算法专题[递归-搜索-回溯-1]
2024-01-08 13:08:53
递归
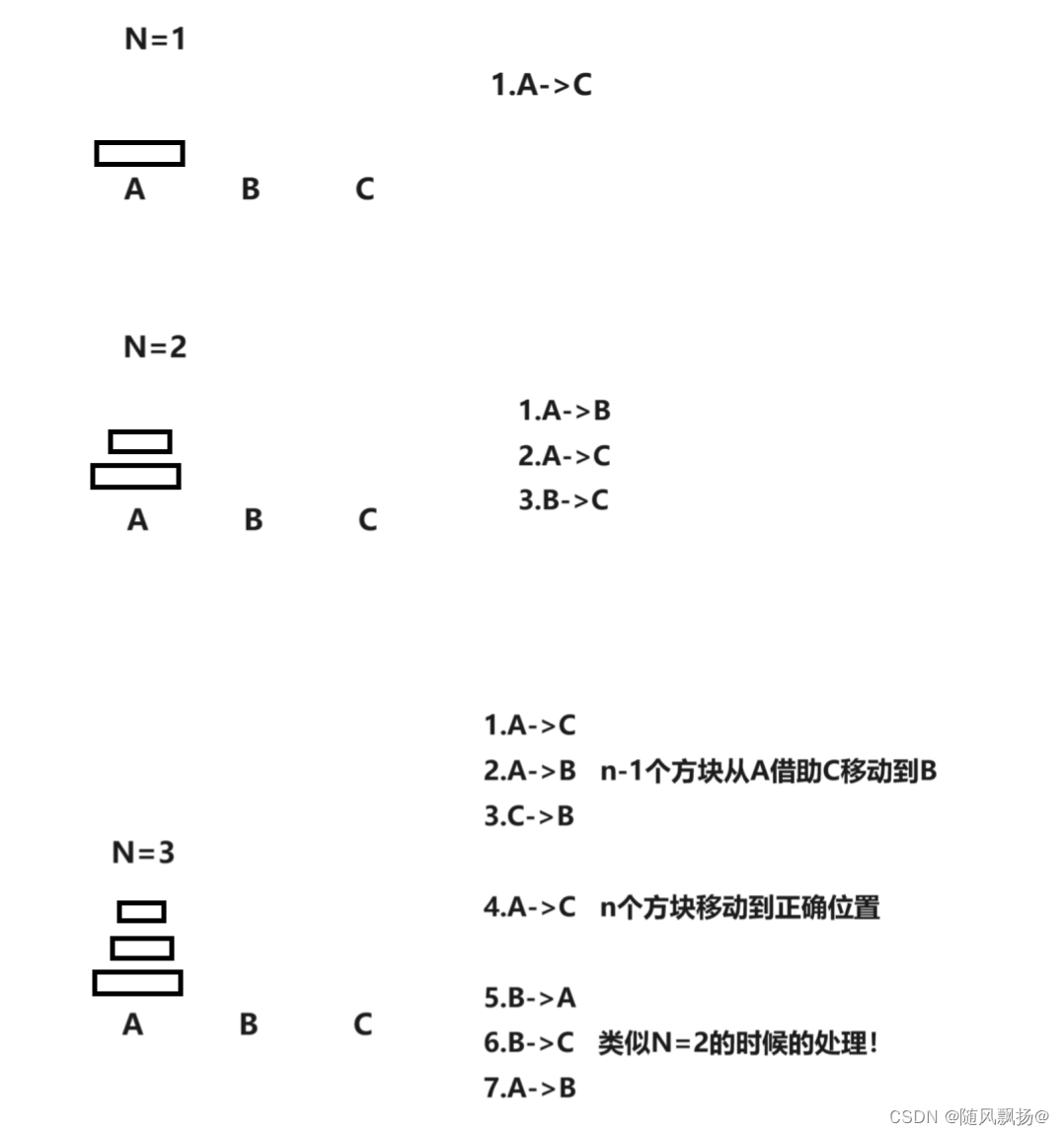
一.汉诺塔
1.思路一:
class Solution {
public:
void hanota(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C) {
int n = A.size();
def(A,B,C,n);
}
void def(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C, int n)
