java --- 集合进阶
2023-12-16 22:52:29
目录
一、单列集合顶层接口?Collection
1.1 基本方法

常用方法:

Collection是一个接口,我们不能直接创建对象,需要通过他实现类的对象
1.2 Collection 的遍历方式

迭代器遍历
public class collection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>(10);
c1.add("zhangsan");
c1.add("lisi");
c1.add("wangwu");
c1.add("maliu");
//迭代器的遍历
Iterator<String> it = c1.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String s = it.next();//返回当前元素,并向后移动
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println(it.hashCode());
System.out.println(it);
}
}注意点

?Collection接口遍历元素:增强 for 循环
所有的单列集合还有数组都可以通过增强for循环遍历
这里和C++的用法是一样的
//使用增强for
for(String s : c1){
System.out.println(s);
}使用lambda简化forEach遍历

二、list集合

List相比于Colection最大的改变就是加入了索引

2.1 List接口常用方法:
- void add (int index,Object ele) :在index位置插入ele元素;
- boolean addAll (int index,Collection eles) :从index位置开始将eles集合中的所有元素添加进来;
- Object get (int index) :获取指定index位置的元素;
- int indexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置;
- int lastIndexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中末次出现的位置;
- Object remove (int index) :移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素;
- Object set (int index,Object ele) :设置指定index的位置的元素为ele,相当于是替换;
- List subList (int fromIndex,int toIndex) :返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向上转型,用List来接收ArrayList
List l1 = new ArrayList();
//1. void add (int index,Object ele) :在index位置插入ele元素;
l1.add(1);
l1.add(2);
l1.add(3);
System.out.println(l1);//[1, 2, 3]
//2. boolean addAll (int index,Collection eles) :从index位置开始将eles集合中的所有元素添加进来;
List l2 = new ArrayList();
l2.add(10);l2.add(20);
l1.addAll(l2);
System.out.println(l1);//[1, 2, 3, 10, 20]
//3. Object get (int index) :获取指定index位置的元素;
Object o1 = l1.get(0);
Object o2 = l1.get(3);
//4. int indexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置;
int x1 = l1.indexOf(10);
int x2 = l1.indexOf(1);
//5. int lastIndexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中末次出现的位置;
int x3 = l1.indexOf(20);
int x4 = l1.indexOf(2);
//6. Object remove (int index) :移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素;
Object o3 = l1.remove(0);
System.out.println(l1);
//7. Object set (int index,Object ele) :设置指定index的位置的元素为ele,相当于是替换;
l1.set(0,666);
System.out.println(l1);
//8. List subList (int fromIndex,int toIndex) :返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合;
List l3 = l1.subList(0,2);
System.out.println(l3);
}1.2 ArrayList
- ArrayList 是由数组来实现数据存储的;
- ArrayList基本等同于 Vector ,除了 ArrayList是线程不安全的,但执行效率高,在多线程的情况下不建议用ArrayList;
?Vector 底层结构
- Vector 底层也是一个对象数组,protected Object[ ] elementData;
- Vector 是线程同步的,即线程安全,Vector类的操作方法带有synchronized
- 在开发中,需要线程同步安全时,考虑使用Vector
底层原理

