数据结构第六弹---带头双向循环链表
2024-01-09 15:26:49
双向循环链表
1、带头双向循环链表概念
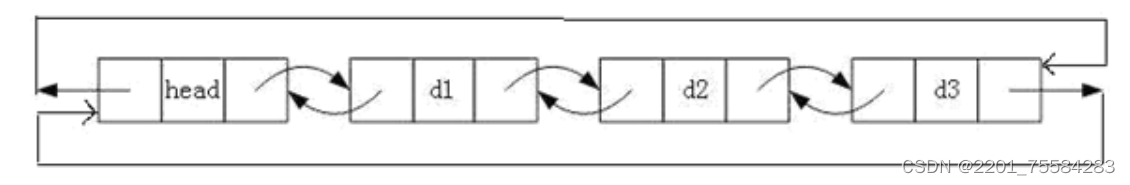
概念:带头双向循环链表是一种特殊类型的链表,它由一系列节点组成,每个
节点包含一个数据域和两个指针域,第一个结点不存储有效数据。其中一个指
针指向下一个节点,另一个指针指向前一个节点。在带头双向循环链表中,首
节点的前一个节点是尾节点,尾节点的下一个节点是首节点,形成一个闭环。
2、带头双向循环链表的优势
1.高效遍历:由于带头双向循环链表可以双向遍历,因此可以在O(1)时间内访问任何节点。
2.内存高效:与双向链表相比,带头双向循环链表不需要额外的内存来存储头部节点。
3.插入和删除操作高效:在带头双向循环链表中插入和删除节点时,只需调整指针即可,无需移动大量数据。
3、带头双向循环链表的实现
实现一个带头双向循环链表首先得创建一个工程。(下图为vs 2022)
List.h(带头双向循环链表的类型定义、接口函数声明、引用的头文件)
List.c(带头双向循环链表接口函数的实现)
test.c (主函数、测试顺序表各个接口功能)
以下是List.h的代码。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
//双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);
//双向链表初始化
ListNode* ListInit();
//双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead);
