《C++PrimerPlus》第12章 类和动态内存分配
2023-12-23 18:01:15
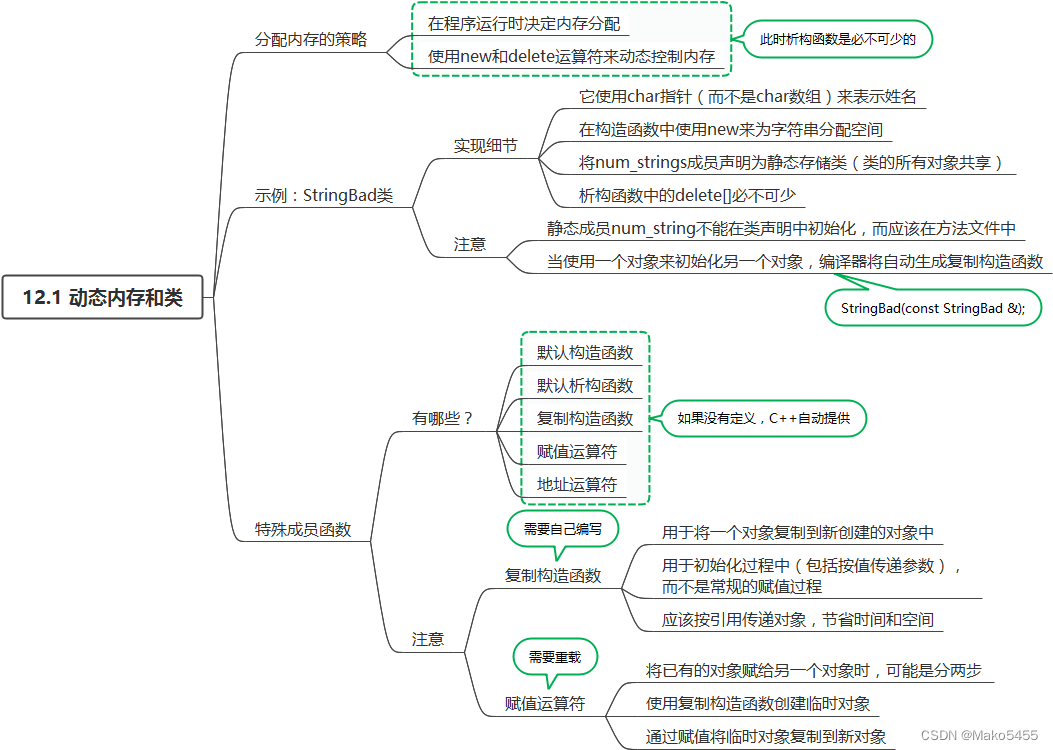
12.1 动态内存和类
12.2 改进后的新String类
动态内存和类示例(编写一个String类,实现字符串的操作)
头文件string1.h
#ifndef __STRING__H__
#define __STRING__H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String {
private:
char *str; // 字符串的地址(字符指针)
int len; // 字符串长度
static int num_strings; // 创建的字符串的数量(静态变量)
static const int CINLIM = 80; // 最多输入n个字符
public:
String(const char *s); // 构造函数
String(); // 默认构造函数
String(const String &st); // 复制构造函数
~String(); // 析构函数
int length() const { return len; } // 返回字符串长度
String &operator=(const String &st); // 重载=运算符
String &operator=(const char *s); // 重载=运算符
char &operator[](int i); // 重载[]运算符
const char &operator[](int i) const; // 重载[]运算符
friend bool operator<(const String &str1, const String &str2); // 重载<运算符
friend bool operator>(const String &str1, const String &str2); // 重载>运算符
friend bool operator==(const String &str1, const String &str2); // 重载==运算符
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const String &st); // 运算符<<重载
friend istream &operator>>(istream &is, String &st); // 运算符<<重载
static int Howmany(); // 返回总共创建了几个字符串
};
#endif源代码main.cpp
#include "string1.h"
using namespace std;
const int MaxLen = 81;
int main() {
cout << "Hi, What's your name?" << endl;
String name;
cin >> name;
cout << name << ", please enter a string: " << endl;
String saystrings;
char temp[MaxLen];
cin.get(temp, MaxLen);
while (cin && cin.get() != '\n') continue;
saystrings = temp;
cout << "Here is your sayings: " << saystrings << endl;
String str = "Hello dad";
if (saystrings.length() < str.length())
cout << "str is longer." << endl;
else
cout << "saystring is longer." << endl;
if (saystrings < str)
cout << "saystrings's first letter is smaller." << endl;
else
cout << "str's first letter is smaller." << endl;
cout << "This program used " << String::Howmany() << " objects." << endl;
return 0;
}
源代码string1.cpp
#include "string1.h"
#include <cstring>
// 注意不能在类声明中初始化静态成员变量
// 声明只是描述如何分配,并不分配内存
int String::num_strings = 0;
int String::Howmany() {
return num_strings;
}
String::String(const char *s) { // StringBad str("Hello")
len = strlen(s); // 获取字符串长度
str = new char[len + 1]; // 开辟内存空间
strcpy_s(str, len + 1, s); // 把s拷贝到str
num_strings++;
}
String::String() {
len = 0;
str = new char[1];
str[0] = '\0';
num_strings++;
}
String::String(const String &st) {
len = st.len;
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy_s(str, len + 1, st.str);
num_strings++;
}
String::~String() {
num_strings--;
delete[] str;
}
String & String::operator=(const String &st) {