扩容机制

1.3 LinkedList
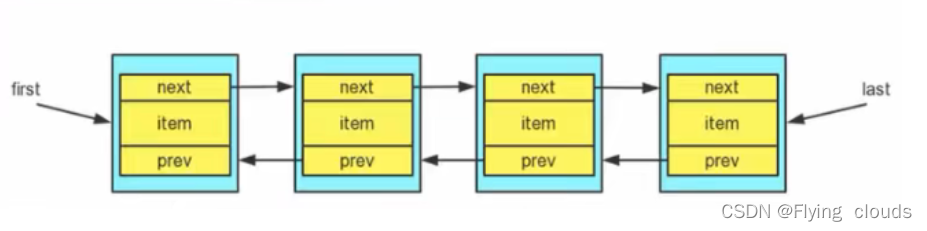
- LinkedList 实现了双向链表和双端队列的特点
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括null;
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表;
- LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last分别指向 首节点 和 尾节点;
- 每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了prev、next、item三个属性,其中通过prev指向前一个,通过next指向后一个节点,最终完成双向链表;
- 所以 LinkedList的元素的添加和删除不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkListCRUD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
//增
linkedList.add(1);//size=0添加一个新节点,首尾指针都指向这个新节点
linkedList.add(2);//last指向新节点,first还是指向第一个节点,next指向新节点
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("增后: "+linkedList);
//删
linkedList.remove();//默认删除第一个
System.out.println("删后: "+linkedList);//就是去掉指针
//改
linkedList.set(1,999);
System.out.println("改后: "+linkedList);
//查
//get(1) 得到双向链表的第二个对象
Object o = linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println(o);//999
//因为LinkedList是实现了List接口,所以遍历方式:
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) { //快捷输入itit
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
//还有增强for 和普通for 遍历
}
}
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 比较
| 集合 | 底层结构 | 增删的效率 | 改查的效率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | 较低,数组扩容 | 较高 |
| LinkedList | 双向链表 | 较高,通过链表追加 | 较低 |
如何选择 ArrayList 和 LinkedList :
- 如果改查的操作较多,选择 ArrayList;
- 如果增删的操作较多,选择 LinkedList;
- 一般程序中,80%-90%都是查询,因此大部分会使用ArrayList;
- 在项目中,灵活选择,可以一个模块用LinkedList,一个模块用ArrayList;
多线程的情况还是考虑 Vector ,因为它是线程安全的
三、set接口
Set 接口介绍:
- 无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引;
- 不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null;
- JDK API 中Set的常用实现类有:HashSet 和 TreeSet;
?3.1、Set 接口和常用方法
Set 接口的常用方法
- 和 List 接口一样,Set 接口也是 Collection 的子接口,所以常用方法和Collection接口一样
Set 接口的遍历方式
- 同 Collection 的遍历一样:
- 迭代器遍历
- 增强 for
- 但?不能用索引?的方式来获取; (因为Set无序)
public class Set1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Set是接口,不能直接实现,通过他的实现类Hashset来模拟
//Set不能放重复元素
//Set遍历的时候无序,和放入顺序不同,但是有固定的顺序
Set s1 = new HashSet();
s1.add("xx1");
s1.add("xx2");
s1.add("xx3");
s1.add("xx4");
System.out.println(s1);
//迭代器遍历
Iterator it = s1.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o1 =it.next();
System.out.println(o1);
}
System.out.println("hhhhhhh");
//增强for遍历
for(Object o : s1){
System.out.println(o);
}
//不能索引遍历,且set接口对象没有get()方法
}
}3.2 HashSet
- HashSet实现了Set接口;
- HashSet实际上是HashMap,可以从源码看出;
- 可以存放 null 值,但是只能有一个null;
- HashSet 不保证元素是有序的,取决于hash后,再确定索引的结果;
- 不能有重复元素 / 对象;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSet1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
hs.add("zhangsan");
hs.add("lisi");
hs.add("wangwu");
hs.add("maliu");
System.out.println(hs);
hs.remove("lisi");
}
}HashSet 底层机制(HashMap)
HashSet 底层其实是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)(链地址法)
?3.3? LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet 的子类,继承HashSet,实现了Set接口;
- LinkedHashSet 底层是一个 LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个 数组+双向链表;
- LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的;
- LinkedHashSet 不允许添加重复元素;

3.4?TreeSet
TreeSet的独特之处在于它的构造器可以传入比较器,所以TreeSet常用来排序,
TreeSet 底层是 TreeMap
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet t1 = new TreeSet();
t1.add("aaa");
t1.add("x");
t1.add("bb");
t1.add("hhhh");
System.out.println(t1);//默认排序:首字母ASCII由小到大
//[aaa, bb, hhhh, x]
//如果我们想按字符串大小排序
//使用TreeSet提供的一个构造器,传入一个比较器(匿名内部类)指定排序规则
TreeSet t2 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String)o1).length() - ((String)o2).length();
}
});
t2.add("aaa");
t2.add("x");
t2.add("bb");
t2.add("hhhh");
System.out.println(t2);//按照字符串长度排序
//[x, bb, aaa, hhhh]
}四、双列集合Map
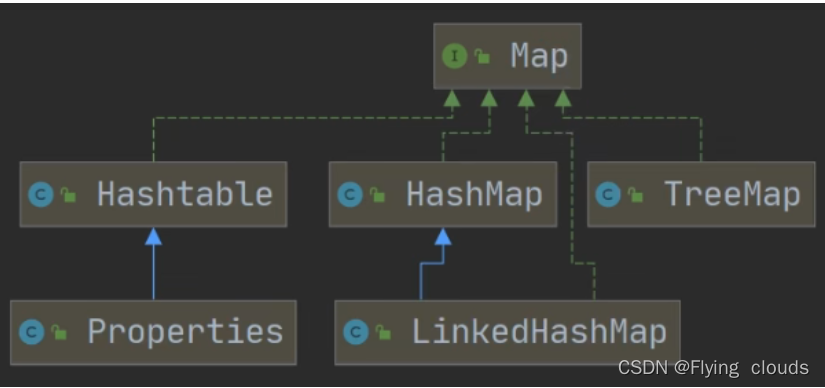
Map为双列集合,Set集合的底层也是Map,只不过有一列是常量所占,只使用到了一列
?4.1? Map 接口实现类的特点
- Map 与 Collection 并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key - Value;
- Map 中的 Key 和 Value 可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到 HashMap$Node对象中;
- Map中的 Key 不允许重复,原因和?HashSet?一样;
- Map 中的 Value 可以重复;
- Map 的 Key 可以为 null,value 也可以为 null,但 key 为 null 只能有一个;
- 常用 String 类作为 Map 的 key,当然,其他类型也可以,但不常用;
- Key 和 Value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 Key 总能找到对应的 Value;
4.2 Map 接口和常用方法
- put :添加
- remove : 根据键删除映射关系
- get : 根据键获取值
- size : 获取元素个数
- isEmpty : 判断个数是否为0
- clear : 清除
- containsKey : 查找键是否存在
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map m1 = new HashMap();
m1.put("zhangsan",100);
m1.put("lisi",99);
m1.put("wangwu",98);
m1.put("maliu",97);
System.out.println(m1);//{lisi=99, zhangsan=100, maliu=97, wangwu=98}
System.out.println(m1.get("zhangsan"));
System.out.println(m1.get("maliu"));
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.isEmpty());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("wangwu"));
m1.clear();
System.out.println(m1);
}4.3 Map 接口的三种遍历方法

