JavaWeb三大组件(Servlet程序、Filter过滤器、Listener监听器)
2023-12-17 11:56:24
一、Servlet
1、Servlet概述和运行流程
概述
- Servlet (server applet) 是运行在服务端(
tomcat)的Java小程序 - Servlet主要负责接收处理请求、协同调度功能以及响应数据
- Servlet是运行在服务端的,Servlet必须在WEB项目中开发且在Tomcat这样的服务容器中运行
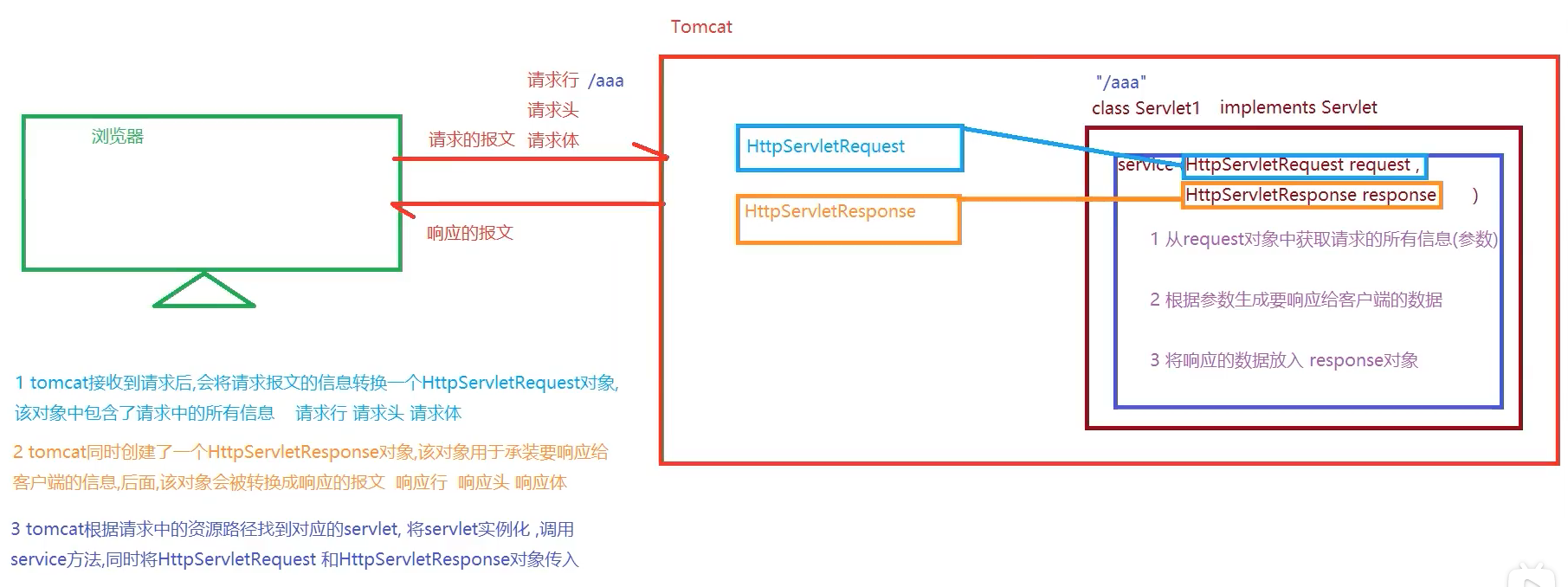
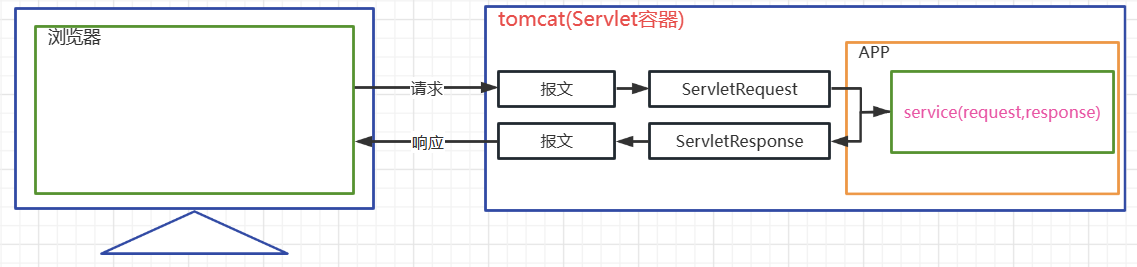
Servlet的请求和响应流程
- tomcat接收到请求后,会将请求报文的信息转换一个
HttpServletRequest对象- 该对象中包含了请求中的所有信息(请求行、请求头、请求体)
- tomcat同时创建了一个
HttpServletResponse对象,该对象用于承装要响应给
客户端的信息- 该对象后面会被转换成响应的报文(响应行、响应头、响应体)
- tomcat根据请求中的资源路径找到对应的
servlet,将servlet实例化,调用
service方法- 同时将HttpServletRequest 和HttpServletResponse对象传入
- 同时将HttpServletRequest 和HttpServletResponse对象传入
2、开发过程(xml和注解方式)
web.xml方式
pom文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xc.mvc</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!-- ServletAPI -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<!--配置Maven中Java的编译版本 -->
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<!--给UserServlet起一个别名-->
<servlet-name>myServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.xc.mvc.servlet.MyServlet</servlet-class>
<!--初始化参数-->
<init-param>
<param-name>k1</param-name>
<param-value>v1</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>k2</param-name>
<param-value>v2</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<!--关联别名和映射路径-->
<servlet-name>myServlet</servlet-name>
<!--可以为一个Servlet匹配多个不同的映射路径,但是不同的Servlet不能使用相同的url-pattern-->
<url-pattern>/myServlet</url-pattern>
<!-- <url-pattern>/myServlet2</url-pattern>-->
<!--
/ 表示通配所有资源,不包括jsp文件
/* 表示通配所有资源,包括jsp文件
/a/* 匹配所有以a前缀的映射路径
*.action 匹配所有以action为后缀的映射路径
-->
<!-- <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>-->
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Servlet程序:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
}
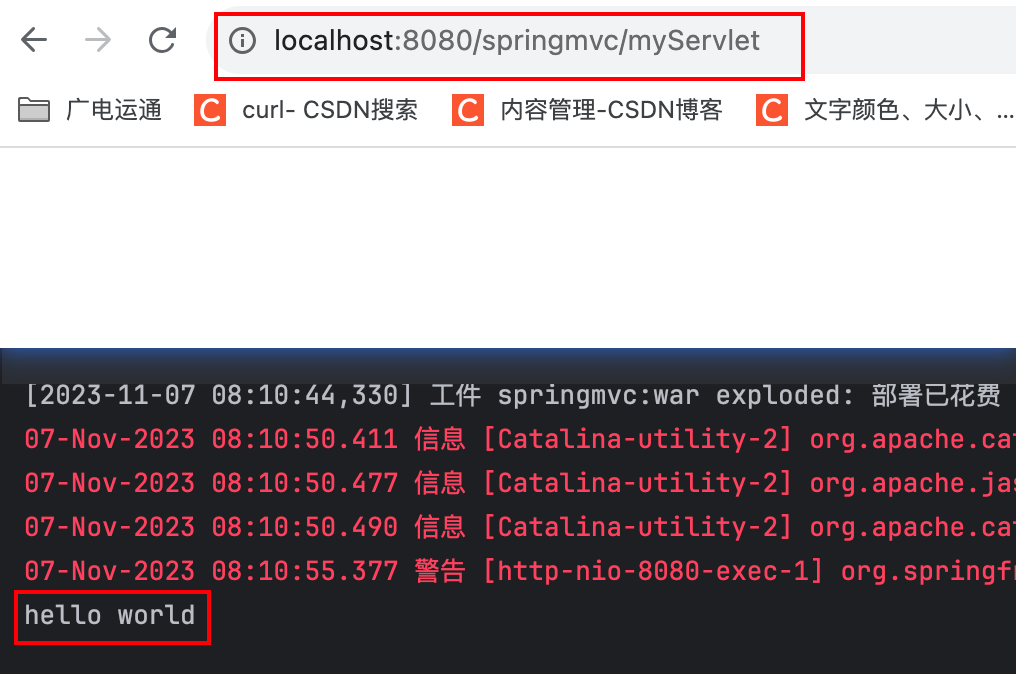
启动tomcat,访问浏览器
@WebServlet注解方式
- nane:相当于<servlet-name>,别名,一般不用设置
- urlPatterns:相当于<url-pattern>,匹配路径
- / 表示通配所有资源,
不包括jsp文件 - /* 表示通配所有资源,包括jsp文件
- /a/* 匹配所有以a前缀的映射路径
- *.action 匹配所有以action为后缀的映射路径
- / 表示通配所有资源,
- initParams:初始化参数,只有当前Servlet的程序中可以获取到(后面讲)
- loadOnStartup:Servlet是否在项目加载(tomcat启动)时实例化
- 默认-1,tomcat启动不实例化
- 因为有很多Servlet,包括自定义和tomcat内置, loadOnStartup数字越小越早实例化
- 这里配置6,因为tomcat内部的web.xml配置的Servlet的loadOnStartup已经到5
- 其实即使数字一样,也会正常运行
@WebServlet(
name = "userServlet",
//value = "/user",
urlPatterns = {"/userServlet","/userServlet1","/userServlet2"},
initParams = {
@WebInitParam(name = "k1",value = "v1"),
@WebInitParam(name = "k2",value = "v2")
},
loadOnStartup = 6
)
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
}
3、Servlet生命周期
- 简单的叙述生命周期,就是对象在容器中从开始创建到销毁的过程
- Servlet对象是Servlet容器
创建的,生命周期方法都是由容器(目前我们使用的是Tomcat)调用的
Servlet主要的生命周期执行特点
| 生命周期 | 对应方法 | 执行时机 | 执行次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 构造对象 | 构造器 | 第一次请求或者容器启动 | 1 |
| 初始化 | init() | 构造完毕后或者容器启动 | 1 |
| 处理服务 | service(req, resp) | 每次请求 | 多次 |
| 销毁 | destory() | 容器关闭 | 1 |
代码测试:
@WebServlet("/servletlifecycle")
public class ServletLifeCycle extends HttpServlet {
public ServletLifeCycle(){
System.out.println("构造器");
}
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("service方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
