【AOP】面向切面编程
2023-12-28 05:16:52
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
AOP主要实现的目的是针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合性的隔离效果,对于我们开发中最常见的可能就是日志记录,事务处理,异常处理等等。
AOP中的相关概念
Aspect(切面): Aspect 声明类似于 Java 中的类声明,在 Aspect 中会包含着一些 Pointcut 以及相应的 Advice。Joint point(连接点):表示在程序中明确定义的点,典型的包括方法调用,对类成员的访问以及异常处理程序块的执行等等,它自身还可以嵌套其它 joint point。Pointcut(切点):表示一组 joint point,这些 joint point 或是通过逻辑关系组合起来,或是通过通配、正则表达式等方式集中起来,它定义了相应的 Advice 将要发生的地方。其中execution用于使用切面的连接点。使用方法:execution(方法修饰符(可选) 返回类型 方法名 参数 异常模式(可选)) ,可以使用通配符匹配字符,*可以匹配任意字符。Advice(增强):Advice 定义了在 Pointcut 里面定义的程序点具体要做的操作,它通过 before、after 和 around 来区别是在每个 joint point 之前、之后还是代替执行的代码。Target(目标对象):织入 Advice 的目标对象.。
Weaving(织入):将 Aspect 和其他对象连接起来, 并创建 Adviced object 的过程
五种通知方式
五种通知方式:Before、After、AfterReturning、AfterThrowing、Around
- Before:在某连接点之前执行的通知
- After:目标方法只要执行完了就会执行后置通知方法
- AfterReturning:在某连接点之后执行的通知,通常在一个匹配的方法返回的时候执行(可以在后置通知中绑定返回值)
- AfterThrowing:定义一个名字,该名字用于匹配通知实现方法的一个参数名,当目标方法抛出异常返回后,将把目标方法抛出的异常传给通知方法;
- Around:可以决定目标方法是否执行,什么时候执行,执行时是否需要替换方法参数,执行完毕是否需要替换返回值。
添加依赖
首先,确保在pom.xml中添加了Spring Boot AOP的依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.13</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建业务服务
@Service
public class UserService {
public void addUser(){
System.out.println("UserService.addUser");
}
public void removeUser(){
System.out.println("UserService.removeUser");
}
}
Before
@Aspect
@Component
public class ServiceAspect {
//ioc容器池里面的
//切点
@Pointcut("bean(userService)")
public void pointCut1(){}
//前置拦截
@Before("pointCut1()")
public void doBefore(){
System.out.println("ServiceAspect.doBefore");
}
}
@Test
void addUser() {
userService.addUser();
}
运行结果:
ServiceAspect.doBefore
UserService.addUser
@Test
void removeUser() {
userService.removeUser();
}
运行结果:
ServiceAspect.doBefore
UserService.removeUser
@After同@Before
Around
@Aspect
@Component
public class ServiceAspect {
//ioc容器池里面的
//切点
@Pointcut("bean(userService)")
public void pointCut1(){}
//环绕
@Around("pointCut1()")
public void doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("doAround前置代码");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("doAround后置代码");
}
}
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
UserService.addUser
doAround后置代码
//环绕
@Around("pointCut1()")
public void doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("doAround前置代码");
// proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
// System.out.println("doAround后置代码");
}
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
public int countUser(){
System.out.println("UserService.countUser");
return 8;
}
//环绕的返回结果,必须与目标方法一致
@Around("pointCut1()")
public int doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("doAround前置代码");
int methodReturned = (int) proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("doAround后置代码");
return methodReturned;
}
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
UserService.countUser
doAround后置代码
countUser = 8
AfterReturning
//返回后通知(advice)
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut1()", returning = "result")
public void doAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("ServiceAspect.doAfterReturning");
}
UserService.countUser
result = 8
ServiceAspect.doAfterReturning
countUser = 8
AfterThrowing
@Service
public class UserService {
public int countUser(){
