图论-并查集
2023-12-13 05:52:21
并查集(Union-find Sets)是一种非常精巧而实用的数据结构,它主要用于处理一些不相交集合的合并问题.一些常见的用途有求连通子图,求最小生成树Kruskal算法和最近公共祖先(LCA)等.
并查集的基本操作主要有:
.1.初始化
2.查询find
3.合并union
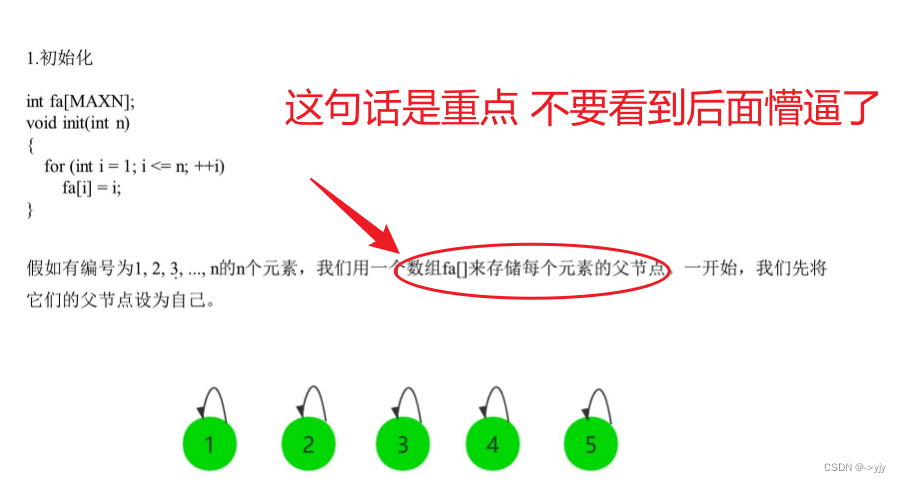
?
一般我们都会采用路径压缩 这样效率更加高 ?



?
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 20001
int fa[MAXN];
void init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fa[i] = i;
}//初始化
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x]) {
return x;
}
else {
fa[x] = find(fa[x]);//路径压缩 也就是一直找到祖先
return fa[x];
}
}
void unionn(int i, int j) {
int i_fa = find(i);//找到i的祖先
int j_fa = find(j);//找到j的祖先
fa[i_fa] = j_fa;//i的祖先指向j的祖先 反过来也可以
}
int main() {
int n, m, x, y, q;
scanf("%d", &n);
init(n);
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
unionn(x, y);
}
scanf("%d", &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
if (find(x) == find(y)) {
printf("Yes\n");
}
else {
printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
或者这样写?
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20010;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x)p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
while (m--) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
p[find(a)] = find(b);//合并 a->b
}
scanf("%d,&m");
while (m--) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (find(a) == find(b))puts("yes");
else puts("no");
}
return 0;
}
 ?
?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x)p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
char op[2];//读入操作的字符串 因为字符串后面有'\0'所以要存多一位
while (m--) {
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d",&op ,&a, &b);
if(*op=='M')p[find(a)] = find(b);//合并
else {
if (find(a) == find(b)) {
puts("Yes");
}
else {
puts("No");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int n, m;
int p[N], s[N];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x)p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i, s[i] = 1;
while (m--)
{
char op[3];
int a, b;
scanf("%s", &op);
if (*op == 'C') {
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b) {//如果相等证明他们在同一个祖先中
s[b] += s[a];
p[a] = b;
}
else if (*op == 'Q1') {
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (find(a) == find(b)) {
puts("Yes\n");
}
else {
puts("No\n");
}
}
else {
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("%d\n", s[find(a)]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79602614/article/details/134901162
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!