【操作系统】实验四 进程调度
2023-12-18 14:18:18
实验名称:?实验四?进程调度
实验目的:??
1. 加深理解有关进程控制块、进程队列的概念
2. 体会和了解优先级和时间片轮转调度算法的具体实施办法
实验内容:
1. 设计进程控制块?PCB?表结构(与实验一的结构相同),分别适用于优先级调度算法和循环轮转调度算法,建立进程就绪队列。实现优先数调度和循环轮转调度两种调度算法。
#include?<stdio.h>
#include?<stdlib.h>
#include?<string.h>
typedef?struct?node
{
????char?name[20];
????int?prio;
????int?round;
????int?cputime;
????int?needtime;
????char?state;
????int?count;
????struct?node?*next;
}?PCB;
PCB?*ready?=?NULL,?*run?=?NULL,?*finish?=?NULL;
int?num;
void?GetFirst();
void?Output(char?algorithm_type,?int?current_time);
void?InsertPrio(PCB?*in);
void?InsertTime(PCB?*in);
void?InsertFinish(PCB?*in);
void?PrioCreate();
void?TimeCreate();
void?Priority();
void?RoundRun();
int?main(void)
{
????char?chose;
????printf("请输入要创建的进程数目:\n");
????scanf("%d",?&num);
????getchar();
????printf("输入进程的调度方法:(P/R)\n");
????scanf("%c",?&chose);
????switch?(chose)
????{
????case?'P':
????case?'p':
????????PrioCreate();
????????Priority();
????????break;
????case?'R':
????case?'r':
????????TimeCreate();
????????RoundRun();
????????break;
????default:
????????break;
????}
????Output(chose,?-1);
????return?0;
}
void?GetFirst()
{
????run?=?ready;
????if?(ready?!=?NULL)
????{
????????run->state?=?'R';
????????ready?=?ready->next;
????????run->next?=?NULL;
????}
}
void?Output(char?algorithm_type,?int?current_time)
{
????PCB?*p;
????printf("CPUTIME:%d\n",?current_time);?//?修改这里,加上?+?1
????if?(algorithm_type?==?'P'?||?algorithm_type?==?'p')
????{
????????printf("NAME\tCPUTIME\tNEEDTIME\tPRIORITY\tSTATE\tCOUNT\n");
????????p?=?ready;
????????while?(p?!=?NULL)
????????{
????????????printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%d\t\t%c\t\t%d\n",?p->name,?p->cputime,?p->needtime,?p->prio,?p->state,?p->count);
????????????p?=?p->next;
????????}
????}
????else?if?(algorithm_type?==?'R'?||?algorithm_type?==?'r')
????{
????????printf("NAME\tCPUTIME\tNEEDTIME\tCOUNT\tSTATE\n");
????????p?=?run;
????????while?(p?!=?NULL)
????????{
????????????printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%d\t\t%c\t\t%d\n",?p->name,?p->cputime,?p->needtime,?p->count,?p->state,?p->count);
????????????p?=?p->next;
????????}
????}
????p?=?finish;
????while?(p?!=?NULL)
????{
????????printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%d\t\t%c\t\t%d\n",?p->name,?p->cputime,?p->needtime,?p->prio,?p->state,?p->count);
????????p?=?p->next;
????}
}
void?InsertPrio(PCB?*in)
{
