OpenCV数字图像处理——基于目标边缘适用于目标部分遮挡或不同光照模板匹配
简介
模板匹配是一种常见的计算机视觉问题,通常用于在一张图像中查找特定的模板图像。在处理模板匹配时,经常会面临对象的姿态未知的情况,其中姿态包括位置(X,Y坐标)和旋转角度(θ)。
模板匹配的步骤包括:
-
获取图像: 从图像中获取源图像和模板图像。
-
特征提取: 对源图像和模板图像进行特征提取,常常使用边缘检测等方法,以捕捉图像中的关键特征。
-
模板匹配: 在源图像中滑动模板图像,计算源图像中每个位置与模板的相似度。这通常涉及使用相关性或其他相似性度量。
-
位置识别: 通过找到相似度最高的位置,确定对象在源图像中的位置。
-
姿态估计: 如果需要,进行进一步的姿态估计,包括位置和旋转角度。
一、模型匹配
1.模板匹配API
OpenCV库提供了模板匹配API,适合应用在比较简单的场景下:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
int main() {
// 读取源图像和模板图像
cv::Mat sourceImage = cv::imread("source_image.jpg", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
cv::Mat templateImage = cv::imread("template_image.jpg", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
// 边缘检测
cv::Mat edgesSource, edgesTemplate;
cv::Canny(sourceImage, edgesSource, 50, 150);
cv::Canny(templateImage, edgesTemplate, 50, 150);
// 模板匹配
cv::Mat result;
cv::matchTemplate(edgesSource, edgesTemplate, result, cv::TM_CCOEFF_NORMED);
// 获取最大匹配值和位置
double minVal, maxVal;
cv::Point minLoc, maxLoc;
cv::minMaxLoc(result, &minVal, &maxVal, &minLoc, &maxLoc);
// 绘制矩形框标记匹配位置
cv::rectangle(sourceImage, maxLoc, cv::Point(maxLoc.x + edgesTemplate.cols, maxLoc.y + edgesTemplate.rows), 255, 2);
// 显示结果
cv::imshow("Matched Image", sourceImage);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
这里使用了OpenCV的cv::Canny函数进行边缘检测,然后使用cv::matchTemplate函数进行模板匹配。最后,通过cv::rectangle函数在源图像中标记匹配位置。
2. 模板匹配的局限性与解决方法
模板匹配是一项具有挑战性的任务,主要受到其速度和可靠性的限制。当对象只有部分可见或与其他对象混合在一起时,解决方案必须具备鲁棒性,特别是对亮度变化要有稳健的适应能力。在此问题中,算法的计算效率也至关重要。为解决这一问题,存在两种主要方法:基于灰度值的匹配(或基于区域的匹配)和基于特征的匹配(非基于区域的匹配)。
基于灰度值的模板匹配:
基于灰度值的匹配方法使用归一化互相关(NCC)算法,这一算法在过去已经得到广泛应用。在该方法中,每一步的操作包括对模板 t(x, y) 和子图像 f(x, y) 进行互相关计算。公式如下:
N C C = 1 n ? 1 ∑ x ? v ( f ( x , y ) ? μ f ) ( t ( x , y ) ? μ t ) σ f . σ t N C C={\frac{1}{n-1}}\sum_{x\cdot v}{\frac{(f(x,y)-\mu f)(t(x,y)-\mu t)}{\sigma f.\sigma t}} NCC=n?11?∑x?v?σf.σt(f(x,y)?μf)(t(x,y)?μt)?
