Apache Commons VFS(虚拟文件系统)使用详解
第1章:Apache Commons VFS简介
大家好,我是小黑,今天我们来聊聊Apache Commons VFS(虚拟文件系统)。想必很多朋友都听说过或者用过Apache Commons的其他库,但是VFS可能还有点陌生。那么,什么是Apache Commons VFS呢?简单来说,它是一个用于处理各种类型文件系统的Java库。不管是本地文件系统、网络文件系统,还是云存储,用VFS都能轻松搞定。
你可能会问,为啥需要用虚拟文件系统呢?其实,随着互联网技术的发展,我们不再仅仅局限于本地文件系统,经常需要处理存储在网络上的文件。比如说,你可能需要从FTP服务器下载文件,或者上传文件到云存储。如果每种文件系统都用一套API来处理,那代码岂不是要乱成一锅粥?这时候,VFS就派上用场了,它提供了一套统一的API,让你无论对哪种文件系统的操作都能游刃有余。
再来说说Apache Commons VFS的特点。首先,它支持多种文件系统,例如本地文件、CIFS、FTP、FTPS、SFTP等等。其次,它的使用方式很灵活,可以很容易地集成到你的Java项目中。而且,VFS还很关注性能和稳定性,这在处理大量文件或大型项目时尤为重要。
第2章:依赖和基础配置
好,现在咱们来看看如何在项目中引入Apache Commons VFS。首先,确保你的项目是一个Java项目,使用的是Maven或者Gradle作为构建工具。这里以Maven为例。打开你的pom.xml文件,添加以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-vfs2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version> <!-- 这里的版本号要根据最新版调整 -->
</dependency>
接下来,我们来配置一个简单的示例环境。比如说,咱们想要读取一个本地文件。首先,创建一个Java类,然后在这个类里面使用VFS的API来实现这个功能。这里先给大家看个基本的框架:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class VfsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建FileSystemManager
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 使用VFS解析文件
FileObject file = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/file.txt");
// 接下来就可以进行文件操作了,比如读取文件内容
// ...(这里会在后续章节详细展开)
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个代码示例中,FileSystemManager是VFS中的核心类,负责管理各种文件系统。通过VFS.getManager()方法可以获得它的实例。resolveFile方法用于解析文件路径,这里的路径是以file://开头的,代表一个本地文件路径。
第3章:文件系统操作基础
读取文件内容
读取文件是日常开发中最常见的操作之一。用VFS来读取文件,步骤简单,让我来给大家演示一下:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class ReadFileExample {
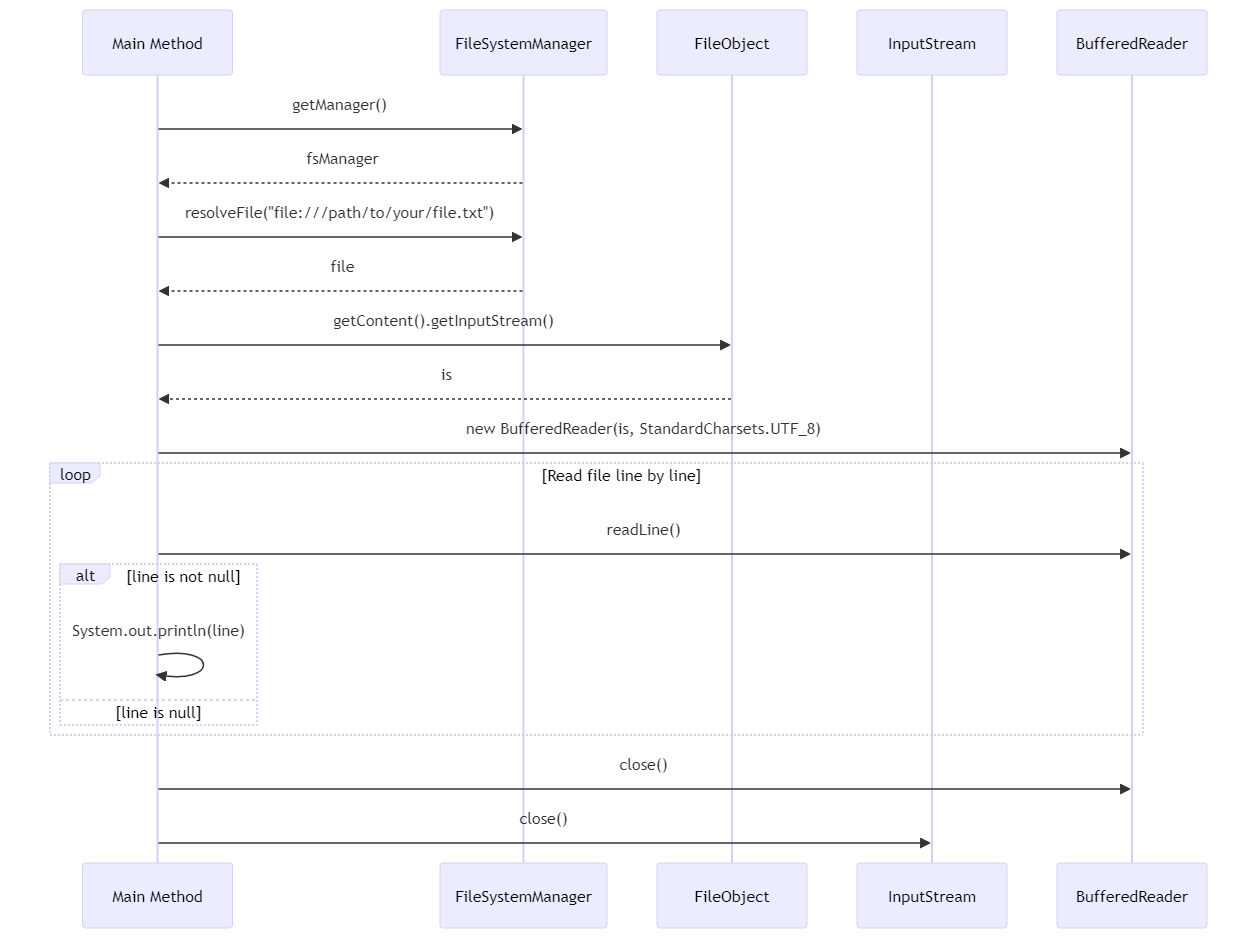
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的文件路径
FileObject file = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/file.txt");
// 打开文件输入流
try (InputStream is = file.getContent().getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line); // 打印文件内容
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个例子里,小黑先是通过FileSystemManager获取了文件对象FileObject。然后,使用getInputStream方法打开文件输入流,接着就是标准的Java读文件流程了。
写入文件内容
写文件也是小菜一碟。看看下面这个例子,我用VFS写文件就像写日记一样简单:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class WriteFileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的文件路径
FileObject file = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/file.txt");
// 确保文件存在
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createFile();
}
// 打开文件输出流
try (OutputStream os = file.getContent().getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os, StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
writer.write("咱们在学习Apache Commons VFS");
writer.newLine();
writer.write("这是文件写入的示例");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这个例子中,咱们同样先获取到FileObject。如果文件不存在,就先创建一个。然后用getOutputStream方法打开文件输出流,接下来就是写入内容了。
删除文件
有时候咱们还需要删除文件,VFS同样可以轻松做到。看这个例子:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class DeleteFileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的文件路径
FileObject file = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/file.txt");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
System.out.println("文件已删除");
} else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个例子中,小黑先检查文件是否存在,如果存在,就直接调用delete方法删除。
第4章:高级文件操作技巧
创建和遍历文件夹
在处理文件的时候,咱们经常需要创建新的文件夹,或者遍历某个文件夹里的所有文件。让我们来看看VFS如何做到这些。
创建文件夹:
