C++进阶学习:map和set的实现
我们知道set和map的底层其实是红黑树,在学习完红黑树这个数据结构之后,我们开始简单模拟实现一下这两个STL容器
目录
1.set和map的泛型编程思想
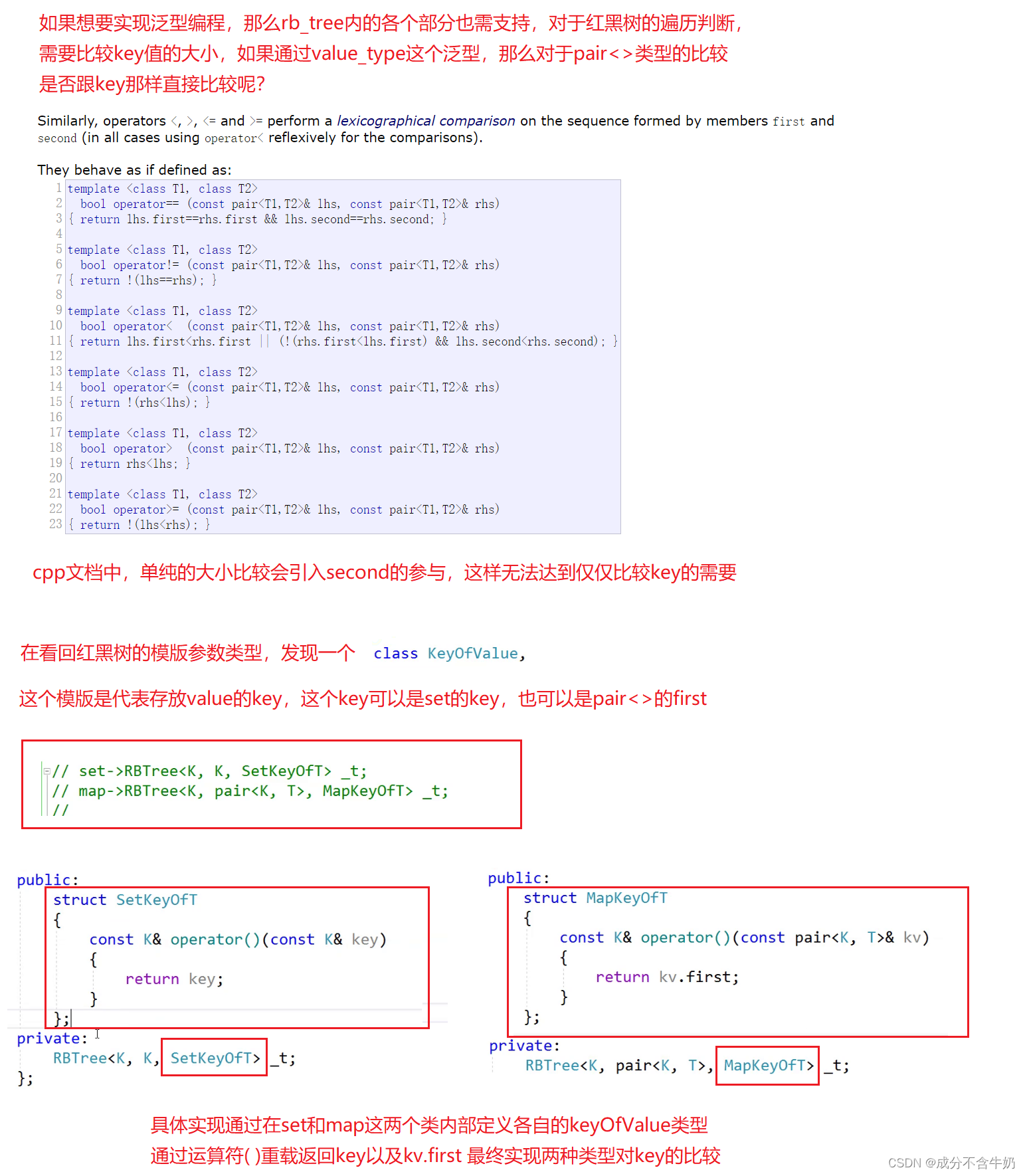
因为set和map底层高度封装所以我们需要通过源码的阅读来确定大致框架,我们发现map和set的内部均有一个value_type类型,其可以是key也可以是pair<>
简化一下上图,我们大致定义出set和map?