????PCB?*fst,?*nxt;
????fst?=?nxt?=?ready;
????if?(ready?==?NULL)
????{
????????in->next?=?ready;
????????ready?=?in;
????}
????else
????{
????????if?(in->prio?>?fst->prio)
????????{
????????????in->next?=?ready;
????????????ready?=?in;
????????}
????????else
????????{
????????????while?(fst->next?!=?NULL)
????????????{
????????????????nxt?=?fst;
????????????????fst?=?fst->next;
????????????}
????????????if?(fst->next?==?NULL)
????????????{
????????????????in->next?=?fst->next;
????????????????fst->next?=?in;
????????????}
????????????else
????????????{
????????????????nxt?=?in;
????????????????in->next?=?fst;
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
void?InsertTime(PCB?*in)
{
????PCB?*fst;
????fst?=?ready;
????if?(ready?==?NULL)
????{
????????in->next?=?ready;
????????ready?=?in;
????}
????else
????{
????????while?(fst->next?!=?NULL)
????????{
????????????fst?=?fst->next;
????????}
????????in->next?=?fst->next;
????????fst->next?=?in;
????}
}
void?InsertFinish(PCB?*in)
{
????PCB?*fst;
????fst?=?finish;
????if?(finish?==?NULL)
????{
????????in->next?=?finish;
????????finish?=?in;
????}
????else
????{
????????while?(fst->next?!=?NULL)
????????{
????????????fst?=?fst->next;
????????}
????????in->next?=?fst->next;
????????fst->next?=?in;
????}
}
void?PrioCreate()
{
????PCB?*tmp;
????int?i;
????printf("输入进程名字和进程所需时间:\n");
????for?(i?=?0;?i?<?num;?i++)
????{
????????if?((tmp?=?(PCB?*)malloc(sizeof(PCB)))?==?NULL)
????????{
????????????perror("malloc");
????????????exit(1);
????????}
????????scanf("%s",?tmp->name);
????????getchar();
????????scanf("%d",?&(tmp->needtime));
????????tmp->cputime?=?0;
????????tmp->state?=?'W';
????????tmp->prio?=?50?-?tmp->needtime;
????????tmp->round?=?0;
????????tmp->count?=?0;
????????InsertPrio(tmp);
????}
}
void?TimeCreate()
{
????PCB?*tmp;
????int?i;
????printf("输入进程名字和进程时间片所需时间:\n");
????for?(i?=?0;?i?<?num;?i++)
????{
????????if?((tmp?=?(PCB?*)malloc(sizeof(PCB)))?==?NULL)
????????{
????????????perror("malloc");
????????????exit(1);
????????}
????????scanf("%s",?tmp->name);
????????getchar();
????????scanf("%d",?&(tmp->needtime));
????????tmp->cputime?=?0;
????????tmp->state?=?'W';
????????tmp->prio?=?0;
????????tmp->round?=?2;
????????tmp->count?=?0;
????????InsertTime(tmp);
????}
}
void?Priority()
{
????int?flag?=?1;
????int?current_time?=?0;
????GetFirst();
????while?(run?!=?NULL)
????{
????????current_time++;
????????Output('P',?current_time);