//双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);
//尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);
//查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//在pos之前插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
//删除pos位置
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
//判断是否为空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead);
//计算大小
int ListSize(ListNode* phead);
3.1、头文件包含和结构定义
以下是实现双向循环链表可能用到的头文件。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
以下是博主创建的双向循环链表的结构,可以根据自己的喜好创建喔。
建议:创建结构时最好能通俗易懂,最好不用拼音创建。
typedef int LTDataType;//定义数据类型,可以根据需要更改
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data; //数据域 存储数据
struct ListNode* next;//指针域 存储指向下一个结点的指针
struct ListNode* prev;//指针域 存储指向前一个结点的指针
}ListNode;
3.2、创建新结点
为什么先创建新结点而不是初始化呢?因为当前链表为带头的链表,初始化时需要创建结点,所以就先封装创建结点函数。
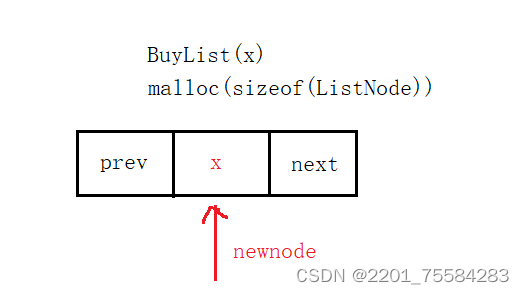
ListNode* BuyList(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}
3.3、打印
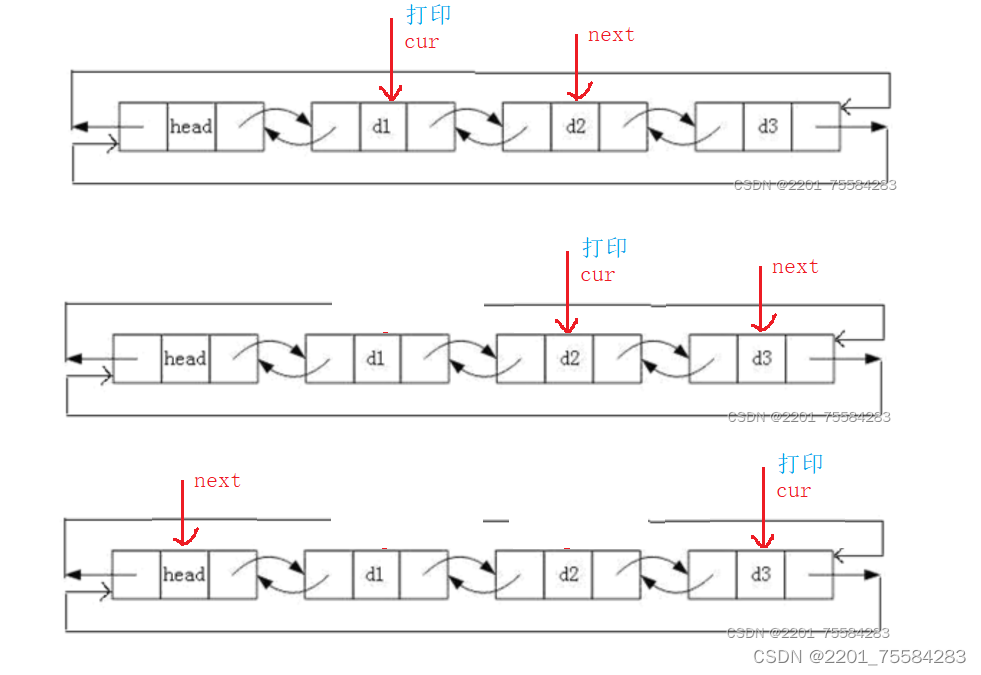
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
3.4、初始化
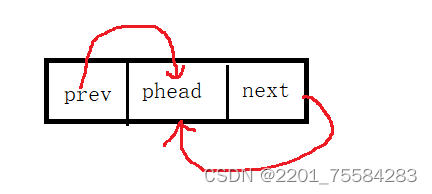
ListNode* ListInit()
{
ListNode* phead = BuyList(0);
phead->next = phead;//构成循环
phead->prev = phead;//构成循环
return phead;
}
3.5、销毁
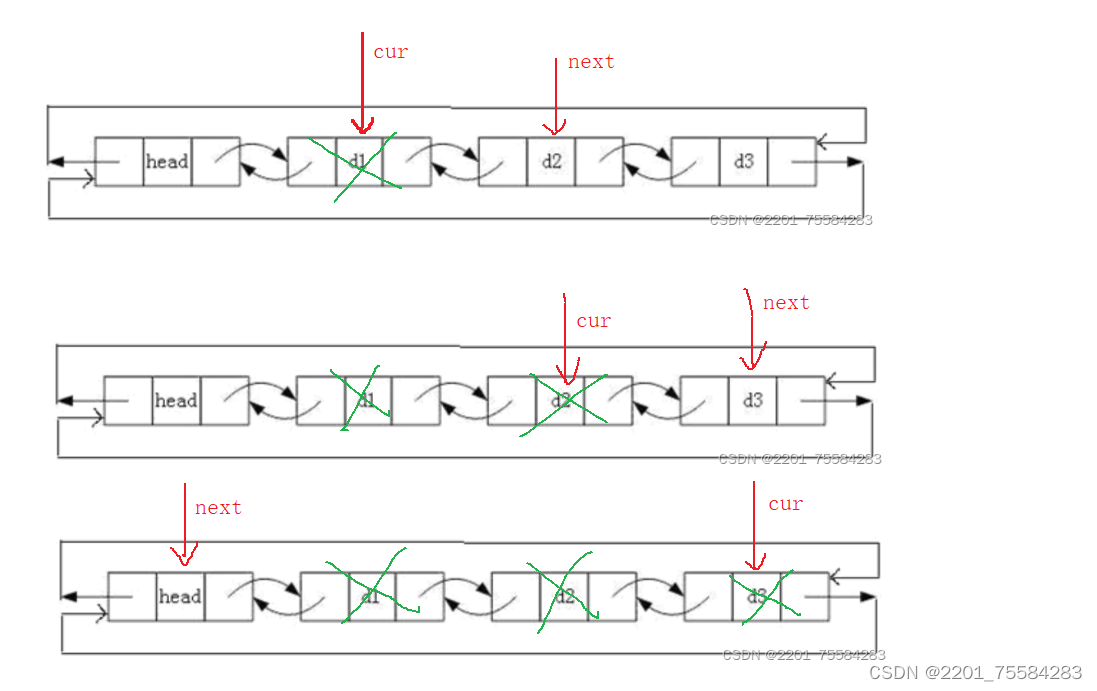
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;//养成好习惯,释放之后手动置为NULL
}
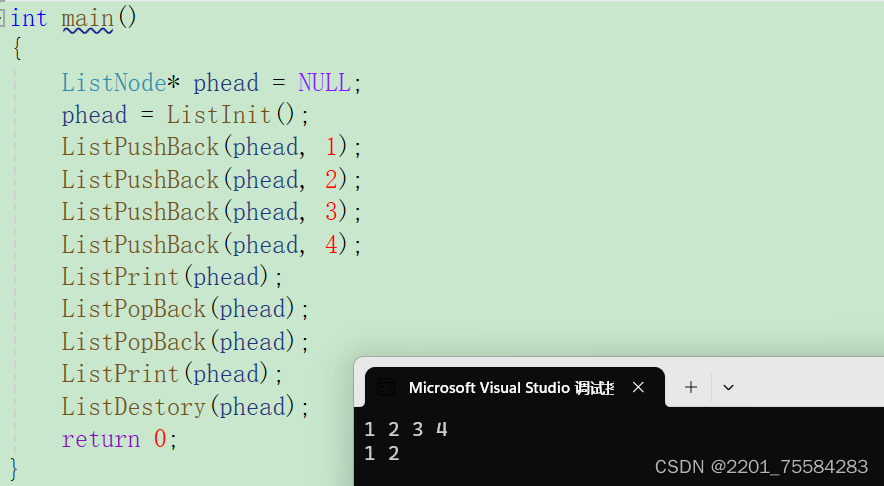
3.6、尾插
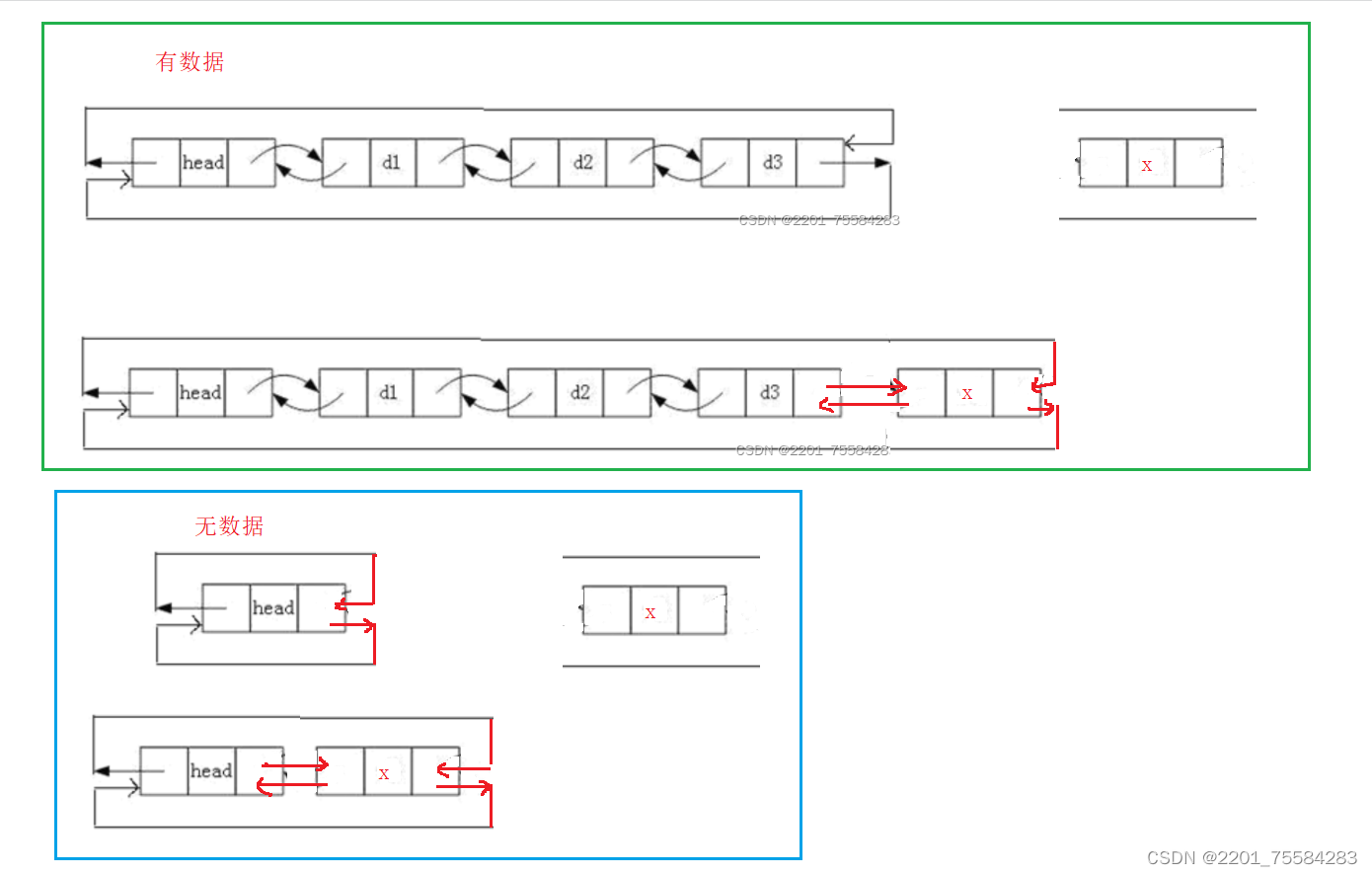
