leetcode算法之队列
2023-12-13 14:36:39
在leetcode中,队列一般都是搭配BFS,即宽度优先搜索算法进行使用
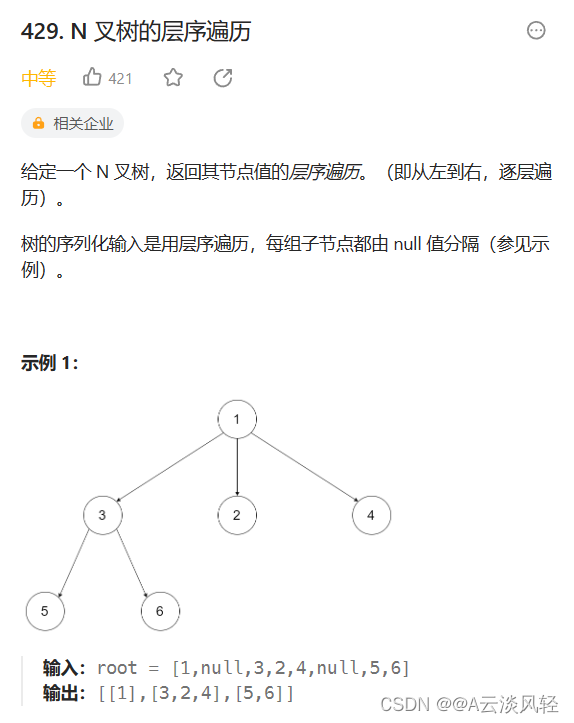
1.N叉树的层序遍历
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
//使用队列
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(root == nullptr) return ret;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
Node* t = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
for(auto children : t->children)
{
if(children)
{
q.push(children);
}
}
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};
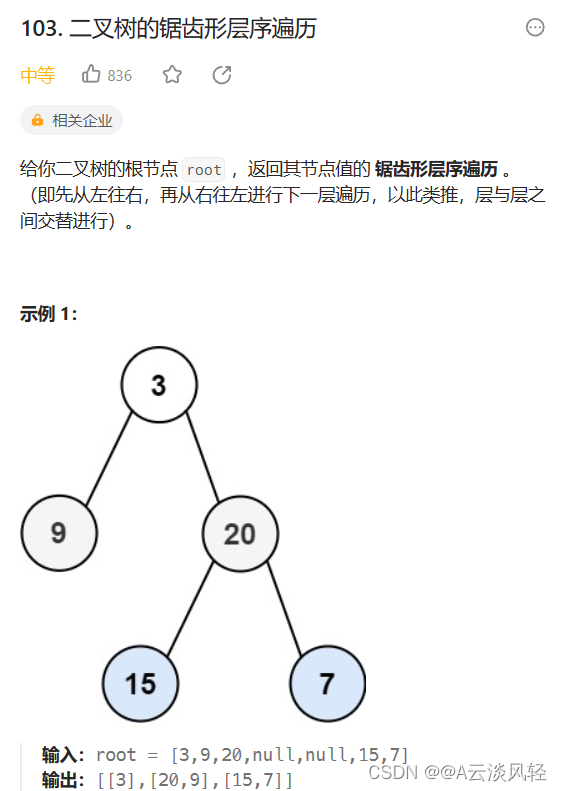
2.二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
//增加一个标志位,偶数行的时候将此行的值逆序即可
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(root == nullptr) return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
int level = 1;//标志位
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
//判断是否需要逆序
if(level%2 == 0) reverse(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
ret.push_back(tmp);
level++;
}
return ret;
}
};
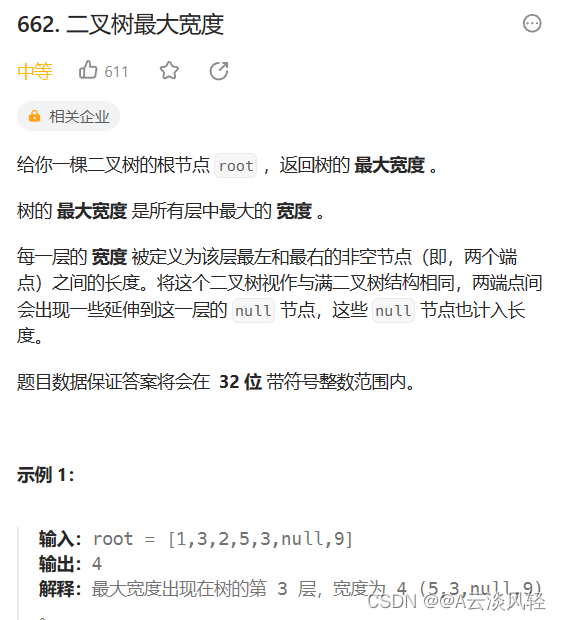
3.二叉树的最大宽度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
vector<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int>> q;//使用数组来模拟队列
q.push_back({root,1});
unsigned int ret = 0;
while(q.size())
{
//先计算此行的最大宽度
auto&[x1,y1] = q[0];
auto&[x2,y2] = q.back();
ret = max(ret,y2-y1+1);
//再让下一行元素入队列
//由于数组头删时间复杂度太高,我们可以再开一个数组,再覆盖
vector<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int>> tmp;
for(auto&[x,y]:q)
{
if(x->left) tmp.push_back({x->left,2*y});
if(x->right) tmp.push_back({x->right,2*y+1});
}
q = tmp;
}
return ret;
}
};
4.在每个树行中找最大值
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
if(root == nullptr) return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int tmp = INT_MIN;
int sz = q.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp = max(tmp,t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_55283616/article/details/134828160
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!