C++相关闲碎记录(14)
2023-12-16 12:53:32
1、数值算法
(1)运算后产生结果accumulate()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 9);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
cout << "sum: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 0) << endl;
cout << "sum: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), -100) << endl;
cout << "product: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 1, multiplies<int>()) << endl;
cout << "product: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 0, multiplies<int>()) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
sum: 45
sum: -55
product: 362880 这里是累称的结果
product: 0(2)计算两数列的内积inner_product()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
list<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// 0 + 1*1 + 2*2 + 3*3+4*4 + 5*5+6*6
cout << "innser product: " << inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
coll.cbegin(),
0) << endl;
// 0 + 1*6 + 2*5 + 3 * 4 + 4*3+5*2+6*1
cout << "inner_product: " << inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
coll.crbegin(),
0) << endl;
// 1 * 1+1 * 2+2 * 3+3 * 4+4 * 5+5 * 6+6
cout << "product of sums: "
<< inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), // first range
coll.cbegin(), // second range
1, // initial value
multiplies<int>(), // outer operation
plus<int>()) // inner operation
<< endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6
innser product: 91
inner_product: 56
product of sums: 46080(3)相对数列和绝对数列之间的转换partial_sum()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),
multiplies<int>());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 3 6 10 15 21
1 2 6 24 120 720(4)将绝对值转换成相对值adjacent_difference()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
deque<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),
plus<int>());
cout << endl;
adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),
multiplies<int>());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 3 5 7 9 11
1 2 6 12 20 30#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> coll = {17, -3, 22, 13, 13, -9};
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "coll: ");
adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
coll.begin());
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "relative: ");
partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),
coll.begin());
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "absolute: ");
return 0;
}
输出:
coll: 17 -3 22 13 13 -9
relative: 17 -20 25 -9 0 -22
absolute: 17 -3 22 13 13 -92、stack堆栈
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stack<int> st;
// push three elements into the stack
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
// pop and print two elements from the stack
cout << st.top() << ' ';
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << ' ';
st.pop();
// modify top element
st.top() = 77;
// push two new elements
st.push(4);
st.push(5);
// pop one element without processing it
st.pop();
// pop and print remaining elements
while (!st.empty()) {
cout << st.top() << ' ';
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
输出:
3 2 4 77 自定义stack 类
#ifndef STACK_HPP
#define STACK_HPP
#include <deque>
#include <exception>
template <typename T>
class Stack {
protected:
std::deque<T> c;
public:
class ReadEmptyStack : public std::exception {
public:
virtual const char* what() const throw() {
return "read empty stack";
}
};
typename std::deque<T>::size_type size() const {
return c.size();
}
bool empty() const {
return c.empty();
}
void push(const T& elem) {
c.push_back(elem);
}
T pop() {
if (c.empty()) {
throw ReadEmptyStack();
}
T elem(c.back());
c.pop_back();
return elem;
}
T& top() {
if (c.empty()) {
throw ReadEmptyStack();
}
return c.back();
}
};
#endif#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include "Stack.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main() {
try {
Stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
cout << st.pop() << " ";
cout << st.pop() << " ";
st.top() = 77;
st.push(4);
st.push(5);
st.pop();
cout << st.pop() << " ";
cout << st.pop() << endl;
cout << st.pop() << endl;
} catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << "EXCEPTION: " << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
