10、RocketMQ的Comsumer的消息队列的分配
前置知识:RocketMQ的topic存在多个队列,而多个topic分配在同一消费组里面,消费组里面存在多个消费者,当消费者注入到消费组时要进行消费者与多个队列之间的分配,而这种分配被称之为Rebalance机制,该机制的本意就是为了提升并行的消费能力。
RocketMQ当中保证的机制就是一个队列最多分给一个消费者,而一个消费者可以消费多个队列,当某个消费组下的消费者数量大于队列数时就会导致存在消费者分配不到任何队列。
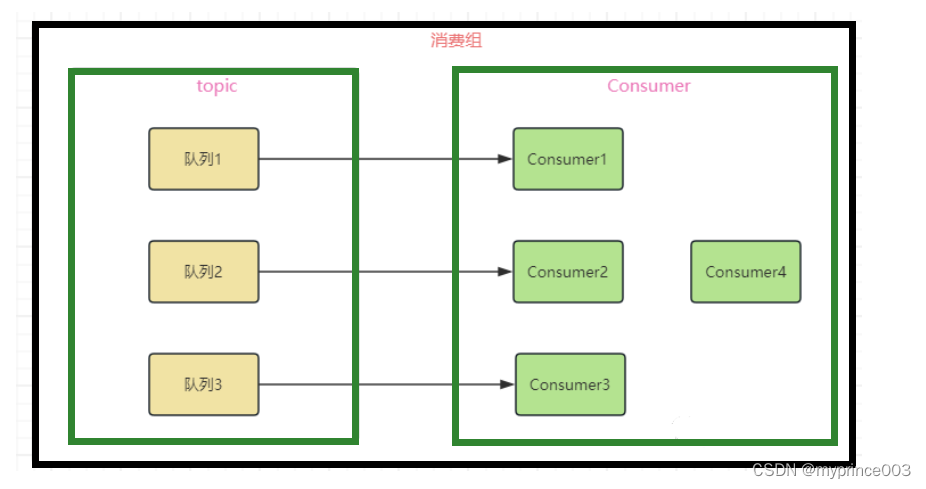
之所以保证一个队列最多给一个消费者消费,就是需要保证消息的顺序性和可靠性,同时一个消费者可以消费多个队列增加消费者的并发消费能力和负载均衡性。
执行RebalanceService进行重分配
在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl执行run方法的最后会去执行rebalanceImmediately()方法主动进行重平衡。
// 新的Consumer服务启动的时候,主动调用rebalanceImmediately唤醒
// 负载均衡服务rebalanceService,进行重分配。
public void rebalanceImmediately() {
this.rebalanceService.wakeup();
}
在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl执行run方法时会去启动CreateMQClientInstance客户端通信实例,这时就会去执行this.rebalanceService.start()方法启动重分配服务,然后就执行rebalanceService服务的run方法,每隔20s执行一次重分配。
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
// 服务没停止一直运行
while (!this.isStopped()) {
// 等待运行,默认休息20s,可以通过rocketmq.client.rebalance.waitInterval来配置
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
// 执行该方法进行负载均衡
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
Broker心跳处理或topic的新增与删除,当新的Consumer被注册进来,MQClientInstance内部的服务也会定时30s发送心跳信息给broker,当发送给Broker之后处理Code为HEART_BEAT,根据Broker启动时候注册处理器方法registerProcessor(),最终处理逻辑由ClientManageProcessor的processRequest方法去处理,最终循环遍历处理consumerDataSet集合,如果consumer信息发生改变,(两个条件判断改变isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable为true,存在updateChannel更新连接,存在updateSubscription更新订阅)broker会发送Code为NOTIFY_CONSUMER_IDS_CHANGED请求给同组的所有consumer客户端,要求进行重分配操作。
public RemotingCommand processRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request)
throws RemotingCommandException {
switch (request.getCode()) {
// 心跳处理
case RequestCode.HEART_BEAT:
return this.heartBeat(ctx, request);
case RequestCode.UNREGISTER_CLIENT:
return this.unregisterClient(ctx, request);
case RequestCode.CHECK_CLIENT_CONFIG:
return this.checkClientConfig(ctx, request);
default:
break;
}
return null;
}
无论是那种方法都会去执行RebalanceService的run方法,实现重分配逻辑。
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
// 执行该方法进行负载均衡
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
doRebalance()方法执行重分配。
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) {
// 获取当前消费者的订阅信息集合
Map<String, SubscriptionData> subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner();
if (subTable != null) {