我们知道泛型编程的核心就是代码的复用,在这一章节体现在同一个RBTree.h文件可以支持mySet.h和myMap.h随时用?
? 而我们在前面红黑树的学习过程中,对于insert的插入位置查找,以及find的数据位置查找都需要遍历树的分支,通过的是key来寻找,如果是set类型就直接寻找,但是如果是pair类型呢?我们可能会说那就是pair<>.first来实现就好了!这个回答是没有问题的,结果却是形成了两棵树或者是需要重载两个insert,一个为bool insert(const K& key),另一个为bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)??,这样无法较好泛型编程思想
2.红黑树的结构??
通过上部分的泛型编程,讲述我们在红黑树的中定义了一个新的变量KeyOfValue来实现这个对应set与map的匹配,又因为在C++学习进阶:set 和 map-CSDN博客中关于【】重载部分,我们知道了insert返回的是pair<iterator, bool>类型,所以我们开始定义迭代器!
2.1.迭代器的实现? ? ??
首先迭代器是一个类似于指针的容器(本质是指针),内部存放节点,那么底层实现也是通过树的节点,并且为了实现const_iterator,需要传入多个模版参数,因为之前我们在list章节,讲过迭代器的实现这里的话就不赘述了,就大概展示一下结构组分
2.2.迭代器的 operator++
++和--这两个操作符重载均是为了通过迭代器进行节点的遍历,而根据红黑树的规律,以及STL库中set和map迭代器遍历规律,我们需要将节点通过正向or负向中序遍历的方式来实现!
2.3.迭代器的代码?
template<class V, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct Tree_iterator
{
typedef Tree_iterator<V, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef RBTreeNode<V> Node;
Node* _node = nullptr;
Tree_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
// 实现const的拷贝构造
Tree_iterator(const Tree_iterator<V, V&, V*>& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
Self& operator=(const Self& s)
{
_node = s._node;
return *this;
}
Self& operator++()
{
// 右子树不为空,遍历到最左节点
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
Node* current = _node->_right;
while (current != nullptr && current->_left != nullptr)
current = current->_left;
_node = current;
}
// 右子树为空 大的节点在祖先处
else
{
Node* current = _node;
Node* parent = current->_parent;
// 如果current在parent的右进入循环,下一个节点就是祖父节点
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->_right)
{
current = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
// 如果current是parent的左,不进入循环,下一个节点就是父亲节点
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left != nullptr)
{
Node* current = _node->_left;
while (current != nullptr && current->_right != nullptr)
current = current->_right;
_node = current;
}
else
{
Node* current = _node;
Node* parent = current->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->_left)
{
current = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) { return _node != s._node; }
bool operator==(const Self& s) { return _node == s._node; }
Ref operator*() { return _node->_value; }
Ptr operator->() { return &_node->_value; }
};
2.4.set和map迭代器
实现完红黑树迭代器后我们开始实现set和map的迭代器,我们知道红黑树需要同时兼容set和map,而set是key类型并且key不能修改,map是pair<const Key, value>类型?,这两个在实现时,set的迭代器不支持修改,而map的迭代器不支持key修改但是支持Value修改
?2.4.1.Insert的代码
// 增查
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const V& value)
{
// 1.先插入节点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(value);
// 根节点默认为黑色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* current = _root;
while (current != nullptr)
{
parent = current;
if (kov(current->_value) < kov(value))
current = current->_right;
else if (kov(current->_value) > kov(value))
current = current->_left;
else
return make_pair(iterator(current), false);
}
Node* newNode = new Node(value);
current = newNode;
// 新增节点默认为红色
current->_col = RED;
// 通过大小插入左右
if (kov(parent->_value) < kov(value))
parent->_right = current;
else
parent->_left = current;
current->_parent = parent;
// 2.实现颜色的变换 情况来回的迭代直至不满足循环 退出时就满足了红黑树
while (parent != nullptr && parent->_col == RED)
{
/*进入循环情况:同时满足父节点不为空,且为红色
原因: 如果父节点为空,则current为_root
如果父节点为黑色,就不用更新颜色了*/
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
// 找到叔叔节点位置
if (parent == grandparent->_left)
{
// uncle在父亲右边
Node* uncle = grandparent->_right;
// 情况一:叔叔存在,且叔叔为红色
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
// 继续向上调整
current = grandparent;
parent = current->_parent;
}
// 情况二:叔叔不存在 或者 叔叔存在但是颜色为黑色
else
{
if (current == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// current在右边
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandparent);