该互相关计算通常在每一步中通过减去平均值并除以标准偏差来完成。这种匹配方法的目标是提高对亮度变化的鲁棒性,确保在对象部分可见或混合的情况下仍能有效工作。
基于特征的方法:
基于特征的模板匹配方法在图像处理领域中有多种应用。与基于边缘的物体识别相似,这些方法利用物体的特征来进行匹配。在广义霍夫变换等技术中,物体的几何特征被用于匹配过程。
二、基于边缘特征的模板匹配
边缘是数字图像中亮度急剧变化或具有不连续性的点,通常通过计算图像强度函数的梯度近似值来定义。
边缘检测方法主要分为两类:基于搜索和基于过零。基于搜索的方法首先计算边缘强度,通常使用一阶导数表达式(如梯度幅度),然后通过估计的局部方向搜索梯度幅度的局部最大值,该方向通常是梯度方向。可以使用 Sobel 算子实现了一种基于搜索的方法,它计算每个点的图像强度梯度,提供从明到暗的最大可能增加方向以及该方向的变化率。
1. 模板边缘检测
对于模板图像,为了获模板的特征属性,首先是要确定目标的位置边缘,这里采用了 Canny 边缘检测方法的一种变体来寻找目标边缘。
Canny 边缘检测方法检测算法步骤如下:
- 获取图像的亮度梯度
对模板图像应用 Sobel 过滤器,该过滤器返回 X(Gx)和 Y(Gy)方向的梯度。基于这些梯度,将使用以下公式计算边缘的大小和方向:
M a g n i t u d e = G x 2 + G y 2 M a g n i t u d e={\sqrt{G x^{2}+G y^{2}}} Magnitude=Gx2+Gy2?
D i r e c t i o n = i n v t a n ( G y G x ) D i r e c t i o n=i n v t a n(\frac{G y}{G x}) Direction=invtan(GxGy?)
一旦确定了边缘的方向,接下来的步骤是将可追踪的边缘方向与图像中的相邻像素关联。有四个可能的方向来描述周围像素的位置:0 度、45 度、90 度和 135 度。就可以将将所有方向映射到这些角度之一。
- 应用非极大值抑制
在确定了边缘方向后,执行非极大值抑制算法。该算法沿边缘方向追踪左右像素,如果当前像素的幅度小于左右像素的幅度,则抑制当前像素的幅度。这一步导致图像中边缘部分的细化。
-
滞后阈值
这里使用两个阈值:高阈值和低阈值。使用高阈值来标记那些相当确定是真实边缘的像素。然后,利用先前导出的方向信息,可以通过图像追踪其他边缘。在跟踪边缘时,应用较低的阈值,这样只要找到一个起点,就能够追踪边缘的较弱部分。 -
保存特征数据
提取边缘后,将所选边缘的 X 和 Y 导数与坐标信息一起保存为模板模型。这些坐标将重新排列以反映作为重心的起点。
使用OpenCV 4.5实现的代码如下:
int GeoMatch::create_match_model(Mat &cv_template,double maxContrast,double minContrast)
{
Mat gx; //Matrix to store X derivative
Mat gy; //Matrix to store Y derivative
Mat nmsEdges; //Matrix to store temp restult
Size Ssize;
Mat src(cv_template); //Above step replicated
// set width and height
Ssize.width = src.cols; //src->width;
Ssize.height = src.rows; //src->height;
modelHeight = src.rows; //src->height; //Save Template height
modelWidth = src.cols; //src->width; //Save Template width
cordinates = std::vector<cv::Point>(modelWidth * modelHeight); //Allocate memory for coorinates of selected points in template image
edge_magnitude = std::vector<double>(modelWidth * modelHeight); //Allocate memory for edge magnitude for selected points
edge_derivativeX = std::vector<double>(modelWidth * modelHeight); //Allocate memory for edge X derivative for selected points
edge_derivativeY = std::vector<double>(modelWidth * modelHeight); Allocate memory for edge Y derivative for selected points
// Calculate gradient of Template
gx = Mat( Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1 ); //create Matrix to store X derivative
gy = Mat( Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1 ); //create Matrix to store Y derivative
Sobel( src, gx, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3 ); //gradient in X direction
Sobel( src, gy, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3 ); //gradient in Y direction
nmsEdges = Mat(Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_32F); //create Matrix to store Final nmsEdges
const short* _sdx;
const short* _sdy;
double fdx,fdy;
double MagG, DirG;
double MaxGradient = -99999.99;
double direction;
int *orients = new int[Ssize.height * Ssize.width];
// count variable;
int count = 0,i,j;
//double **magMat;
std::vector<std::vector<double>> magMat;
create_double_matrix(magMat ,Ssize);
for( i = 1; i < Ssize.height - 1; i++ )
{
for( j = 1; j < Ssize.width - 1; j++ )
{
fdx = gx.at<short>(i, j);
fdy = gy.at<short>(i, j);
MagG = sqrt((float)(fdx * fdx) + (float)(fdy * fdy)); //Magnitude = Sqrt(gx^2 +gy^2)
direction = atan2f((float)fdy, (float)fdx);//cvFastArctan((float)fdy,(float)fdx); //Direction = invtan (Gy / Gx)
magMat[i][j] = MagG;
if(MagG > MaxGradient)
MaxGradient = MagG; // get maximum gradient value for normalizing.
