[嵌入式AI从0开始到入土]9_yolov5在昇腾上推理
[嵌入式AI从0开始到入土]嵌入式AI系列教程
注:等我摸完鱼再把链接补上
可以关注我的B站号工具人呵呵的个人空间,后期会考虑出视频教程,务必催更,以防我变身鸽王。
第一章 昇腾Altas 200 DK上手
第二章 下载昇腾案例并运行
第三章 官方模型适配工具使用
第四章 炼丹炉的搭建(基于Ubuntu23.04 Desktop)
第五章 Ubuntu远程桌面配置
第六章 下载yolo源码及样例运行验证
第七章 转化为昇腾支持的om离线模型
第八章 jupyter lab的使用
第九章 yolov5在昇腾上推理
未完待续…
前言
注:本人代码在pc机上完成编写,运行需要昇腾推理卡或者开发者套件
先说下我的环境,pc机是ubuntu23.04,CANN版本7.0.0.alpha001,mindx版本5.0.RC3。Atlas 200 DK上CANN版本5.1.RC2.alpha007,mindx版本3.0.0。务必注意版本兼容性问题
别问我为什么鸽了这么久,不信你就跳过第一节!!!
一、环境准备
1、确认驱动版本
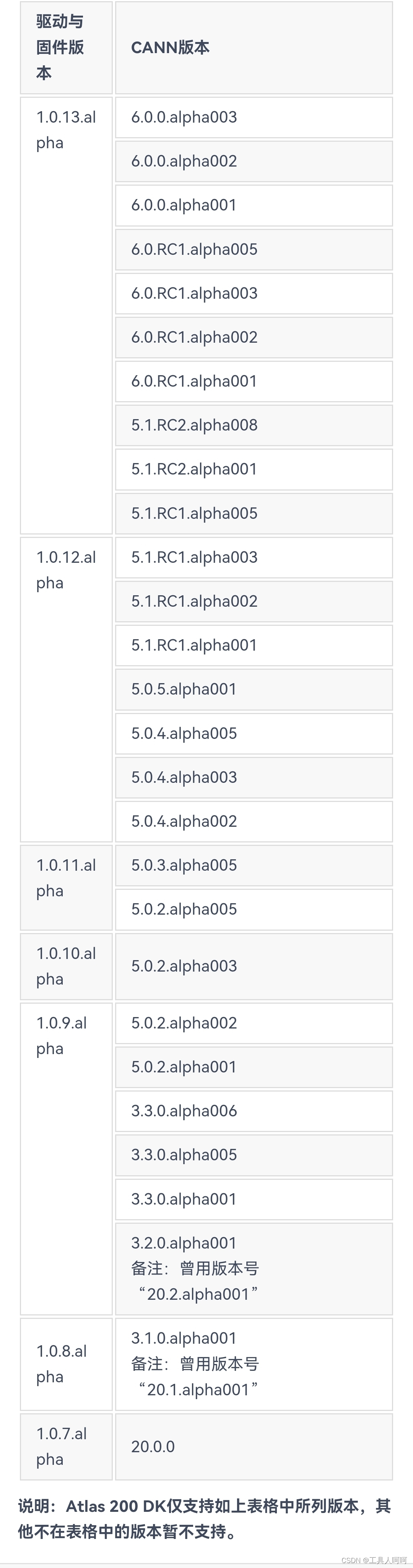
如下图所示,为200DK的驱动和CANN的对照表,需严格按照图中所写版本进行安装,否则运行报错。
关于驱动版本的查看,使用npu-smi info,version后的数字对应版本,但没找到具体对应关系。目前我只确定200DK官方制卡工具提供的镜像是最新的1.0.13.alpha的驱动,也就是version:21.0.4。
似乎200i A2需要使用CANN6.2,一般就是镜像自带的。
2、CANN安装
如果版本符合要求,直接跳过,否则需要重新安装。这个不在重复,看往期文章就可以了。下载地址点这里。社区版,记得添加硬件信息,不然找不到对应的版本。
注意一点,下载aarch64的,别下成x86_64的就行。
3、Mindx sdk安装
我们需要的是mxVision,另外两个现在暂时用不上
这里我卡了好久,后来才查到也需要安装当前CANN匹配的Mindx。具体对照表没查到,根据论坛和我个人的测试,6.2或者6.3的cann应该安装5.0的mindx,6.0.0或者5.1应该是3.0mindx。
下载地址放在这,我使用镜像自带的5.1cann和3.0.0mindx测试通过。
注意:因为安装mindx的时候会复制算子到cann的文件夹内,所以需要先装cann再装mindx,即使是升降级版本
二、新建项目
这是我的项目结构,项目也已经上传,在本文最上方的绑定资源中。没找到点这里跳转。
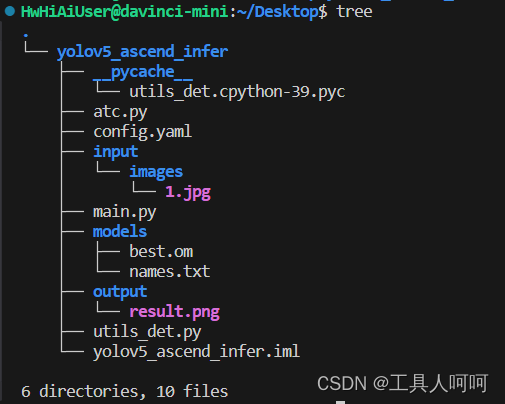
这里atc虽然在里面,但是我们已经转换了模型,所以不再解析了。
1、input
这里我使用了一个images的文件夹用来存放需要检测的图片。正常的jpg图片都可以,但是需要图中有你数据集中的类(我这用的coco128的数据集,支持的物体还是很多的)。
2、models
这里负责存放模型文件和类别名称。names.txt格式如下
person
bicycle
car
motorcycle
airplane
......
3、output
存放输出的结果
4、utils_det.py
主要是模型的前后处理函数,内容如下
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
# Resize image to a 32-pixel-multiple rectangle https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 64), np.mod(dh, 64) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detections
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
device = prediction.device
mps = 'mps' in device.type # Apple MPS
if mps: # MPS not fully supported yet, convert tensors to CPU before NMS
prediction = prediction.cpu()