int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("UserService.countUser");
return 8;
}
}
//当发生异常之后被触发
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut1()")
public void doAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("joinPoint = " + joinPoint);
}
joinPoint = execution(int com.it.springbootaop.service.UserService.countUser())
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
如果想要拿到具体的异常信息, 可以在注解中throwing中指明一个变量名称, 然后在方法参数中声明这个异常名称, 就会拿到
注意: 异常参数的声明必须在joinpoint之后
//当发生异常之后被触发
//如果想要拿到具体的异常信息, 可以在注解中throwing中指明一个变量名称, 然后在方法参数中声明这个异常名称, 就会拿到
//注意: 异常参数的声明必须在joinpoint之后
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut1()", throwing = "throwable")
public void doAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable){
System.out.println("joinPoint = " + joinPoint);
System.out.println("throwable = " + throwable);
}
joinPoint = execution(int com.it.springbootaop.service.UserService.countUser())
throwable = java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
切点表达式
@Pointcut(“execution(public * com.it.springbootaop.service..(…))”)
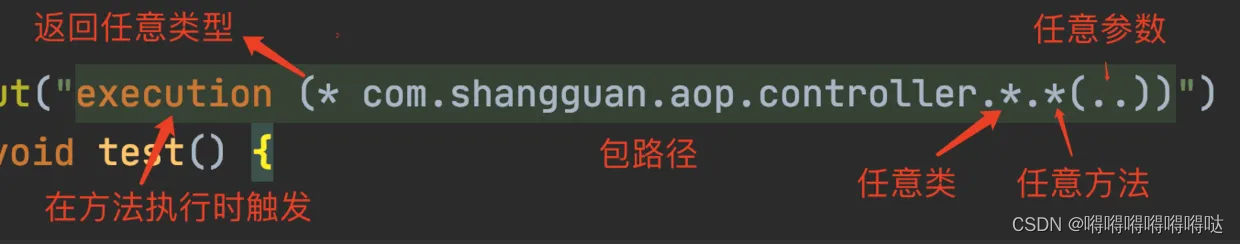
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.it.springbootaop.service.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut1(){}
@Around("pointCut1()")
public int doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("doAround前置代码");
int methodReturned = (int) proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("doAround后置代码");
return methodReturned + 10;
}
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
UserService.countUser
doAround后置代码
countUser = 18
@Service
public class JobService {
public int countJob(){
System.out.println("JobService.countJob");
return 9;
}
@Test
void countUser() {
int countUser = userService.countUser();
System.out.println("countUser = " + countUser);
int jobResult = jobService.countJob();
System.out.println("jobResult = " + jobResult);
}
对任意service都生效
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
UserService.countUser
doAround后置代码
countUser = 18
doAround前置代码
JobService.countJob
doAround后置代码
jobResult = 19
也可以指定类型
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.it.springbootaop.service.*.*(..))")
利用自定义注解使用AOP
注解
自定义注解
public @interface BiaoJi {
}
注释掉原先的切点注解
@Service
public class JobService {
@BiaoJi
public int countJob(){
System.out.println("JobService.countJob");
return 9;
}
@BiaoJi
public int countUser(){
System.out.println("UserService.countUser");
return 8;
}
@Around("@annotation(BiaoJi)")
public int doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("doAround前置代码");
int methodReturned = (int) proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("doAround后置代码");
return methodReturned + 10;
}
可以正常运行
运行结果:
doAround前置代码
UserService.countUser
doAround后置代码
countUser = 18
doAround前置代码
JobService.countJob
doAround后置代码
jobResult = 19
public @interface Logj4Info {
}
@Around("@annotation(Logj4Info)")
public void doAround2(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我是log4j打印日志");
int methodReturned = (int) joinPoint.proceed();//放通, 执行原始被拦截的那个方法
System.out.println("我是log4j2打印方法的返回结果: " + methodReturned);
//return methodReturned + 10;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_47450919/article/details/133522830
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!