代理和AOP
一:java代理
整体分为两种:静态代理和动态代理
静态代理:23种设计模式里面有个代理模式,那个就是静态代理。
动态代理:分为编译时增强(AspectJ)和运行时增强(JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理)
1:静态代理
???这种代理在我们日常生活中其实非常常见,例如房屋中介就相当于是一个代理,当房东需要出租房子的时候,需要发布广告、寻找客户、清理房间。。。由于比较麻烦,因此房东可以将租房子这件事情委托给中间代理去做。这就是一个静态代理。我通过一个简单的代码来演示一下,首先我们有一个租房的接口,如下:
public interface Rent {
void rent();
}
房东实现了该接口,想要出租房屋:
/**
* 房东
*/
public class Loadlord implements Rent{
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房屋出租");
}
}
中介作为中间代理,也实现了该接口,同时代理了房东,如下:
public class HouseAgent implements Rent{
private Loadlord loadlord;
public HouseAgent(Loadlord loadlord) {
this.loadlord = loadlord;
}
@Override
public void rent() {
published();
loadlord.rent();
agentFee();
}
private void published(){
System.out.println("发布广告");
}
private void agentFee(){
System.out.println("收取中介费");
}
}
可以看到,中介的 rent 方法中,除了调用房东的rent方法之外,还调用了 publishAd 和agencyFee两个方法。
接下来客户租房,只需要和代理打交道就行。如下:
/**
* 静态代理demo
*/
public class StaticDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HouseAgent houseAgent = new HouseAgent(new Loadlord());
houseAgent.rent();
//输出:发布广告
// 房屋出租
// 收取中介费
}
}
这就是简单的代理模式。
2:动态代理
????动态代理讲究在不改变原类原方法的情况下,增强目标方法的功能,例如,大家平时使用的Spring 事务功能,在不改变目标方法的情况下,就可以通过动态代理为方法添加事务处理能力。日志处理、接口幂等性处理、多数据源处理等,都是动态代理能力的体现。
例如,我有一个转账的业务:
public class MoneyService{
public void transferMoney(){
System.out.println("执行转账操作");
}
}
如果通过动态代理来为上面的业务代码添加事务,那么我们只需要做一些配置,系统会自动生成动态代理的类和方法:
public class MoneyServiceProxy{
public void transferMoney() {
try {
//开启事务
//执行事务
//提交事务
}catch (Exception e){
//回滚事务
}
}
}
上面这个是自动生成的代理类,不需要开发者开发。
从实现原理上来看又分为两类:编译时增强,运行时增强。
2.1:编译时增强
????编译时增强,这种有点类似于 Lombok的感觉,就是在编译阶段就直接生成了代理类,将来运行的时候,就直接运行这个编译生成的代理类,AspectJ就是这样一种编译时增强的工具。
????AspectJ 全称是 Eclipse AspectJ,其官网地址是:http://www.eclipse.or g/aspectj ,截止到本文写作时,目前最新版本为:1.9.7。从官网我们可以看到AspectJ的定位:
- 基于 Java 语言的面向切面编程语言
- 兼容 Java。
- 易学易用。
使用 AspectJ 时需要使用专门的编译器ajc。
编译时增强配置:
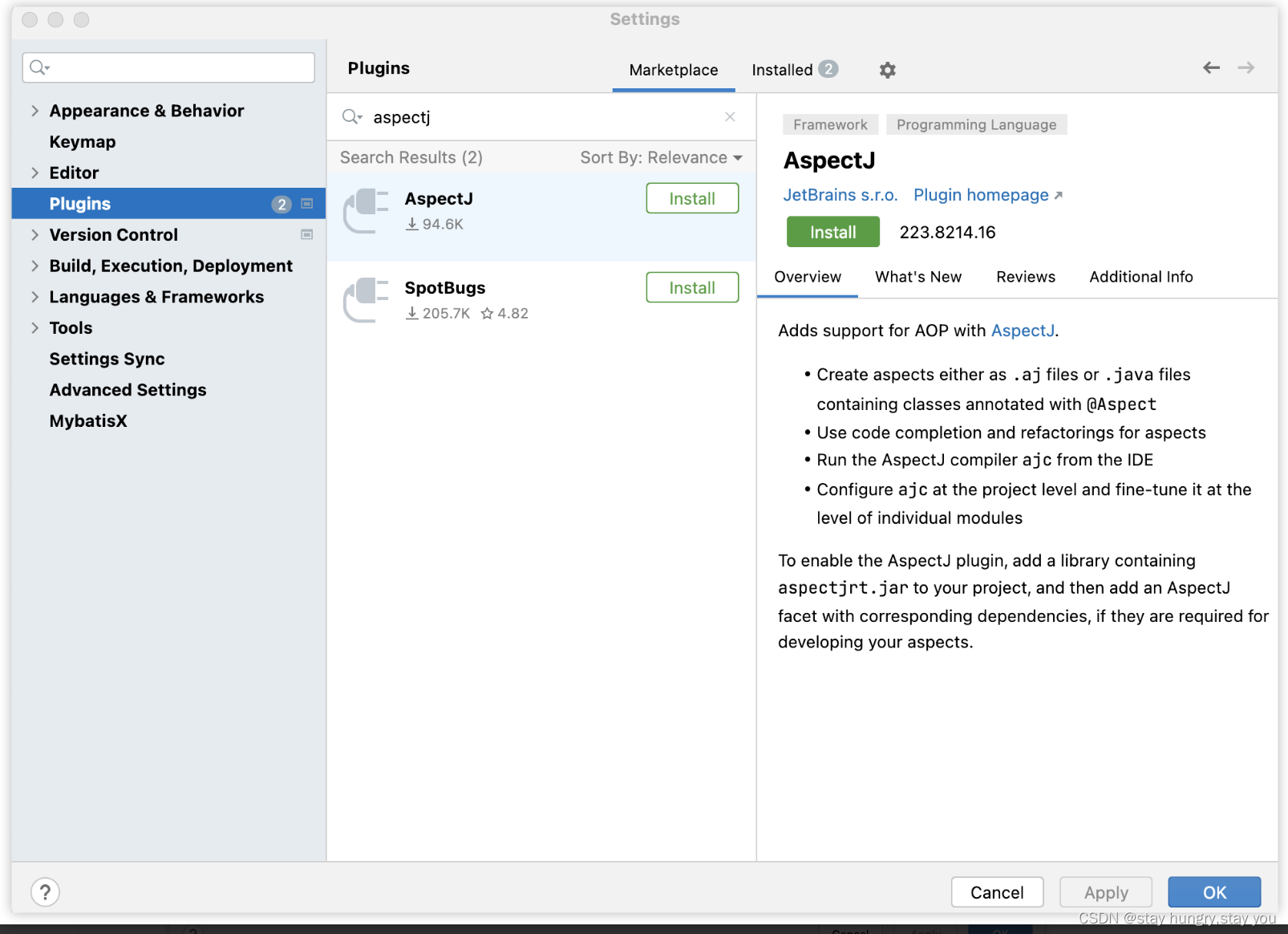
???? 首先在idea里面运行AspectJ,需要先安装AspectJ插件,如下:
安装好之后我们需要在idea中配置一下,使用ajc编译器代替javac:
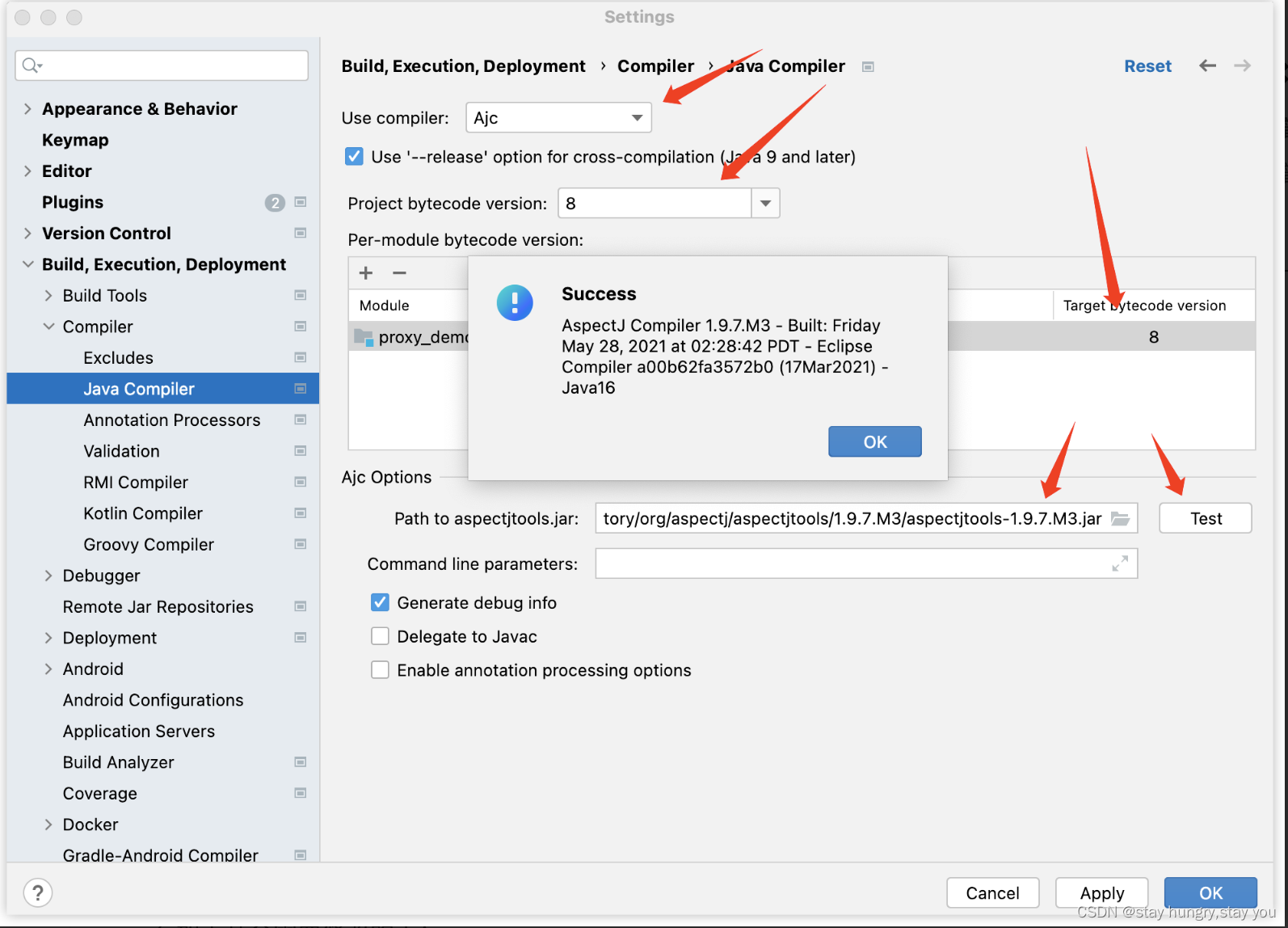
有如下几个需要修改的点:
- 首先修改编译器为ajc。
- 将使用的 Java 版本改为8,这个一共有两个地方需要修改。
- 设置 aspectjtools.jar 的位置,这个jar 包需要自己提前准备好,可以从Maven 官网下载,然后在这里配置jar的路径,配置完成之后,点击test 按钮进行测试,测试成功就会弹出来图中的弹框。
对于第 3 步所需要的jar,也可以在项目的Maven中添加如下依赖,自动下载,下载到本地仓库之后,再删除掉 pom.xml 中的配置即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjtools</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7.M3</version>
</dependency>
这样开发环境就准备好了。
接下来,假设我有一个银行转帐的方法:
public class MoneyService {
public void transferMoney(){
System.out.println("转账操作");
}
}
我想给这个操作添加事务,那么我就添加一个Aspect,如下:
public aspect TxAspect {
void around( ):call(void MoneyService.transferMoney()){
System.out.println("开启事务");
try{
proceed();
System.out.println("提交事务事务");
} catch (Exception e){
System,out.println("回滚事务");
}
}
}
这就是 AspectJ的语法,跟Java有点像,但是不太一样。需要注意的是,这个 TxAspect 不是一个 Java类,它的后缀是.aj。
proceed 表示继续执行目标方法,前后逻辑比较简单,我就不多说了。
最后我们去运行转帐服务:
public class Demo01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MoneyService moneyService = new MoneyService();
moneyService.transferMoney();
}
}
运行结果如下:

这就是一个静态代理
实际编译后底层代码如下(所以代码包括main方法也变了):

最后执行的都是修改之后的内容。所以说 AspectJ的作用就有点类似于Lombok,直接在编译时期将我们的代码改了,这就是编译时增强。
2.2:运行时增强
????运行时增强则是指借助于JDK动态代理或者 CGLIB 动态代理等,在内存中临时生成 AOP 动态代理类,我们在Spring AOP 中常说的动态代理,一般是指这种运行时增强。
我们平日开发写的Spring AOP,基本上都是属于这一类。
1:JDK动态代理
????这个代理有一个要求就是,被代理的对象必须要有一个接口,没有接口不行。但是CGLIB没有这个要求。
假如我有一个计算机接口:
public interface ICalculator {
int add(int a,int b);
}
这个接口有个实现类:
public class CalculatorImpl implements ICalculator{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("a+b最终输出:"+(a+b));
return a+b;
}
}
现在我想实现统计该接口执行时间的功能,JDK动态代理如下:
public class Demo2 {
/**
*
*
* 下面生成的 calculator 是一个代理对象,注意,这个 calculator 对象并不是 CalculatorImpl 的对象
*
* 相当于,在代码运行的过程中,自动生成了一个代理类:
*
* public CalculatorProxy implements ICalculator{
* int add(int a,int b){
* long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
* //这个地方调用了 CalculatorImpl 类的实例的 add 方法,去执行了真正的 add 操作