创建文件夹其实很简单。下面这个例子会展示给你看:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class CreateDirectoryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你想创建的文件夹路径
FileObject dir = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/new/dir");
// 如果文件夹不存在,则创建
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.createFolder();
System.out.println("文件夹创建成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这段代码中,我们使用createFolder方法来创建一个新的文件夹。
遍历文件夹:
接下来,如果你想看看某个文件夹里都有些什么,VFS也可以帮到你。看这个例子:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSelectInfo;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSelector;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileType;
public class ListFilesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的文件夹路径
FileObject dir = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/dir");
// 使用自定义的文件选择器来列出所有文件
FileObject[] files = dir.findFiles(new FileSelector() {
@Override
public boolean includeFile(FileSelectInfo fileInfo) throws Exception {
return fileInfo.getFile().getType() == FileType.FILE;
}
@Override
public boolean traverseDescendents(FileSelectInfo fileInfo) throws Exception {
return true;
}
});
for (FileObject file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个例子中,我们用findFiles方法和一个自定义的FileSelector来获取文件夹中所有的文件。通过这种方式,你可以灵活地选择要列出哪些文件。
文件的复制和移动
在文件操作中,复制和移动文件也是常见需求。VFS让这些操作变得轻而易举。
复制文件:
来看看如何使用VFS复制文件:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class CopyFileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的源文件和目标文件路径
FileObject sourceFile = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/source/file.txt");
FileObject targetFile = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/target/file.txt");
// 执行文件复制
targetFile.copyFrom(sourceFile, Selectors.SELECT_SELF);
System.out.println("文件复制成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码展示了如何将一个文件从一个位置复制到另一个位置。
移动文件:
最后,如果你想移动文件而不是复制,也可以轻松实现:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class MoveFileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 这里替换成你的源文件和目标文件路径
FileObject sourceFile = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/source/file.txt");
FileObject targetFile = fsManager.resolveFile("file:///path/to/your/target/file.txt");
// 执行文件移动
sourceFile.moveTo(targetFile);
System.out.println("文件移动成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码演示了如何将文件从一个位置移动到另一个位置。
第5章:处理不同类型的文件系统
连接到FTP服务器
FTP(文件传输协议)是互联网上广泛使用的一种文件传输方式。让我们来看看如何使用VFS连接到FTP服务器并进行文件操作。
连接到FTP服务器:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemOptions;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.UserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.auth.SimpleUserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.impl.DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class FtpExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 准备认证信息
UserAuthenticator auth = new SimpleUserAuthenticator("用户名", "密码", null);
FileSystemOptions opts = new FileSystemOptions();
DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder.getInstance().setUserAuthenticator(opts, auth);
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 使用ftp协议,连接到FTP服务器
FileObject remoteFile = fsManager.resolveFile("ftp://ftp.example.com/path/to/file.txt", opts);
// 接下来就可以对remoteFile进行操作了,比如读取、写入等
// ...