3 2 4 77
EXCEPTION: read empty stack3、queue队列
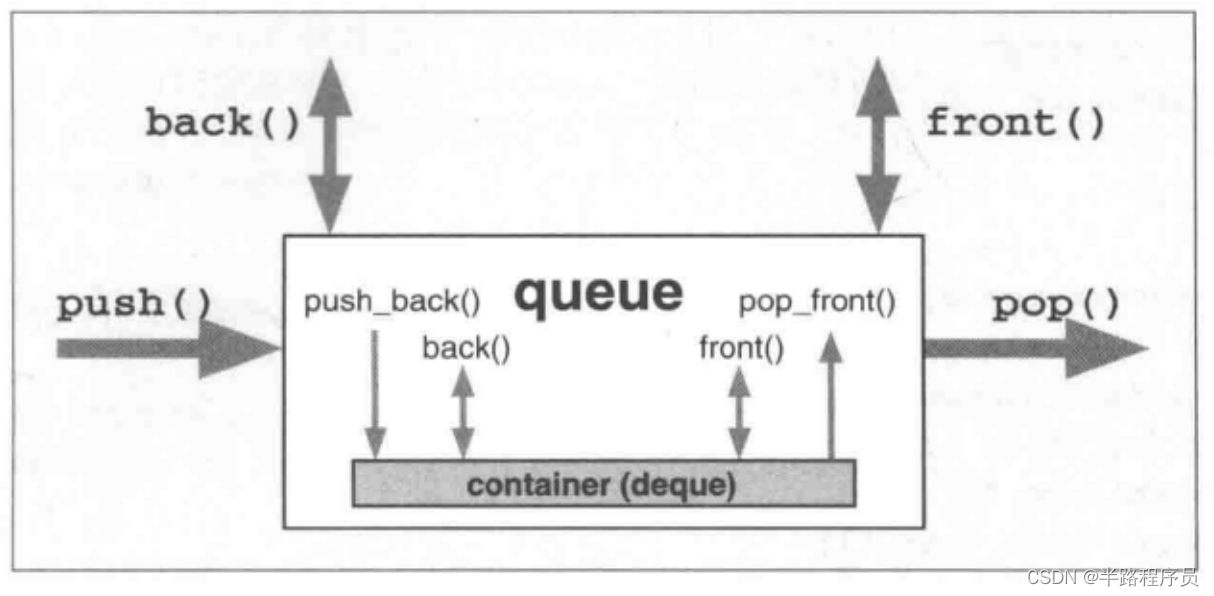
自定义queue
#ifndef QUEUE_HPP
#define QUEUE_HPP
#include <deque>
#include <exception>
template <typename T>
class Queue {
protected:
std::deque<T> c;
public:
class ReadEmptyQueue : public std::exception {
public:
virtual const char* what() const throw() {
return "read empty queue";
}
};
typename std::deque<T>::size_type size() const {
return c.size();
}
bool empty() const {
return c.empty();
}
void push(const T& elem) {
c.push_back(elem);
}
T pop() {
if (c.empty()) {
throw ReadEmptyQueue();
}
T elem(c.front());
c.pop_front();
return elem;
}
T& fron() {
if (c.empty()) {
throw ReadEmptyQueue();
}
return c.front();
}
};
#endif#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <exception>
#include "Queue.hpp" // use special queue class
using namespace std;
int main()
{
try {
Queue<string> q;
// insert three elements into the queue
q.push("These ");
q.push("are ");
q.push("more than ");
// pop two elements from the queue and print their value
cout << q.pop();
cout << q.pop();
// push two new elements
q.push("four ");
q.push("words!");
// skip one element
q.pop();
// pop two elements from the queue and print their value
cout << q.pop();
cout << q.pop() << endl;
// print number of remaining elements
cout << "number of elements in the queue: " << q.size()
<< endl;
// read and print one element
cout << q.pop() << endl;
}
catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << "EXCEPTION: " << e.what() << endl;
}
}
输出:
These are four words!
number of elements in the queue: 0
EXCEPTION: read empty queue4、priority queue 带优先级的队列
namespace std {
template <typename T, typename Container = vector<T>,
typename Compare = less<typename Container::value_typy>>
class priority_queue {
protected:
Compare comp;
Container c;
public:
explicit priority_queue(const Compare& cmp = Compare(),
const Container& cont = Container()):comp(cmp),c(cont) {
make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
void push(const value_type& x) {
c.push_back(x);
push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
void pop() {
pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
c.pop_back();
}
bool empty() const {return c.empty();}
size_type size() const {return c.size();}
const value_type& top() const {return c.front();}
...
};
}priority_queue()内部使用的heap相关算法。
5、bitset
#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// enumeration type for the bits
// - each bit represents a color
enum Color { red, yellow, green, blue, white, black, //...,
numColors };
// create bitset for all bits/colors
bitset<numColors> usedColors;
// set bits for two colors
usedColors.set(red);
usedColors.set(blue);
// print some bitset data
cout << "bitfield of used colors: " << usedColors << endl;
cout << "number of used colors: " << usedColors.count() << endl;
cout << "bitfield of unused colors: " << ~usedColors << endl;
// if any color is used
if (usedColors.any()) {
// loop over all colors
for (int c = 0; c < numColors; ++c) {
// if the actual color is used
if (usedColors[(Color)c]) {
//...
}
}
}
}#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// print some numbers in binary representation
cout << "267 as binary short: "
<< bitset<numeric_limits<unsigned short>::digits>(267)
<< endl;
cout << "267 as binary long: "
<< bitset<numeric_limits<unsigned long>::digits>(267)
<< endl;
cout << "10,000,000 with 24 bits: "
<< bitset<24>(1e7) << endl;
// write binary representation into string
string s = bitset<42>(12345678).to_string();
cout << "12,345,678 with 42 bits: " << s << endl;
// transform binary representation into integral number
cout << "\"1000101011\" as number: "
<< bitset<100>("1000101011").to_ullong() << endl;
}
输出:
267 as binary short: 0000000100001011
267 as binary long: 00000000000000000000000100001011
10,000,000 with 24 bits: 100110001001011010000000
12,345,678 with 42 bits: 000000000000000000101111000110000101001110
"1000101011" as number: 555
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/wj617906617/article/details/135025848
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!