启动tomcat,浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/springmvc/servletlifecycle,控制台打印:
构造器
初始化方法
service方法
关闭tomcat服务器,控制台打印:
销毁方法
特别说明
- 服务器启动,控制台没有任何输出,说明ServletLifeCycle对象没实例化、初始化
- 如果@WebServlet注解添加属性
loadOnStartup = 1,服务启动时候,构造器和init方法就会执行
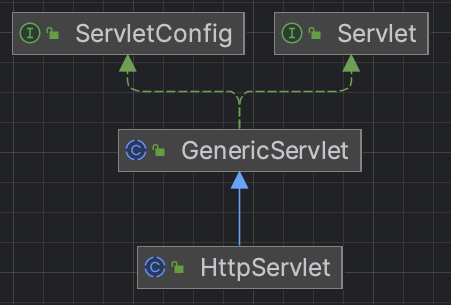
4、Servlet继承结构
抽象父类HttpServlet的类图
4.1、Servlet规范接口
- init方法
- 容器在构造servlet对象后,自动调用的方法
- 容器负责实例化一个ServletConfig对象,并在调用该方法时传入
- ServletConfig对象可以为Servlet 提供初始化参数
- service方法
- 处理请求并做出响应的服务方法,每次请求产生时由容器调用
- 容器创建一个ServletRequest对象和ServletResponse对象,容器在调用service方法时,传入这两个对象
- destroy方法
- Servlet实例在销毁之前调用的方法
public interface Servlet {
# 初始化方法
void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
# 获取ServletConfig对象
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
# service(服务)
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
# 获取servlet的信息
String getServletInfo();
# destroy(销毁)
void destroy();
}
4.2、ServletConfig配置接口
public interface ServletConfig {
# 获取Servlet的名称 -----> 可能和web.xml里面的 servlet-name 有关系
String getServletName();
# 获取上下文ServletContext对象
ServletContext getServletContext();
# 获取初始化参数
String getInitParameter(String name);
# 获取初始化的参数列表--可以理解为Iterable迭代去
Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}
4.3、GenericServlet抽象类
- tomcat创建ServletConfig对象,并且调用init方法,传入config
init和destroy方法都是空实现,子类去实现,调用时机tomcat来把握- ServletConfig对象可以获取此Servlet的
初始化参数和全局上下文对象 - service核心方法这里依然只是声明,需要子类去重写
public abstract class GenericServlet
implements Servlet, ServletConfig, java.io.Serializable
{
private transient ServletConfig config;
public GenericServlet() { }
// tomcat创建ServletConfig对象
// 并且调用init方法,传入config
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
// 这里是空实现,留给子类重写
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
// 实现Servlet规范的销毁方法,但是空实现
// 这样继承GenericServlet就可以选择是否重写destroy都可以
public void destroy() {
}
// 获取初始化时候,tomcat传入的ServletConfig对象
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return config;
}
/**
* 通过ServletConfig对象获取初始化参数,通过key获取value
*/
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
ServletConfig sc = getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
}
return sc.getInitParameter(name);
}
/**
* 获取所有的初始化参数
* Enumeration可以理解为Iterable迭代器
* hasMoreElements判断是否有值,nextElement获取值
*/
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
ServletConfig sc = getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
}
return sc.getInitParameterNames();
}
// 获取上下文对象ServletContext的方法
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
ServletConfig sc = getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
}
return sc.getServletContext();
}
// 返回空
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
// 服务方法再次声明,需要子类去实现
public abstract void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* 返回Servlet的名称
*/
public String getServletName() {
ServletConfig sc = getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
}
return sc.getServletName();
}
}
4.4、HttpServlet抽象类
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
//请求会先访问这个service
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
if(req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse) {
//将req 和res强制转换为带Http的request 和response
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