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
//1.创建结点
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;//先找到尾结点
//2.链接next
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
//3.链接prev
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;
}
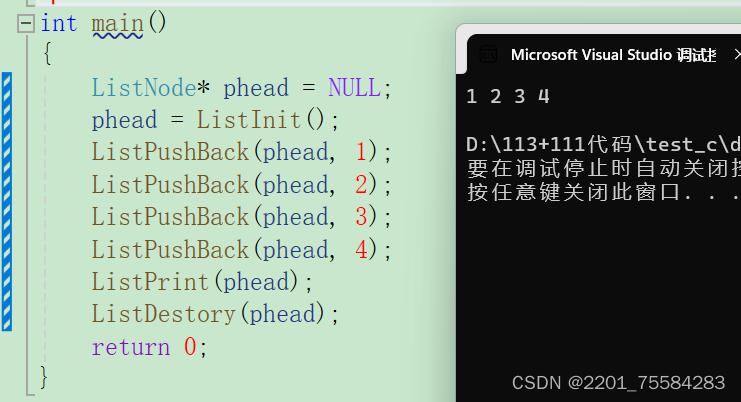
尾插测试
建议养成有初始化函数就有销毁函数的习惯。
3.7、头插
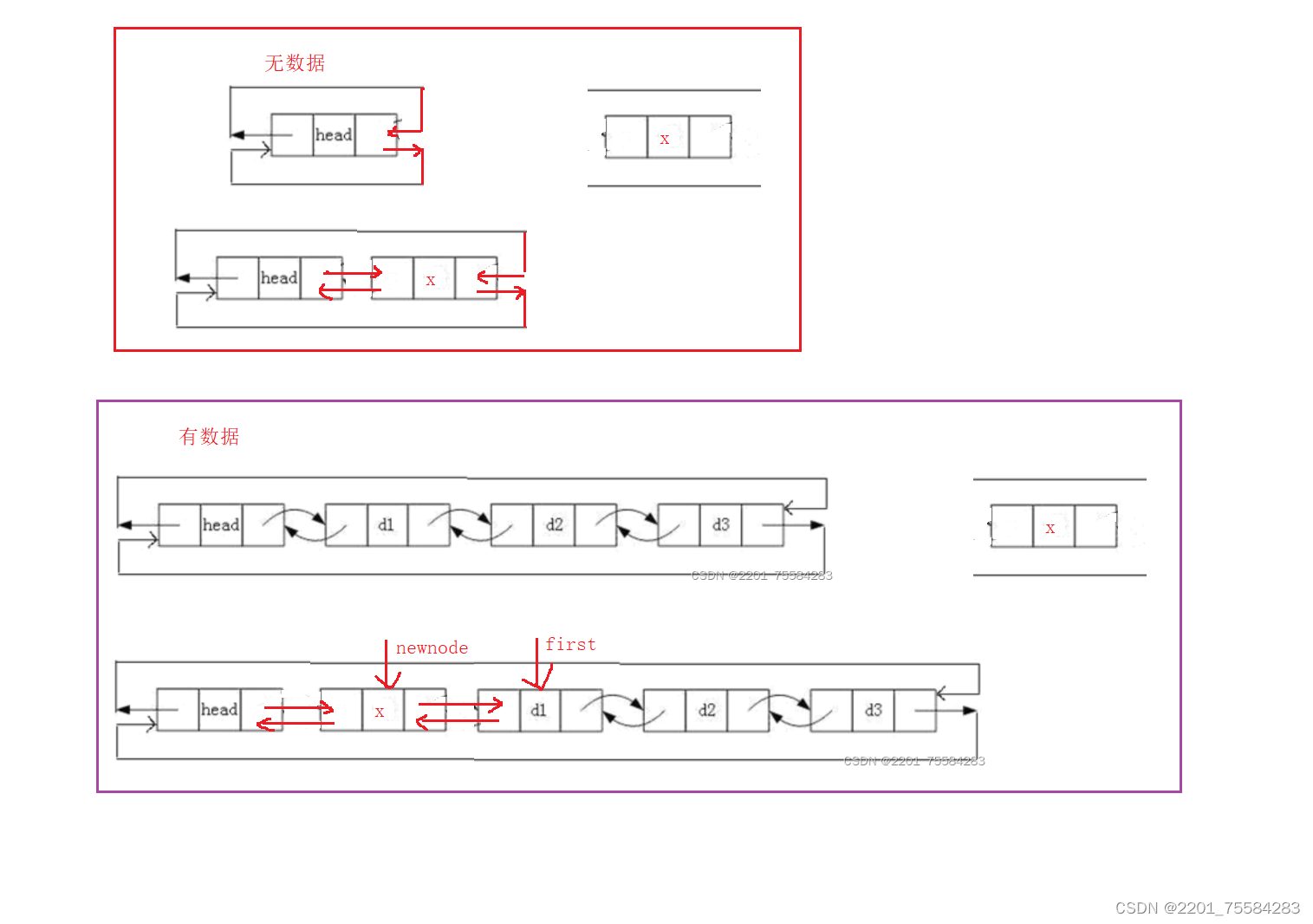
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* first = phead->next;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = first;
first->prev = newnode;
}
头插测试
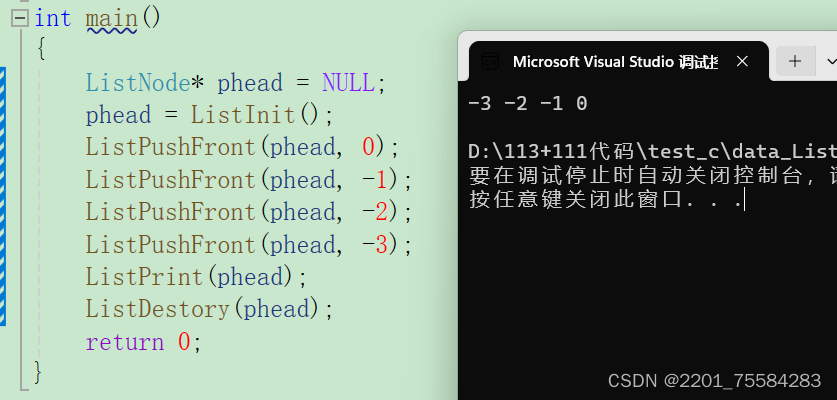
3.8、头删
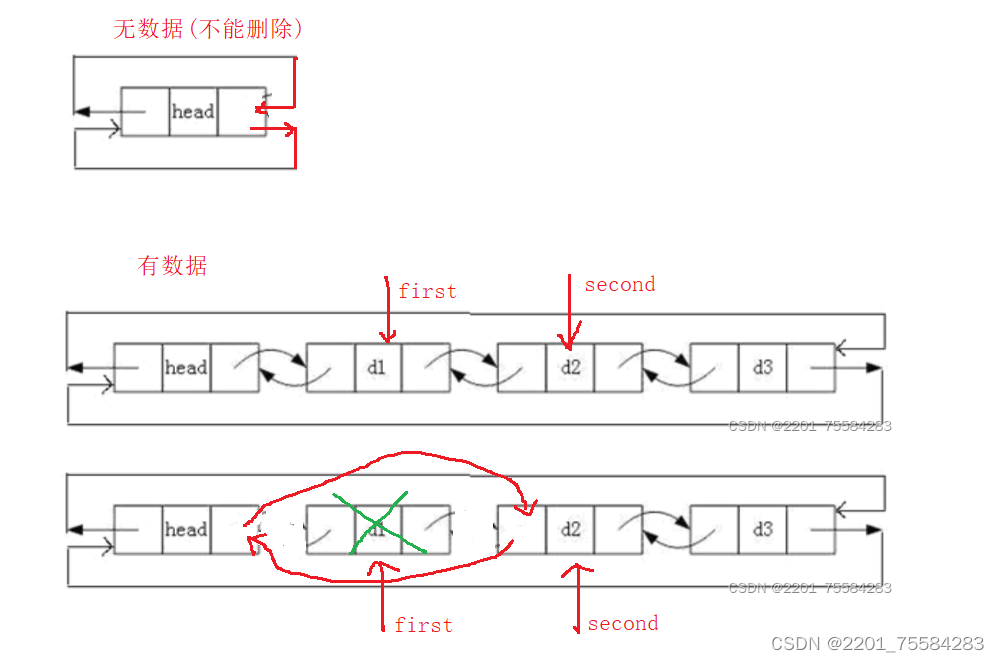
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
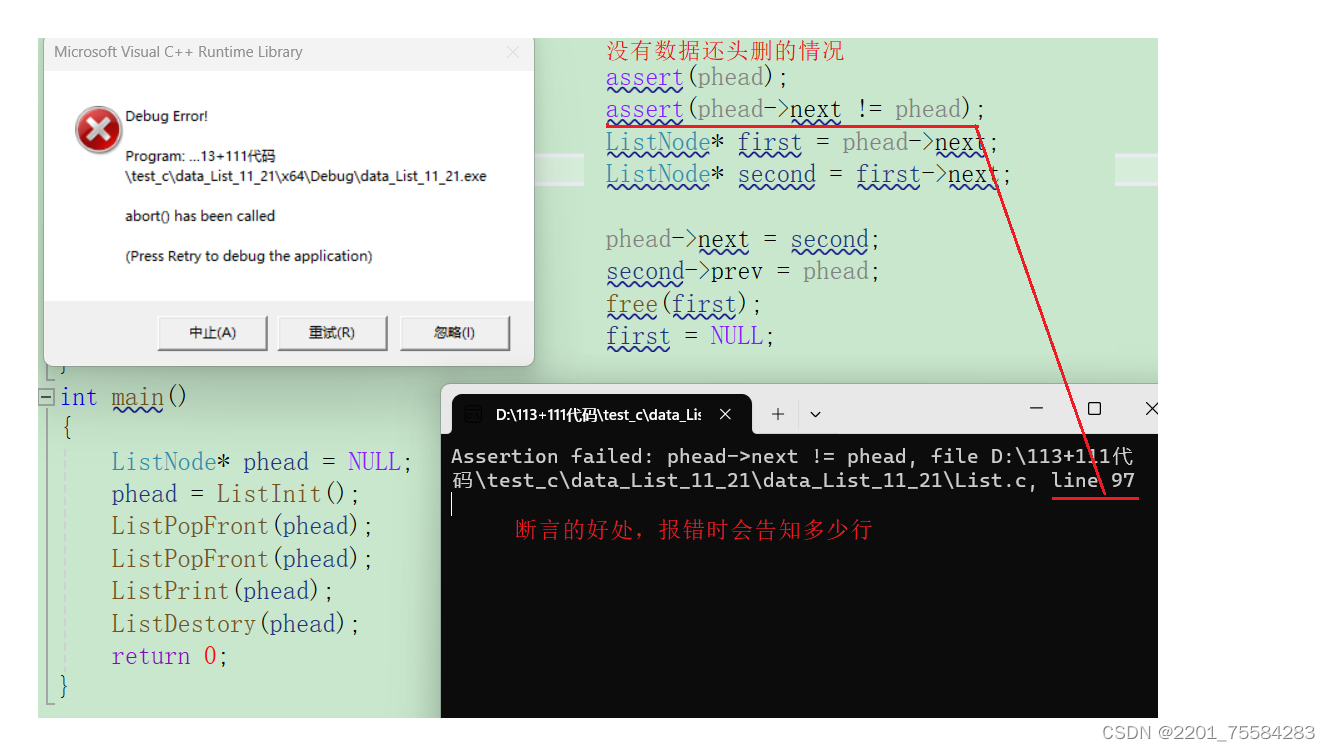