{
//1.只有一个块的时候:
if(n==1)
{
C.push_back(A.back());
A.pop_back();
return;
}
//2.两块以上
def(A,C,B,n-1);
C.push_back(A.back());
A.pop_back();
def(B,A,C,n-1);
}
};
2.GIF题目解析
二.合并两个有序链表
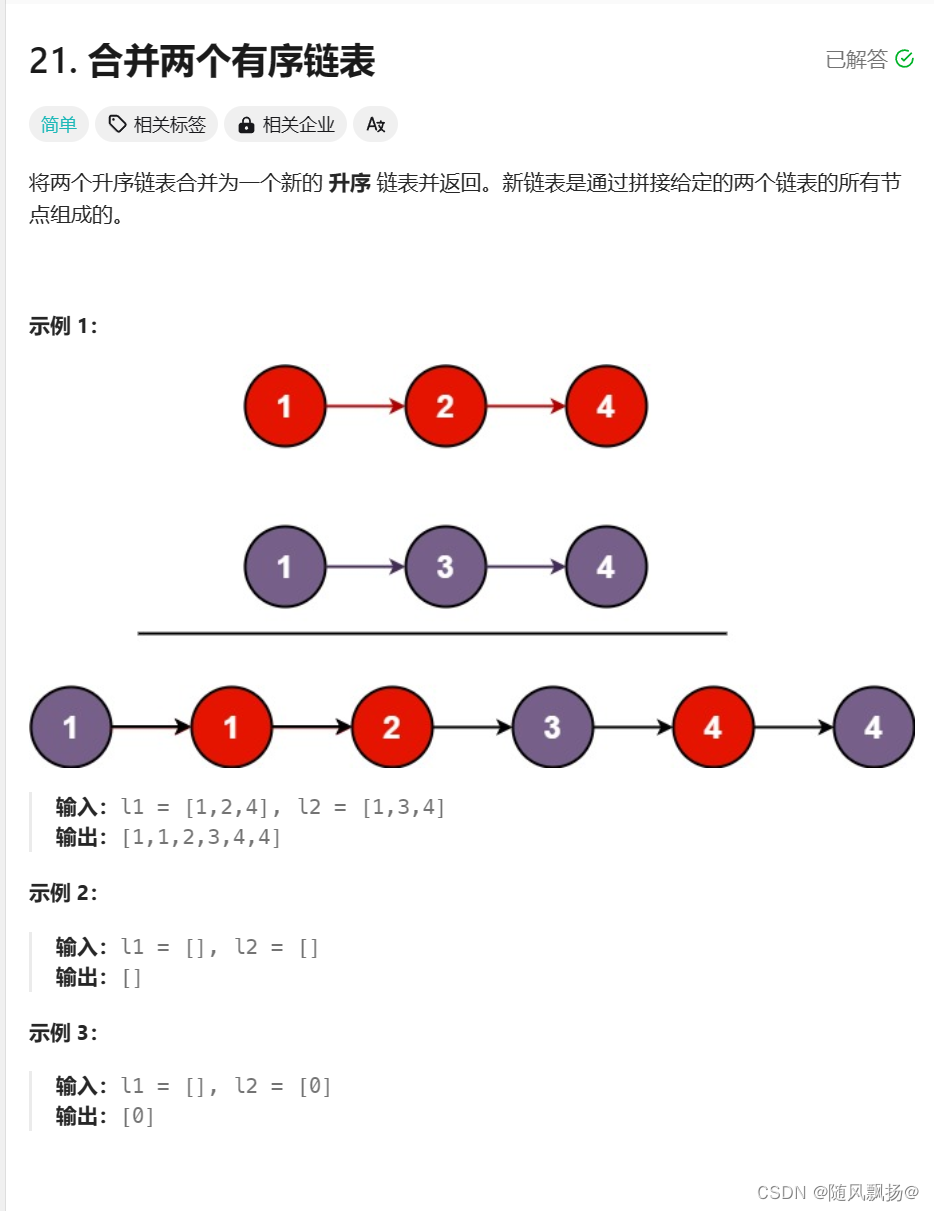

1.思路一:
//2.合并两个有序链表:
//2-1:冗余版本
//Definition for singly-linked list.