法一:先获取key的单列集合,再通过key获取vale
keySet()
public class Map遍历 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> m1 = new HashMap();
m1.put("zhangsan",100);
m1.put("lisi",99);
m1.put("wangwu",98);
m1.put("maliu",97);
//方法一:先获取键(先获取key的单列集合),再通过键获取值
//1.增强for
Set<String> keys = m1.keySet();
for(String k : keys){
System.out.println(k + " - "+m1.get(k));
}
System.out.println();
//2.迭代器
Iterator it1 = keys.iterator();
while(it1.hasNext()){
Object s = it1.next();
System.out.println(s+" - "+m1.get(s));
}
System.out.println();
//3.lambda表达式
keys.forEach(str ->{
System.out.println(str + " - "+m1.get(str));
});
}
}法二 获取每个键值对,再getKey ,getValue
entrySet()
public class map遍历02_entrySet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> m1 = new HashMap();
m1.put("zhangsan",100);
m1.put("lisi",99);
m1.put("wangwu",98);
m1.put("maliu",97);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> setentry = m1.entrySet();
//接下来就是三种遍历,和keySet一样的
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> e1 : setentry){
String k = e1.getKey();
Integer v = e1.getValue();
System.out.println(k+" - "+v);
}
System.out.println();
//迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> it = setentry.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> tmp = it.next();
String k = tmp.getKey();
Integer v = tmp.getValue();
System.out.println(k+" - "+v);
}
System.out.println();
//lamdba表达式
setentry.forEach(tmp ->{
String k = tmp.getKey();
Integer v = tmp.getValue();
System.out.println(k+" - "+v);
});
}
}法三:lambda表达式,利用Map的forEach方法
public class Map遍历03_lambda {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> m1 = new HashMap();
m1.put("zhangsan",100);
m1.put("lisi",99);
m1.put("wangwu",98);
m1.put("maliu",97);
//利用forEach可以直接进行遍历
m1.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(String k, Integer v) {
System.out.println(k+" - "+v);
}
});
System.out.println();
//lambda表达式改进
m1.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+" - "+v);
});
}
}4.4? HashMap
- Map 接口的常用实现类:HashMap、Hashtable、Properties;
- HashMap 是 Map 接口使用频率最高的实现类;
- HashMap 是以 key - value 对的形式来存储的;
- key 不能重复添加,但value可以,都允许使用null;
- 如果添加相同的 key,则会覆盖原来的 key - value,等同于修改;
- 与 HashSet一样,不保证映射的顺序,因为底层是以哈希表的方式来存储的;
- HashMap 没有实现同步,所以线程不安全;
HashMap的用法以及扩容机制和C++中的unorded_map是一样的
利用HashMap来统计80个同学对四个景点的意向
public class HashMap01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.先来定义几个景点
String[] s = new String[]{"A","B","C","D"};
//2.定义一个HashMap
HashMap<String,Integer> hm = new HashMap<>();
//3.用随机数模拟同学们的投票
Random r = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<80;++i){
int index = r.nextInt(s.length);
if(hm.containsKey(s[index])){
//已经插入过了
int count = hm.get(s[index]);
count++;
hm.put(s[index],count);
}else{
//第一次插入
hm.put(s[index],1);
}
}
//4.将HashMap的结果输出
System.out.println(hm);
//5.遍历求最多的那个
int res = 0;
Set<String> entry = hm.keySet();
for(String str : entry){
int tmp = hm.get(str);
res = Math.max(res,tmp);
}
System.out.println(res);
System.out.println();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> e : entries){
res = Math.max(res,e.getValue());
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}4.5 LinkedHashMap

4.6 TreeMap

这和C++当中的Map是几乎一样的。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/flyingcloud6/article/details/135008089
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!