【已解决】Python Bresenham 3D算法
2023-12-23 19:24:37
放一段使用Python实现Bresenham 3D 算法的代码,并通过Matplot可视化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from numba import njit
@njit
def bresenham_safe(grid, x0, y0, z0, x1, y1, z1, value_to_fill):
start_point = [int(x0), int(y0), int(z0)]
end_point = [int(x1), int(y1), int(z1)]
steep_xy = (abs(end_point[1] - start_point[1]) > abs(end_point[0] - start_point[0]))
if steep_xy:
start_point[0], start_point[1] = start_point[1], start_point[0]
end_point[0], end_point[1] = end_point[1], end_point[0]
steep_xz = (abs(end_point[2] - start_point[2]) > abs(end_point[0] - start_point[0]))
if steep_xz:
start_point[0], start_point[2] = start_point[2], start_point[0]
end_point[0], end_point[2] = end_point[2], end_point[0]
delta = [abs(end_point[0] - start_point[0]), abs(end_point[1] - start_point[1]), abs(end_point[2] - start_point[2])]
error_xy = delta[0] / 2
error_xz = delta[0] / 2
step = [
-1 if start_point[0] > end_point[0] else 1,
-1 if start_point[1] > end_point[1] else 1,
-1 if start_point[2] > end_point[2] else 1
]
y = start_point[1]
z = start_point[2]
for x in range(start_point[0], end_point[0], step[0]):
point = [x, y, z]
if steep_xz:
point[0], point[2] = point[2], point[0]
if steep_xy:
point[0], point[1] = point[1], point[0]
if 0 <= point[0] < grid.shape[0] and 0 <= point[1] < grid.shape[1] and 0 <= point[2] < grid.shape[2]:
grid[point[0], point[1], point[2]] = value_to_fill
error_xy -= delta[1]
error_xz -= delta[2]
if error_xy < 0:
y += step[1]
error_xy += delta[0]
if error_xz < 0:
z += step[2]
error_xz += delta[0]
@njit
def get_free_area(obstacle, x, y, z):
free = np.zeros_like(obstacle)
obstacle = obstacle > 0
xs, ys, zs = np.where(obstacle)
for ox, oy, oz in zip(xs, ys, zs):
bresenham_safe(free, ox, oy, oz, x, y, z, 1)
free -= obstacle
return free
# 创建三维网格和障碍物示例
grid = np.zeros((65, 65, 12))
obstacle = np.zeros_like(grid)
start = np.zeros_like(grid)
obstacle[20:30, 4:60, 2:9] = 1
# 获取自由区域
x = 8
y = 8
z = 11
import time
start_time = time.time()
free_area = get_free_area(obstacle, x, y, z)
end_time = time.time()
execution_time = end_time - start_time
print("□□□□□□□□□□程序执行时间为:", execution_time, "秒")
start[8,8,11]=1
# 翻转颜色映射
cmap = plt.cm.gray
cmap_inverted = cmap.reversed()
# # 可视化
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# 设置坐标轴范围和比例,让显示比例正常
x_dim, y_dim, z_dim = obstacle.shape
max_dim = max(x_dim, y_dim, z_dim)
ax.set_xlim(0, max_dim)
ax.set_ylim(0, max_dim)
ax.set_zlim(0, max_dim)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# x_indices, y_indices, z_indices = np.where(free_area)
ax.voxels(free_area, facecolors='green',)
ax.voxels(obstacle, facecolors='red',)
ax.voxels(start, facecolors='blue')
# print(grid)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
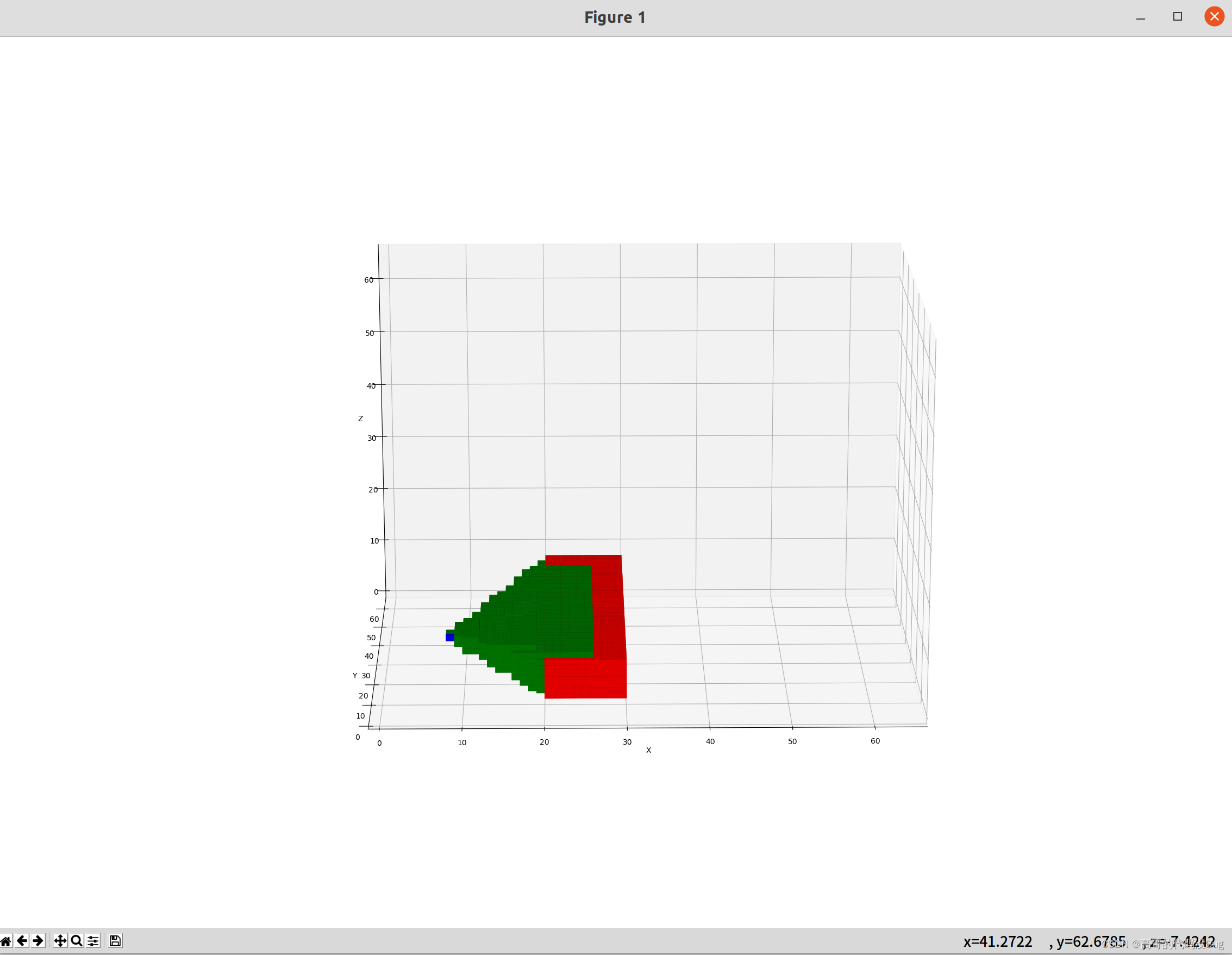
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/u013593554/article/details/135167414
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!