????????while?(flag)
????????{
????????????run->prio?-=?3;
????????????run->cputime++;
????????????run->needtime--;
????????????if?(run->needtime?==?0)
????????????{
????????????????run->state?=?'F';
????????????????run->count++;
????????????????InsertFinish(run);
????????????????flag?=?0;
????????????}
????????????else
????????????{
????????????????run->state?=?'W';
????????????????run->count++;
????????????????InsertTime(run);
????????????????flag?=?0;
????????????}
????????}
????????flag?=?1;
????????GetFirst();
????}
}
void?RoundRun()
{
????int?flag?=?1;
????int?current_time?=?0;
????GetFirst();
????while?(run?!=?NULL)
????{
????????current_time++;
????????Output('R',?current_time);
????????flag?=?1;
????????while?(flag)
????????{
????????????run->count++;
????????????run->cputime++;
????????????run->needtime--;
????????????if?(run->needtime?==?0)
????????????{
????????????????run->state?=?'F';
????????????????InsertFinish(run);
????????????????flag?=?0;
????????????}
????????????else?if?(run->count?==?run->round)
????????????{
????????????????run->state?=?'W';
????????????????run->count?=?0;
????????????????InsertTime(run);
????????????????flag?=?0;
????????????}
????????}
????????GetFirst();
????}
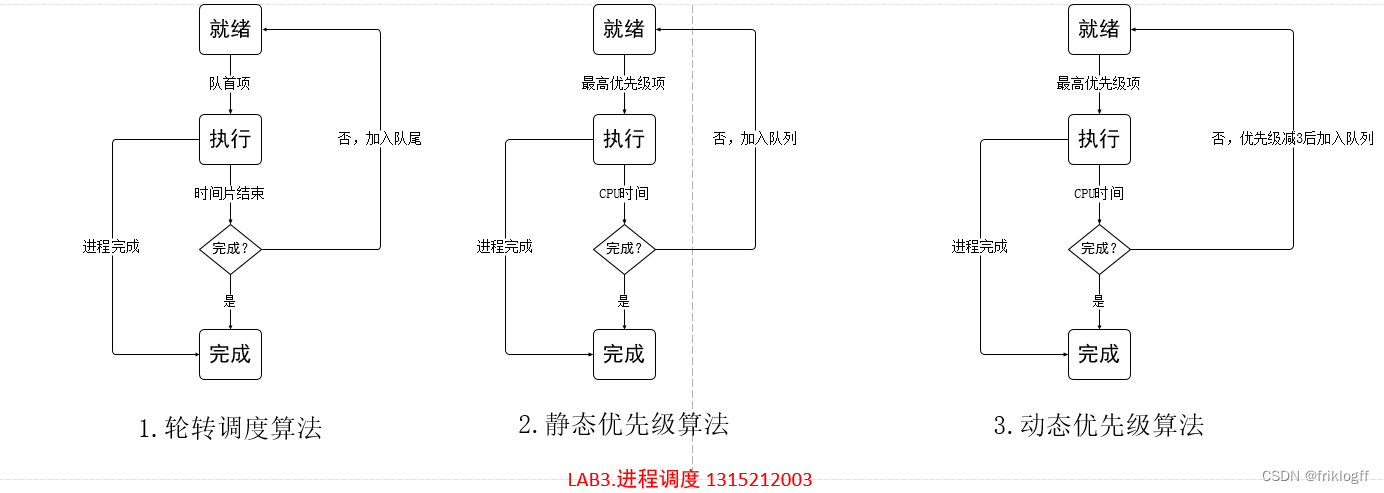
}算法设计与实现(附流程图和源代码):
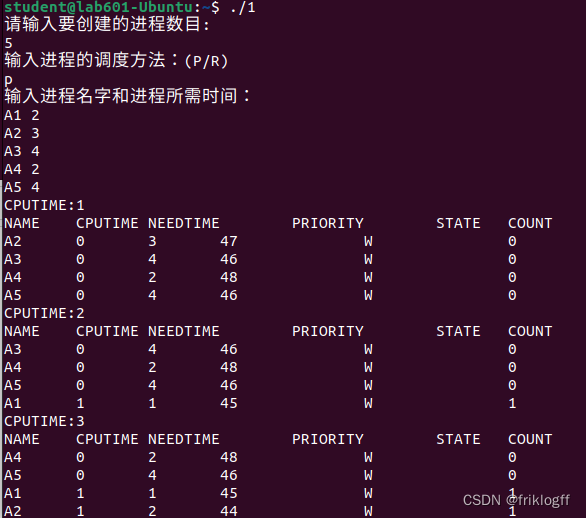
调试过程及实验结果(附截图):?
思考题:
如果设计一个基于优先级的时间片轮转调度算法,请给出你的设计思想和方案。进程ID;
设计基于优先级的时间片轮转调度算法思路:
在基于优先级的时间片轮转调度算法中,每个进程拥有一个优先级,进程按照优先级的高低进行调度。当处于运行状态的进程的时间片用完时,系统将根据优先级选择下一个进程执行。这种算法结合了优先级和时间片轮转两种调度策略,确保高优先级的进程能够更快地得到执行,同时也防止了低优先级的进程永远无法执行的情况。
基本设计思路:
- 优先级赋值:?每个进程创建时,根据其属性和历史行为确定一个优先级。这个优先级可以包括进程的重要性、紧急程度、资源需求等因素,以确保系统能够更好地满足业务需求。
- 时间片轮转:?每个进程被分配一个时间片,当时间片用完时,系统将根据进程的优先级选择下一个进程执行。如果就绪队列中有高优先级的进程,它将被选择执行;否则,根据时间片轮转策略选择下一个进程。
- 动态调整优先级:?系统可以根据进程的行为动态调整其优先级。例如,等待时间较长的进程可以提高其优先级,以避免饥饿现象。
- 就绪队列管理:?就绪队列按照优先级进行排序,确保高优先级的进程在队列头部,方便系统快速选择下一个执行的进程。
- 合理设置时间片:?时间片的大小需要根据系统的特点和需求进行合理设置。过大的时间片可能导致低优先级进程得不到及时执行,而过小的时间片可能导致上下文切换频繁。
实验小结:
- 优势和局限性:?基于优先级的时间片轮转调度算法能够更好地满足不同进程的优先级需求,提高系统的响应速度。然而,需要注意的是,如果高优先级的进程数量过多,低优先级的进程可能会受到影响,产生饥饿现象。
- 系统性能:?该调度算法需要合理权衡进程的优先级和时间片大小,以确保系统整体性能的优化。在实际应用中,需要根据具体的场景和要求进行调整和优化。
- 动态调整:?动态调整优先级是提高系统灵活性的关键。通过监控进程的行为,系统可以实时调整进程的优先级,以适应不断变化的工作负载。
- 综合考虑:?在设计调度算法时,需要综合考虑系统的特点、任务的性质以及用户需求,以找到最适合的调度策略。不同场景可能需要不同的优先级调度算法来实现最佳性能。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42531954/article/details/135049431
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!