// 不为空,编辑订阅信息
for (final Map.Entry<String, SubscriptionData> entry : subTable.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
try {
// 根据topic重新分配
this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e);
}
}
}
}
this.truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic();
}
获取当前消费者的订阅信息集合,然后遍历订阅信息集合,获取订阅的topic,调用rebalanceByTopic方法对该topic进行重分配。
rebalanceByTopic方法
private void rebalanceByTopic(final String topic, final boolean isOrder) {
switch (messageModel) {
// 广播模式
case BROADCASTING: {
// 根据topic获取MessageQueue集合
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
if (mqSet != null) {
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, mqSet, isOrder);
if (changed) {
this.messageQueueChanged(topic, mqSet, mqSet);
log.info("messageQueueChanged {} {} {} {}",
consumerGroup,
topic,
mqSet,
mqSet);
}
} else {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumerGroup, topic);
}
break;
}
// 集群模式
case CLUSTERING: {
// 获取Topic下的所有的队列
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
// 获取同一个消费者组的所有实例
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
if (null == mqSet) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumerGroup, topic);
}
}
if (null == cidAll) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {} {}, get consumer id list failed", consumerGroup, topic);
}
// 负载均衡分配MessageQueue
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List<MessageQueue> mqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 备份所有队列
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
// 两个队列进行排序
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
// 获取分配策略
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
List<MessageQueue> allocateResult = null;
try {
// 进行分配,存在6种不同的策略
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("AllocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate Exception. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}", strategy.getName(),
e);
return;
}
Set<MessageQueue> allocateResultSet = new HashSet<MessageQueue>();
if (allocateResult != null) {
allocateResultSet.addAll(allocateResult);
}
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, allocateResultSet, isOrder);
if (changed) {
log.info(
"rebalanced result changed. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}, group={}, topic={}, clientId={}, mqAllSize={}, cidAllSize={}, rebalanceResultSize={}, rebalanceResultSet={}",
