11.关注、取消关注 + 关注列表、粉丝列表
2023-12-14 20:46:24
目录
1.关注、取消关注?
- 需求:开发关注、取消关注功能;统计用户的关注数、粉丝数
- 关键:若 A 关注了 B,则 A 是 B 的 Follower(粉丝),B 是 A 的 Followee(目标);关注的目标可以是用户、帖子、题目等,在实现时将这些目标抽象为实体

1.1 把数据存到 Redis 中,构造 key
规划 key,在 RedisKeyUtil 包下添加方法:
- 声明两个前缀(follower、followee),定义常量
- 添加 某个用户关注的实体方法拼接?key:followee:userId:entityType -> zset(entityId,now)
- 添加 某个用户拥有的粉丝 方法拼接 key:follower:entityType:entityId -> zset(userId,now)
//声明两个前缀(follower、followee),定义常量——关注与取消关注
private static final String PREFIX_FOLLOWEE = "followee";
private static final String PREFIX_FOLLOWER = "follower";
// 某个用户关注的实体
// followee:userId:entityType -> zset(entityId,now)
public static String getFolloweeKey(int userId, int entityType) {
return PREFIX_FOLLOWEE + SPLIT + userId + SPLIT + entityType;
}
// 某个实体拥有的粉丝
// follower:entityType:entityId -> zset(userId,now)
public static String getFollowerKey(int entityType, int entityId) {
return PREFIX_FOLLOWER + SPLIT + entityType + SPLIT + entityId;
}1.2 开发业务层
在 service 包下新建?FollowService 类(相关关注和取消关注的业务):
- 将数据存入 Redis 中,注入 RedisTemplate
- 添加关注的业务方法:传入 用户 id 和实体
- 存入关注目标 和 粉丝,一项业务有两次存储需要保证事务,调用 redisTemplate.execute
- 然后构造上述的两个 key(目标 key、粉丝 key)
- 首先开启事务,再做两次增加存储操作(有序的存储)
- 再添加取消关注的业务方法:和 添加关注方法一样,只是再开启事务的时候,做两次删除操作
package com.example.demo.service;
import com.example.demo.util.RedisKeyUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SessionCallback;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* 关注与取消关注业务方法
*/
@Service
public class FollowService {
//将数据存入 Redis 中,注入 RedisTemplate
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//添加关注的业务方法:传入 用户 id 和实体
public void follow(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) {
//存入关注目标 和 粉丝,一项业务有两次存储需要保证事务,调用 redisTemplate.execute
redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException {
//然后构造上述的两个 key(目标 key、粉丝 key)
//目标 key
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
//粉丝 key
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(entityType, entityId);
//开启事务
operations.multi();
//做两次增加存储操作(有序的存储)
operations.opsForZSet().add(followeeKey, entityId, System.currentTimeMillis());
operations.opsForZSet().add(followerKey, userId, System.currentTimeMillis());
return operations.exec();
}
});
}
public void unfollow(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) {
redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(entityType, entityId);
operations.multi();
做两次删除操作(有序的存储)、删除操作不需要当前时间
operations.opsForZSet().remove(followeeKey, entityId);
operations.opsForZSet().remove(followerKey, userId);
return operations.exec();
}
});
}
// 查询关注的实体的数量
public long findFolloweeCount(int userId, int entityType) {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(followeeKey);
}
// 查询实体的粉丝的数量
public long findFollowerCount(int entityType, int entityId) {
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(entityType, entityId);
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(followerKey);
}
// 查询当前用户是否已关注该实体
public boolean hasFollowed(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(followeeKey, entityId) != null;
}
}
1.3 开发表现层
在 controller 包中添加?FollowController 类(关注、取消关注的请求):
- 注入 FollowService
- 分为两次请求,是一个异步请求:在页面点击关注,整个页面不刷新,只是一个局部刷新;提交数据:POST 请求
- 关注请求:当前登陆用户关注某一个实体,传入实体参数并且注入 HostHolder
- 首先获取当前用户、然后再去关注,给页面返回结果
- 取消关注请求类似
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.service.FollowService;