//然后调用带Http req和res的service方法
this.service((HttpServletRequest)request, (HttpServletResponse)response);
} else {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获得请求方法的类型
String method = req.getMethod();
long errMsg;
//如果是GET请求
if(method.equals("GET")) {
errMsg = this.getLastModified(req);
if(errMsg == -1L) {
//调用doGet方法
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if(ifModifiedSince < errMsg) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, errMsg);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
//如果是HEAD请求
} else if(method.equals("HEAD")) {
errMsg = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, errMsg);
this.doHead(req, resp);
//如果是POST请求
} else if(method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
//如果是PUT请求
} else if(method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
//如果是DELETE请求
} else if(method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
//如果是OPTIONS请求
} else if(method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if(method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg1 = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg1 = MessageFormat.format(errMsg1, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg1);
}
}
// 不论get还是post,抛出异常405或400
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
// HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
// HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST = 400
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
...
}
- 将ServletRequest和ServletResponse参数强制转换为
HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse - 希望子类去重写需要的请求方式的具体实现,如果不重写但发请求报错405,如下:

5、ServletConfig和ServletContext
ServletConfig
- 为Servlet提供
初始配置参数的一种对象,每个Servlet都有自己独立唯一的ServletConfig对象 - 容器会为每个Servlet实例化一个ServletConfig对象,并通过Servlet生命周期的init方法传入给Servlet作为属性
xml配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>servletA</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.xc.servlet.ServletA</servlet-class>
<!--配置ServletA的初始参数-->
<init-param>
<param-name>param1</param-name>
<param-value>value1</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>param2</param-name>
<param-value>value2</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
注解配置
@WebServlet(
name = "servletA",
urlPatterns = {"/servletA"},
initParams = {
@WebInitParam(name = "param1", value = "value1"),
@WebInitParam(name = "param2", value = "value2")
}
)
service方法中使用
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletConfig servletConfig = this.getServletConfig();
// 根据参数名获取单个参数
String value = servletConfig.getInitParameter("param1");
System.out.println("param1:" + value);
// 获取所有参数名
Enumeration<String> parameterNames = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
// 迭代并获取参数名
while (parameterNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramaterName = parameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(paramaterName+":"+servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramaterName));
}
}
}
源码,底层也就是将数据封装到map集合中
public class StandardWrapper extends ContainerBase implements ServletConfig, Wrapper, NotificationEmitter {
protected HashMap<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>();
...
