第十九章 IO 流
2023-12-27 13:49:26
一、文件
1. 文件流
文件在程序中是以流的形式来操作的。
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径。
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径。
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径。
2. 常用的文件操作
2.1创建文件对象相关构造器和方法
(1)new File(String pathname):根据路径构建一个File对象
public class Demo {
public void create01() throws IOException {
String pathname = "d:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(pathname);
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
}
(2)new File(File parent,String child):根据父目录文件+子路径构建
public class Demo {
public void create02() throws IOException {
File parent = new File("d:\\");
String child = "news2.txt";
File file = new File(parent, child);
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
}
(3)new File(String parent,String child):根据父目录+子路径构建
public class Demo {
public void create03() throws IOException {
String parent = "d:\\";
String child = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parent, child);
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
}
2.2 获取文件的相关信息
public class Demo {
public void info() {
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");
String name = file.getName(); // 文件名字
String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); // 文件绝对路径
String parent = file.getParent(); // 文件父级目录
long length = file.length(); // 文件大小(字节)
boolean exists = file.exists(); // 文件是否存在
boolean b1 = file.isFile(); // 是不是一个文件
boolean b2 = file.isDirectory(); // 是不是一个目录
}
}
2.3 目录的操作和文件删除
public class Demo {
public void m1(){
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");
if (file.exists()){
if (file.delete()){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("文件或目录不存在");
}
}
}
public class Demo {
public void m2(){
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("该文件或目录存在");
}else {
// file.mkdir() 创建一级目录
// file.mkdirs() 创建多级目录
if (file.mkdirs()){
System.out.println("该目录创建成功");
}else {
System.out.println("该目录创建失败");
}
}
}
}
二、IO 流原理及流的分类
1. Java IO 流原理
(1)I/O 是 input/output 的缩写,I/O 技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
(2)Java 程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(stream)”的方式进行。
(3)java.io 包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或输出数据。
(4)输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
(5)输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中。
2. 流的分类
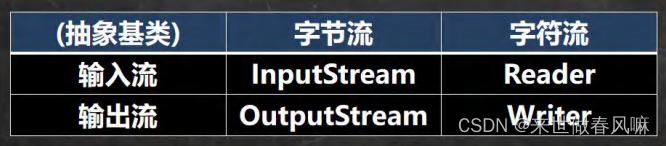
(1)按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8bit)【二进制文件】,字符流(按字符)【文本文件】。
(2)按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流。
(3)按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流。
(1)Java的 IO 流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如上4个抽象基类派生的。
(2)由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
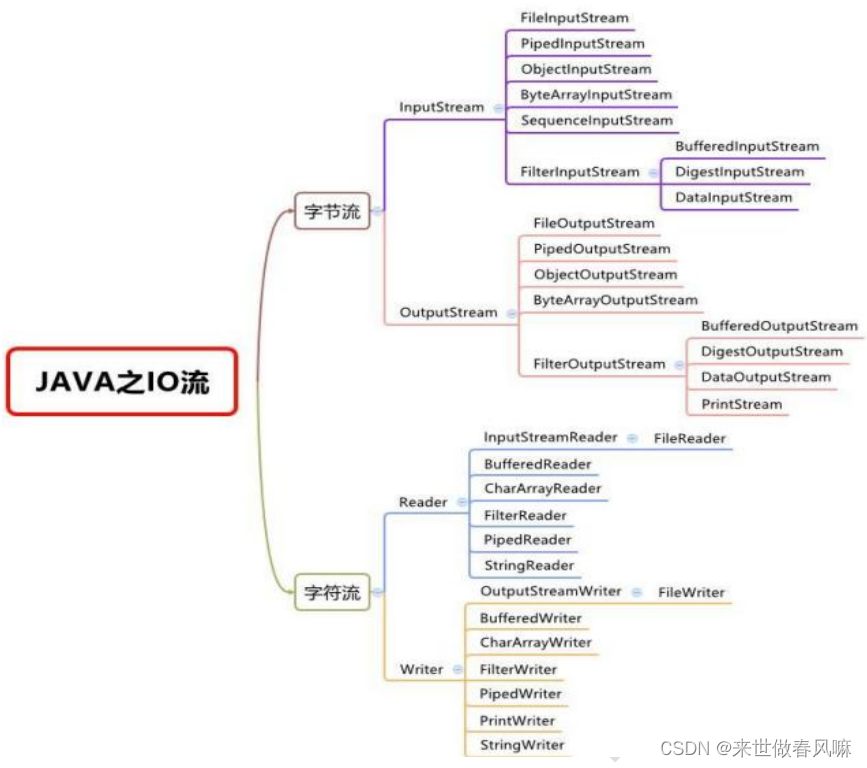
三、IO 流体系图-常用的类
1. IO 流体系图
2. FileInputStream 介绍
2.1 单个字节的读取
单个字节的读取,效率比较低
public class Demo {
@Test
public void readFile01() {
String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) readData);//转成 char 显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源.
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.2 字节数组读取
使用 read(byte[] b) 读取文件,提高效率
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class Demo {
@Test
public void readFile02() {
String filePath = "e:\\hello.txt";
//字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; //一次读取 8 个字节.
int readLen = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取最多 b.length 字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。
//如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常, 返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));//显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源.
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3. FileOutputStream 介绍
2.1 使用 FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中
如果文件不存在,会创建文件(注意:前提是目录已经存在)。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class Demo {
@Test
public void writeFile() {
//创建 FileOutputStream 对象
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//得到 FileOutputStream 对象 对象
//老师说明
//1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容
//2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true);
//写入一个字节
//fileOutputStream.write('H');//
//写入字符串
String str = "hsp,world!";
//str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组
//fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
/*
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len 字节从位于偏移量 off 的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
*/
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, 3);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.1 案例 - 文件拷贝
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建文件的输入流 , 将文件读入到程序
//2. 创建文件的输出流, 将读取到的文件数据,写入到指定的文件.
String srcFilePath = "e:\\Koala.jpg";
String destFilePath = "e:\\Koala3.jpg";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
//读取到后,就写入到文件 通过 fileOutputStream
//即,是一边读,一边写
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen);//一定要使用这个方法
}
System.out.println("拷贝 ok~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭输入流和输出流,释放资源
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/yirenyuan/article/details/135237704
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!