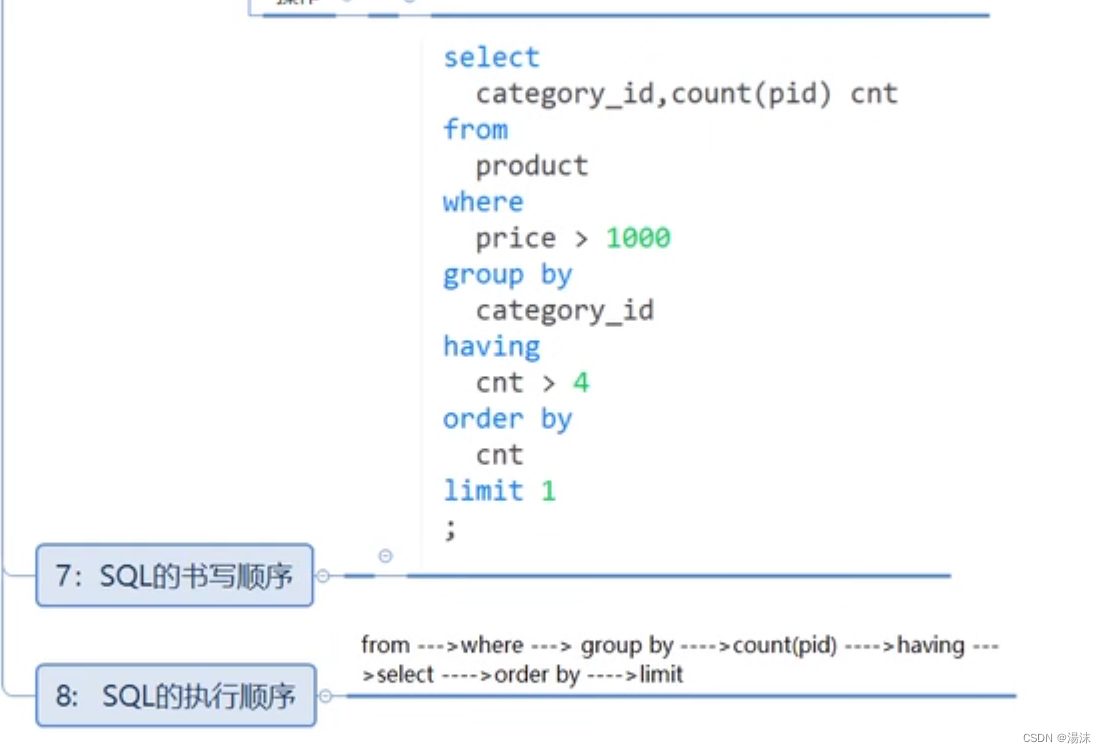
--分类,显示大于4的商品信息
--SQL执行顺序:from -> group by -> count(pid) -> select -> having -order by
select category_id,count(pid) as cnt from product group by category_id having count(pid)>4 order by cnt;7,分页查询
简介:
分页查询在项目开发中常见,由于数据量很大,显示屏长度有限,因此对数据需要采取分页显示方式。例如数据共有30条,每页显示5条,第一页显示1-5条,第二页显示6-10条
格式:
--方式1-显示前n条
select 字段1,字段2... from 表明 limit n
--方式2-分页显示
select 字段1,字段2... from 表名 limit m,n
m:整数,表示从第几条索引开始,计算方式(当前页-1)*每页显示条数
n:整数,表示查询多少条数据select * from product limit 5;--查询product表的前5条记录
select * from product limit 3,5;--从第4条开始,显示5条8,insert into select语句
简介:
将一张表的数据导入到另一张表中,可以使用INSERT INTO SELECT语句
格式:
insert into Table2 (field1 ,field2,...) select value1,value2,... from Table1
或者:
insert into Table2 select * from Table1
要求目标表Table2必须存在insert into product2(pname,price) select pname,price from product;
insert into product3 select category_id,count(*) from product group by category_id;
?
?
?
?
?
?9,正则表达式
正则表达式(regular expression)描述了一种字符串匹配的规则,正则表达式本身就是一个字符串,使用这个字符串来描述、用来定义匹配规则,匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串。在开发中,正则表达式通常被用来检索、替换那些符合某个规则的文本
MySQL通过REGEXP关键字支持正则表达式进行字符串匹配
格式:
| 模式 | 描述 |
| ^ | 匹配输入字符串的开始位置 |
| $ | 匹配输入字符串的结束位置 |
| . | 匹配除"\n"之外的任何单个字符 |
| [...] | 字符集合。匹配所包含的任意一个字符。例如,'[abc]'可以匹配"plain"中的'a' |
| [^...] | 负值字符集合。匹配未包含的任意字符。例如,'[^abc]'可以匹配"plain"中的'p' |
| p1|p2|p3 | 匹配p1或p2或p3。例如,'z/ food'能匹配"z”或"food"。'(zlf)ood'则匹配"zood"或"food" |
| 格式 | 描述 |
| * | 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。例如,zo*能匹配"z"以及"zoo"。*等价于{0,} |
| + | 匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。例如,'zo+'能匹配"zo"以及"zoo",但不能匹配"z"。+等价于{1,} |
| {n} | n是一个非负整数。匹配确定的n次。例如,'o{2}不能匹配"Bob"中的'o',但是能匹配"food"中的两个o |
| {n,m} | m和n均为非负整数,其中n <= m。最少匹配n次且最多匹配m次 |
| ? | 出现0次或者1次 |
--^在字符串开始进行匹配
select 'abc' REGEXP '^a';--1
select * from product where pname REGEXP '^海';
--$在字符串末尾开始匹配
select 'abc' REGEXP 'a$';
select 'abc' REGEXP 'a$';
--.匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
select 'abc' REGEXP '.b';--1
select 'abc' REGEXP '.c';--1
select 'abc' REGEXP 'a.';--1
--[...]匹配括号内的任意单个字符
select 'abc' REGEXP '[xyz]';--0
select 'abc' REGEXP '[xaz]';--1
--[^...]取反
select 'a' REGEXP '[^abc]';--0
select 'x' REGEXP '[^abc]';--1
select 'abc' REGEXP '[^a]';--1本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!