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution_2_1 {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
//1.特殊情况有一个链表为空返回另一个!
if (list1 == nullptr)
return list2;
if (list2 == nullptr)
return list1;
//2.给一个头节点进入递归去进行连接:
ListNode* head = new ListNode();
ListNode* cur = head;
//3.递归
recursion(list1, list2, cur);
//4.返回
return head->next;
}
void recursion(ListNode*& list1, ListNode*& list2, ListNode*& cur)
{
//1.递归返回条件
if (list1 == nullptr || list2 == nullptr)
{
if (list1 == nullptr && list2 != nullptr)
cur->next = list2;
else if (list1 != nullptr && list2 == nullptr)
cur->next = list1;
return;
}
//2.递归移动:
int val1 = list1->val;
int val2 = list2->val;
if (val1 >= val2)
{
cur->next = list2;
cur = cur->next;
ListNode* next2 = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
recursion(list1, next2, cur);
}
else
{
cur->next = list1;
cur = cur->next;
ListNode* next1 = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
recursion(next1, list2, cur);
}
}
};
//2-2:优化版本
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
//1.特殊情况有一个链表为空返回另一个!
if (list1 == nullptr)
return list2;
if (list2 == nullptr)
return list1;
//2.选择一个作为返回的!
int val1 = list1->val;
int val2 = list2->val;
if (val1 >= val2)
{
list2->next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2->next);
return list2;
}
else
{
list1->next = mergeTwoLists(list1->next, list2);
return list1;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
2.GIF题目解析

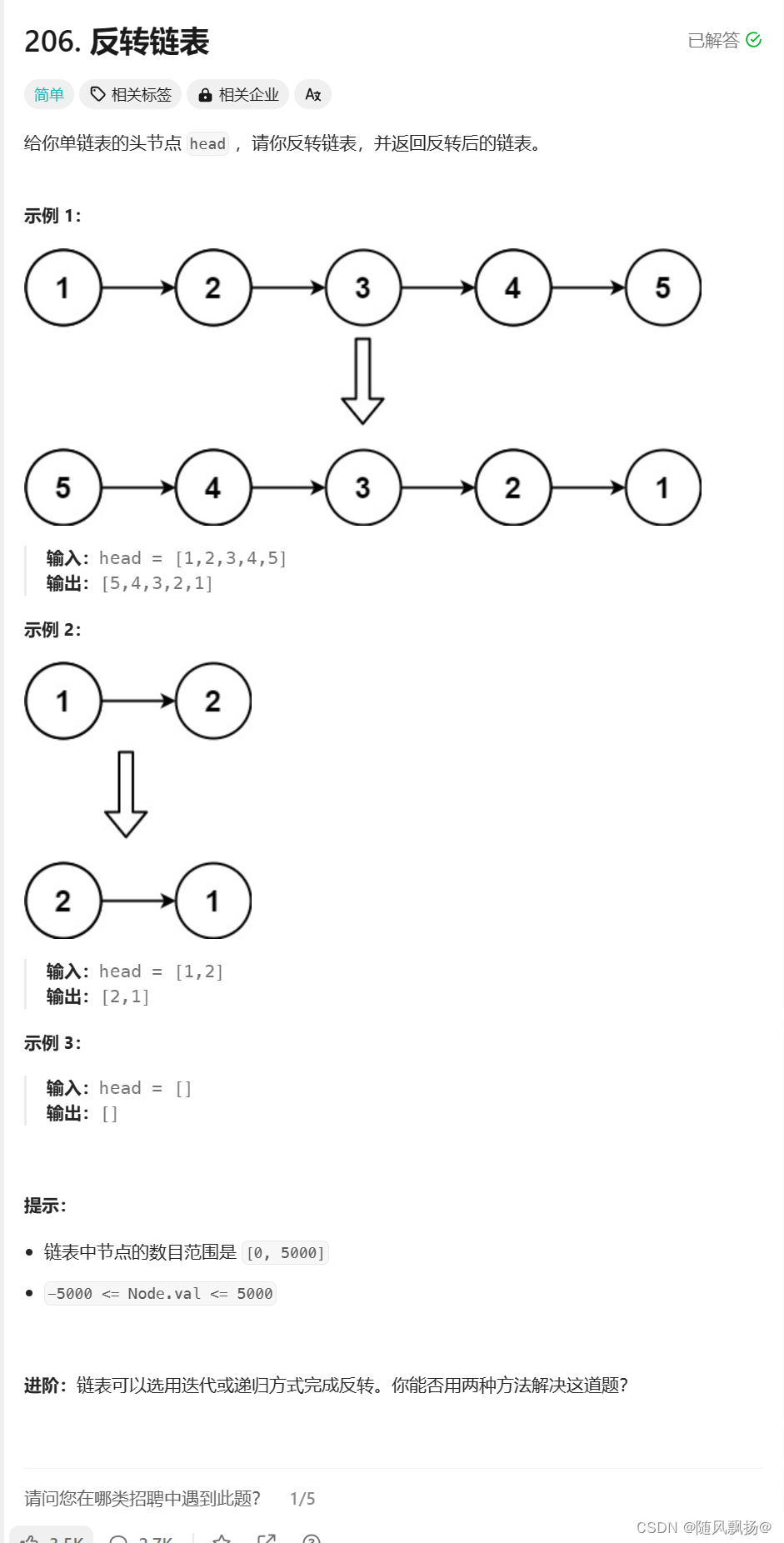
三.反转链表
1.思路一:
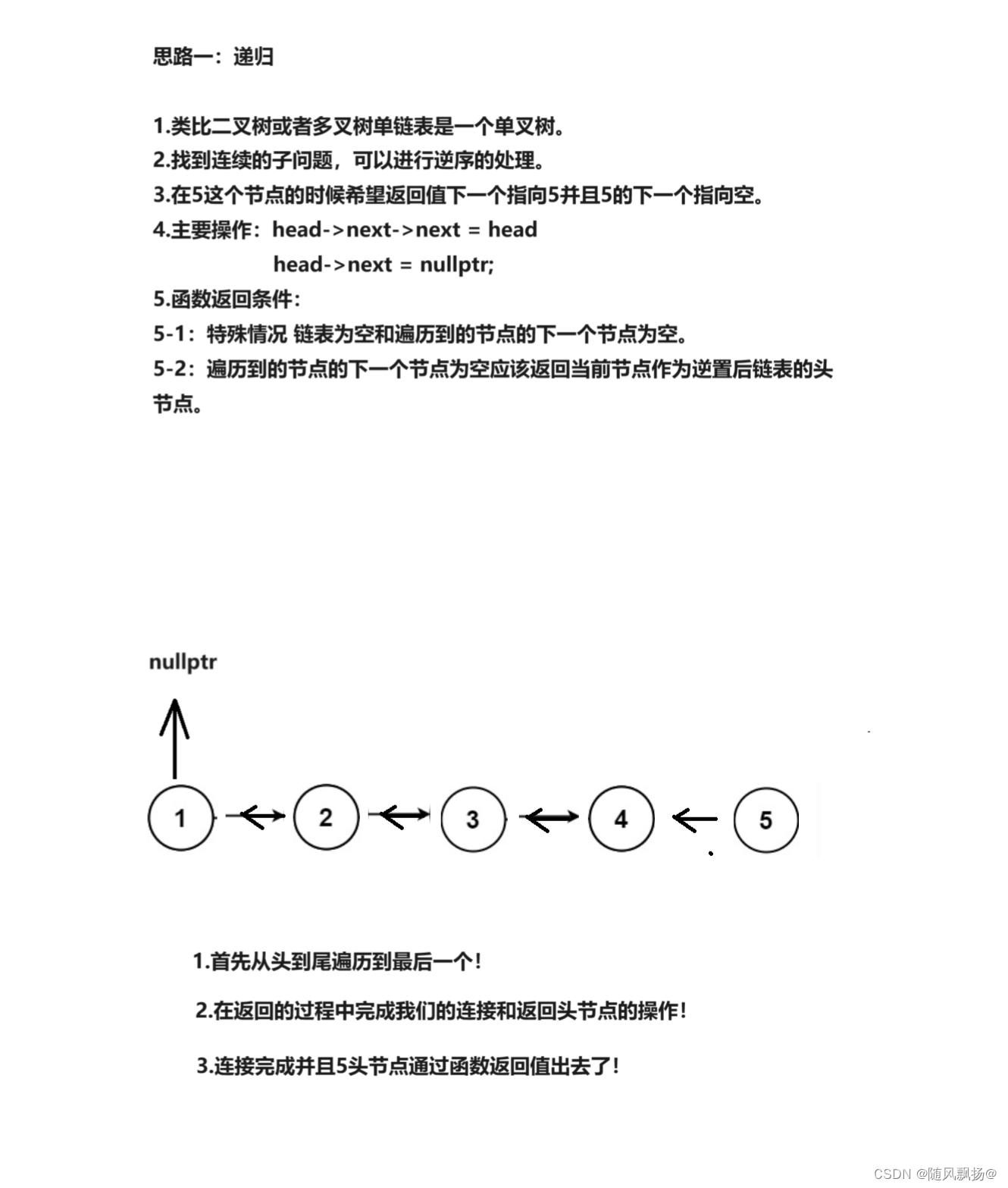
//3.反转链表:
//Definition for singly-linked list.