// get closest angle from 0, 45, 90, 135 set
if ( (direction > 0 && direction < 22.5) || (direction > 157.5 && direction < 202.5) || (direction > 337.5 && direction < 360) )
direction = 0;
else if ( (direction > 22.5 && direction < 67.5) || (direction > 202.5 && direction < 247.5) )
direction = 45;
else if ( (direction > 67.5 && direction < 112.5)||(direction > 247.5 && direction < 292.5) )
direction = 90;
else if ( (direction > 112.5 && direction < 157.5)||(direction > 292.5 && direction < 337.5) )
direction = 135;
else
direction = 0;
orients[count] = (int)direction;
count++;
}
}
count = 0; // init count
// non maximum suppression
double leftPixel, rightPixel;
for( i = 1; i < Ssize.height - 1; i++ )
{
for( j = 1; j < Ssize.width - 1; j++ )
{
switch ( orients[count] )
{
case 0:
leftPixel = magMat[i][j - 1];
rightPixel = magMat[i][j + 1];
break;
case 45:
leftPixel = magMat[i - 1][j + 1];
rightPixel = magMat[i + 1][j - 1];
break;
case 90:
leftPixel = magMat[i - 1][j];
rightPixel = magMat[i + 1][j];
break;
case 135:
leftPixel = magMat[i - 1][j - 1];
rightPixel = magMat[i + 1][j + 1];
break;
}
// compare current pixels value with adjacent pixels
if ((magMat[i][j] < leftPixel) || (magMat[i][j] < rightPixel))
nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j) = 0.0f;//(nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]=0;
else
nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j) = (uchar)(magMat[i][j] / MaxGradient * 255);//(nmsEdges->data.ptr + nmsEdges->step*i)[j]=(uchar)(magMat[i][j]/MaxGradient*255);
count++;
}
}
int RSum = 0,CSum = 0;
int curX, curY;
int flag = 1;
//Hysterisis threshold
for( i = 1; i < Ssize.height - 1; i++ )
{
for( j = 1; j < Ssize.width; j++ )
{
fdx = gx.at<short>(i, j);
fdy = gy.at<short>(i, j);
MagG = sqrt(fdx * fdx + fdy * fdy);
DirG = atan2f((float)fdy, (float)fdx);
flag = 1;
double val = nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j);
if( val < maxContrast)
{
if(val < minContrast)
{
nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
flag = 0; // remove from edge
}
else
{
if ( (nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j - 1) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j + 1) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j) < maxContrast) &&
(nmsEdges.at<float>(i + 1, j + 1) < maxContrast)
)
{
nmsEdges.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
flag = 0;
}
}
}
// save selected edge information
curX = i; curY = j;
if(flag != 0)
{
if(fdx != 0 || fdy != 0)
{
// Row sum and column sum for center of gravity
RSum = RSum + curX;
CSum = CSum + curY;
cordinates[cordinates_num].x = curX;
cordinates[cordinates_num].y = curY;
edge_derivativeX[cordinates_num] = fdx;
edge_derivativeY[cordinates_num] = fdy;
//handle divide by zero
if(MagG != 0)
edge_magnitude[cordinates_num] = 1/MagG; // gradient magnitude
else
edge_magnitude[cordinates_num] = 0;
cordinates_num++;
}
}
}
}
center_gravity.x = RSum / cordinates_num; // center of gravity
center_gravity.y = CSum / cordinates_num; // center of gravity
// change coordinates to reflect center of gravity
for(int m = 0; m < cordinates_num; m++)
{
int temp;
temp = cordinates[m].x;
cordinates[m].x = temp - center_gravity.x;
temp = cordinates[m].y;
cordinates[m].y = temp - center_gravity.y;
}
modelDefined = true;
return 1;
}
2. 查找模板
要在图像中查找指定的模板对象。先要从包含一组点的模板图像创建的模型:
P i τ = ( X i τ , Y i τ ) ? P_{i}^{\tau}=(X_{i}^{\tau},Y_{i}^{\tau})\, Piτ?=(Xiτ?,Yiτ?)