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);//没有数据则报错
ListNode* first = phead->next;
ListNode* second = first->next;
phead->next = second;
second->prev = phead;
free(first);
first = NULL;
}
测试头删

3.9、尾删
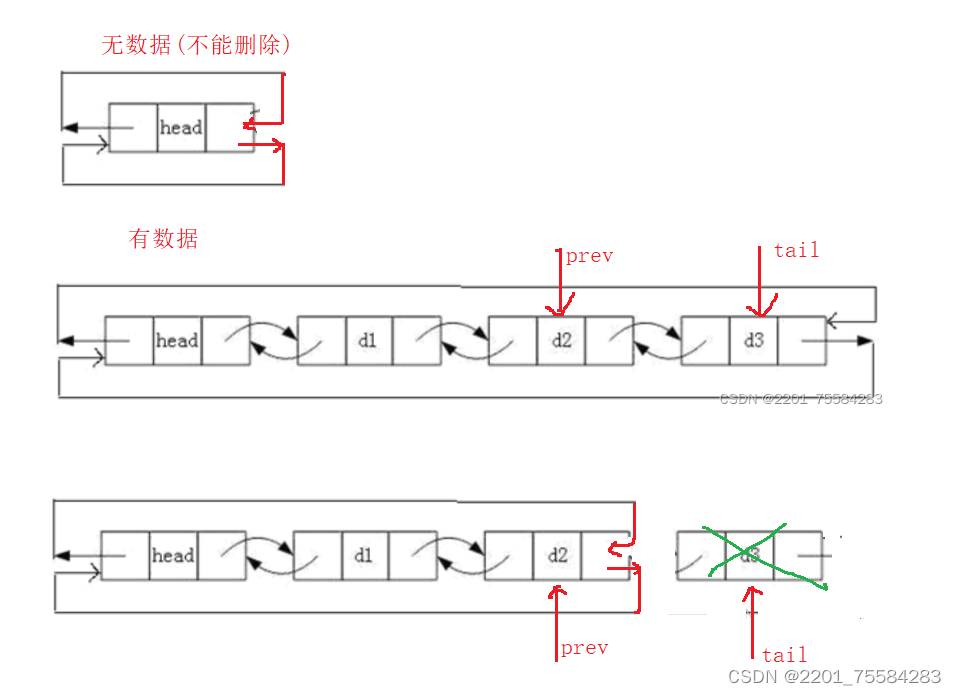
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* prev = tail->prev;
prev->next = phead;
phead->prev = prev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
}
尾删测试
3.10、查找
思想:遍历一遍链表,如果该结点的data等于x则返回该结点的地址,遍历一遍没有找到则返回NULL,跟后面在pos位置插入函数结合起来用。
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
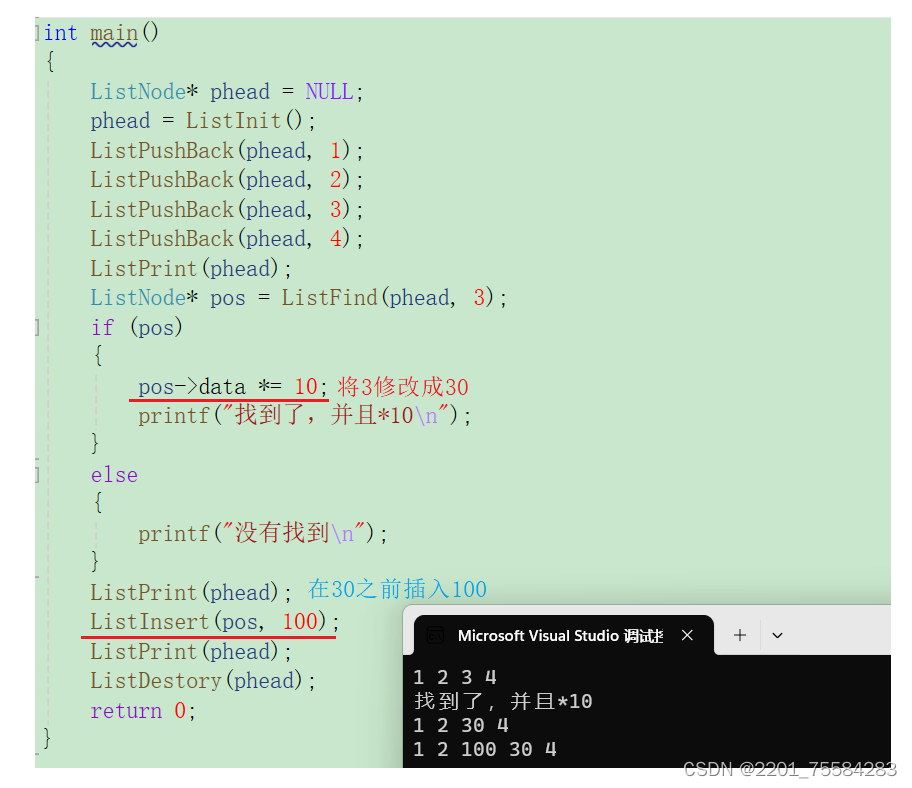
3.11、在pos之前插入
跟头插尾插思想差不多,可以自己画图理解理解喔,如果有不理解的可以私信博主喔!这里就没有画图啦!
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
测试
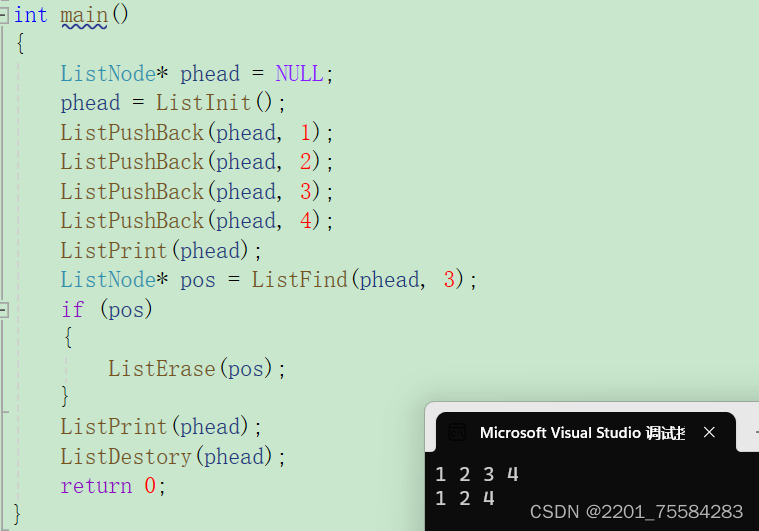