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
max_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 0.5 + 0.05 * bs # seconds to quit after
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
t = time.time()
mi = 5 + nc # mask start index
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # zero columns if no masks
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 5 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
else:
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
output[xi] = x[i]
if mps:
output[xi] = output[xi].to(device)
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING ?? NMS time limit {time_limit:.3f}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def get_labels_from_txt(path):
labels_dict = dict()
with open(path) as f:
for cat_id, label in enumerate(f.readlines()):
labels_dict[cat_id] = label.strip()
return labels_dict
def scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
coords[:, :4] /= gain
clip_coords(coords, img0_shape)
return coords
def clip_coords(boxes, shape):
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def nms(box_out, conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.5):
try:
boxout = non_max_suppression(box_out, conf_thres=conf_thres, iou_thres=iou_thres, multi_label=True)
except:
boxout = non_max_suppression(box_out, conf_thres=conf_thres, iou_thres=iou_thres)
return boxout
def draw_bbox(bbox, img0, color, wt, names):
det_result_str = ''
for idx, class_id in enumerate(bbox[:, 5]):
if float(bbox[idx][4] < float(0.05)):
continue
img0 = cv2.rectangle(img0, (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1])), (int(bbox[idx][2]), int(bbox[idx][3])), color, wt)
img0 = cv2.putText(img0, str(idx) + ' ' + names[int(class_id)], (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] + 16)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)
