Discrete Time Signals and Systems
Discrete Time Signals and Systems
文章目录
Signal classification
- Periodic and non-periodic
- Odd and even signals
- energy signal and power signal
basic signal
- Impulse function
- unit step function
- Ramp function
Operation on signal
?
Periodic and Aperiodic Discrete-Time Sinusoids
x
(
n
)
=
A
c
o
s
[
2
π
f
0
n
]
=
x
(
n
+
N
)
=
A
c
o
s
[
2
π
f
0
(
n
+
N
)
]
=
A
c
o
s
[
2
π
f
0
n
+
2
π
f
0
N
]
x(n)=Acos[2 \pi f_0 n]=x(n+N)=Acos[2 \pi f_0 (n+N)]=Acos[2 \pi f_0 n+2 \pi f_0 N]
x(n)=Acos[2πf0?n]=x(n+N)=Acos[2πf0?(n+N)]=Acos[2πf0?n+2πf0?N]
2
π
f
0
N
=
2
π
k
2\pi f_0 N =2 \pi k
2πf0?N=2πk just
f
0
=
k
N
f_0 = \frac{k}{N}
f0?=Nk?
n is integer: Periodic
n is not integer: Aperiodic
Periodic judgment of composite signals
-
Find N for each signal
if N 1 N 2 = r a t i o n a l ? n u m b e r \frac{N_1}{N_2} = rational \ number N2?N1??=rational?number it is Periodic
-
Find the lowest common multiple($ LCM(N_1,N_2)$)
Periodic is $ LCM(N_1,N_2)$
Odd and even signals
odd: x 0 ( t ) = 1 2 [ x ( t ) ? x ( ? t ) ] x_0(t)=\frac{1}{2}[x(t)-x(-t)] x0?(t)=21?[x(t)?x(?t)]
even: x e ( t ) = 1 2 [ x ( t ) + x ( ? t ) ] x_e(t) = \frac{1}{2}[x(t)+x(-t)] xe?(t)=21?[x(t)+x(?t)]
x ( t ) = x 0 ( t ) + x e ( t ) x(t) = x_0(t) + x_e(t) x(t)=x0?(t)+xe?(t)
energy signal and power signal
energy: E = ∑ n = ? ∞ ∞ ∣ x [ n ] ∣ 2 E=\sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}|x[n]|^2 E=∑n=?∞∞?∣x[n]∣2
power:
Periodic: P ∞ = lim ? N → ∞ 1 2 N + 1 ∑ n = ? ∞ + ∞ ∣ x [ n ] ∣ 2 P_\infty=\lim_{N\to\infty}\frac1{2N+1}\sum_{n=-\infty}^{+\infty}|x[n]|^2 P∞?=limN→∞?2N+11?∑n=?∞+∞?∣x[n]∣2
Aperiodic: P x = 1 N ∑ n = 0 N ? 1 ∣ x [ n ] ∣ 2 P_x=\frac1{N}\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}|x[n]|^2 Px?=N1?∑n=0N?1?∣x[n]∣2
energy signal:energy is finite,power is zero
power signal:energy is infinite,power is finite
?
find the energy and power for
- Impulse function
- unit step function
- Ramp function
?
- Time Shifting(left is +;right is -)
- Time-scale
- Time Reversal
?
