数据结构课程设计 1.0 栈的应用 迷宫问题
2023-12-31 03:49:34
一、迷宫问题
从入口出发,按某一方向向前探索,若能走通(未走过的),即某处可以到达,则到达新点,否则试探下一方向;若该点所有的方向均没有通路,则沿原路返回前一个点,换下一个方向再继续试探,直到所有可能的通路都探索到,再找到下一条通路,或无路可走又退回到入口点。
退回到的“前一点”正是刚刚被访问过的,具有“后进前出”的特性,需要用栈保存所能够到达的每一点的下标及从该点前进的方向。
二、迷宫问题数据结构
用二维数组maze[M+2][N+2]来表示迷宫,图中红色的部分为迷宫,而迷宫的四周的值全部为1(即不通)。这样设计的话,将迷宫中所有点都演变成迷宫中部的某点,可以保证无论那个点的试探方向都是四个。
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
三、方向试探表示
typedef struct{
//x,y方向上的增量
int incX,intcY;
}Direction;
Direction direct[4];
/*
从某点(x,y)按某一方向
v(0<=v<=3)到达的新点
(line,col)的坐标:
*/
line =x + direct[v].intcX;
col = y + direct[v].intcY;
direct[0].intcX = 0;
direct[0].intcY = 1;
direct[1].intcX = 1;
direct[1].intcY = 0;
direct[2].intcX = 0;
direct[2].intcY = -1;
direct[3].intcX = -1;
direct[3].intcY = 0;四、栈中数据元素的组织
栈中元素是一个由行、列、方向组成的三元组;
typedef struct{
int x,y;//当前访问的迷宫格子的纵横坐标
int di;//当前方向
}Box;?五、防止重复达到某点
方案一:
另外设置一标志数组flag[m][n],其所有元素都初始化为0,一旦到达了某点(i,j)之后,将对应flag[i][j]置1,下次再试探该位置时,因为已经置1了,就不能再选它了;
方案二:
当到达某点(i,j)后将对应maze[i][j]置-1,其他未到达过的点其值只能是1或0,可与未到达过的点区分开来。
bool findpath(int maze[M+2][N+2],Direction direct[],Stack &s){
Box temp;
int x,y,di;//迷宫格子当前处理单元的纵横坐标和方向
int line,col;//迷宫数组下一单元的行坐标和列坐标
maze[1][1]=-1;
temp={1,1,-1};
s.push(temp);
while(!s.isEmpty()){//栈不为空
temp = s.pop();
x=temp.x;y=temp.y;di=temp.di+1;
while(di<4){//方向未尝试完
line = x + direct[di].intcX;
col = y + direct[di].intcY;
if(maze[line][col]==0){
temp = {x,y,di};
s.push(temp);
x=line;y=col;maze[line][col]=-1;
if(x==M && y==N) return true;//迷宫有路
else di=0;
}
else di=0;
}
}
return false;//迷宫没有路
}
//栈中存的是一条迷宫通路上述代码为伪代码,只提供算法,实际运行不了。
以下是课程设计要求及完成代码和运行结果
课设要求
基本要求:
? 编写非递归程序求解。
? 迷宫存储在文件中,通过输入文件名(in.* ),
创建相应的迷宫。迷宫文件的格式自己设计。
? 最终的解要求在屏幕上显示并存入文件(out.*)中。
解的显示方式以及解文件的格式自己设计。
?完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXSIZE 100
#define li 10
#define colum 10
typedef struct {
int elem[MAXSIZE][3];
int top;
} Stack;
// 判断栈是否为空
int Empty(Stack *s) {
if (s->top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// 入栈操作
int Push(Stack *s, int x[3]) {
if (s->top == MAXSIZE - 1)
return 0;
else {
s->top++;
s->elem[s->top][0] = x[0];
s->elem[s->top][1] = x[1];
s->elem[s->top][2] = x[2];
return 1;
}
}
// 出栈操作
int Pop(Stack *s) {
if (Empty(s))
return 0;
else {
s->top--;
return 1;
}
}
// 寻找迷宫路径
_Bool findPath(int maze[li][colum], Stack *s) {
int temp[3];
int x, y, di;
int line, col;
int direct[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
maze[1][1] = -1;
temp[0] = 1;
temp[1] = 1;
temp[2] = -1;
Push(s, temp);
while (!Empty(s)) {
Pop(s);
temp[0] = s->elem[s->top + 1][0];
temp[1] = s->elem[s->top + 1][1];
temp[2] = s->elem[s->top + 1][2];
x = temp[0];
y = temp[1];
di = temp[2] + 1;
while (di < 4) {
line = x + direct[di][0];
col = y + direct[di][1];
if (maze[line][col] == 0) {
temp[0] = x;
temp[1] = y;
temp[2] = di;
Push(s, temp);
x = line;
y = col;
maze[line][col] = -1;
if (x == 8 && y == 8)
return true;
else
di = 0;
} else
di++;
}
}
return false;
}
// 打印栈中元素
void print(Stack *s) {
for (int i = 0; i <= s->top; i++) {
printf("(%d,%d) ", s->elem[i][0], s->elem[i][1]);
if ((i + 1) % 4 == 0)
printf("\n");
}
}
// 打印迷宫
void Print(int maze[li][colum]) {
for (int i = 0; i < li; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < colum; j++) {
printf("%2d", maze[i][j]);
if (j % 10 == 9) {
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
// 将迷宫保存到文件
void saveMazeToFile(int maze[li][colum], const char *filename) {
FILE *file = fopen(filename, "w");
if (file == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening file: %s\n", filename);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
fprintf(file, "%d ", maze[i][j]);
}
fprintf(file, "\n");
}
fclose(file);
}
// 将解保存到文件
void saveSolutionToFile(Stack *s, const char *filename) {
FILE *file = fopen(filename, "w");
if (file == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening file: %s\n", filename);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= s->top; i++) {
fprintf(file, "(%d,%d) ", s->elem[i][0], s->elem[i][1]);
if ((i + 1) % 4 == 0)
fprintf(file, "\n");
}
fclose(file);
}
int main() {
int maze[li][colum] = {
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
};
Stack s;
s.top = -1;
saveMazeToFile(maze, "in.txt");
if (findPath(maze, &s)) {
printf("Maze:\n");
Print(maze);
printf("\nSolution:\n");
print(&s);
saveSolutionToFile(&s, "out.txt");
} else {
printf("No path\n");
}
return 0;
}
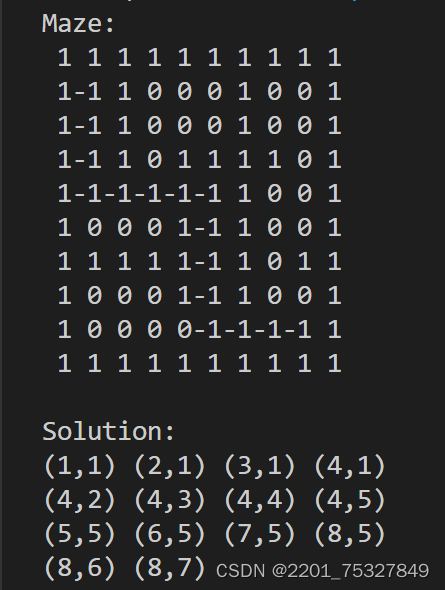
运行结果
???????
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2201_75327849/article/details/135242357
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!