Java:字节流 文件输出与读入方法 并 实现文件拷贝
2023-12-13 04:29:24
字节 流
FileOutputStream
- 创建对象,指定位置(产生数据传输通道)
参数可以是File对象,也可以是路径
如果文件不存在,且父级路径正确,会新建文件
如果文件存在,会清空文件 - 写出数据
ASCII对应 字符
可以传入字节流,指定起始位置,长度 - 释放资源
解除资源占用
package com.io.testdemo1;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建对象,指定位置(产生数据传输通道)
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/aaa.txt");
// 写入数据
fos.write(97);
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100};
fos.write(bytes);
fos.write(bytes, 0, 2);
// 释放资源
fos.close();
}
}
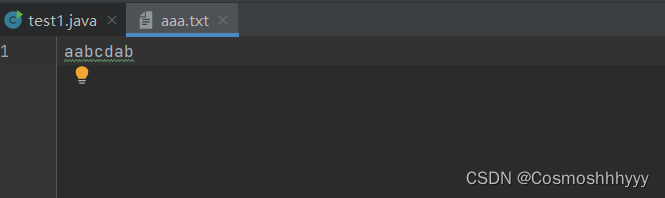
换行 与 续写
换行:
write(“\r\n”) 即可 linux只写\n即可 mac写\r
\r 表示回车 \n 表示换行
早期\r表示,回到此行开头,\n才表示换行,一直沿用了下来。
续写: 在输出流对象的第二个参数中,加入true,表示打开续写开关。
例子:
package com.io.testdemo1;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/aaa.txt", true);
// 写入数据
String str1 = "hello";
byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes1);
// 写入换行
String str2 = "\r\n";
byte[] bytes2 = str2.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes2);
fos.close();
}
}
运行两次的结果:
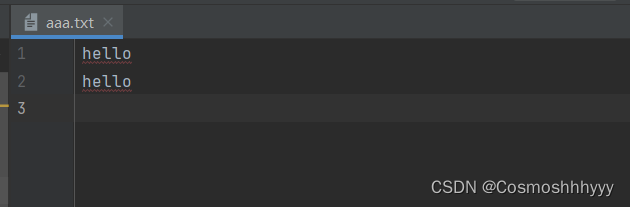
可以发现第二次续写了,并没有清空,同时换行了。
FileInputstream
与输出相似。
- 创建对象(搭建桥梁)
如果文件不存在则直接报错 - 读入(返回值为int)
一次读一个字节,ASCII对应的数字 (每次读相当于一次指针的移动)
读到末尾时返回-1 - 释放资源
package com.io.testdemo2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/aaa.txt");
// 循环 读入
int b; // 用变量去接收,要是条件和循环体内都read会跳两次
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)b);
}
// 释放资源
fis.close();
}
}
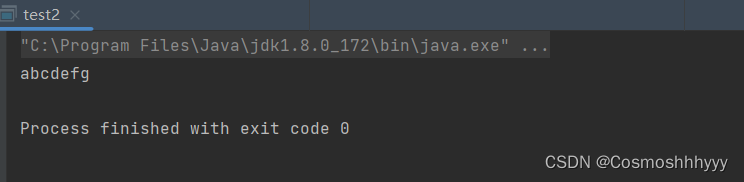
运行结果与文件内容相同,说明成功读取成功:

实现 文件拷贝(字节数组 读入方法)
read可以传入byte数组,这样可以一次读入一个字节数组大小,速度会快很多,大小最好为1024的整数倍。
注意:返回值变成了长度,读完会返回-1。
将aaa.txt拷贝bbb.txt:
package com.io.copydemo;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/aaa.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/bbb.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[4096];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
运行结果:
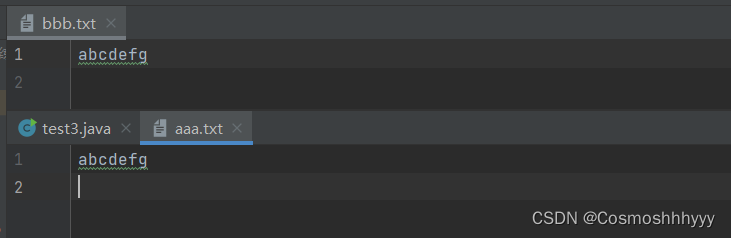
字节流 编码
最好不要用字节流取读取文本文件。
编码和解码要统一。
idea默认utf-8,字母1字节,汉字3字节
eclipse默认jbk,字母1字节,汉字2字节
package com.io;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str = "abc你好";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes("GBK");
String res1 = new String(bytes, "GBK");
String res2 = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(res1); // abc你好
System.out.println(res2); // abc���
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Cosmoshhhyyy/article/details/134899230
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!