Android--Jetpack--Databinding详解
不经一番寒彻骨,怎得梅花扑鼻香
一,定义
DataBinding, 又名数据绑定,是Android开发中非常重要的基础技术,它可以将UI组件和数据模型连接起来,使得在数据模型发生变化时,UI组件自动更新。是 MVVM 模式在 Android 上的一种实现,用于降低布局和逻辑的耦合性,使代码逻辑更加清晰。MVVM 相对于 MVP,其实就是将 Presenter 层替换成了 ViewModel 层。DataBinding 能够省去我们一直以来的 findViewById() 步骤,大量减少 Activity 内的代码,数据能够单向或双向绑定到 layout 文件中,有助于防止内存泄漏,而且能自动进行空检测以避免空指针异常
二,基本使用
1,在app的build.gradle中 开启databinding:
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.yuanzhen.lifecycledemo"
minSdk 24
targetSdk 33
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
//使用databinding
dataBinding{
enabled true
}
}2,在布局文件XML中,选中根布局,ALT+回车:
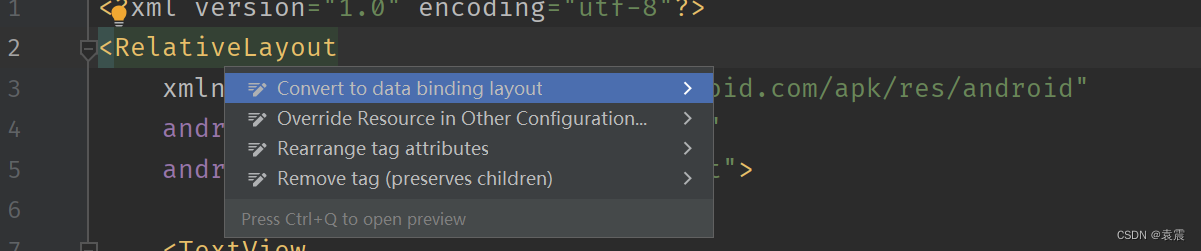
选择Convert to data binding layout ,会自动转换为 DataBinding 需要的布局规则:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
</data>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt_name"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</layout>3, 创建数据bean:
public class YuanZhen {
public YuanZhen(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}4,在XML中设置创建的数据bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<import type="com.yuanzhen.lifecycledemo.databing.YuanZhen"/>
<variable
name="yuanzhen"
type="YuanZhen"/>
</data>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{yuanzhen.name}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(yuanzhen.age)}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt_name"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</layout>注意:这里的int需要转换为String?
5,在Activity中用DatabindingUtil 替换原来的setContentView,创建数据源,绑定databinding
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActivityMainBinding dataBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
dataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
YuanZhen yuanZhen =new YuanZhen("袁震",18);
dataBinding.setYuanzhen(yuanZhen);
}
}运行:

三,特殊用法
1,在上面我们使用的ActivityMainBinding 是自动生成的,这里我们可以自定义它的名称:MyDataBing
<data class="MyDataBing">
<import type="com.yuanzhen.lifecycledemo.databing.YuanZhen"/>
<variable
name="yuanzhen"
type="YuanZhen"/>
</data>public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MyDataBing dataBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
dataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
YuanZhen yuanZhen =new YuanZhen("袁震",18);
dataBinding.setYuanzhen(yuanZhen);
}
}2,我们可以通过databinding获取在XML里面赋值的组件:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MyDataBing dataBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
dataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
YuanZhen yuanZhen =new YuanZhen("袁震",18);
dataBinding.setYuanzhen(yuanZhen);
dataBinding.txtName.setText("袁震1111");
dataBinding.txtAge.setText("28");
}
}注意:这里赋值了并不会刷新
四,单向数据绑定
实现数据变化自动驱动 UI 刷新的方式有三种:BaseObservable、ObservableField、ObservableCollection
BaseObservable是一个纯净的 ViewModel 类被更新后,并不会让 UI 自动更新。而数据绑定后,我们自然会希望数据变更后 UI 会即时刷新,Observable 就是为此而生的概念
BaseObservable?提供了?notifyChange()?和?notifyPropertyChanged()?两个方法,前者会刷新所有的值域,后者则只更新对应?BR?的?flag,该 BR 的生成通过注释?@Bindable?生成,可以通过?BR notify?特定属性关联的视图
下面来看下使用案例:
1,将数据Bean继承BaseObservable 并实现刷新方法:
public class YuanZhen extends BaseObservable {
public YuanZhen(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.name);
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.age);
}
@Bindable
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Bindable
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}2,在Activity中每隔1s改变一下name和age:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MyDataBing dataBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
dataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
YuanZhen yuanZhen =new YuanZhen("袁震",18);
dataBinding.setYuanzhen(yuanZhen);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
yuanZhen.setName(yuanZhen.getName()+i);// view.setText(text);
yuanZhen.setAge(18+i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}运行结果:

?五,双向数据绑定
双向绑定的意思即为当数据改变时同时使视图刷新,而视图改变时也可以同时改变数据
我们在xml里面增加一个EditText,这个EditText绑定了yuanzhen.name:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data class="MyDataBing">
<import type="com.yuanzhen.lifecycledemo.databing.YuanZhen"/>
<variable
name="yuanzhen"
type="YuanZhen"/>
</data>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{yuanzhen.name}"
android:textSize="40sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(yuanzhen.age)}"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt_name"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt_age"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="@={yuanzhen.name}"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</layout>其余代码还是保持不变,让我们来看运行结果:

六,运算符
DataBinding 支持在布局文件中使用以下运算符、表达式和关键字
* 算术 + - / \* %
* 字符串合并 +
* 逻辑 && ||
* 二元 & | ^
* 一元 + - ! ~
* 移位 >> >>> <<
* 比较 == > < >= <=
* Instanceof
* Grouping ()
* character, String, numeric, null
* Cast
* 方法调用
* Field 访问
* Array 访问 \[\]
* 三元 ?:
目前不支持以下操作
* this
* super
* new
* 显示泛型调用?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!