img0 = cv2.putText(img0, '{:.4f}'.format(bbox[idx][4]), (int(bbox[idx][0]), int(bbox[idx][1] + 32)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)
det_result_str += '{} {} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(names[bbox[idx][5]], str(bbox[idx][4]), bbox[idx][0], bbox[idx][1], bbox[idx][2], bbox[idx][3])
return img0
5、main.py
这里也是卡了我好几天,mindx.sdk那两行ide一直在报错,但似乎能跑。
import cv2 # 图片处理三方库,用于对图片进行前后处理
import numpy as np # 用于对多维数组进行计算
import torch # 深度学习运算框架,此处主要用来处理数据
from mindx.sdk import Tensor # mxVision 中的 Tensor 数据结构
from mindx.sdk import base # mxVision 推理接口
from utils_det import get_labels_from_txt, letterbox, scale_coords, nms, draw_bbox # 模型前后处理相关函数
# 初始化资源和变量
base.mx_init() # 初始化 mxVision 资源
DEVICE_ID = 0 # 设备id
model_path = 'models/best.om' # 模型路径
image_path = 'input/images/1.jpg' # 测试图片路径
# 数据前处理
img_bgr = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # 读入图片
img, scale_ratio, pad_size = letterbox(img_bgr, new_shape=[640, 640]) # 对图像进行缩放与填充,保持长宽比
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, HWC to CHW
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0).astype(np.float16) # 将形状转换为 channel first (1, 3, 640, 640),即扩展第一维为 batchsize
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) / 255.0 # 转换为内存连续存储的数组
img = Tensor(img) # 将numpy转为转为Tensor类
# 模型推理, 得到模型输出
model = base.model(modelPath=model_path, deviceId=DEVICE_ID) # 初始化 base.model 类
output = model.infer([img])[0] # 执行推理。输入数据类型:List[base.Tensor], 返回模型推理输出的 List[base.Tensor]
# 后处理
output.to_host() # 将 Tensor 数据转移到内存
output = np.array(output) # 将数据转为 numpy array 类型
boxout = nms(torch.tensor(output), conf_thres=0.4, iou_thres=0.5) # 利用非极大值抑制处理模型输出,conf_thres 为置信度阈值,iou_thres 为iou阈值
pred_all = boxout[0].numpy() # 转换为numpy数组
scale_coords([640, 640], pred_all[:, :4], img_bgr.shape, ratio_pad=(scale_ratio, pad_size)) # 将推理结果缩放到原始图片大小
labels_dict = get_labels_from_txt('models/names.txt') # 得到类别信息,返回序号与类别对应的字典