获取它在 X 和 Y 方向上的梯度 :
G i T = ( G x i T , G y i T ) G_{i}^{T}=(G x_{i}^{T},G y_{i}^{T}) GiT?=(GxiT?,GyiT?)
当i = 1…n,n是模板 (T) 数据集中的元素数。还可以在搜索图像 (S) 中找到梯度:
G a ˉ , ν S = ( G x a , ν S , G y a , ν S ) ? G_{\bar{a},\nu}^{S}=(G x_{a,\nu}^{S},G y_{a,\nu}^{S})\, Gaˉ,νS?=(Gxa,νS?,Gya,νS?)
当u = 1…搜索图像中的行数,v = 1…搜索图像中的列数。
在匹配过程中,应使用相似性度量将模板模型与所有位置的搜索图像进行比较。相似性度量背后的思想是取模板图像梯度向量的所有归一化点积之和,并在模型数据集中的所有点上搜索图像。这会导致搜索图像中每个点的分数。
公式为:
S u , v = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n ( G x i T . G x ( u + X i , v + Y i ) S ) + ( G y i T . G y ( u + X i , v + Y i ) S ) G x i T + G y i T . G x ( u + X i , v + Y i ) T + G y ( u + X i , v + Y i ) T S_{u,v}=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}\frac{(G x_{i}^{T}.G x_{(u+X i,v+Y i)}^{S})+(G y_{i}^{T}.G y_{(u+X i,v+Y i)}^{S})}{\sqrt{G x_{i}^{T}+G y_{i}^{T}.\sqrt{G x_{(u+X i,v+Y i)}^{T}}+G y_{(u+X i,v+Y i)}^{T}}} Su,v?=n1?∑i=1n?GxiT?+GyiT?.Gx(u+Xi,v+Yi)T??+Gy(u+Xi,v+Yi)T??(GxiT?.Gx(u+Xi,v+Yi)S?)+(GyiT?.Gy(u+Xi,v+Yi)S?)?
如果模板模型和搜索图像之间存在完美匹配,则相似性度量函数将返回分数 1。该分数对应于搜索图像中可见的对象部分与模板模型的匹配程度。如果搜索图像中不存在对象或对象不可见,则分数将为 0。分数的范围在 0 到 1 之间,可用于衡量匹配的相似程度。
在实际情况下,处理的时候需要加快搜索过程。这可以使用各种方法来实现。第一种方法是使用平均的属性。在寻找相似性度量时,如果可以为相似性度量设置一个最小分数(S min),就不需要评估模板模型中的所有点。为了检查特定点 J 处的部分分数 S u,v,必须找到部分总和 Sm。点 m 处的 Sm 可以定义如下:
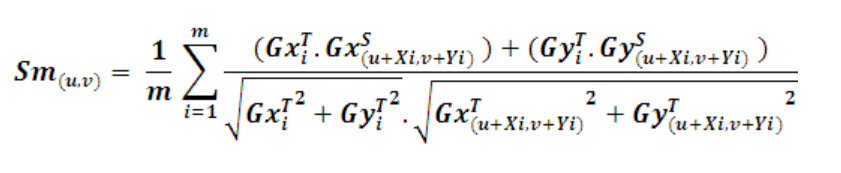
当剩余项小于或等于 1,可以停止评估 ,另一个标准可以是任何点的部分分数应大于最低分数。
使用硬标准和安全停止标准结合的方法是为了提高匹配的效率。这种方法允许在匹配的早期阶段更快速地排除那些不太可能是匹配项的位置,从而加速整个匹配过程。
在这个过程中,贪婪参数 (g) 起着关键的作用。通过调整 (g) 的值,用户可以灵活地控制使用硬标准检查的模板模型的部分。当 (g = 1) 时,模板模型中的所有点都用硬标准检查,这意味着在整个匹配过程中都使用硬标准。而当 (g = 0) 时,所有点只用安全标准检查,这意味着整个匹配过程都使用安全停止标准。
S m ? < M I N ( ( S m i n ? 1 + 1 ? g ? S m i n 1 ? g ?? ? ?? m n ) , ( S m i n ?? ? ?? m n ) ) S_{m}\ \lt M I N\bigg(\Big(S^{m i n}-1+{\frac{1-g\,S^{m i n}}{1-g}}\!\cdot\!{\frac{m}{n}}\Big),(S^{m i n}\!\cdot\!{\frac{m}{n}})\bigg) Sm??<MIN((Smin?1+1?g1?gSmin??nm?),(Smin?nm?))
