凸包&半平面求交 - 洛谷 - P7397 雨水收集系统
2024-01-02 20:42:29
欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
题目大意
题目链接
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P7397
城市中有很多高楼,使用矩形表示。
云层用凸多边形表示,云层会移动,在特定的时间段下雨,云层经过的地方就会接受到雨。
求高楼能够接受到雨的面积总和。
解析

C到C’与虚线围成的区域既为降水区域,灰色为可以接受雨水的面积。
只要求出降水区域,再逐各与多边形求交即可。
凸多边形求交点击前往
降水区域多边形求解步骤:
- 先求出云层所在的凸包 点击前往
- 利用向量和降雨起止时间点得到C, C’位置。
- 添加虚线,并删除中间线条,具体步骤如下图。
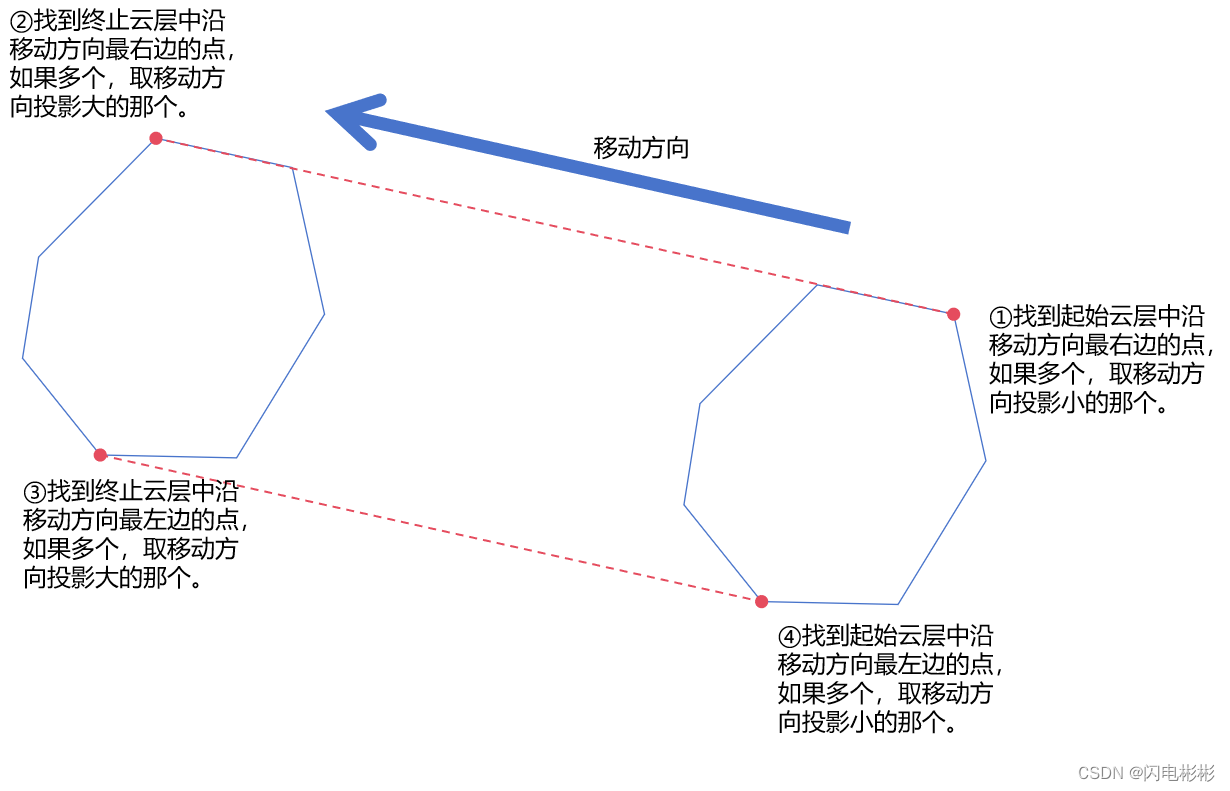
上图中按照步骤1,2,3,4找到4个标记点,合围区域内的边可以删除。
注意有边与移动方向平行的情况,需要用投影来判断取哪个。
tips:题目输入为整数,计算中能用整数尽量用整数,减少浮点误差,提升精度。矩阵坐标不一定是左下右上表示
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
const int N = 2e3 + 10;
namespace FloatSys {
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d > 0)return 1;
return -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.3f %.3f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (abs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return abs(x - a.x) < EPS && abs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b, const Point& c) {
return cross(b - a, c - a);
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Line {
public:
Point front, tail;
double ang;
int u, v;
Line() {}
Line(const Point& a, const Point& b) :front(a), tail(b) {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
void initAng() {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
};
int cmp(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
//if (a.u == b.u && a.v == b.v)return 0;
return cmp(a.ang - b.ang);
}
// 点在直线哪一边>0 左边,<0边
double SideJudge(const Line& a, const Point& b) {
//return cmp(cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail));
return cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail);
}
int LineSort(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
int c = cmp(a, b);
if (c)return c < 0;
return cross(b.front - b.tail, a.front - b.tail) > 0;
}
/*
点p 到 p+r 表示线段1
点q 到 q+s 表示线段2
线段1 上1点用 p' = p+t*r (0<=t<=1)
线段2 上1点用 q' = q+u*s (0<=u<=1)
让两式相等求交点 p+t*r = q+u*s
两边都叉乘s
(p+t*r)Xs = (q+u*s)Xs
pXs + t*rXs = qXs
t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
同理,
u = (p-q)Xr/(sXr) -> u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
以下分4种情况:
1. 共线,sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr==0, 计算 (q-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t0,
计算(q+s-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t1,查看[t0, t1]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
如果t0>t1, 则比较[t1, t0]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
t0 = (q-p)*r/(r*r)
t1 = (q+s-p)*r/(r*r) = t0 + s · r / (r · r)
2. 平行sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr!=0
3. 0<=u<=1 && 0<=t<=1 有交点
4. 其他u, t不在0到范围内,没有交点。
*/
pair<double, double> intersection(const Point& q, const Point& s, const Point& p, const Point& r, bool& oneline) {
// 计算 (q-p)Xr
auto qpr = cross(q - p, r);
auto qps = cross(q - p, s);