@Override
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
return findInitParameter(name);
}
@Override
public String findInitParameter(String name) {
parametersLock.readLock().lock();
try {
return parameters.get(name);
} finally {
parametersLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
parametersLock.readLock().lock();
try {
return Collections.enumeration(parameters.keySet());
} finally {
parametersLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
ServletContext
- ServletContext对象有称呼为上下文对象,或者叫应用域对象
- 容器会为每个
app创建一个独立的唯一的ServletContext对象 - ServletContext对象为所有的Servlet
共享 - ServletContext可以为所有的Servlet提供初始配置参数
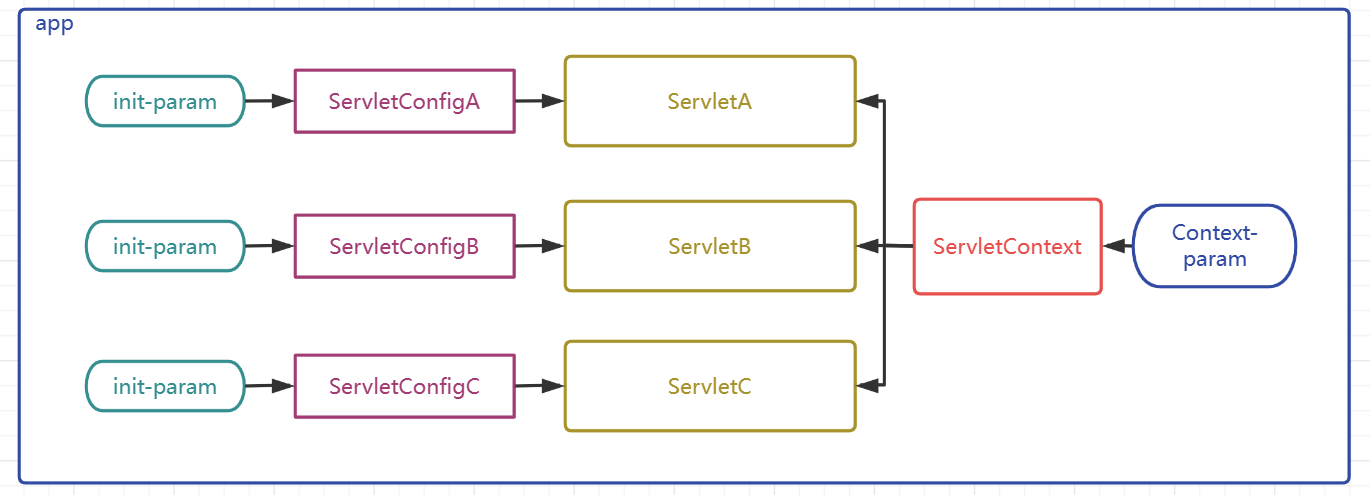
配置ServletContext参数
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>paramA</param-name>
<param-value>valueA</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>paramB</param-name>
<param-value>valueB</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
service方法中使用
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 从ServletContext中获取为所有的Servlet准备的参数
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String valueA = servletContext.getInitParameter("paramA");
System.out.println("paramA:" + valueA);
// 获取所有参数名
Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
// 迭代并获取参数名
while (initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramaterName = initParameterNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(paramaterName+":"+servletContext.getInitParameter(paramaterName));
}
}
}
源码,也是将数据封装到map集合中
public class ApplicationContext implements ServletContext {
private final Map<String, String> parameters = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public String getInitParameter(final String name) {
// Special handling for XML settings as the context setting must
// always override anything that might have been set by an application.
if (Globals.JASPER_XML_VALIDATION_TLD_INIT_PARAM.equals(name) && context.getTldValidation()) {
return "true";
}
if (Globals.JASPER_XML_BLOCK_EXTERNAL_INIT_PARAM.equals(name)) {
if (!context.getXmlBlockExternal()) {
// System admin has explicitly changed the default
return "false";
}
}
return parameters.get(name);
}
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
Set<String> names = new HashSet<>(parameters.keySet());
// Special handling for XML settings as these attributes will always be
// available if they have been set on the context
if (context.getTldValidation()) {
names.add(Globals.JASPER_XML_VALIDATION_TLD_INIT_PARAM);
}
if (!context.getXmlBlockExternal()) {
names.add(Globals.JASPER_XML_BLOCK_EXTERNAL_INIT_PARAM);
}
return Collections.enumeration(names);
}
}
ServletContext域对象API
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void setAttribute(String key,Object value); | 向域中存储/修改数据 |
| Object getAttribute(String key); | 获得域中的数据 |
| void removeAttribute(String key); | 移除域中的数据 |
6、HttpServletRequest和HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletRequest是一个
接口,其父接口是ServletRequest - HttpServletRequest是Tomcat将
请求报文转换封装而来的对象,在Tomcat调用service方法时传入 - HttpServletRequest代表客户端发来的请求,所有请求中的信息都可以通过该对象获得
常用api如下:
- 获取请求行信息相关(方式,请求的url,协议及版本)
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| StringBuffer getRequestURL(); | 获取客户端请求的url |
| String getRequestURI(); | 获取客户端请求项目中的具体资源 |
| int getServerPort(); | 获取客户端发送请求时的端口 |
| int getLocalPort(); | 获取本应用在所在容器的端口 |
| int getRemotePort(); | 获取客户端程序的端口 |
| String getScheme(); | 获取请求协议 |
| String getProtocol(); | 获取请求协议及版本号 |
| String getMethod(); | 获取请求方式 |
- 获得请求头信息相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getHeader(String headerName); | 根据头名称获取请求头 |
| Enumeration getHeaderNames(); | 获取所有的请求头名字 |
| String getContentType(); | 获取content-type请求头 |
