Labelme2Yolo labelme格式的json标注转yolo格式txt
2023-12-13 03:48:16
该工作适用于目标检测工作。
由于labelme标注出的文件是如下图的单个json文件格式,不符合yolo的训练格式,需要转格式。
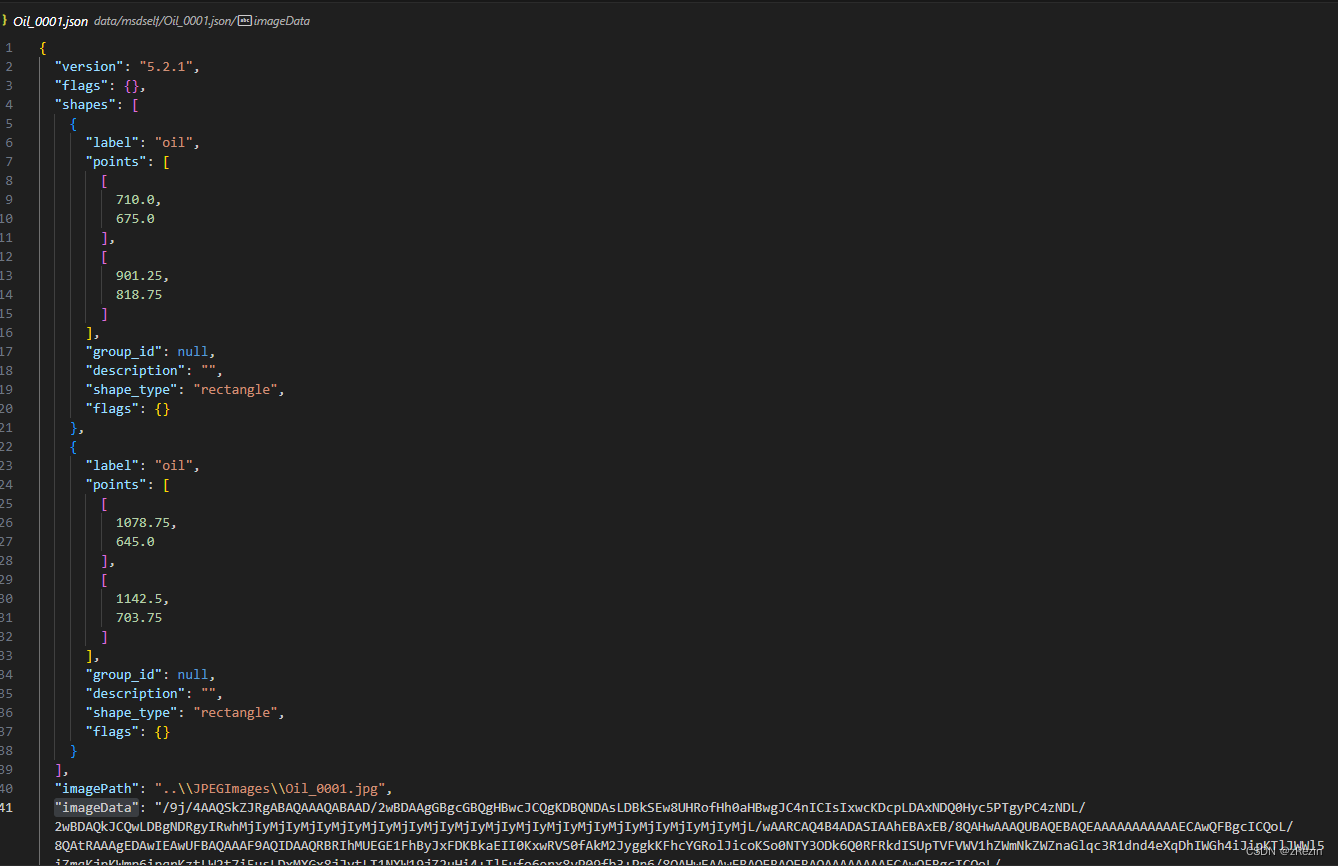
观察发现labelme标注的json文件中有imageData,还挺大的,查阅后得知是base64后的图片数据,也就是说json文件中,只要带有imageData就其实是包含了图片文件的数据,可以用json文件直接输出图片文件。
所以利用labelme的json可以直接完成yolo格式标注的输出。使用该代码可以直接按比例分割train,val,test,并输出文件到如下标准格式文件目录
yoloformat
|--images
| |--train
| |--val
| |--test
|--labels
|--train
|--val
|--test代码如下:
import base64
import os
import io
import json
import glob
from PIL import Image
import random
def labelme_to_yolo(json_file, output_img_dir, output_label_dir, class_dict):
# 读取JSON文件
with open(json_file, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 解析imageData并获取图像的宽度和高度
image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(base64.b64decode(data['imageData'])))
width, height = image.size
# 提取JSON文件的基础文件名
base_name = os.path.basename(json_file).replace('.json', '')
# 保存图像
image_path = os.path.join(output_img_dir, base_name + '.png')
image.save(image_path)
# 创建YOLO标注文件
txt_path = os.path.join(output_label_dir, base_name + '.txt')
with open(txt_path, 'w') as f:
for shape in data['shapes']:
# 获取对象的类别和边界框
label = shape['label']
points = shape['points']
# 计算YOLO格式的中心点和宽度/高度
x_center = (points[0][0] + points[1][0]) / 2 / width
y_center = (points[0][1] + points[1][1]) / 2 / height
box_width = abs(points[1][0] - points[0][0]) / width
box_height = abs(points[1][1] - points[0][1]) / height
# 将此行写入YOLO标注文件
f.write(f"{class_dict[label]} {x_center} {y_center} {box_width} {box_height}\n")
# 类别字典,将类别名称映射为整数
class_dict = {"oil": 0, "scr": 1, "sta": 2} # 根据你的数据集来替换这些类别
# 设置输出目录
output_dir = 'newlabel'
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'test'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'test'), exist_ok=True)
# 获取所有的JSON文件
json_files = glob.glob('*.json')
# 打乱文件列表
random.shuffle(json_files)
# 计算训练集、验证集和测试集的大小
n_total = len(json_files)
n_val = int(n_total * 0.12)
n_test = int(n_total * 0.12)
n_train = n_total - n_val - n_test
# 分割文件列表
train_files = json_files[:n_train]
val_files = json_files[n_train:n_train+n_val]
test_files = json_files[n_train+n_val:]
# 处理所有的JSON文件
for json_file in train_files:
labelme_to_yolo(json_file, os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'train'), os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'train'), class_dict)
for json_file in val_files:
labelme_to_yolo(json_file, os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'val'), os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'val'), class_dict)
for json_file in test_files:
labelme_to_yolo(json_file, os.path.join(output_dir, 'images', 'test'), os.path.join(output_dir, 'labels', 'test'), class_dict)
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/shuaikang9864/article/details/134866373
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!