if (this == &st) return *this; // 避免自己赋值自己(不可以有删除操作)
delete[] str; // 删掉旧的数据
len = st.len;
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy_s(str, len + 1, st.str);
return *this; // this是指针,需要取值(值为对象的引用)
}
String & String::operator=(const char *s) {
delete[] str;
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy_s(str, len + 1, s);
return *this;
}
char & String::operator[](int i) {
return str[i];
}
const char & String::operator[](int i) const {
return str[i];
}
bool operator<(const String &str1, const String &str2) {
return (strcmp(str1.str, str2.str) < 0);
}
bool operator>(const String &str1, const String &str2) {
return str2 < str1;
}
bool operator==(const String &str1, const String &str2) {
return (strcmp(str1.str, str2.str) == 0);
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const String &st) {
os << st.str;
return os;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &is, String &st) {
char temp[String::CINLIM];
is.get(temp, String::CINLIM);
if (is) st = temp;
while (is && is.get() != '\n') continue;
return is;
}12.3 在构造函数中使用new时的注意事项

12.4 有关返回对象的说明

12.5 使用指向对象的指针

使用new运算符示例(注意创建的地址偏移和析构函数的调用)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <new>
using namespace std;
const int BUF = 512;
class JustTesting{
private:
string words;
int number;
public:
JustTesting(const string &s = "Just Testing", int n = 0) {
words = s;
number = n;
cout << words << " constructed\n";
} // 构造函数
~JustTesting() {
cout << words << " destroyed\n";
} // 析构函数
void Show() const {
cout << words << ", " << number << endl;
}
};
int main() {
char *buffer = new char[BUF];
JustTesting *pc1, *pc2;
pc1 = new(buffer) JustTesting; // 定位new运算符,没有开辟空间,定位到之前开辟过的空间
pc2 = new JustTesting("Heap1", 20); // 开辟了新的空间
cout << "buffer: " << (void *)buffer << endl; // 打印地址
cout << "heap: " << pc2 << endl;
cout << pc1 << ": "; // 打印地址
pc1->Show(); // 打印值
cout << pc2 << ": ";
pc2->Show();
JustTesting *pc3, *pc4;
// pc3 = new(buffer) JustTesting("Bad Idea", 6); // 极其不推荐这么做,存到同一个地方可能会数据冲突
pc3 = new(buffer + sizeof(JustTesting)) JustTesting("Better Idea", 6);
pc4 = new JustTesting("Heap2", 10);
cout << pc3 << ": ";
pc3->Show();
cout << pc4 << ": ";
pc4->Show();
delete pc2; // 仅当显式调用delete的时候,析构函数被调用
delete pc4;
pc1->~JustTesting(); // 显式调用析构函数
pc3->~JustTesting();
delete[] buffer;
return 0;
}12.6 复习各种技术

12.7 队列模拟
设计一个队列类
头文件queue1.h
#ifndef __QUEUE_H__
#define __QUEUE_H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Customer { // 客户信息
private:
long arrive; // 开始操作的时间
int processtime; // 操作的总时间
public:
Customer() {
arrive = processtime = 0;
} // 都初始化为0