- 获得请求参数相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getParameter(String parameterName); | 根据请求参数名获取请求单个参数值 |
| String[] getParameterValues(String parameterName); | 根据请求参数名获取请求多个参数值数组 |
| Enumeration getParameterNames(); | 获取所有请求参数名 |
| Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap(); | 获取所有请求参数的键值对集合 |
| BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException; | 获取读取请求体的字符输入流 |
| ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException; | 获取读取请求体的字节输入流 |
| int getContentLength(); | 获得请求体长度的字节数 |
- 其他API
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| String getServletPath(); | 获取请求的Servlet的映射路径 |
| ServletContext getServletContext(); | 获取ServletContext对象 |
| Cookie[] getCookies(); | 获取请求中的所有cookie |
| HttpSession getSession(); | 获取Session对象 |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String encoding) ; | 设置请求体字符集 |
HttpServletResponse
- HttpServletResponse是一个
接口,其父接口是ServletResponse - HttpServletResponse是Tomcat预先创建的,在Tomcat调用service方法时传入
- HttpServletResponse代表对客户端的响应,该对象会被转换成
响应报文发送给客户端,通过该对象我们可以设置响应信息
常用api如下:
- 设置响应行相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void setStatus(int code); | 设置响应状态码 |
- 设置响应头相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void setHeader(String headerName, String headerValue); | 设置/修改响应头键值对 |
| void setContentType(String contentType); | 设置content-type响应头及响应字符集(设置MIME类型) |
- 设置响应体相关
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException; | 获得向响应体放入信息的字符输出流 |
| ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException; | 获得向响应体放入信息的字节输出流 |
| void setContentLength(int length); | 设置响应体的字节长度,其实就是在设置content-length响应头 |
- 其他API
| API | 功能解释 |
|---|---|
| void sendError(int code, String message) throws IOException; | 向客户端响应错误信息的方法,需要指定响应码和响应信息 |
| void addCookie(Cookie cookie); | 向响应体中增加cookie |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String encoding); | 设置响应体字符集 |
MIME类型
- MIME类型,可以理解为文档类型,用户表示传递的数据是属于什么类型的文档
- 浏览器可以根据MIME类型决定该用什么样的方式解析接收到的响应体数据
- 可以这样理解: 前后端交互数据时,告诉对方发给对方的是 html/css/js/图片/声音/视频/… …
- tomcat/conf/web.xml中配置了常见文件的拓展名和MIMIE类型的对应关系
- 常见的MIME类型举例如下
| 文件拓展名 | MIME类型 |
|---|---|
| .html | text/html |
| .css | text/css |
| .js | application/javascript |
| .png /.jpeg/.jpg/… … | image/jpeg |
| .mp3/.mpe/.mpeg/ … … | audio/mpeg |
| .mp4 | video/mp4 |
| .m1v/.m1v/.m2v/.mpe/… … | video/mpeg |
二、过滤器
1、过滤器概述
- Filter,即过滤器,是JAVAEE技术规范之一,作用目标资源的请求进行过滤的一套技术规范,是Java Web项目中
最为实用的技术之一 Filter接口定义了过滤器的开发规范,所有的过滤器都要实现该接口- Filter的常用应用包括但不限于: 登录权限检查,解决网站乱码,过滤敏感字符,日志记录,跨域的处理…
过滤器工作位置图解
- Filter的工作位置是项目中所有目标资源之前,容器在
创建HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象后,会先调用Filter的doFilter方法 - Filter的doFilter方法可以控制请求是否继续,如果放行,则请求继续,如果拒绝,则请求到此为止,由过滤器本身做出响应
- Filter不仅可以对请求做出过滤,也可以在目标资源做出响应前,对响应再次进行处理
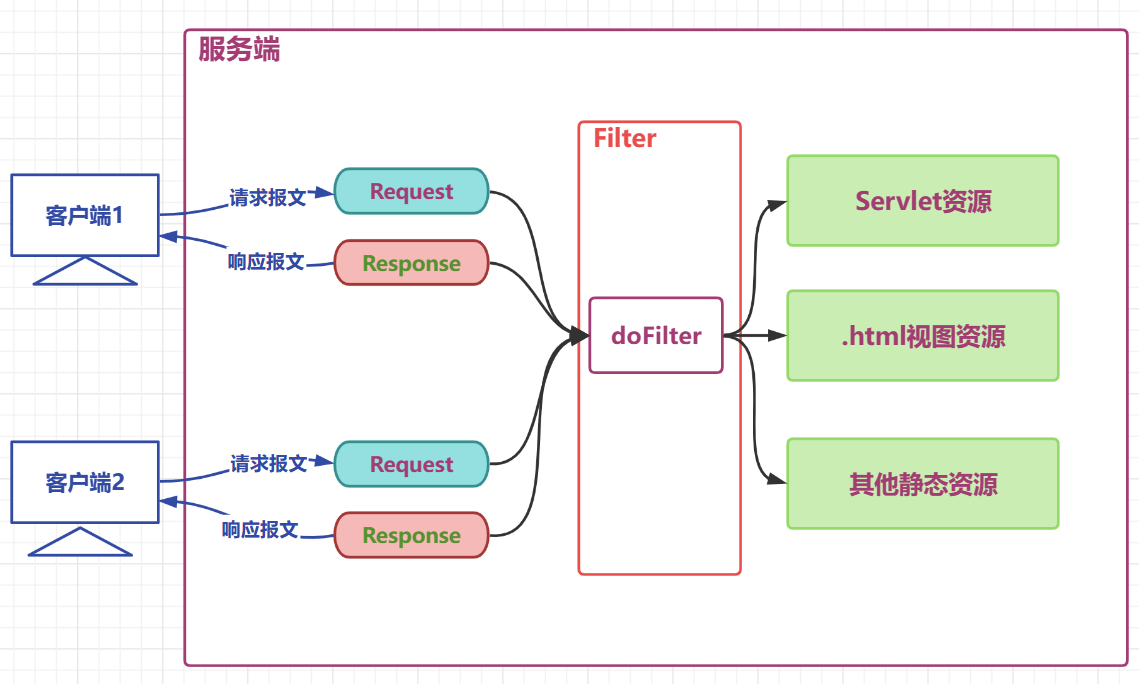
2、过滤器使用
2.1、Filter接口
- init:初始化方法,由容器调用并传入初始配置信息filterConfig对象
- doFilter:过滤方法,核心方法,过滤请求,决定是否放行,响应之前的其他处理等都在该方法中
- destroy:销毁方法,容器在回收过滤器对象之前调用的方法
package jakarta.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Filter {
// 初始化方法
default public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
// 过滤方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException;
// 销毁方法
default public void destroy() {
}
}
2.2、web.xml配置过滤器
过滤器实现程序执行时间
日志过滤器,实现Filter接口
public class LoggingFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 参数父转子
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
// 拼接日志文本
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
String time = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());
// 打印日志
System.out.println(requestURI + "在" + time + "被请求了");
// 获取系统时间
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 放行请求
// 如果没有这一行代码,则请求到此为止
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
// 获取系统时间
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 打印日志