// 通过旋转后,旋转内部就已经完成了指针的指向
current->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// 直接退出循环即可,也可以不退出,因为父亲已经为黑色了
break;
}
}
else
{
// uncle在父亲左边
Node* uncle = grandparent->_left;
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
// 继续向上调整
current = grandparent;
parent = current->_parent;
}
else
{
if (current == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// current在左边
else {
// 注意这里单旋的节点不同
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandparent);
grandparent->_col = RED;
current->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
// 保持根节点始终为黑色,当current到达根节点可能为RED,这里就在外部变黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newNode), true);
}?所以我们实现set和map时也需要按照这个规律,这里我们以set为例子,结合insert为pair<iterator, bool>类型的函数?
2.4.2迭代器结构
set的迭代器结构
这样子我们应该是实现了const_iterator的作用,那我们通过插入数据来判断一下?,插入是成功的,不过最终会出现报错
如下图所示
那如何解决呢?
法一:
我们知道这里是,普通类型的迭代器不能作为const_iterator的接收值,也就是类型无法匹配,那么我们可以通过类型的拷贝构造,将const_iterator可以转化为原生的iterator迭代器,这样子iterator既可以作为普通的迭代器,也可以实现为const_iterator,带着这样的想法我们实现一个拷贝构造函数,代码在2.3.处有样例
法二:
另外,我们在研究pair类型时,发现pair也通过法一类似的方法实现了一个拷贝构造函数,也就是我们可以通过其他类型来实现const_iterator,我们知道迭代器的本质就是一个节点的指针,那么Node* 转化为const_iterator理论上是可行的,在通过iterator的( )默认构造函数,就可以通过iterator(pointer)
有了set的迭代器为例子,以及insert的实现,我们现在开始实现map的迭代器,map和set主要不同就是,map支持普通迭代器修改,但是会限制key的修改,也就是我们不能像set一样锁死map?
map的迭代器
我们在测试用例中尝试修改key,发现会出错,而value不受影响
 ?3.代码实现
?3.代码实现
3.1. set.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include "RBTree.h"
using namespace std;
namespace zhong
{
// set的实现
template<class V>
class set
{
// 类型匹配 对应树的 class keyOfValue
struct SetKetOf
{
const V& operator()(const V& value_type) { return value_type; } // 通过定义keyOfValue kov 然后 借助()重载 来 找到key
};
public:
// 这里体现了typename的作用
// 对类模板取内嵌类型,需要加typename告知编译器这里是内嵌类型
typedef typename RBTree<V, V, SetKetOf>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<V, V, SetKetOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;
// 迭代器
iterator begin() const { return _tree.begin(); }
iterator end() const { return _tree.end(); }
// 增查
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const V& value) { return _tree.insert(value); }
// iterator find(const V& value) { return _tree.find(value); }
private:
RBTree<V, V, SetKetOf> _tree;
};
void test_set1()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(2);
s1.insert(3);
s1.insert(4);
s1.insert(1);
set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// *it = 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
3.2. map.h
#pragma once
#include<map>
#include<iostream>
#include"RBTree.h"
using namespace std;
namespace zhong
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKetOf
{
// 通过定义keyOfValue kov 然后 借助()重载 来 找到pair的first
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& value_type) { return value_type.first; }
};
public:
// 这里体现了typename的作用
// 对类模板取内嵌类型,需要加typename告知编译器这里是内嵌类型
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKetOf>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKetOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;
V& operator[] (const K& key)
{
// insert返回pair<iterator, bool>,用ret接收插入节点的迭代器,解引用找到这个节点,接着 . 找到second
iterator ret = _tree.insert(make_pair(key, V())).first;
return (*ret).second;
//pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
// return ret.first->second;
}
// 迭代器
iterator begin() { return _tree.begin(); }
iterator end() { return _tree.end(); }
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& value_type) { return _tree.insert(value_type); }
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKetOf> _tree;
};
void test_map1()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("name", "zhong"));
dict.insert(make_pair("age", "21"));
dict.insert(make_pair("id", "2022044026"));
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
++it;
}
}
void test_map2()
{
