Ubuntu18.04使用SCP协议进行文件传输
2023-12-20 19:51:46
Ubuntu18.04使用SCP协议进行文件传输
前言
- 此版代码,相较于Python将已标注的两张图片进行上下拼接并修改、合并其对应的Labelme标注文件,将文件夹批量处理图片和json文件考虑进去,而不是单个图片和json文件。
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- YOLOv8 Ultralytics:使用Ultralytics框架训练RT-DETR实时目标检测模型
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
前提条件
- 熟悉Linux
相关介绍
- Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) 是一种用于在网络上安全传输文件的协议,基于SSH(Secure Shell)协议来传输文件,因此可以保证文件在传输过程中的安全性。它使用SSH加密技术来保证数据在传输过程中的安全性,因此通常需要向远端主机发送凭证才能成功复制数据。
- SCP的优点有:
- 安全性:SCP基于SSH协议,支持数据加密和身份验证,可以保证数据在传输过程中的安全性。
- 简易性:SCP使用单一命令完成传输,操作简单,方便使用。
- 高可靠性:SCP使用校验和防止数据损坏,保证了数据的完整性。
- 强兼容性:SCP适用于几乎所有操作系统,具有很好的兼容性。
- SCP也存在一些缺点:
- 对于大量数据的传输,SCP可能会出现性能问题。
- SCP需要向远端主机发送凭证,如果频繁使用SCP进行文件传输,可能会出现性能瓶颈。
- SCP的详细语法如下:
scp [options] [user@]SRC_HOST:]file1 [user@]DEST_HOST:]file2
- 其中,
[options]是可选项,用于指定SCP命令的参数;[user@]SRC_HOST:]file1表示源文件所在的计算机和文件名;[user@]DEST_HOST:]file2表示目标文件所在的计算机和文件名。- 以下是一些常用的SCP命令选项:
-r:递归复制整个目录。-P:指定端口号。-i:指定用于身份验证的密钥文件。-p:保留文件的权限和时间戳。-v:显示详细输出。
SCP(1) BSD General Commands Manual SCP(1)
NAME
scp — secure copy (remote file copy program)
SYNOPSIS
scp [-346BCpqrTv] [-c cipher] [-F ssh_config] [-i identity_file]
[-l limit] [-o ssh_option] [-P port] [-S program]
[[user@]host1:]file1 ... [[user@]host2:]file2
DESCRIPTION
scp copies files between hosts on a network. It uses ssh(1) for data
transfer, and uses the same authentication and provides the same security
as ssh(1). scp will ask for passwords or passphrases if they are needed
for authentication.
File names may contain a user and host specification to indicate that the
file is to be copied to/from that host. Local file names can be made
explicit using absolute or relative pathnames to avoid scp treating file
names containing ‘:’ as host specifiers. Copies between two remote hosts
are also permitted.
The options are as follows:
-3 Copies between two remote hosts are transferred through the local
host. Without this option the data is copied directly between
the two remote hosts. Note that this option disables the
progress meter.
-4 Forces scp to use IPv4 addresses only.
-6 Forces scp to use IPv6 addresses only.
-B Selects batch mode (prevents asking for passwords or
passphrases).
-C Compression enable. Passes the -C flag to ssh(1) to enable com‐
pression.
-c cipher
Selects the cipher to use for encrypting the data transfer. This
option is directly passed to ssh(1).
-F ssh_config
Specifies an alternative per-user configuration file for ssh.
This option is directly passed to ssh(1).
-i identity_file
Selects the file from which the identity (private key) for public
key authentication is read. This option is directly passed to
ssh(1).
-l limit
Limits the used bandwidth, specified in Kbit/s.
-o ssh_option
Can be used to pass options to ssh in the format used in
ssh_config(5). This is useful for specifying options for which
there is no separate scp command-line flag. For full details of
the options listed below, and their possible values, see
ssh_config(5).
AddressFamily
BatchMode
BindAddress
CanonicalDomains
CanonicalizeFallbackLocal
CanonicalizeHostname
CanonicalizeMaxDots
CanonicalizePermittedCNAMEs
CertificateFile
ChallengeResponseAuthentication
CheckHostIP
Ciphers
Compression
ConnectionAttempts
ConnectTimeout
ControlMaster
ControlPath
ControlPersist
GlobalKnownHostsFile
GSSAPIAuthentication
GSSAPIDelegateCredentials
HashKnownHosts
Host
HostbasedAuthentication
HostbasedKeyTypes
HostKeyAlgorithms
HostKeyAlias
HostName
IdentitiesOnly
IdentityAgent
IdentityFile
IPQoS
KbdInteractiveAuthentication
KbdInteractiveDevices
KexAlgorithms
LogLevel
MACs
NoHostAuthenticationForLocalhost
NumberOfPasswordPrompts
PasswordAuthentication
PKCS11Provider
Port
PreferredAuthentications
ProxyCommand
ProxyJump
PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes
PubkeyAuthentication
RekeyLimit
SendEnv
ServerAliveInterval
ServerAliveCountMax
StrictHostKeyChecking
TCPKeepAlive
UpdateHostKeys
UsePrivilegedPort
User
UserKnownHostsFile
VerifyHostKeyDNS
-P port
Specifies the port to connect to on the remote host. Note that
this option is written with a capital ‘P’, because -p is already
reserved for preserving the times and modes of the file.