System.out.println(requestURI + "在" + time + "的请求耗时:" + (t2 - t1) + "毫秒");
}
}
Servlet程序
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servletFilter",name = "servletFilterName")
public class ServletFilter extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 处理器请求
System.out.println("servletFilter处理请求的方法,耗时10毫秒");
// 模拟处理请求耗时
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--配置filter,并为filter起别名-->
<filter>
<filter-name>loggingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.xc.mvc.filter.LoggingFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--为别名对应的filter配置要过滤的目标资源-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>loggingFilter</filter-name>
<!--方式一:通过映射路径确定过滤资源-->
<url-pattern>/servletFilter</url-pattern>
<!--方式二:通过servlet别名确定过滤资源-->
<servlet-name>servletFilterName</servlet-name>
<!--方式三:通过后缀名确定过滤资源-->
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
- filter-mapping标签中定义了过滤器对那些资源进行过滤
- 子标签
url-pattern通过映射路径确定过滤范围- /servletA 精确匹配,表示对servletA资源的请求进行过滤
- .html 表示对以.action结尾的路径进行过滤
/*表示对所有资源进行过滤一个filter-mapping下可以配置多个url-pattern
- 子标签
servlet-name通过servlet别名确定对那些servlet进行过滤- 使用该标签确定目标资源的前提是servlet已经起了别名
- 一个filter-mapping下可以定义多个servlet-name
- 一个filter-mapping下,servlet-name和url-pattern子标签可以同时存在
2.3、@WebFilter注解方式配置过滤器
@WebFilter(
filterName = "loggingFilter",
urlPatterns = {"/servletA","*.html"},
servletNames = {"servletBName"}
)
public class LoggingFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 过滤业务代码
}
}
3、过滤器生命周期
- 过滤器作为web项目的组件之一,和Servlet的生命周期类似,略有不同
- 没有servlet的load-on-startup的配置,
默认就是系统启动立刻构造
| 阶段 | 对应方法 | 执行时机 | 执行次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 创建对象 | 构造器 | web应用启动时 | 1 |
| 初始化方法 | void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) | 构造完毕 | 1 |
| 过滤请求 | void doFilter(ServletRequest , ServletResponse , FilterChain ) | 每次请求 | 多次 |
| 销毁 | default void destroy() | web应用关闭时 | 1次 |
测试代码
@WebFilter("/*")
public class LifeCycleFilter implements Filter {
public LifeCycleFilter(){
System.out.println("LifeCycleFilter 构造函数执行");
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("LifeCycleFilter 初始化方式执行");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("LifeCycleFilter 过滤方法执行");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("LifeCycleFilter 销毁方法执行");
}
}
执行结果:
- 项目启动
LifeCycleFilter 构造函数执行
LifeCycleFilter 初始化方式执行
- 请求Servlet
LifeCycleFilter 过滤方法执行
- 关闭tomcat
LifeCycleFilter 销毁方法执行
4、过滤器链的使用
- 一个web项目中,可以同时定义
多个过滤器 - 多个过滤器对同一个资源进行过滤时,工作位置有
先后,整体形成一个工作链,称之为过滤器链
图解过滤器
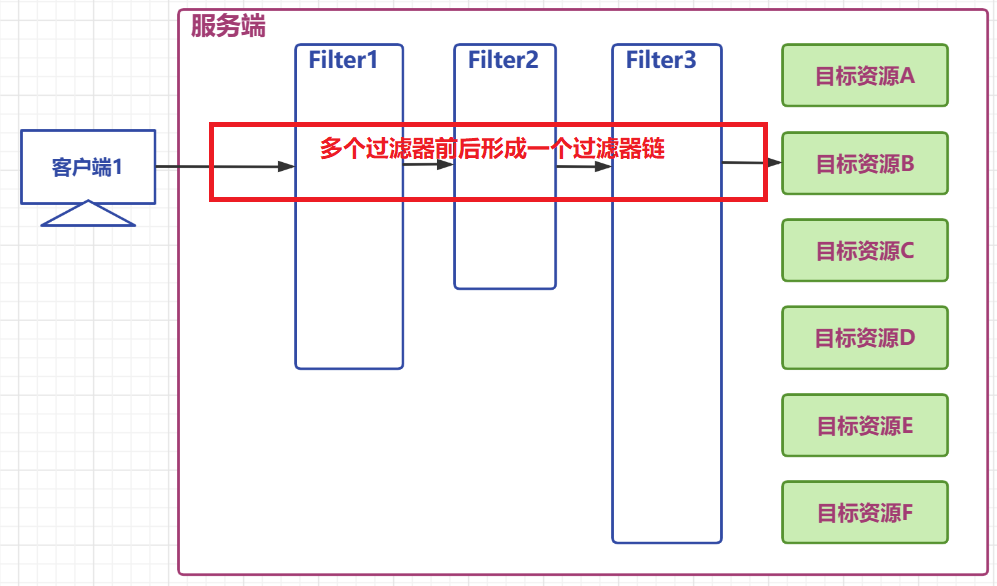
过滤器链功能测试
定义三个过滤器,对目标资源Servlet的请求进行过滤
目标Servlet资源代码:
@WebServlet("/servletTest")
public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("ServletTest的service方法执行");
}
}
三个过滤器代码:
public class Filter1 implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("filter1 before chain.doFilter code invoked");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
System.out.println("filter1 after chain.doFilter code invoked");
}
}
public class Filter2 implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("filter2 before chain.doFilter code invoked");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
System.out.println("filter2 after chain.doFilter code invoked");
}
}
public class Filter3 implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("filter3 before chain.doFilter code invoked");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
System.out.println("filter3 after chain.doFilter code invoked");
}
}
过滤器配置代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd"
version="5.0">
<filter>
<filter-name>filter1</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.xc.mvc.filter.Filter1</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter>