* long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
* System.out.println(method.getName() + " 方法执行耗时 " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
* return invoke;
* }
* }
*
* 最后,我们调用 calculator.add 方法的时候,其实执行的是这个代理的对象的 add 方法
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
CalculatorImpl calculatorImpl = new CalculatorImpl();
//第二个参数表示生成的代理对象要实现哪些接口
ICalculator calculator = (ICalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Demo2.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{ICalculator.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* @param proxy 当前代理对象
* @param method 被拦截下来的方法
* @param args 被拦截下来的方法参数
*
* @return 被拦截下来的方法的返回值
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object invoke = method.invoke(calculatorImpl, args);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(method.getName() + " 方法执行耗时 " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
return invoke;
}
});
System.out.println("calculator.getClass() = " + calculator.getClass());
calculator.add(3, 4);
}
}
不需要任何额外依赖,都是JDK 自带的能力:
1.Proxy.newProxyInstance方法表示要生成一个动态代理对象。
2.newProxylnstance方法有三个参数,第一个是一个类加载器,第二个参数是一个被代理的对象所实现的接口,第三个则是具体的代理逻辑。
3.在 InvocationHandler 中,有一个 invoke 方法,该方法有三个参数,分别表示当前代理对象,被拦截下来的方法以及方法的参数,我们在该方法中可以统计被拦截方法的执行时间,通过方式执行被拦截下来的目标方法。
4.最终,第一步的方法返回了一个代理对象,执行该代理对象,就有代理的效果了。上面这个案例就是一个JDK动态代理。这是一种运行时增强,在编译阶段并未修改我们的代码。
2:CGLIB动态代理
????从SpringBoot2 开始,AOP 默认使用的动态代理就是CGLIB动态代理了,相比于 JDK 动态代理,CGLIB动态代理支持代理一个类。使用 CGLIB 动态代理,需要首先添加依赖,如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
假设我有一个计算器,如下:
这个没有接口
public class Calculator {
int minus(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + (a - b));
return a - b;
}
}
随后在添加一个拦截器
public class CalculatoProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
/**
* 这个就是拦截器,将来 org.javaboy.demo.Calculator#minus(int, int) 方法执行的时候,这个拦截器会被触发,额外的工作就可以在这个方法中完成
*
* @param o 代理对象
* @param method 代理方法
* @param objects 方法的参数
* @param methodProxy 方法的代理对象