System of discrete signal
-
Linear systems and nonlinear systems
-
Causal and Acausal Systems
-
Time-varying and time-invariant systems
-
static system and dynamic system
-
Stable and unstable systems
-
convolution
-
convolution sum
-
circular convolution
-
Stability of linear time-invariant systems
Linear systems and nonlinear systems
- Linear systems satisfy uniformity and superposition
- A system that satisfies uniformity and superposition is a linear system
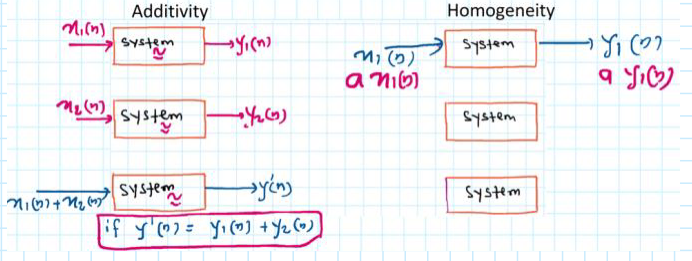
Must have: x ( n ) = y ( n ) = 0 x(n) = y(n) = 0 x(n)=y(n)=0
Four steps to solve problems:
- x1 to y1 = F(x1)
- x2 to y2 = F(x2)
- y3 = ay1 + by2
- F(ax1 +bx2) = y4
if y4 = y3 ,the system is linear
?
Causal and non-causal Systems
casual system: The output depends only on present and past signals
Acausal Systems:The output depends on at least one future input
eg:Y(n) = x(-n) is non-casual (at n = -1)
even and odd is non-casual
ps: anti-casual system: output only upon “only future input” for all time
?
Time-varying and time-invariant systems
Time-varying system(TVS):
y(n) = F[x(n)] = x(n)cos(2 w π w \pi wπn)
y(n,k) = F[x(n-k)] = x(n-k)cos(2 w π w \pi wπn)
y(n-k) $\ne $ y(n,k)
y(n) to y(n,k):only change n for x(n)
time-invariant systems :
y(n,k) = y(n-k)
eg:y(n-k) = sin (x(n-k))
y change n for all n
?
static system and dynamic system
static system (memory-less system):
output only depends on now input for all time
dynamic system:
output depends on past and/or future inputs
?
Stable and unstable systems
Stable system: BIBO
bounded input to bounded output
unstable systems:
bounded input to unbounded output
eg: y ( n ) = y 2 ( n ? 1 ) + 2 δ ( n ) y(n)=y^2(n-1)+2\delta (n) y(n)=y2(n?1)+2δ(n)
?
convolution
- time-invariant systems
y ( n ) = ∑ k = ? ∞ ∞ x ( k ) h ( n ? k ) y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}x(k)h(n-k) y(n)=∑k=?∞∞?x(k)h(n?k)
y ( n ) = x ( n ) ? h ( n ) y(n)=x(n)*h(n) y(n)=x(n)?h(n)
- time reversal
- shifting of h(-k) to h(n-k)
- multiply x(k)h(n-k)
- Sum
- linear convolution
- circular convolution
matrix method:
x(n) = {1,2,3,4} h(n)={0,2,2,2}
length of x(n):4 samples;k
length of h(n):4 samples;m
length of y(n): = k + m - 1 = 4 + 4 - 1 = 7 samples
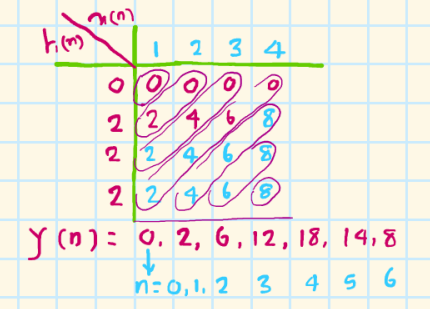
?
circular convolution
x(n) = {2,1,2} h(n) = {1,2,3}
y ( n ) = ∑ k = ? ∞ ∞ x ( k ) h ( n ? k ) y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}x(k)h(n-k) y(n)=∑k=?∞∞?x(k)h(n?k)

?
Stability of linear time-invariant systems
S = ∑ k = ? ∞ ∞ ∣ h ( n ) ∣ < ∞ S=\sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}|h(n)|<\infty S=∑k=?∞∞?∣h(n)∣<∞
it is stability
eg: h ( n ) = ( 0.8 ) n u ( n + 2 ) h(n) = (0.8)^n u(n+2) h(n)=(0.8)nu(n+2)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!