strategy.getName(), consumerGroup, topic, this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(), mqSet.size(), cidAll.size(),
allocateResultSet.size(), allocateResultSet);
this.messageQueueChanged(topic, mqSet, allocateResultSet);
}
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
广播模式下没有重分配之说,每个Consumer都会去消费所有消息。
集群模式下获取同一消费组下的消费者,查找分配策略AllocateMessageQueueStrategy,执行allocate方,进行重分配。
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy是RocketMQ消费者之间消息分配的策略算法接口,本身来说RocketMQ提供6个内置实现,同时我们也可以通过实现该接口来定义自己的策略。
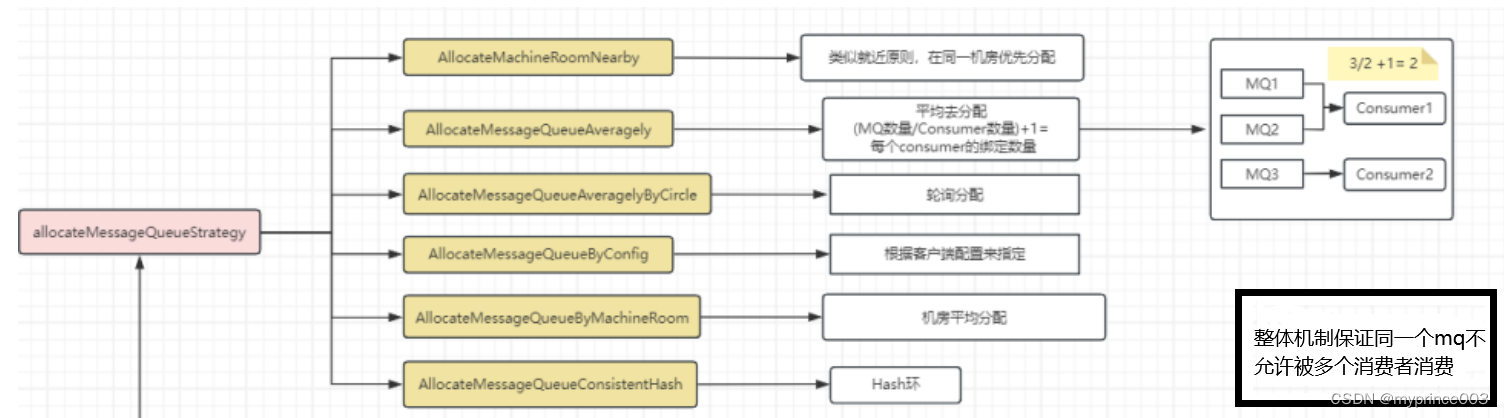
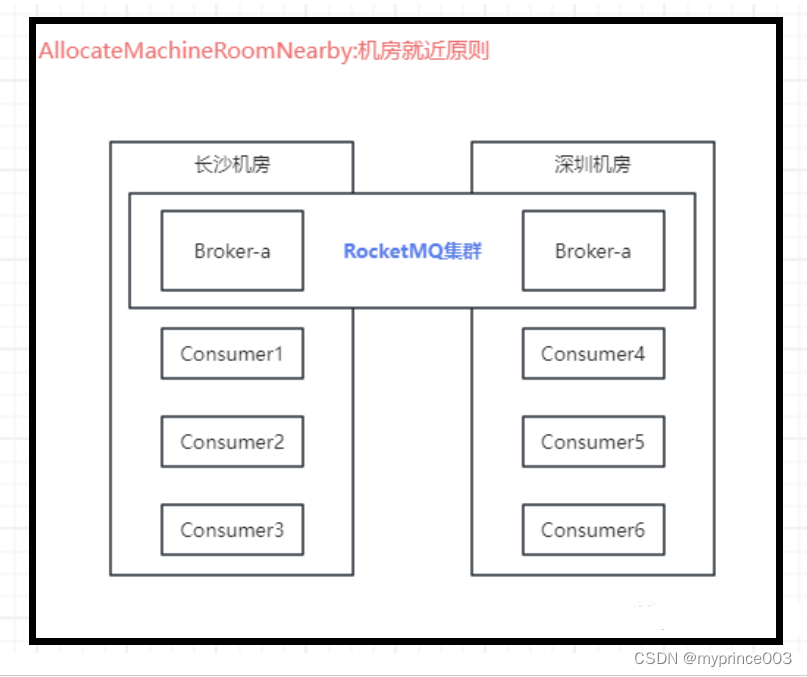
AllocateMachineRoomNearby表示机房就近分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 参数校验
if (!check(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqAll, cidAll)) {
return result;
}
// 将消息队列根据机房分组
Map<String/*machine room */, List<MessageQueue>> mr2Mq = new TreeMap<String, List<MessageQueue>>();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) {
String brokerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.brokerDeployIn(mq);
if (StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(brokerMachineRoom)) {
if (mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom) == null) {
mr2Mq.put(brokerMachineRoom, new ArrayList<MessageQueue>());
}
mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom).add(mq);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Machine room is null for mq " + mq);
}
}
// 将消息者根据机房分组
Map<String/*machine room */, List<String/*clientId*/>> mr2c = new TreeMap<String, List<String>>();
for (String cid : cidAll) {
String consumerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(cid);
if (StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(consumerMachineRoom)) {
if (mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom) == null) {
mr2c.put(consumerMachineRoom, new ArrayList<String>());
}
mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom).add(cid);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Machine room is null for consumer id " + cid);
}
}
List<MessageQueue> allocateResults = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 获取当前消费者的机房,然后就当前消费者分配到就近机房
String currentMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(currentCID);
List<MessageQueue> mqInThisMachineRoom = mr2Mq.remove(currentMachineRoom);