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个例子中,我们首先创建了一个UserAuthenticator,用于认证FTP服务器的登录信息。然后通过FileSystemManager建立了一个FTP连接。注意,这里的URL是以ftp://开头的,表示这是一个FTP协议的连接。
使用SFTP进行安全文件传输
SFTP(SSH文件传输协议)是FTP的安全版本。它通过SSH协议为文件传输提供了加密和安全的认证机制。
使用SFTP连接:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemOptions;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.UserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.auth.SimpleUserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.impl.DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class SftpExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 准备认证信息
UserAuthenticator auth = new SimpleUserAuthenticator("用户名", "密码", null);
FileSystemOptions opts = new FileSystemOptions();
DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder.getInstance().setUserAuthenticator(opts, auth);
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
// 使用sftp协议,连接到SFTP服务器
FileObject remoteFile = fsManager.resolveFile("sftp://sftp.example.com/path/to/file.txt", opts);
// 接下来就可以对remoteFile进行操作了,比如读取、写入等
// ...
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个示例中,连接到SFTP服务器的方式与FTP类似,不同之处在于URL的协议部分是sftp://。这样,我们就可以利用SFTP的安全性来进行文件传输了。
第6章:异常处理与安全性
异常处理
在使用VFS进行文件操作时,可能会遇到各种各样的异常,比如文件找不到、读写错误等。正确地处理这些异常是非常重要的。
基本的异常处理:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemException;
public class ExceptionHandlingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 这里放置你的VFS操作代码
// ...
} catch (FileSystemException e) {
System.err.println("发生了文件系统异常:" + e.getMessage());
// 这里可以进行更详细的异常处理,比如根据不同的异常类型做不同的处理
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("发生了其他异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
在这个示例中,咱们捕获了FileSystemException,这是VFS操作中常见的异常类型。同时,也捕获了其他类型的异常,以确保程序的健壮性。
安全性考虑
在进行文件操作时,安全性是一个不容忽视的话题。尤其是在处理网络文件系统时,正确地管理认证信息尤为重要。
安全地处理认证信息:
在连接到需要认证的文件系统(如FTP、SFTP)时,咱们需要提供用户名和密码。这些信息需要安全地处理。
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.UserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.auth.SimpleUserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.impl.DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemOptions;
public class SecureAuthExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 安全地存储用户名和密码
char[] username = "你的用户名".toCharArray();
char[] password = "你的密码".toCharArray();
UserAuthenticator auth = new SimpleUserAuthenticator(new String(username), new String(password), null);
FileSystemOptions opts = new FileSystemOptions();
DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder.getInstance().setUserAuthenticator(opts, auth);
// 在这里进行文件操作
// ...
// 清除认证信息
java.util.Arrays.fill(username, ' ');
java.util.Arrays.fill(password, ' ');
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在这个示例中,咱们使用字符数组来存储用户名和密码,并在使用完毕后立即清除这些敏感信息。这是一种提高安全性的常见做法。
第7章:性能优化和最佳实践
性能优化技巧
在使用VFS进行文件操作时,性能是一个不容忽视的因素。尤其是在处理大量文件或者大型项目时,性能优化显得尤为重要。
缓存文件系统管理器:
一个常见的性能优化技巧是缓存FileSystemManager的实例。因为创建FileSystemManager实例可能是一个资源密集型的操作,所以重用实例可以节省时间和资源。
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
public class VfsOptimizationExample {
private static FileSystemManager fsManager;
static {
try {
// 初始化并缓存FileSystemManager实例
fsManager = VFS.getManager();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static FileSystemManager getManager() {
return fsManager;
}
// 在这里进行你的文件操作
// ...