auto rXs = cross(r, s);
if (cmp(rXs) == 0) {
oneline = true;
return { -1, -1 }; // 平行或共线
}
// 求解t, u
// t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
auto t = qps / rXs;
// u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
auto u = qpr / rXs;
return { u, t };
}
Point LineCross(const Line& a, const Line& b, bool& f) {
Point dira = a.front - a.tail;
Point dirb = b.front - b.tail;
bool oneline = false;
auto p = intersection(a.tail, dira, b.tail, dirb, oneline);
if (oneline)f = false;
return a.tail + dira * p.first;
}
class HalfPlane {
public:
vector<Line> lines;
void addLine(const Line& a) {
lines.push_back(a);
}
vector<Point> run() {
sort(lines.begin(), lines.end(), LineSort);
vector<int> q(lines.size() + 10);
vector<Point> t(lines.size() + 10);
int l = -1, r = 0;
q[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < lines.size(); ++i) {
if (cmp(lines[i], lines[i - 1]) == 0)continue;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[r]) < 0)r--;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[l + 2]) < 0)l++;
q[++r] = i;
bool f = true;
t[r] = LineCross(lines[q[r]], lines[q[r - 1]], f);
}
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[q[l + 1]], t[r]) < 0)r--;
if (r - l > 1) {
bool f = true;
t[r + 1] = LineCross(lines[q[l + 1]], lines[q[r]], f);
r++;
}
// 统计交点
l++;
vector<Point> ans(r - l);
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = t[i + l + 1];
}
return ans;
}
};
}
typedef long long lld;
namespace IntSys {
class Point {
public:
int x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(int a, int b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%d %d\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
int dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(int d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
/*Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}*/
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(int d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
/*void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}*/
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (x == a.x && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return x == a.x && y == a.y;
}
};
// 向量操作
lld cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return lld(a.x) * lld(b.y) - lld(a.y) * lld(b.x);
}
lld cross(const Point& a, const Point& b, const Point& c) {
return cross(b - a, c - a);
}
lld dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return lld(a.x) * lld(b.x) + lld(a.y) * lld(b.y);
}
}
namespace CONVEX {
IntSys::Point P[N];
IntSys::Point lowPoint;
int ind[N];
int st[N];
int top;
bool cmp(int i, int j) {
lld m = IntSys::cross(lowPoint, P[i], P[j]);
if (m != 0) {
return m > 0;
}
return (lowPoint - P[i]).dis2() < (lowPoint - P[j]).dis2();
}
void samcp(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)ind[i] = i;