// 测试map中的[]
string str[] = { "嗯","哦","噢","喔","好","噢","噢","好" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& s : str)
{
// map中实现计数要求
// 借助[]重载实现
countMap[s]++;
// 分成多样的功能
}
map<string, int>::iterator ret = countMap.begin();
while (ret != countMap.end())
{
cout << (*ret).first << " " << (*ret).second << endl;
++ret;
}
}
}
3.3. RBTree.h
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// 实现颜色
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
// 三叉链结构
RBTreeNode<V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<V>* _parent;
V _value;
// 实现颜色
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const V& value)
: _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _value(value)
, _col(RED) // 默认新节点红色 根节点为黑
{}
};
template<class V, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct Tree_iterator
{
typedef Tree_iterator<V, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef RBTreeNode<V> Node;
Node* _node = nullptr;
Tree_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
// 实现const的拷贝构造
Tree_iterator(const Tree_iterator<V, V&, V*>& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
Self& operator=(const Self& s)
{
_node = s._node;
return *this;
}
Self& operator++()
{
// 右子树不为空,遍历到最左节点
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
Node* current = _node->_right;
while (current != nullptr && current->_left != nullptr)
current = current->_left;
_node = current;
}
// 右子树为空 大的节点在祖先处
else
{
Node* current = _node;
Node* parent = current->_parent;
// 如果current在parent的右进入循环,下一个节点就是祖父节点
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->_right)
{
current = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
// 如果current是parent的左,不进入循环,下一个节点就是父亲节点
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left != nullptr)
{
Node* current = _node->_left;
while (current != nullptr && current->_right != nullptr)
current = current->_right;
_node = current;
}
else
{
Node* current = _node;
Node* parent = current->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && current == parent->_left)
{
current = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) { return _node != s._node; }
bool operator==(const Self& s) { return _node == s._node; }
Ref operator*() { return _node->_value; }
Ptr operator->() { return &_node->_value; }
};
template<class K, class V, class keyOfValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<V> Node;
public:
typedef Tree_iterator<V, V&, V*> iterator;
typedef Tree_iterator<V, const V&, const V*> const_iterator;
// 迭代器
iterator begin()
{
Node* current = _root;
while (current != nullptr && current->_left != nullptr)
current = current->_left;
return iterator(current);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* current = _root;
while (current != nullptr && current->_left != nullptr)
current = current->_left;
return const_iterator(current);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
// 增查
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const V& value)
{
// 1.先插入节点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(value);
// 根节点默认为黑色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* current = _root;
while (current != nullptr)
{
parent = current;
if (kov(current->_value) < kov(value))
current = current->_right;
else if (kov(current->_value) > kov(value))
current = current->_left;
else
return make_pair(iterator(current), false);
}
Node* newNode = new Node(value);
current = newNode;
// 新增节点默认为红色
current->_col = RED;
// 通过大小插入左右
if (kov(parent->_value) < kov(value))
parent->_right = current;
else
parent->_left = current;
current->_parent = parent;
// 2.实现颜色的变换 情况来回的迭代直至不满足循环 退出时就满足了红黑树
while (parent != nullptr && parent->_col == RED)
{
/*进入循环情况:同时满足父节点不为空,且为红色
原因: 如果父节点为空,则current为_root
如果父节点为黑色,就不用更新颜色了*/
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