}
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个静态的FileSystemManager实例,并在整个应用中重用它。
优化文件读取和写入:
在进行文件读取和写入操作时,使用合适的缓冲和流处理技术也是提升性能的一个重要方面。
// 这里以文件写入为例
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class FileWriteOptimizationExample {
public static void writeFile(FileObject file, String content) {
try (OutputStream out = file.getContent().getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(out, StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
writer.write(content);
// 使用合适的缓冲可以提高写入性能
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 在这里调用writeFile方法
// ...
}
最佳实践
除了性能优化,遵循一些最佳实践也能让你的VFS使用更加高效和安全。
合理管理文件系统的生命周期:
在使用VFS时,合理管理文件系统资源的生命周期是很重要的。这意味着在不需要文件系统资源时,应该及时释放它们。
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
public class LifecycleManagementExample {
public static void processFile(String filePath) {
FileObject file = null;
try {
file = VfsOptimizationExample.getManager().resolveFile(filePath);
// 对文件进行操作
// ...
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 确保文件对象被正确关闭
if (file != null) {
try {
file.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 在这里调用processFile方法
// ...
}
在这个示例中,无论操作成功还是发生异常,我们都确保了在finally块中关闭文件对象,这有助于防止资源泄露。
第8章:实际案例分析
案例一:从远程FTP服务器下载文件
在很多应用场景中,我们需要从远程FTP服务器下载文件。使用VFS,这个过程可以简化许多。
下载文件的示例代码:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemOptions;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.UserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.auth.SimpleUserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.impl.DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
public class FtpDownloadExample {
public static void downloadFile(String remoteFilePath, String localFilePath) {
FileObject remoteFile = null;
try {
// 设置FTP登录信息
UserAuthenticator auth = new SimpleUserAuthenticator("用户名", "密码", null);
FileSystemOptions opts = new FileSystemOptions();
DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder.getInstance().setUserAuthenticator(opts, auth);
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
remoteFile = fsManager.resolveFile("ftp://ftp.example.com" + remoteFilePath, opts);
// 执行下载操作
try (InputStream in = remoteFile.getContent().getInputStream();
BufferedOutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(localFilePath))) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (remoteFile != null) {
try {
remoteFile.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
在这个案例中,我们通过VFS连接到FTP服务器,并从中下载文件到本地路径。这个过程展示了VFS在网络文件操作中的便捷性。
案例二:将日志文件上传到SFTP服务器
假设在一个企业应用中,我们需要将生成的日志文件定期上传到安全的SFTP服务器。使用VFS可以轻松实现这一功能。
上传文件的示例代码:
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileObject;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemManager;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.FileSystemOptions;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.UserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.auth.SimpleUserAuthenticator;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.impl.DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.vfs2.VFS;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
public class SftpUploadExample {
public static void uploadFile(String localFilePath, String remoteFilePath) {
FileObject localFile = null;
FileObject remoteFile = null;
try {
// 设置SFTP登录信息
UserAuthenticator auth = new SimpleUserAuthenticator("用户名", "密码", null);
FileSystemOptions opts = new FileSystemOptions();
DefaultFileSystemConfigBuilder.getInstance().setUserAuthenticator(opts, auth);
FileSystemManager fsManager = VFS.getManager();
localFile = fsManager.resolveFile("file://" + localFilePath);
remoteFile = fsManager.resolveFile("sftp://sftp.example.com" + remoteFilePath, opts);
// 执行上传操作
try (BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(localFilePath))) {
remoteFile.copyFrom(localFile, Selectors.SELECT_SELF);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (localFile != null) {
try {
localFile.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (remoteFile != null) {
try {
remoteFile.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
在这个案例中,我们将本地的日志文件上传到SFTP服务器。这个过程不仅简化了文件上传的代码,还保证了数据传输的安全性。
第9章:总结
Apache Commons VFS是一个非常强大和灵活的工具,它为处理各种文件系统提供了统一的接口。无论你是在处理本地文件,还是需要与远程服务器进行文件交换,VFS都能提供简洁高效的解决方案。通过合理地使用VFS,我们不仅能提高代码的可读性和可维护性,还能确保应用的性能和安全性。
希望这个博客能帮助大家在日常工作中更好地使用Apache Commons VFS。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!