lowPoint = P[0]; // 最低最左边的点
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (P[i].y < lowPoint.y || (P[i].y == lowPoint.y && P[i].x < lowPoint.x)) lowPoint = P[i];
}
if (n == 1) {
exit(1);
}
else if (n == 2) {
exit(2);
}
sort(ind, ind + n, cmp);
/*
puts("");
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("%d %d %d\n", P[ind[i]].x, P[ind[i]].y, ind[i]);
}
puts("");
*/
top = 2;
st[0] = ind[0];
st[1] = ind[1];
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
while (top >= 2 && IntSys::cross(P[st[top - 2]], P[ind[i]], P[st[top - 1]]) >= 0) {
top--;
}
st[top++] = ind[i];
}
st[top] = ind[0];
}
double getArcLength() {
double ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < top; ++i) {
ans += (P[st[i]] - P[st[i + 1]]).dis();
// printf("%d %d\n", P[st[i]].x, P[st[i]].y);
}
return ans;
}
}
IntSys::Point tangs[N];
int getMinute(int hh, int mm) {
return hh * 60 + mm;
}
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0)return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// cmpOp: 叉乘比较-1:<0, 1>0
// disOp: 叉乘为0时比较距离更远还更近,
int findKey(IntSys::Point dir, int cmpOp, int disOp) {
using namespace CONVEX;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < CONVEX::top; ++i) {
IntSys::Point p = CONVEX::P[st[i]] - P[st[k]];
lld crossv = IntSys::cross(dir, p);
if (crossv == 0) {
// 比较距离
lld dis1 = dot(dir, P[st[k]]);
lld dis2 = dot(dir, P[st[i]]);
if (dis1 == dis2)continue;
dis2 -= dis1;
dis2 /= abs(dis2);
if (dis2 == disOp) k = i;
continue;
}
// 不相等
crossv /= abs(crossv);
if (crossv == cmpOp) k = i;
}
return k;
}
void solve() {
int T;
int n, m;
int v;
FloatSys::Point dir;
IntSys::Point sp, ep;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
tangs[i].in();
tangs[i+n].in();
// 不一定是左下右上,需要调整一下
if (tangs[i].x > tangs[i + n].x)swap(tangs[i].x, tangs[i + n].x);
if (tangs[i].y > tangs[i + n].y)swap(tangs[i].y, tangs[i + n].y);
}
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
CONVEX::P[i].in();
}
sp.in();
ep.in();
scanf("%d", &v);
int hh, mm;
scanf("%d:%d", &hh, &mm);
int t1 = getMinute(hh, mm);
scanf("%d:%d", &hh, &mm);
int t2 = getMinute(hh, mm);
int totalTime = t2 - t1;
//printf("%d %d %d\n", hh, mm, totalTime);
//continue;
dir.x = ep.x - sp.x;
dir.y = ep.y - sp.y;
dir /= dir.dis();
dir *= v * totalTime;
// 查找凸包关键点
IntSys::Point diri = ep - sp;
auto g = gcd(abs(diri.x), abs(diri.y));
diri.x /= g;
diri.y /= g;
CONVEX::samcp(m);
int k1, k2, k3, k4;
k1 = findKey(diri, -1, 1);//最右边最前面点
k2 = findKey(diri, 1, 1);//最左边最前面点
k3 = findKey(diri, 1, -1);//最左边最后面点
k4 = findKey(diri, -1, -1);//最右边最后面点
FloatSys::HalfPlane hp;
vector<FloatSys::Line> lines;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)lines.push_back(FloatSys::Line());// 前面占用4个给矩形
//添加初始云层线条
for (int i = k1; i != k2; i = (i + 1) % CONVEX::top) {
int i2 = (i + 1) % CONVEX::top;