<filter-name>filter2</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.xc.mvc.filter.Filter2</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter>
<filter-name>filter3</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.xc.mvc.filter.Filter3</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--filter-mapping的顺序决定了过滤器的工作顺序-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter1</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletTest</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletTest</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter3</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletTest</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
执行结果:
filter1 before chain.doFilter code invoked
filter2 before chain.doFilter code invoked
filter3 before chain.doFilter code invoked
ServletTest的service方法执行
filter3 after chain.doFilter code invoked
filter2 after chain.doFilter code invoked
filter1 after chain.doFilter code invoked
工作流程图解
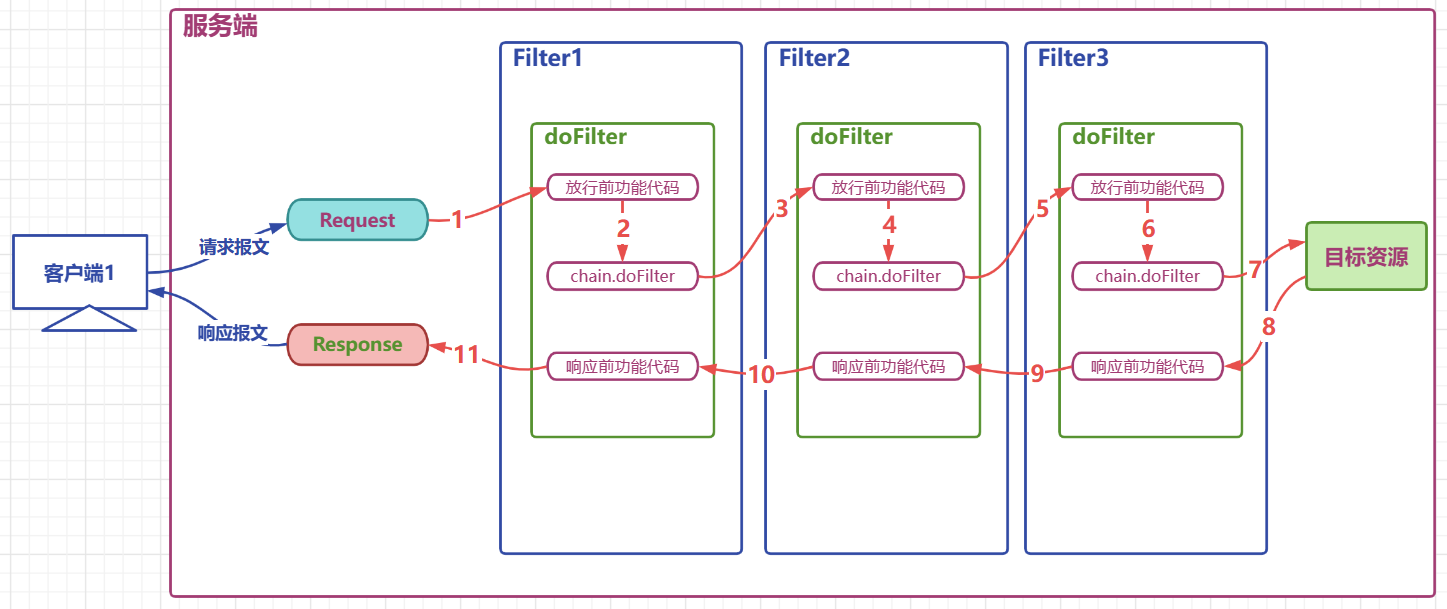
多个过滤器顺序
- xml方式:从上往下根据
<filter-mapping>定义先后顺序 - @WebFilter注解方式:根据
过滤器名称自然排序
三、监听器
1、监听器概述
- 监听器:专门用于对
域对象对象身上发生的事件或状态改变进行监听和相应处理的对象 - 监听器使用的感受类似JS中的事件,被观察的对象发生某些情况时,自动触发代码的执行
- 监听器并不监听web项目中的所有组件,仅仅是对
三大域对象做相关的事件监听 - 监听器的分类
application域监听器ServletContextListenerServletContextAttributeListenersession域监听器 HttpSessionListener HttpSessionAttributeListener HttpSessionBindingListener HttpSessionActivationListenerrequest域监听器 ServletRequestListener ServletRequestAttributeListener
2、application域监听器
- ServletContextListener 监听ServletContext对象的
创建与销毁 - ServletContextEvent对象代表从ServletContext对象身上捕获到的事件,通过这个事件对象我们可以获取到ServletContext对象
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) | ServletContext创建时调用 |
| contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) | ServletContext销毁时调用 |
- ServletContextAttributeListener 监听ServletContext中
属性的添加、移除和修改
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 向ServletContext中添加属性时调用 |
| attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 从ServletContext中移除属性时调用 |
| attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 当ServletContext中的属性被修改时调用 |
- ServletContextAttributeEvent对象代表属性变化事件,它包含的方法如下:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| getName() | 获取修改或添加的属性名 |
| getValue() | 获取被修改或添加的属性值 |
| getServletContext() | 获取ServletContext对象 |
定义监听器
@WebListener
public class ApplicationListener implements ServletContextListener, ServletContextAttributeListener {
// 监听初始化
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
ServletContext application = sce.getServletContext();
System.out.println("application" + application.hashCode() + " initialized");
}
// 监听销毁
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
ServletContext application = sce.getServletContext();
System.out.println("application" + application.hashCode() + " destroyed");
}
// 监听数据增加
@Override
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
String name = scae.getName();
Object value = scae.getValue();
ServletContext application = scae.getServletContext();
System.out.println("application" + application.hashCode() + " add:" + name + "=" + value);
}
// 监听数据移除
@Override
public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
String name = scae.getName();
Object value = scae.getValue();
ServletContext application = scae.getServletContext();
System.out.println("application" + application.hashCode() + " remove:" + name + "=" + value);
}
// 监听数据修改
@Override
public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
String name = scae.getName();
Object value = scae.getValue();
ServletContext application = scae.getServletContext();
Object newValue = application.getAttribute(name);
System.out.println("application" + application.hashCode() + " change:" + name + "=" + value + " to " + newValue);