import com.example.demo.util.CommunityUtil;
import com.example.demo.util.HostHolder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* 关注、取消关注的请求
*/
@Controller
public class FollowController {
@Autowired
private FollowService followService;
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
//分为两次请求,是一个异步请求:在页面点击关注,整个页面不刷新,只是一个局部刷新;提交数据:POST 请求
//关注请求:当前登陆用户关注某一个实体,传入实体参数并且注入 HostHolder
@RequestMapping(path = "/follow", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String follow(int entityType, int entityId) {
//首先获取当前用户、然后再去关注,给页面返回结果
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
followService.follow(user.getId(), entityType, entityId);
return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, "已关注!");
}
//取消关注
@RequestMapping(path = "/unfollow", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String unfollow(int entityType, int entityId) {
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
followService.unfollow(user.getId(), entityType, entityId);
return CommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, "已取消关注!");
}
}
CommunityConstant 类?添加实体用户:
/**
* 实体类型: 用户
*/
int ENTITY_TYPE_USER = 3;处理主页关注按钮 profile.html:
<!-- 个人信息 -->
<div class="media mt-5">
<img th:src="${user.headerUrl}" class="align-self-start mr-4 rounded-circle" alt="用户头像" style="width:50px;">
<div class="media-body">
<h5 class="mt-0 text-warning">
<span th:utext="${user.username}">nowcoder</span>
<input type="hidden" id="entityId" th:value="${user.id}">
<button type="button" th:class="|btn ${hasFollowed?'btn-secondary':'btn-info'} btn-sm float-right mr-5 follow-btn|"
th:text="${hasFollowed?'已关注':'关注TA'}" th:if="${loginUser!=null&&loginUser.id!=user.id}">关注TA</button>
</h5>
<div class="text-muted mt-3">
<span>注册于 <i class="text-muted" th:text="${#dates.format(user.createTime,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">2015-06-12 15:20:12</i></span>
</div>
<div class="text-muted mt-3 mb-5">
<span>关注了 <a class="text-primary" href="followee.html" th:text="${followeeCount}">5</a> 人</span>
<span class="ml-4">关注者 <a class="text-primary" href="follower.html" th:text="${followerCount}">123</a> 人</span>
<span class="ml-4">获得了 <i class="text-danger" th:text="${likeCount}">87</i> 个赞</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>profile.js:
$(function(){
$(".follow-btn").click(follow);
});
function follow() {
var btn = this;
if($(btn).hasClass("btn-info")) {
// 关注TA
$.post(
CONTEXT_PATH + "/follow",
{"entityType":3,"entityId":$(btn).prev().val()},
function(data) {
data = $.parseJSON(data);
if(data.code == 0) {
window.location.reload();
} else {
alert(data.msg);
}
}
);
// $(btn).text("已关注").removeClass("btn-info").addClass("btn-secondary");
} else {
// 取消关注
$.post(
CONTEXT_PATH + "/unfollow",
{"entityType":3,"entityId":$(btn).prev().val()},
function(data) {
data = $.parseJSON(data);
if(data.code == 0) {
window.location.reload();
} else {
alert(data.msg);
}
}
);
//$(btn).text("关注TA").removeClass("btn-secondary").addClass("btn-info");
}
}1.4 显示正确的关注数据
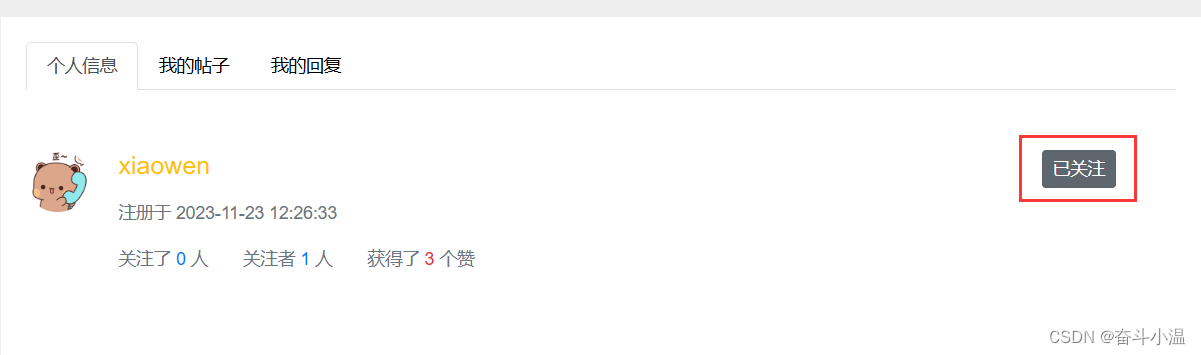
访问用户主页,关注数量、状态显示正确,打开 FollowService 类添加正确的数量等等:
- 补充查询目标实体的数量,传入用户 id、实体类别,构造目标 key,统计数量
- 查询实体粉丝的数量,传入实体Type、实体 id,构造粉丝 key,统计数量
- 查询当前用户是否已关注该实体类(传入当前用户、实体类型、实体 id):当前用户关注目标中有无实体,构造目标 key,在 redis 中查询某一个数据的分数,能查到说明已经关注
// 查询关注的实体的数量
public long findFolloweeCount(int userId, int entityType) {
//构造目标 key,统计数量
