如何进行更好的面试回复之缓存函数在项目中的性能优化?
2023-12-15 12:28:15
缓存函数是一种提高函数性能的技术,在函数被调用时,会将计算结果缓存起来,以便在后续的调用中直接返回缓存的结果,从而减少了重复计算的时间。
缓存函数的实现通常包括两个步骤:
-
判断缓存是否存在:在函数被调用时,首先判断缓存对象中是否已经存在该参数对应的缓存结果,如果有则直接返回缓存结果,否则进入下一步。
-
计算并缓存结果:如果缓存不存在,则进行函数的计算,并将计算结果保存到缓存对象中,然后返回计算结果。
使用缓存函数可以大大提高程序的性能,特别是对于一些需要耗费大量时间计算的函数,例如递归计算、数学公式计算等。但需要注意的是,由于缓存函数的缓存对象会占用一定的内存空间,因此需要适度使用缓存函数,避免出现内存溢出等问题。
首先查看以下的代码,当我每次点击的时候,都会打印一次5以内的随机数,那么每次都要进行一次请求。这时我们就可以将数据进行一个缓存,当我们再次打印相同的结果时,直接返回缓存中的结果。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>缓存函数在项目中的性能优化</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>缓存函数在项目中的性能优化</h1>
<button id="fetchButton">获取数据</button>
<div id="resultContainer">
<script>
function fetchDataFromServer(postId) {
console.log('从服务器端获取数据:', postId)
}
const fetchButton = document.getElementById("fetchButton")
const resultContainer = document.getElementById("resultContainer")
fetchButton.addEventListener("click",() => {
const postId = Math.floor(Math.random() * 5) + 1
//调用这个函数传递参数
fetchDataFromServer(postId)
})
</script>
</div>
</body>
</html>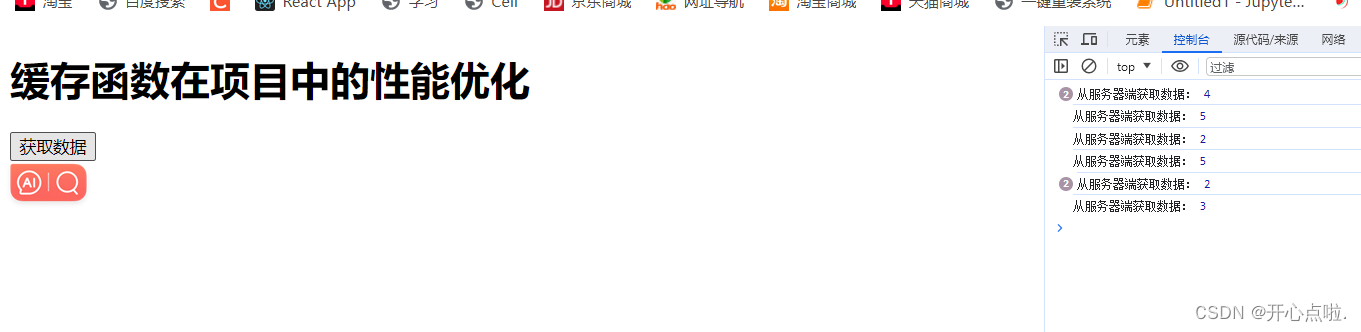
这时,我们定义一个缓存函数
function createCachedFunction(originalFunction){
const cache = {};
return function(arg){
if(cache[arg]){
console.log("从缓存中进行数据获取",arg)
return Promise.resolve(cache[arg])
}
}
return originalFunction(arg).then(result => {
cache[arg] = result;
console.log('第一次进行数据获取,并实现了缓存',arg);
return result;
})
}?定义之后我们也要去使用这个函数
const cacheFetchData = createCachedFunction(fetchDataFromServer)fetchButton.addEventListener("click",() => {
const postId = Math.floor(Math.random() * 5) + 1
// fetchDataFromServer(postId)
cacheFetchData(postId).then(data => {
resultContainer.innerHTML = `<pre>${JSON.stringify(
data,
null,
2
)}</pre>`
})
})?
全部代码为下列?
<h1>缓存函数在项目中的性能优化</h1>
<button id="fetchButton">获取数据</button>
<div id="resultContainer">
<script>
//
function fetchDataFromServer(postId) {
console.log('从服务器端获取数据:', postId)
return fetch(
`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${postId}`
).then(response => response.json());
}
function createCachedFunction(originalFunction){
const cache = {};
return function(arg){
if(cache[arg]){
console.log("从缓存中进行数据获取",arg)
return Promise.resolve(cache[arg])
}
}
return originalFunction(arg).then(result => {
cache[arg] = result;
console.log('第一次进行数据获取,并实现了缓存',arg);
return result;
})
}
const cacheFetchData = createCachedFunction(fetchDataFromServer)
const fetchButton = document.getElementById("fetchButton")
const resultContainer = document.getElementById("resultContainer")
fetchButton.addEventListener("click",() => {
const postId = Math.floor(Math.random() * 5) + 1
// fetchDataFromServer(postId)
cacheFetchData(postId).then(data => {
resultContainer.innerHTML = `<pre>${JSON.stringify(
data,
null,
2
)}</pre>`
})
})
</script>
</div>
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zxcvb0825/article/details/134880202
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!