这种方法的优势在于可以根据具体情况调整 (g) 的值,以在保持一定匹配准确性的同时实现更高的匹配速度。
模板查找代码:
double GeoMatch::find_match_model(Mat &cv_src, double minScore, double greediness, cv::Point &result_point)
{
Mat Sdx, Sdy;
double resultScore = 0;
double partialSum = 0;
double sumOfCoords = 0;
double partialScore;
const short* _Sdx;
const short* _Sdy;
int i,j,m ; // count variables
double iTx, iTy, iSx, iSy;
double gradMag;
int curX,curY;
std::vector<std::vector<double>> matGradMag;
Mat src = cv_src.clone();
// source image size
Size Ssize;
Ssize.width = src.cols;
Ssize.height= src.rows;
create_double_matrix(matGradMag, Ssize); // 创建图像以保存梯度大小值
Sdx = Mat( Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1 ); // X derivatives
Sdy = Mat( Ssize.height, Ssize.width, CV_16SC1 ); // y derivatives
Sobel( src, Sdx, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3 ); // find X derivatives
Sobel( src, Sdy, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3 ); // find Y derivatives
// stoping criterias to search for model
double normMinScore = minScore / cordinates_num; // precompute minumum score
double normGreediness = ((1 - greediness * minScore)/(1 - greediness)) / cordinates_num; // precompute greedniness
for( i = 0; i < Ssize.height; i++ )
{
for( j = 0; j < Ssize.width; j++ )
{
iSx = Sdx.at<short>(i, j);
iSy = Sdy.at<short>(i, j);
gradMag = sqrt((iSx * iSx) + (iSy * iSy)); //Magnitude = Sqrt(dx^2 +dy^2)
if(gradMag != 0) // hande divide by zero
matGradMag[i][j] = 1 / gradMag; // 1/Sqrt(dx^2 +dy^2)
else
matGradMag[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for( i = 0; i < Ssize.height; i++ )
{
for( j = 0; j < Ssize.width; j++ )
{
partialSum = 0; // initilize partialSum measure
for(m = 0; m < cordinates_num; m++)
{
curX = i + cordinates[m].x ; // template X coordinate
curY = j + cordinates[m].y ; // template Y coordinate
iTx = edge_derivativeX[m]; // template X derivative
iTy = edge_derivativeY[m]; // template Y derivative
if(curX < 0 || curY < 0 || curX > Ssize.height - 1 || curY > Ssize.width - 1)
continue;
iSx = Sdx.at<short>(curX, curY); //CHECK IF curX AND curY NEED TO BE SWITCHED
iSy = Sdy.at<short>(curX, curY);
if((iSx != 0 || iSy != 0) && (iTx != 0 || iTy != 0))
{
//partial Sum = Sum of(((Source X derivative* Template X drivative) + Source Y derivative * Template Y derivative)) / Edge magnitude of(Template)* edge magnitude of(Source))
partialSum = partialSum + ((iSx * iTx) + (iSy * iTy)) * (edge_magnitude[m] * matGradMag[curX][curY]);
}
sumOfCoords = m + 1;
partialScore = partialSum / sumOfCoords ;
// check termination criteria
// if partial score score is less than the score than needed to make the required score at that position
// break serching at that coordinate.
if( partialScore < (MIN((minScore - 1) + normGreediness * sumOfCoords, normMinScore * sumOfCoords)))
break;
}
if(partialScore > resultScore)
{
resultScore = partialScore; // Match score
result_point.x = i;
result_point.y = j;
}
}
}
Sdx.release();
Sdy.release();
return resultScore;
}
测试效果如下:

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!