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(followeeKey);
}
// 查询实体的粉丝的数量
public long findFollowerCount(int entityType, int entityId) {
//构造粉丝 key,统计数量
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(entityType, entityId);
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(followerKey);
}
// 查询当前用户是否已关注该实体
public boolean hasFollowed(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
//在 redis 中查询某一个数据的分数,能查到说明已经关注
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(followeeKey, entityId) != null;
}在主页中显示正确数量,主页是通过 UserController 访问,则需要处理 UserController
- 在个人主页的方法中,添加关注数量、粉丝数量、是否已关注,最后传给模板
- 注入 FollowService
// 个人主页
@RequestMapping(path = "/profile/{userId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getProfilePage(@PathVariable("userId") int userId, Model model) {
User user = userService.findUserById(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("该用户不存在!");
}
// 用户
model.addAttribute("user", user);
// 点赞数量
int likeCount = likeService.findUserLikeCount(userId);
model.addAttribute("likeCount", likeCount);
// 关注数量
long followeeCount = followService.findFolloweeCount(userId, ENTITY_TYPE_USER);
model.addAttribute("followeeCount", followeeCount);
// 粉丝数量
long followerCount = followService.findFollowerCount(ENTITY_TYPE_USER, userId);
model.addAttribute("followerCount", followerCount);
// 是否已关注
boolean hasFollowed = false;
//判断是否登陆
if (hostHolder.getUser() != null) {
hasFollowed = followService.hasFollowed(hostHolder.getUser().getId(), ENTITY_TYPE_USER, userId);
}
model.addAttribute("hasFollowed", hasFollowed);
return "/site/profile";
}

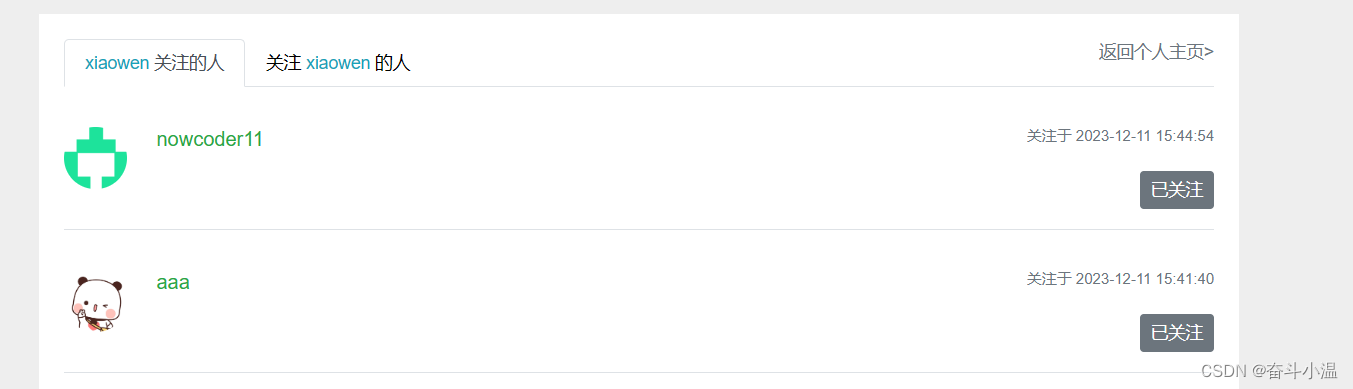
2.关注列表、粉丝列表


- 业务层:查询某个用户关注的人、支持分页;查询某个用户的分析,支持分页
- 表现层:处理“查询关注的人”、“查询粉丝”请求;编写“查询关注的人”、“查询粉丝”模板
2.1 业务层
在 FollowService 类中添加方法:
- 补充新的方法:查询某个用户关注的人(传入用户,分页条件)
- 拼接用户关注的?key:实现 CommunityConstant 接口
- 从集合中查询数据(范围查询):传入 key,范围查询传入两个索引,从哪里到哪里——offset 到 offset + limit - 1
- 查询的数据为整数:关注的目标 id
- 判断目标 id 是 空值,直接返回空
- 不为 空值,将目标 id 转化为详细数据传入集合中:首先实例化集合、遍历目标 id 查询封装到 map 中,实例化 map
- 注入 UserService,根据 id 查询用户,并放入 map 中
- 查询关注时间(有序集合中的分数)放入 map 中
- 最后返回列表
- 补充新的方法:查询某用户的粉丝(同理上述操作)
public class FollowService implements CommunityConstant {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//查询某个用户关注的人(传入用户,分页条件)
public List<Map<String, Object>> findFollowees(int userId, int offset, int limit) {
//拼接用户关注的 key:实现 CommunityConstant 接口
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, ENTITY_TYPE_USER);
//从集合中查询数据(范围查询):传入 key,范围查询传入两个索引,从哪里到哪里——offset 到 offset + limit - 1
Set<Integer> targetIds = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRange(followeeKey, offset, offset + limit - 1);
if (targetIds == null) {
return null;
}
//首先实例化集合、遍历目标 id 查询封装到 map 中,实例化 map
//注入 UserService,根据 id 查询用户,并放入 map 中
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer targetId: targetIds) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
User user = userService.findUserById(targetId);
map.put("user", user);
Double score = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(followeeKey, targetId);
map.put("followTime", new Date(score.longValue()));
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
// 查询某用户的粉丝(同理上述操作)
public List<Map<String, Object>> findFollowers(int userId, int offset, int limit) {
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(ENTITY_TYPE_USER, userId);
