【Linux C 几种锁的性能对比】 1.读写锁 2.互斥锁 3.自旋锁 4.信号量 5.rcu
2023-12-30 10:45:21
直接上代码
rcu.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <urcu.h>
/* 1.读写锁
2.互斥锁
3.自旋锁
4.信号量
5.rcu
*/
#define RW_LOCK 0
#define MUTEX_LOCK 0
#define SPIN_LOCK 0
#define _SEM 0
#define URCU 1
struct point{
int x;
int y;
};
struct point *gp;
int done = 0;
long reads = 0;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_t;
pthread_spinlock_t spinlock;
sem_t sem;
void *timer(void *arg){
struct timespec ts, ts2;
timespec_get(&ts, TIME_UTC);
while(!done){
sleep(1);
timespec_get(&ts2, TIME_UTC);
time_t sec = ts2.tv_sec - ts.tv_sec;
printf("reads: %ld, %ld K reads/sec\n", reads, (reads/sec)/1000);
}
}
void *updater(void *arg){
struct point *p;
struct point *old;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i< INT_MAX; i ++){
p = malloc(sizeof(struct point));
p->x = i;
p->y = i+1;
old = gp;
#if 0
gp = p;
#elif RW_LOCK
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
gp = p;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
#elif MUTEX_LOCK
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_t);
gp = p;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_t);
#elif SPIN_LOCK
pthread_spin_lock(&spinlock);
gp = p;
pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock);
#elif URCU
rcu_assign_pointer(gp, p);
synchronize_rcu();
#else
sem_wait(&sem);
gp = p;
sem_post(&sem);
#endif
free(old);
}
}
void *reader(void *arg){
rcu_register_thread();//urcu
while(!done){
int x, y;
#if 0
x = gp->x;
y = gp->y;
#elif RW_LOCK
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
x = gp->x;
y = gp->y;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
#elif MUTEX_LOCK
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_t);
x = gp->x;
y = gp->y;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_t);
#elif SPIN_LOCK
pthread_spin_lock(&spinlock);
x = gp->x;
y = gp->y;
pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock);
#elif URCU
rcu_read_lock();
struct point *p = rcu_dereference(gp);
x = p->x;
y = p->y;
rcu_read_unlock();
#else
sem_wait(&sem);
x = gp->x;
y = gp->y;
sem_post(&sem);
#endif
reads ++;
if(y != x+1){
printf("Error: x:%d, y:%d\n", x, y);
done = 1;
break;
}
}
rcu_unregister_thread();
exit(1);
}
// gcc -o rcu rcu.c -lpthread -lurcu
int main(){
pthread_t tid[3];
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_t, NULL);
pthread_spin_init(&spinlock, PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED);
sem_init(&sem, 0, 1);
rcu_init();//rcu
gp = malloc(sizeof(struct point));
gp->x = 1;
gp->y = 2;
pthread_create(&tid[0], NULL, updater, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid[1], NULL, reader, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid[2], NULL, timer, NULL);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i ++){
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
free(gp);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_t);
pthread_spin_destroy(&spinlock);
return 0;
}
读写线程相当情况下 读写速度 对比
1.读写锁
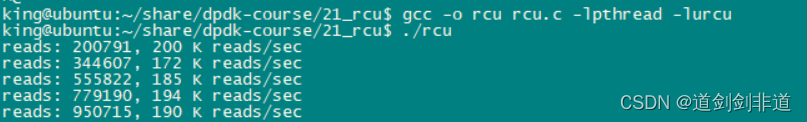
2.互斥锁
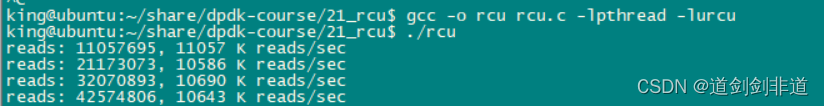
3.自旋锁
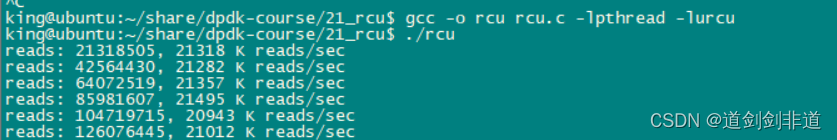
4.信号量
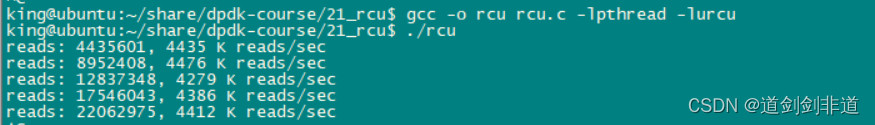
5.rcu
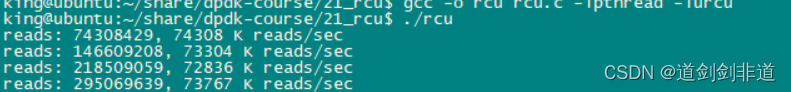
可以看出rcu读写性能优异 , 多线程同步不建议使用读写锁,嫌麻烦可以直接用互斥锁
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45397344/article/details/135209177
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!