* @return 拦截下来的方法的返回值
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//相当于调用父类的方法,因为 CGLIB 动态代理,相当于给当前类生成了一个子类,在子类中添加了额外的逻辑
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(method.getName() + " 方法执行耗时 " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
return result;
}
}
通过methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);调用到代理方法,最后如下配置CGLIB为方法增强
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(Calculator.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new CalculatoProxy());
Calculator calculator = (Calculator) enhancer.create();
System.out.println("calculator.getClass() = " + calculator.getClass());
calculator.minus(3, 4);
}
????这里其实就是创建了字节增强器,为生成的代理对象配置superClass,然后设置拦截下来之后的回调函数就行了,最后通过create方法获取到一个代理对象。这就是 CGLIB 动态代理。
????Spring AOP 底层,本质上就是JDK 动态代理和CGLIB动态代理(运行时增强),它会根据我们的配置,自动去创建代理对象,可以做到零侵入。但是,这并不意味着Spring AOP 就脱离了 AspectJ,实际上,Spring AOP 中还是需要用到 AspectJ,只不过,Spring AOP使用的是 AspectJ中的一些注解,如@Apsect、@Before、@Pointcut 等,并没有使用AspectJ中的编译时增强。因此大家会发现,我们在使用Spring AOP 中,也需要添加AspectJ相关的依赖。
如果有接口但是也想用CGLIB有java方式和xml(xml有两种)方式,如下代码:
xml第一种方式:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
xml第二种方式:
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut id="pc1" expression="execution(* com.richfit.richfit.service.XqyServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logAdvice">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="exception" throwing="e" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after-returning method="returnAdvice" returning="object" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
上面主要是:
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
java方式
@Aspect
@Component
//这个相当于 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>,这个注解是用来识别项目中的 Aspect 的
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass =true)
public class LogAspect {
}
二:Spring AOP 和 AspectJ AOP
Spring AOP 和 AspectJ AOP 是两种完全不同的 AOP实现。
2.1:Spring AOP