}
}
定义触发监听器的Servlet
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servletListener")
public class ServletListener extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext application = this.getServletContext();
// 新增application域的数据
application.setAttribute("k1", "v1");
// 修改application域中的数据
application.setAttribute("k1", "value1");
// 删除application域中的数据
application.removeAttribute("k1");
}
}
执行结果:
tomcat启动和关闭会执行ServletContextListener监听器的初始化和销毁方法Application域对象的增删改会执行ServletContextAttributeListener监听器的对应方法
application110534608 initialized
...
application110534608 add:k1=v1
application110534608 change:k1=v1 to value1
application110534608 remove:k1=value1
...
application110534608 destroyed
session域监听器和request域监听器与application域监听器唯一不同的就是监听对象不一样
3、session域的两个特殊监听器
3.1、session绑定监听器
- HttpSessionBindingListener 监听
当前监听器对象在Session域中的增加与移除
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 该类的实例被放到Session域中时调用 |
| valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 该类的实例从Session中移除时调用 |
- HttpSessionBindingEvent对象代表属性变化事件,它包含的方法如下:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| getName() | 获取当前事件涉及的属性名 |
| getValue() | 获取当前事件涉及的属性值 |
| getSession() | 获取触发事件的HttpSession对象 |
定义监听器
public class MySessionBindingListener implements HttpSessionBindingListener {
// 监听绑定
@Override
public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
HttpSession session = event.getSession();
String name = event.getName();
System.out.println("MySessionBindingListener"+this.hashCode()+" binding into session"+session.hashCode()+" with name "+name);
}
// 监听解除绑定
@Override
public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
HttpSession session = event.getSession();
String name = event.getName();
System.out.println("MySessionBindingListener"+this.hashCode()+" unbond outof session"+session.hashCode()+" with name "+name);
}
}
定义触发监听器的Servlet
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servletA",name = "servletAName")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 绑定监听器
session.setAttribute("bindingListener",new MySessionBindingListener());
// 解除绑定监听器
session.removeAttribute("bindingListener");
}
}
3.2、钝化活化监听器
- HttpSessionActivationListener 监听
某个对象在Session中的序列化与反序列化 - HttpSessionEvent对象代表事件对象,通过getSession()方法获取事件涉及的HttpSession对象
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) | 该类实例和Session一起钝化到硬盘时调用 |
| sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) | 该类实例和Session一起活化到内存时调用 |
如何配置钝化活化
文件中配置钝化
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context>
<Manager className="org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManager" maxIdleSwap="1">
<Store className="org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore" directory="d:\mysession"></Store>
</Manager>
</Context>
定义监听器
public class ActivationListener implements HttpSessionActivationListener, Serializable {
// 监听钝化
@Override
public void sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {
HttpSession session = se.getSession();
System.out.println("session with JSESSIONID "+ session.getId()+" will passivate");
}
// 监听活化
@Override
public void sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {
HttpSession session = se.getSession();
System.out.println("session with JSESSIONID "+ session.getId()+" did activate");
}
}
定义触发监听器的Servlet
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servletA",name = "servletAName")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 添加数据
session.setAttribute("k1","v1");
// 添加钝化活化监听器
session.setAttribute("activationListener",new ActivationListener());
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35512802/article/details/134257185
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!