Set<Integer> targetIds = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRange(followerKey, offset, offset + limit - 1);
if (targetIds == null) {
return null;
}
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer targetId : targetIds) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
User user = userService.findUserById(targetId);
map.put("user", user);
Double score = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(followerKey, targetId);
map.put("followTime", new Date(score.longValue()));
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
}2.2 表现层
在 FollowController 类中添加请求:
- 添加方法:声明访问路径(查询某个用户关注的人,通过路径传入用户 id),查询为 GET 请求
- 添加方法:某个用户关注的人(得到路径当中的 id 做进一步查询、支持分页、给页面传数据传入 Model)
- 查询得到 User ,注入 UserService
- 如果用户为空,抛异常
- 不为空将 User 传给页面
- 查询列表中的数据,支持分页、访问路径、一共有多少行数据
- 分页查询显示的数据:用 map 封装
- 判断当前用户是否进行关注:遍历数据,得到 User,判断当前用户对此用户是否关注(添加是否关注方法),将此关注方法封装到 map 中
- 将集合传给模板、返回模板
- 添加查询某个用户的粉丝的请求(同理查询某个用户关注的人)
- 添加方法:声明访问路径(查询某个用户关注的人,通过路径传入用户 id),查询为 GET 请求
public class FollowController implements CommunityConstant {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//某个用户关注的人
//添加方法:声明访问路径(查询某个用户关注的人,通过路径传入用户 id),查询为 GET 请求
@RequestMapping(path = "/followees/{userId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
//添加方法:某个用户关注的人(得到路径当中的 id 做进一步查询、支持分页、给页面传数据传入 Model)
public String getFollowees(@PathVariable("userId") int userId, Page page, Model model) {
//查询得到 User ,注入 UserService
User user = userService.findUserById(userId);
//如果用户为空,抛异常
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("该用户不存在");
}
//不为空将 User 传给页面
model.addAttribute("user", user);
//查询列表中的数据,支持分页、访问路径、一共有多少行数据
page.setLimit(5);
page.setPath("/followees/" + userId);
//findFolloweeCount 查询得到 long,强转为 int
page.setRows((int) followService.findFolloweeCount(userId, ENTITY_TYPE_USER));
//分页查询显示的数据:用 map 封装
List<Map<String, Object>> userList = followService.findFollowees(userId, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit());
//判断当前用户是否进行关注:遍历数据,得到 User,判断当前用户对此用户是否关注(添加是否关注方法),将此关注方法封装到 map 中
if (userList != null) {
for (Map<String, Object> map : userList) {
User u = (User) map.get("user");
map.put("hasFollowed", hasFollowed(u.getId()));
}
}
//将集合传给模板、返回模板
model.addAttribute("users", userList);
return "/site/followee";
}
//添加查询某个用户的粉丝的请求(同理查询某个用户关注的人)
@RequestMapping(path = "/followers/{userId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getFollowers(@PathVariable("userId") int userId, Page page, Model model) {
User user = userService.findUserById(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("该用户不存在!");
}
model.addAttribute("user", user);
page.setLimit(5);
page.setPath("/followers/" + userId);
page.setRows((int) followService.findFollowerCount(ENTITY_TYPE_USER, userId));
List<Map<String, Object>> userList = followService.findFollowers(userId, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit());
if (userList != null) {
for (Map<String, Object> map : userList) {
User u = (User) map.get("user");
map.put("hasFollowed", hasFollowed(u.getId()));
}
}
model.addAttribute("users", userList);
return "/site/follower";
}
//添加是否关注方法
private boolean hasFollowed(int userId) {
if (hostHolder.getUser() == null) {
return false;
}
return followService.hasFollowed(hostHolder.getUser().getId(), ENTITY_TYPE_USER, userId);
}
}最后处理页面
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72161237/article/details/134682715
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!