img_dw = draw_bbox(pred_all, img_bgr, (0, 255, 0), 2, labels_dict) # 画出检测框、类别、概率
# 保存图片到文件
cv2.imwrite('output/result.png', img_dw)
print('save infer result success')
三、运行
很简单,但是务必注意,200DK默认的python是2.7.17,而镜像中配置的是python3.9.7,我们的包也是安装到python3里的。当然,你可以直接做软连接,具体方便请自行搜索。
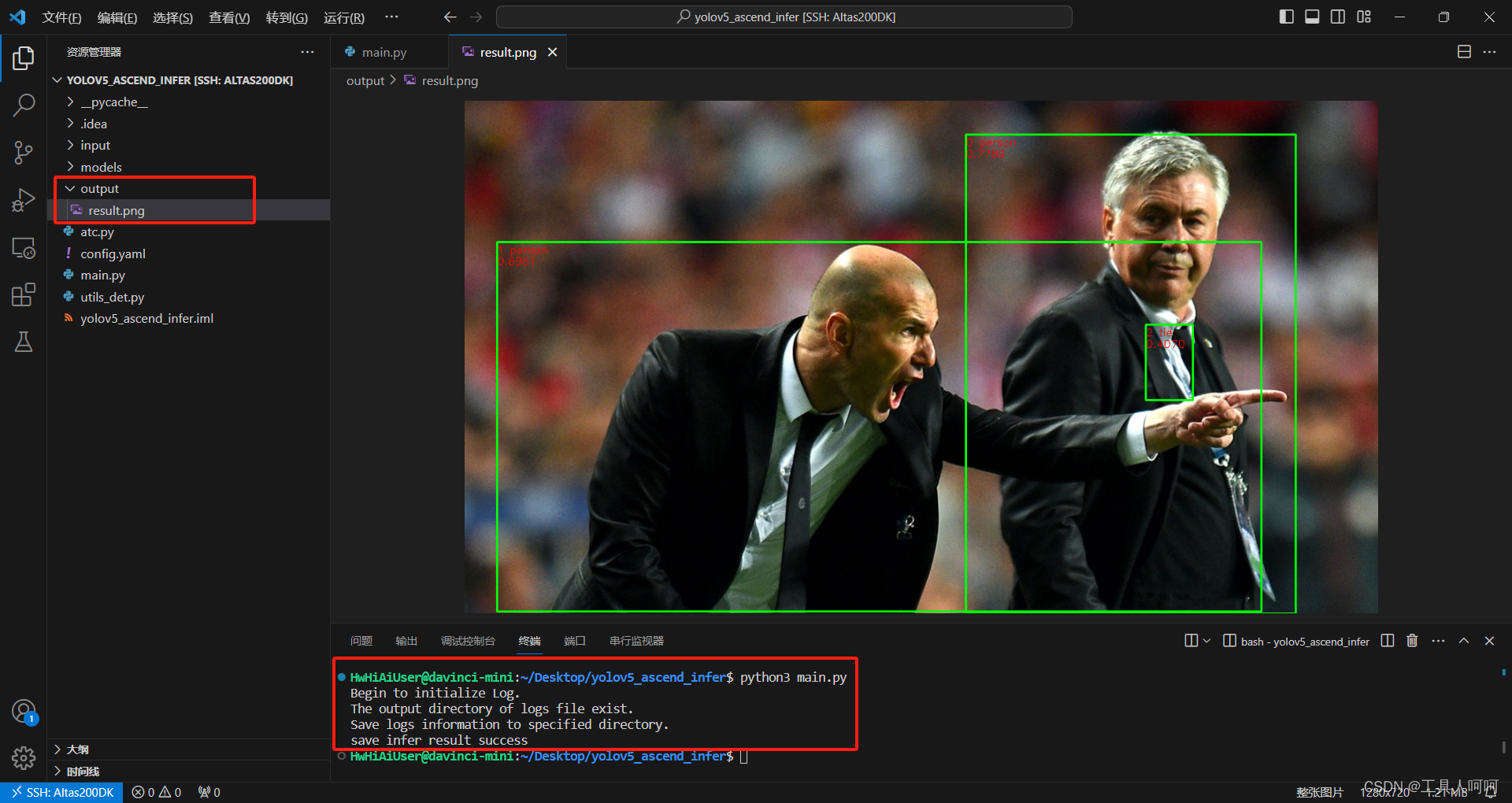
python3 main.py
运行成功会有如图所示的提示
四、IDE
这里我必须狠狠的压力一下华为,mindstudio竟然不支持打开远程ssh的工程,甚至选了远程的python,还读取不到pip软件包。
这里pycharm虽然可以远程,包也读取正常,但是运行代码后似乎不会同步结果到本地。当然,你愿意的话可以远程打开工程,当然,没记错的话这个是收费的功能。
所以,那肯定得掏出我们祖传多年的vscode啦。我们只需要安装Remote-SSH这个插件,然后添加如下配置
Host Altas200DK
HostName 192.168.3.2
User HwHiAiUser
点击连接,然后安装python扩展,即可开始愉快的敲代码啦!
五、问题
1、No module named cv2
首先确认安装,使用pip list命令查询是否有opencv-python和opencv-python-headless。如果存在,请检查你的运行main.py的python版本是否是这个pip列出包的这个环境。在200DK上就需要使用python3而不是python。
如果不存在,使用这个命令安装opencv。
pip install opencv-python
之后重复以上动作。
2、No module named mindx
在mindx sdk的安装目录下找到这个包,pip安装即可。
pip install mindx-5.0rc3-py3-none-any.whl
3、undefined symbol: aclrtCreateStreamWithConfig
这大概率就是mindx和cann版本不匹配导致的。更换匹配的版本即可。
4、AttributeError: ‘NoneType’ object has no attribute ’ infer ’
请检查模型路径是否正确,没错,我承认我真的没看见路径错了,花了两天去怀疑环境有问题,甚至重新制卡了。
另外,没有昇腾的推理卡也会报这个错误。可以使用npu-smi info来查看推理卡是否正常被识别。
5、libpython3.9.so.1.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
这个问题会在安装mindx的时候出现,请务必注意。解决方法如下:
将Python安装路径下的libpython3.9.so.1.0对象(我的在/usr/local/python3.9.7/lib/下),复制到“/usr/lib”下。
6、libxxx.so :cannot open shared object file
这里可能是类似libadump_server.so这种的,其他运行库都一样的操作。
- 搜索这个文件,发现在
ascend-toolkit/latest/x86_64-linux/lib64下面。 - 添加路径至环境变量
.bashrc发现还是找不到 - 执行
vim /etc/ld.so.conf,如果不能保存的话使用sudo提权 - 在最下面加入这个共享库的绝对路径,例如
/home/ai/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/latest/x86_64-linux/lib64 - 执行
ldconfig更新共享库路径 - 问题解决
总结
这个案例基本就是按照华为官方文档里写的改的,但他那个案例似乎下载不了。目前推理好像有点慢,应该是在前后处理耗时比较长,大家可以自行对前后处理函数做优化。或者直接换成c++的版本,性能会有所提高,但我是废物[大哭],根本看不懂。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!