if (CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]] == CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]])continue;
lines.push_back(FloatSys::Line(FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]].y)+dir,
FloatSys::Point( CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]].y )+dir));
}
// 添加中间线
lines.push_back(FloatSys::Line(FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k3]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k3]].y),
FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k2]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k2]].y)+dir));
//添加初始云层线条
for (int i = k3; i != k4; i = (i + 1) % CONVEX::top) {
int i2 = (i + 1) % CONVEX::top;
if (CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]] == CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]])continue;
lines.push_back(FloatSys::Line(FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i2]].y),
FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[i]].y)));
}
// 添加中间线
lines.push_back(FloatSys::Line(FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k1]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k1]].y)+dir,
FloatSys::Point(CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k4]].x, CONVEX::P[CONVEX::st[k4]].y)));
double ans = 0;
// 对每个大厦与云层进行求交
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
lines[0].front.x = tangs[i + n].x;
lines[0].front.y = tangs[i].y;
lines[0].tail.x = tangs[i].x;
lines[0].tail.y = tangs[i].y;
lines[0].initAng();
lines[1].front.x = tangs[i + n].x;
lines[1].front.y = tangs[i + n].y;
lines[1].tail.x = tangs[i + n].x;
lines[1].tail.y = tangs[i].y;
lines[1].initAng();
lines[2].front.x = tangs[i].x;
lines[2].front.y = tangs[i + n].y;
lines[2].tail.x = tangs[i + n].x;
lines[2].tail.y = tangs[i + n].y;
lines[2].initAng();
lines[3].front.x = tangs[i].x;
lines[3].front.y = tangs[i].y;
lines[3].tail.x = tangs[i].x;
lines[3].tail.y = tangs[i + n].y;
lines[3].initAng();
hp.lines = lines;
/*printf("%d\n", hp.lines.size());
for (auto l : hp.lines) {
l.tail.out();
l.front.out();
}*/
auto hpps = hp.run();
//puts("lines end");
//printf("hpps size: %d\n", hpps.size());
/*hpps[0].out();
hpps[1].out();*/
for (int j = 2; j < hpps.size(); ++j) {
//hpps[j].out();
ans += FloatSys::cross(hpps[0], hpps[j - 1], hpps[j]);
}
//printf("# %d: \n", i);
}
printf("%.3f\n", ans/2);
}
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
2
2
0 0 10 10
20 20 30 10
4
-10 8 -5 8 -5 13 -10 13
15 0 25 0
1
15:30 16:05
2
0 0 10 10
20 20 30 10
4
-10 8 -5 8 -5 13 -10 13
-5 8 19 1
1
15:30 16:30
1
1
20 20 30 10
4
-10 8 -5 8 -5 13 -10 13
15 0 25 0
1
15:30 16:05
2
2
0 0 10 10
20 20 30 10
4
-10 -10 -5 -10 -5 -5 -10 -5
15 0 25 0
1
15:30 16:05
*/
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/chenbb1989/article/details/135033937
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!