List<String> consumerInThisMachineRoom = mr2c.get(currentMachineRoom);
if (mqInThisMachineRoom != null && !mqInThisMachineRoom.isEmpty()) {
allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqInThisMachineRoom, consumerInThisMachineRoom));
}
//2.allocate the rest mq to each machine room if there are no consumer alive in that machine room
for (Entry<String, List<MessageQueue>> machineRoomEntry : mr2Mq.entrySet()) {
if (!mr2c.containsKey(machineRoomEntry.getKey())) { // no alive consumer in the corresponding machine room, so all consumers share these queues
allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, machineRoomEntry.getValue(), cidAll));
}
}
return allocateResults;
}
首先将消费者和队列按照机房进行分组,然后得到当前消费者的机房信息,如果消费者和队列属于同一个机房就对其进行分配,具体使用何种策略根据传递进来的allocateMessageQueueStrategy确定,如果没有对应上的消费者,那么消费队列就有所有的消费者分配,具体策略也由传入的allocateMessageQueueStrategy确定。
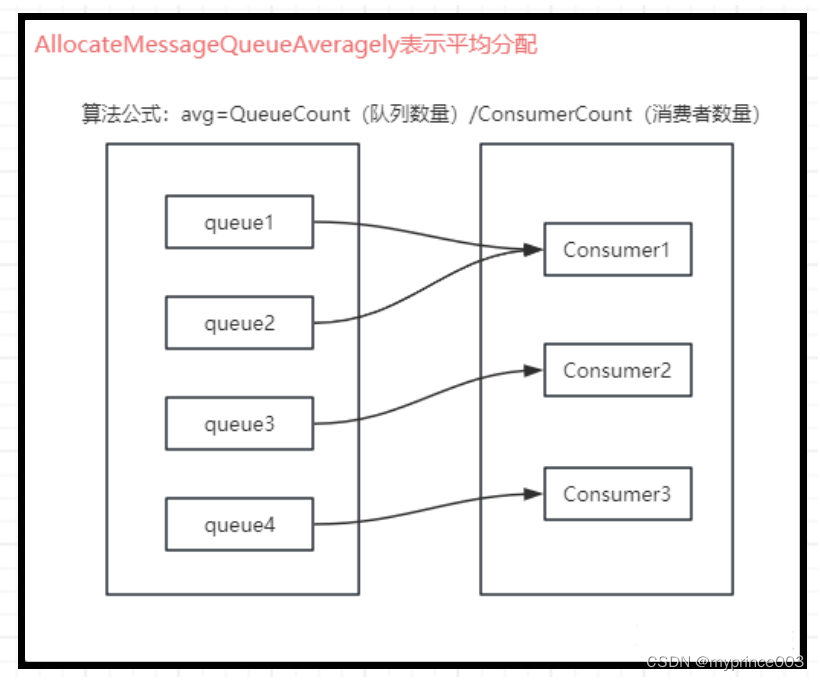
AllcateMessageQueueAveragely表示平均分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 检验参数
if (!check(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqAll, cidAll)) {
return result;
}
// currentCID在cidAll中的索引位置
int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
// 计算平均分配后的余数,大于0表示不能被整除
int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size();
// 计算当前消费者分配的队列数
int averageSize =
mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size()
+ 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size());
int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod;
int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex);
// 按顺序分配
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) {
result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size()));
}
return result;
}
简单理解就是消息队列数与消费者数量进行相除,余数为0则正好平均分配,余数不为0则每个消费者最少分配除数个数的数量而余数只有排在前面的消费者能够分配到。
AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle表示环形平均分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
//检查参数
if (!check(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqAll, cidAll)) {
return result;
}
// 获取下标
int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
// 依次分配(轮询)
for (int i = index; i < mqAll.size(); i++) {
if (i % cidAll.size() == index) {
result.add(mqAll.get(i));
}
}
return result;
}
简单的理解就是依次去分配,直到分配完所有消息队列(归根结底就是轮询)。
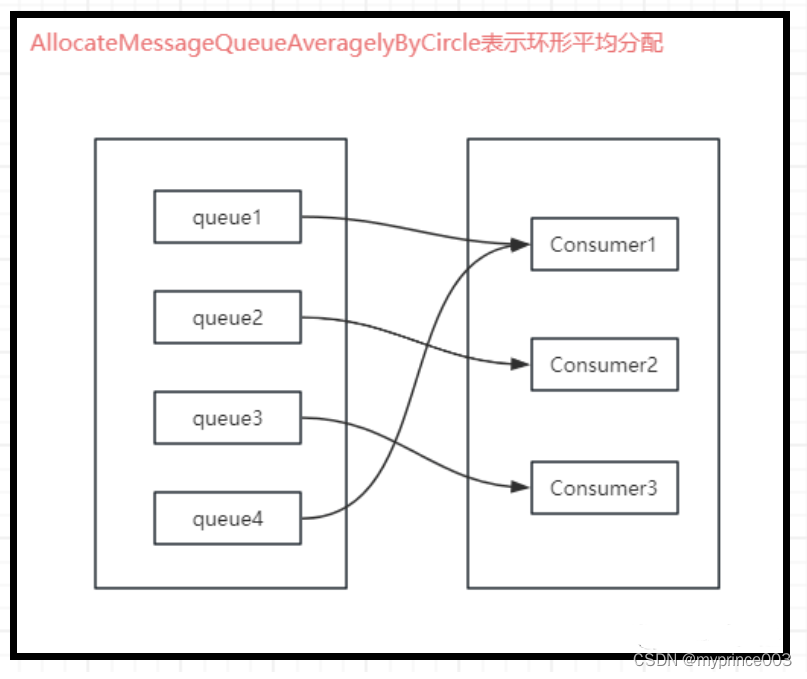
AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle表示环形平均分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
return this.messageQueueList;
}
就是给我们一些扩容能够在调用setMessageQueueList方法来自定义需要消费的消息队列集合。
AllocateMessageQueueByMachineRoom表示机房平均分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 检查配置
if (!check(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqAll, cidAll)) {
return result;
}
// 获取下标
int currentIndex = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
if (currentIndex < 0) {
return result;
}
List<MessageQueue> premqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) {
String[] temp = mq.getBrokerName().split("@");
if (temp.length == 2 && consumeridcs.contains(temp[0])) {
premqAll.add(mq);
}
}
// 平均分配的对立
int mod = premqAll.size() / cidAll.size();
int rem = premqAll.size() % cidAll.size();
int startIndex = mod * currentIndex;
int endIndex = startIndex + mod;
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
result.add(premqAll.get(i));
}
if (rem > currentIndex) {
result.add(premqAll.get(currentIndex + mod * cidAll.size()));
}
return result;
}
消息者只要绑定对应组里面的broker,这种策略要求brokerName的命名必须按照“机房名@brokerName”,消费者在分配队列的时候,首先会按照机房名称过来出所有的MesgeQueue,然后按照对应策略进行分配。同时AllocateMessageQueueByMachineRoom 更关注机房的划分和分配,而 AllocateMachineRoomNearby 则更关注就近部署和网络延迟的优化。
AllocateMessageQueueConsisterntHash表示一致性哈希分配
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
// 检查配置
if (!check(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqAll, cidAll)) {
return result;
}
Collection<ClientNode> cidNodes = new ArrayList<ClientNode>();
for (String cid : cidAll) {
cidNodes.add(new ClientNode(cid));
}
final ConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode> router; //for building hash ring
if (customHashFunction != null) {
router = new ConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt, customHashFunction);
} else {
router = new ConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt);
}
List<MessageQueue> results = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqAll) {
ClientNode clientNode = router.routeNode(mq.toString());
if (clientNode != null && currentCID.equals(clientNode.getKey())) {
results.add(mq);
}
}
return results;
}
这个队列策略将Consumer的哈希值与Queue的哈希值作为Node节点都存放在hash环上,通过逆时针方向,距离Queue最近的那个Consumer就是该Queue要分配的Consumer,其中存在virtualNodeCnt对象,virtualNodeCnt表示物理节点的虚拟线程。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!