void set(long when); // 设置开始操作的时间
long when() const { return arrive; } // 返回开始操作的时间
int ptime() const { return processtime; } // 返回操作总时间
};
typedef Customer Item; // Item是Customer类的对象
class Queue {
private:
enum { Q_SIZE = 10 };
struct Node {
Item item; // 存放的信息(Item表示任意类型)
struct Node *next; // 指向下一个结构体的指针
};
Node *front; // 指向队列头的指针
Node *rear; // 指向队列尾的指针
int items; // 当前队列的长度(当前有多少人)
const int qsize; // 队列最大值
public:
Queue(int qs = Q_SIZE); // 构造函数
~Queue(); // 析构函数
bool isempty() const; // 判断队列是否为空
bool isfull() const; // 判断队列是否为满
int queuecount() const; // 返回队列长度
bool enqueue(const Item &item); // 入队(返回bool表示是否成功)
bool dequeue(Item &item); // 出队(返回bool表示是否成功),值存在形参中
};
#endif // !__QURUE_H__
源代码main.cpp
#include "queue1.h"
int main() {
int qs; // 队列长度
Item temp; // 创建一个Customer对象
int i = 0;
int customers = 0; // 有几个顾客
cout << "Enter maxium size of queue: ";
cin >> qs;
Queue line(qs); // 创建队列
while (!line.isfull()) { // 入队,直到队列为满
temp.set(i++); // 填充temp的值
line.enqueue(temp);
customers++;
}
cout << "Customers: " << customers << endl;
while (!line.isempty()) { // 出队,直到队列为空
line.dequeue(temp);
customers--;
}
cout << "Now, customers: " << customers << endl;
return 0;
}源代码queue1.cpp
#include "queue1.h"
#include <cstdlib>
Queue::Queue(int qs) : qsize(qs) {
front = rear = nullptr;
items = 0;
// qsize = qs; // 错误!qsize是常量,可以初始化,不可以赋值
// 成员初始化列表(member Initializer list)
// 只能用于构造函数,位于参数列表的右括号之后,函数体左括号之前
}
Queue::~Queue() {
Node *temp;
while (front != nullptr) {
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
}
}
bool Queue::isempty() const {
return items == 0;
}
bool Queue::isfull() const {
return items == qsize;
}
int Queue::queuecount() const {
return items;
}
bool Queue::enqueue(const Item &item) {
if (isfull()) return false; // 满队列直接返回false
Node *add = new Node; // 开辟新的内存空间来存储新节点
add->item = item; // 值就是传递进来的参数
add->next = nullptr; // 因为是末尾节点,所以指向空
items++; // 队列数量+1
if (front == nullptr) front = add; // 如果为空队列,则当前节点变为头节点
else rear->next = add; // 否则,插入前的尾节点指向当前节点
rear = add; // 当前节点变为尾节点
return true;
}
bool Queue::dequeue(Item &item) {
if (isempty()) return false; // 空队列直接返回false
item = front->item; // 把头结点的值赋给形参
items--; // 队列数量-1
Node *temp = front; // 使用临时指针存一下头结点的值
front = front->next; // 调整头结点为下一个值
delete temp; // 释放临时指针所指向的内存空间
if (items == 0) rear = nullptr; // 如果为空队列,则尾节点变为空
return true;
}
void Customer::set(long when) {
arrive = when; // 记录开始操作的时间
processtime = rand() % 3 + 1; // 随机出一个1~3分钟的总操作时长
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Mako5455/article/details/134813806
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!