Spring AOP 是 Spring 框架中的 AOP 实现,依赖于 Spring 框架,要结合 Spring Bean 才能使用。Spring AOP是基于动态代理实现的,它的逻辑是这样,如果被代理的对象有接口,Spring AOP底层就会使用JDK动态代理;如果被代理的对象没有接口,那么Spring AOP底层就会使用CGLIB 动态代理。Spring AOP关注的点主要是方法级别的内容,即只能增强方法。
由于Spring AOP底层是动态代理,而动态代理底层是JDK动态代理或者 CGLIB动态代理(动态代理相当于生成了一个子类),所以,这就意味着如果方法或者类是 final 的,或者方法是static 的,都会导致动态代理失效(AOP失效),其实这也是 Spring 事务失效的原因。
2.2:AspectJ AOP
AspectJ AOP 是一个完整的、独立的、并且功能十分强大的AOP解决方案,
Spring AOP 只能增强方法,而AspectJ AOP 不仅能增强方法,还能增强属性、构造器、static 方法、final 类、final 方法、private方法等等,都能增强。AspectJ AOP 是编译时增强,所以性能也要高于Spring AOP(当然,它也支持运行时增强)。
Spring AOP 虽然在多项数据上落后于AspectJ AOP,但是Spring AOP简单易用易上手,所以开发中还是以Spring AOP为主。
三:Spring AOP核心概念
Target/目标对象:被拦截下来的对象/要被增强的对象,如前面MoneyService、 Calculator 都是。
Join Point/连接点:可以被切面插入的地方,方法调用、异常抛出等。被切面增强的连接点。
PointCut/切点:被切面增强的连接点。
Advice/通知/增强:切点在连接处执行的代码,其实就是把目标方法拦截下来之后,要做的事情。
Aspect/切面:切点+通知。
Weaving/织入:将 Aspect应用到Target 的过程,就是Weaving。
Introduction/引介:为 target增强属性和方法。
四:AOP做日志通知(xml配置,基于springboot项目):
首先有一个aopadvice-spring.xml xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--
加载aopadvice-spring.xml 步骤:https://pythonjishu.com/uwrtruqtkjkhjud/
本项目需要的类:LogAdvice
xml:aopadvice-spring.xml
application.properties中加
spring.config.name=aopadvice-spring
spring.config.location=classpath:/
启动类里面加:
@ImportResource("classpath:aopadvice-spring.xml")
-->
<bean class="com.richfit.richfit.bootConfig.AopLog.LogAdvice" id="logAdvice"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pc1" expression="execution(* com.richfit.richfit.service.XqyServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logAdvice">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="exception" throwing="e" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:after-returning method="returnAdvice" returning="object" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
之后application.properties
spring.config.name=aopadvice-spring
spring.config.location=classpath:/
最后在启动类上加@ImportResource(“classpath:aopadvice-spring.xml”)即可。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!