-p Preserves modification times, access times, and modes from the
original file.
-q Quiet mode: disables the progress meter as well as warning and
diagnostic messages from ssh(1).
-r Recursively copy entire directories. Note that scp follows sym‐
bolic links encountered in the tree traversal.
-S program
Name of program to use for the encrypted connection. The program
must understand ssh(1) options.
-T Disable strict filename checking. By default when copying files
from a remote host to a local directory scp checks that the
received filenames match those requested on the command-line to
prevent the remote end from sending unexpected or unwanted files.
Because of differences in how various operating systems and
shells interpret filename wildcards, these checks may cause
wanted files to be rejected. This option disables these checks
at the expense of fully trusting that the server will not send
unexpected filenames.
-v Verbose mode. Causes scp and ssh(1) to print debugging messages
about their progress. This is helpful in debugging connection,
authentication, and configuration problems.
EXIT STATUS
The scp utility exits 0 on success, and >0 if an error occurs.
SEE ALSO
sftp(1), ssh(1), ssh-add(1), ssh-agent(1), ssh-keygen(1), ssh_config(5),
sshd(8)
HISTORY
scp is based on the rcp program in BSD source code from the Regents of
the University of California.
AUTHORS
Timo Rinne <tri@iki.fi>
Tatu Ylonen <ylo@cs.hut.fi>
BSD May 3, 2017 BSD
实验环境
- Ubuntu 18.04
使用SCP协议进行文件传输
scp [options] [user@]SRC_HOST:]file1 [user@]DEST_HOST:]file2
- 其中,
[options]是可选项,用于指定SCP命令的参数;[user@]SRC_HOST:]file1表示源文件所在的计算机和文件名;[user@]DEST_HOST:]file2表示目标文件所在的计算机和文件名。- 以下是一些常用的SCP命令选项:
-r:递归复制整个目录。-P:指定端口号。-i:指定用于身份验证的密钥文件。-p:保留文件的权限和时间戳。-v:显示详细输出。
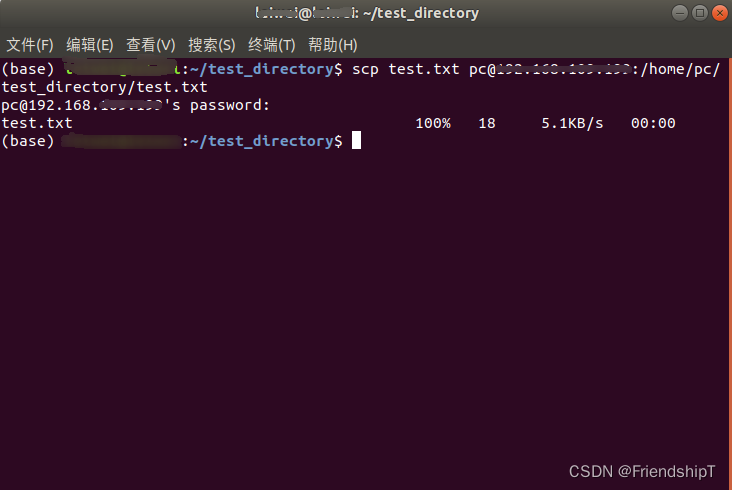
从本地主机将文件传输到目标主机
scp [本地文件的路径] [目标主机用户名]@[目标主机ip地址]:[目标主机上存放文件的路径]
scp test.txt user@DEST_HOST:/home/user/test_directory
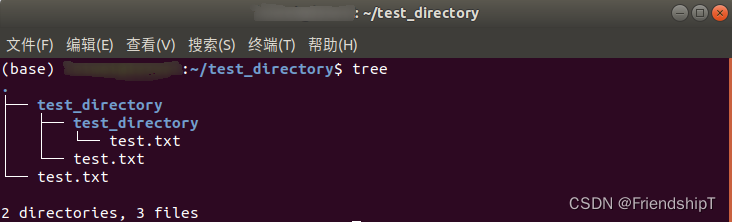
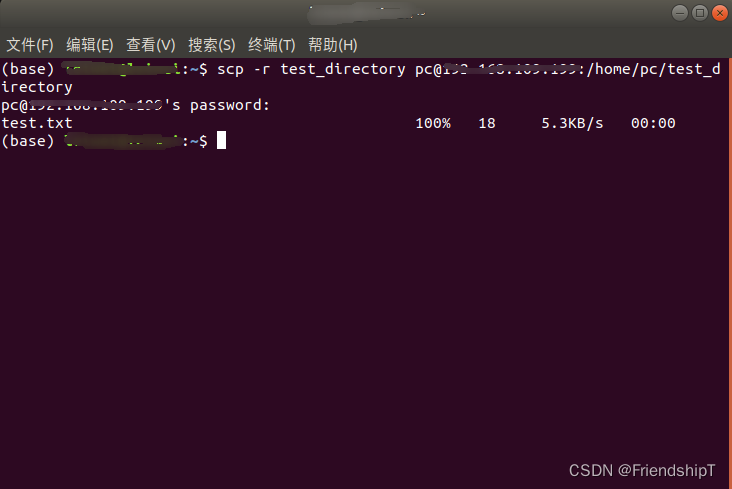
从本地主机将文件夹传输到目标主机
scp -r [本地文件夹的路径] [目标主机用户名]@[目标主机ip地址]:[目标主机上存放文件的路径]
scp -r test_directory user@DEST_HOST:/home/user/test_directory
将目标主机上的文件传输到本地主机
scp [目标主机用户名]@[目标主机ip地址]:[目标主机上存放文件的路径] [本地主机上存放文件的路径]
scp user@DEST_HOST:/home/user/test_directory/test.txt test.txt
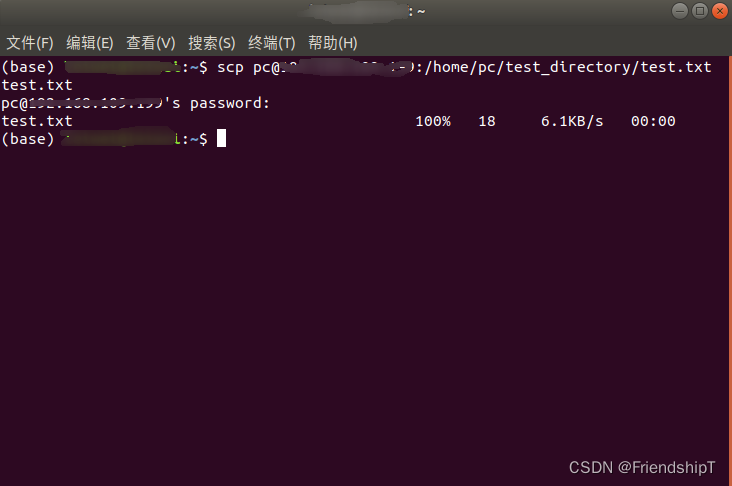
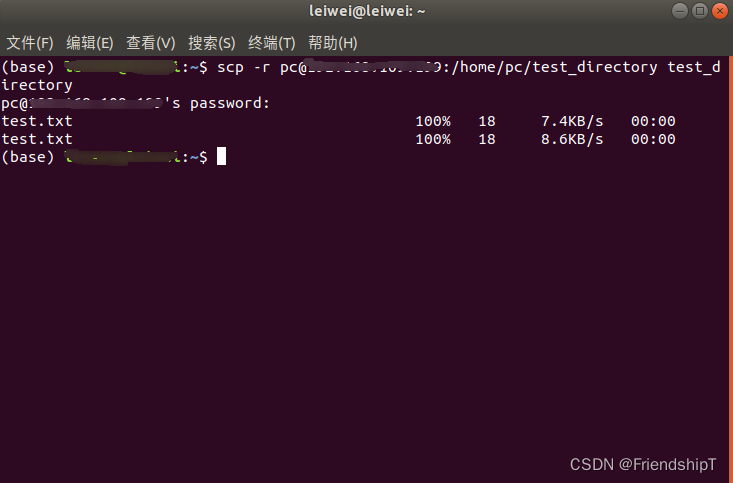
将目标主机上的文件夹传输到本地主机
scp -r [目标主机用户名]@[目标主机ip地址]:[目标主机上存放文件的路径] [本地主机上存放文件的路径]
scp -r user@DEST_HOST:/home/user/test_directory test_directory
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- YOLOv8 Ultralytics:使用Ultralytics框架训练RT-DETR实时目标检测模型
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/FriendshipTang/article/details/135111031
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!