// 找到叔叔节点位置
if (parent == grandparent->_left)
{
// uncle在父亲右边
Node* uncle = grandparent->_right;
// 情况一:叔叔存在,且叔叔为红色
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
// 继续向上调整
current = grandparent;
parent = current->_parent;
}
// 情况二:叔叔不存在 或者 叔叔存在但是颜色为黑色
else
{
if (current == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// current在右边
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandparent);
// 通过旋转后,旋转内部就已经完成了指针的指向
current->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// 直接退出循环即可,也可以不退出,因为父亲已经为黑色了
break;
}
}
else
{
// uncle在父亲左边
Node* uncle = grandparent->_left;
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
// 继续向上调整
current = grandparent;
parent = current->_parent;
}
else
{
if (current == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
}
// current在左边
else {
// 注意这里单旋的节点不同
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandparent);
grandparent->_col = RED;
current->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
// 保持根节点始终为黑色,当current到达根节点可能为RED,这里就在外部变黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newNode), true);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
}
// 外部调用封装函数
// 中序遍历
void inOrder() { _inOrder(_root); cout << endl; }
// 判断是否平衡
bool ifBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col == RED)
return false;
// 作为辅助判断
int flag = 0;
Node* current = _root;
while (current != nullptr)
{
if (current->_col == BLACK)
flag++;
current = current->_left;
}
// 设置一个flag值记录某一条路径的长度
// 如果flag不等于任何一条路径的长度就表示某一条路径黑色节点数有误
cout << "flag大小为:" << flag << endl;
// 根节点到当前节点路径上黑色节点数量
int blackNum = 0;
return check(_root, blackNum, flag);
}
// 返回树节点个数
int size() { return _size(_root); }
// 返回树的高度
int Height() { return _Height(_root); }
// 封装函数区
private:
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* root)
{
Node* parent = root;
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL != nullptr)
subRL->_parent = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
parent = subR;
if (grandparent == nullptr)
{
_root = parent;
}
else
{
if (grandparent->_left == root)
grandparent->_left = parent;
else
grandparent->_right = parent;
}
parent->_parent = grandparent;
}
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* root)
{
Node* parent = root;
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR != nullptr)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
parent->_parent = subL;
parent = subL;
if (grandparent == nullptr)
{
_root = parent;
}
else
{
if (grandparent->_left == root)
grandparent->_left = parent;
else
grandparent->_right = parent;
}
parent->_parent = grandparent;
}
// 中序遍历
void _inOrder(Node* root)
{
keyOfValue kov;
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_inOrder(root->_left);
cout << kov(root->_value) << " ";
_inOrder(root->_right);
}
// 检查是否出现连续红色节点
bool check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int flag)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
// cout << "黑色节点数目:" << blackNum << endl;
if (blackNum != flag)
{
cout << "路径上的黑色节点数存在不同" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
// 子节点和父节点均为红色,不符合红黑树
cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
++blackNum;
// 传值调用,只影响函数块,上一层不影响下一层
return check(root->_left, blackNum, flag) && check(root->_right, blackNum, flag);
}
// 计算树的节点个数
int _size(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return _size(root->_left) + _size(root->_right) + 1;
}
// 计算树的高度
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
keyOfValue kov;
};
到了这里通过红黑树初步封装map和set就讲到这里了,我们再来讲一下什么是封装,封装本质就是套个盒子在外面,当我们研究封装好的某一个类时,我们需要逐层剖析,找到封装前到底是什么牛鬼蛇神,进而有助于我们阅读源码
封装是面向对象编程中的一种重要特性,它指的是将对象的状态信息隐藏在对象内部,不允许外部程序直接访问对象内部的信息,而是通过该类所提供的方法来实现对内部信息的操作和访问。封装可以有效地保护对象的数据安全性,同时也可以提高代码的可维护性和可重用性。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!