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
//3-1:复杂版本
class Solution_3 {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
ListNode* newhead = nullptr;
dfs(head, newhead);
return newhead;
}
ListNode*& dfs(ListNode*& head, ListNode*& rehead)
{
if (head->next == nullptr)
{
rehead = head;
return head;
}
ListNode* prev = dfs(head->next, rehead);
prev->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
};
//3-2:优化版本
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* newhead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return newhead;
}
};
2.GIF题目解析
四.两两交换链表中的节点
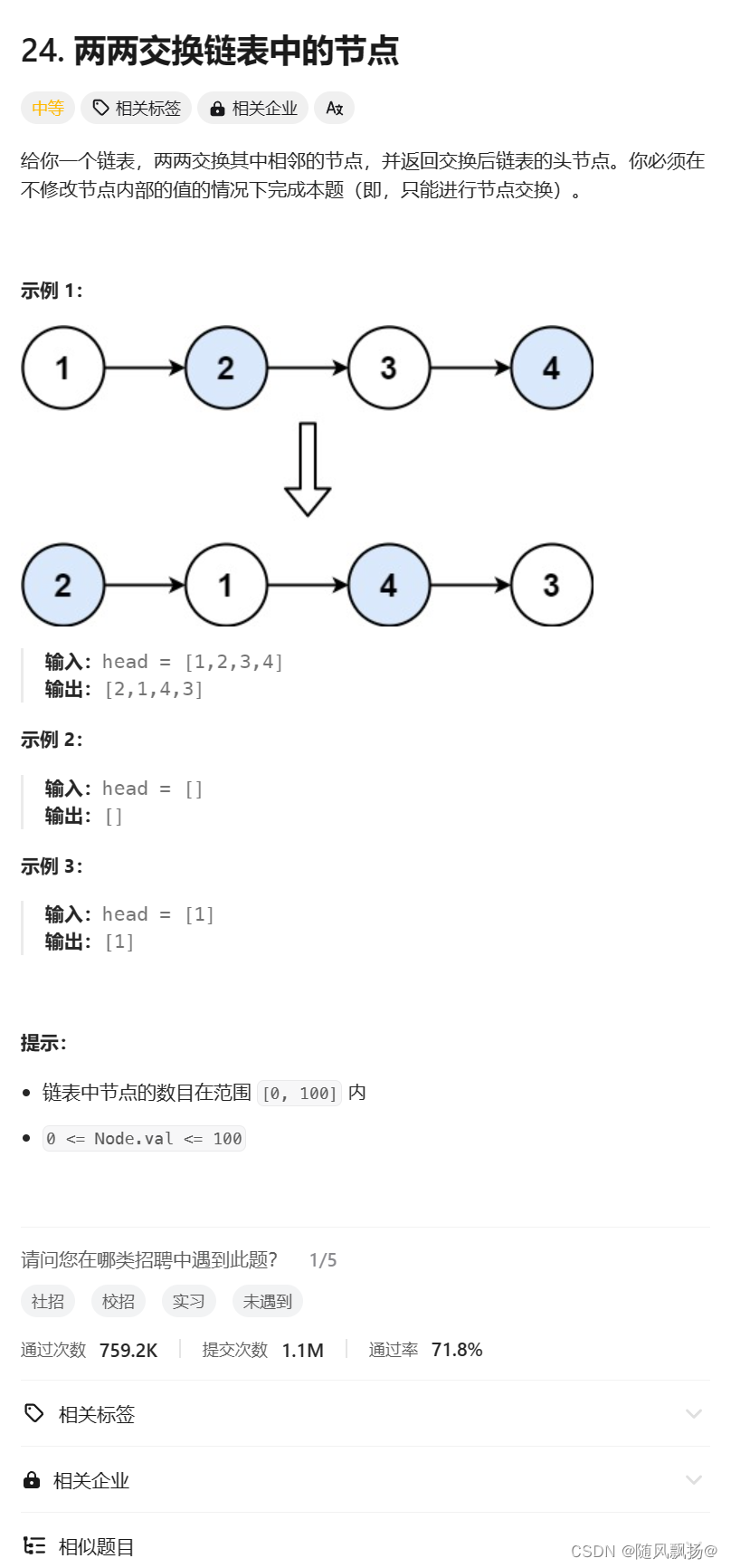
1.思路一:
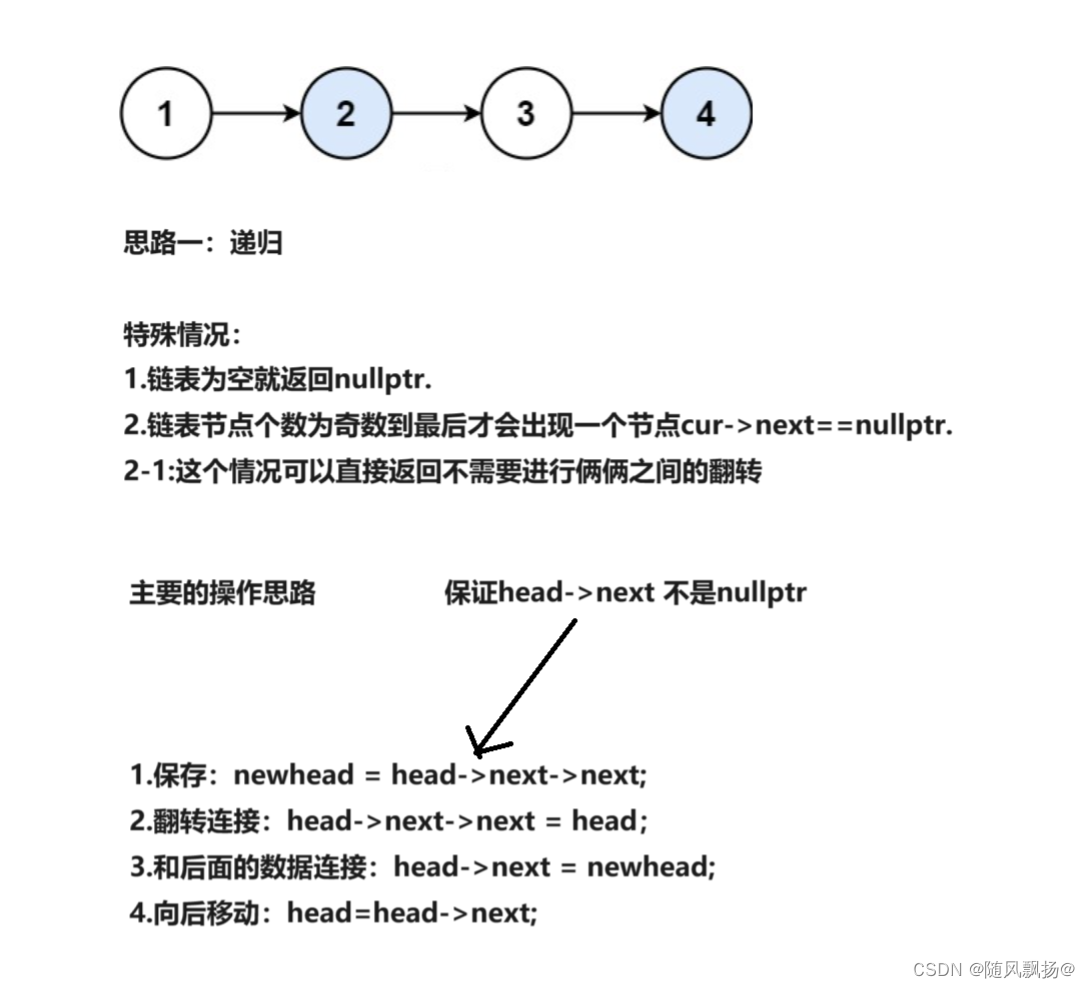
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
//1.没有节点和只有一个节点
if(head==nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(head->next == nullptr)
return head;
//2.正常情况:
ListNode* newnext_r = head->next->next;
ListNode* newnext_l = head->next;
head->next->next = head;
head->next = swapPairs(newnext_r);
return newnext_l;
}
};
2.GIF题目解析
五.pow(X,N)-快速幂

1.思路一:快速幂递归

//5.pow(x,n)实现
class Solution_5 {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
//1.特殊情况的处理:n值无穷小的情况!
//2.在这个地方去处理n的正负带来的影响!
return n < 0 ? 1.0 / pow(x, -(long long)n) : pow(x, n);
}
double pow(double x, long long n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
double tmp = pow(x, n / 2);
return (n % 2 == 0 ? tmp * tmp : tmp * tmp * x);
}
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2201_75943325/article/details/135431067
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!