3.12、删除pos位置
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = pos->next;
next->prev = prev;
}
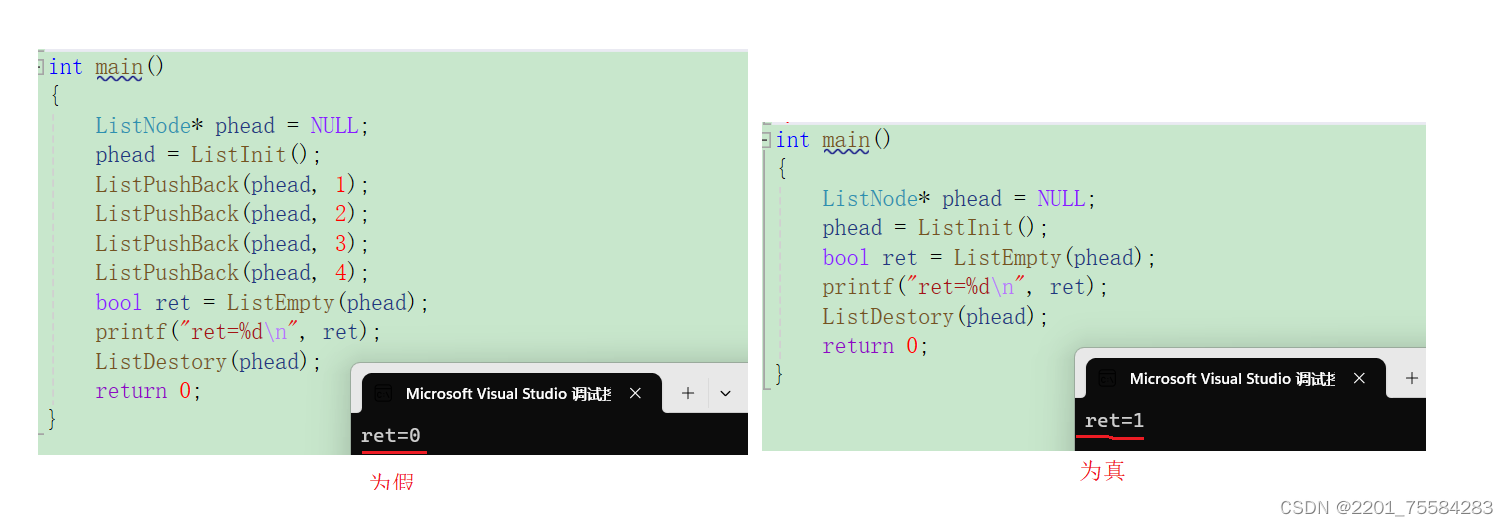
3.13、判断是否为空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;//相等则为真,不相等则为假
}
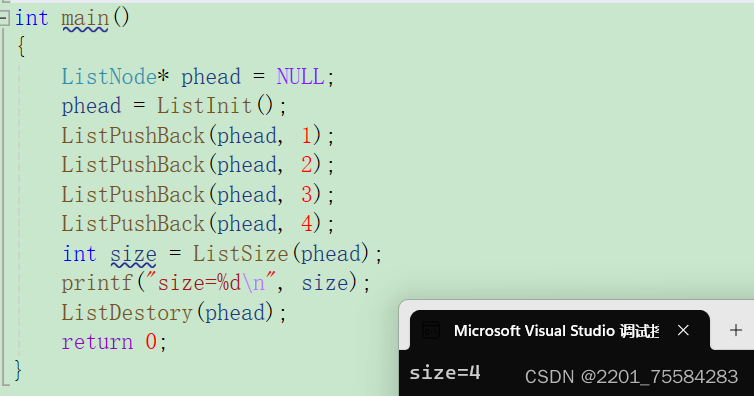
3.14、计算大小
思想:创建一个size变量,从头结点的下一个结点遍历链表,不等于头结点则将size++。
int ListSize(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
int size = 0;
while (cur != phead)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
测试
4、代码汇总
以下是SList.c的代码
//创建结点
ListNode* BuyList(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//初始化
ListNode* ListInit()
{
ListNode* phead = BuyList(0);
phead->next = phead;//构成循环
phead->prev = phead;//构成循环
return phead;
}
//销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;//养成好习惯,释放之后手动置为NULL
}
//尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;
}
//头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* first = phead->next;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = first;
first->prev = newnode;
}
//头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* first = phead->next;
ListNode* second = first->next;
phead->next = second;
second->prev = phead;
free(first);
first = NULL;
}
//尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* prev = tail->prev;
prev->next = phead;
phead->prev = prev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
}
//查找元素为X的地址
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos之前插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = BuyList(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
//删除pos位置
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = pos->next;
next->prev = prev;
}
//判断是否为空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//1.
//if (phead->next == phead)
//{
// return true;
//}
//else
//{
// return false;
//}
//2.
return phead->next == phead;
}
//获取有效数据个数
int ListSize(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
int size = 0;
while (cur != phead)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
总结
本篇博客就结束啦,谢谢大家的观看,如果公主少年们有好的建议可以留言喔,谢谢大家啦!
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2201_75584283/article/details/135298372
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!