知识蒸馏理论及实操
2023-12-28 22:46:46
一、理论介绍
蒸馏:把水变成纯净水
知识蒸馏:把大的模型(教师模型)中的知识蒸馏出来浓缩到小的模型上(学生模型)
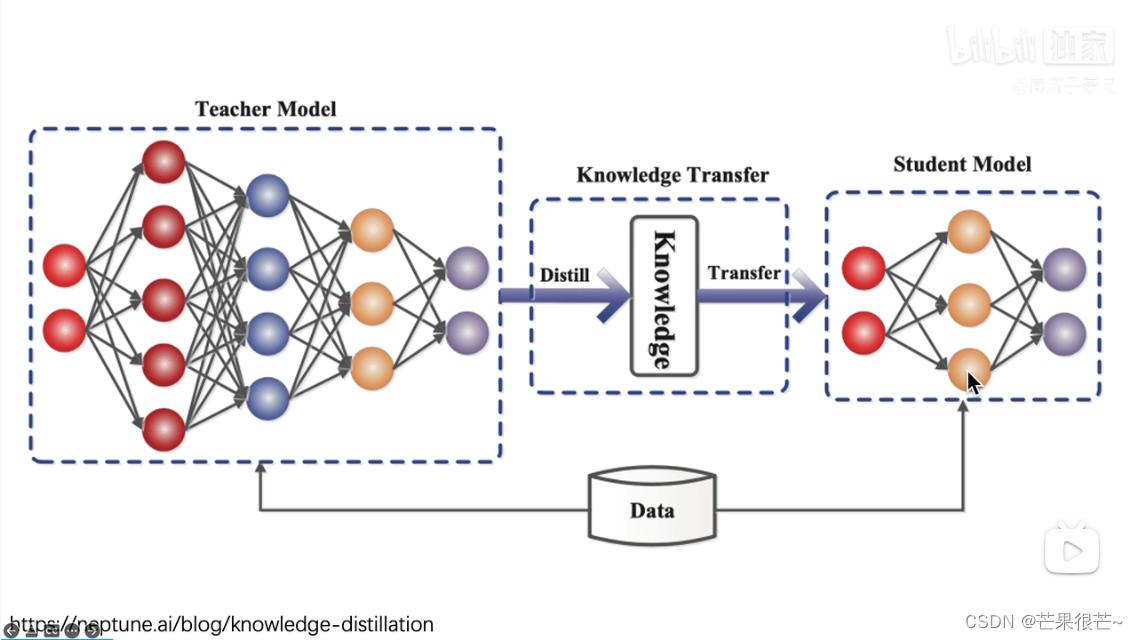
在这篇论文的开头,作者说昆虫在幼年时其形态是利于从周围环境获取营养的;成虫形态进化成迁徙和繁殖。需求是变化的。

知识蒸馏的过程:
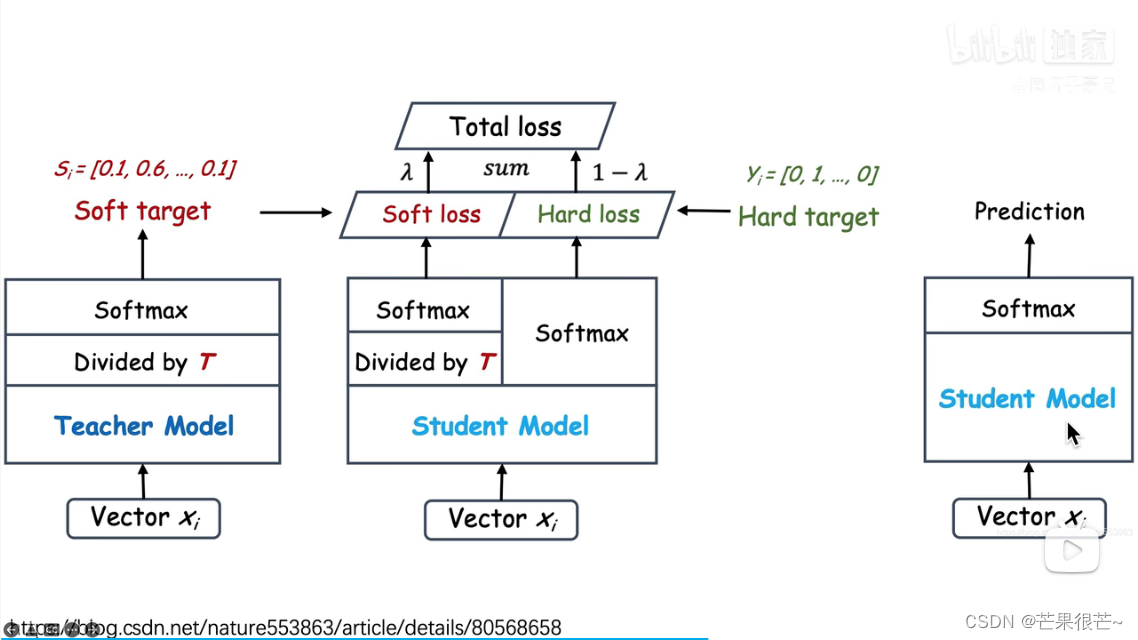
其中soft loss和hard loss的区别:
Soft Labe包含了更多“知识”和信息,像谁,不像谁,有多像,有多不像,特别是非正确类别概率的相对大小(驴和车)
 还有蒸馏温度的概念:
还有蒸馏温度的概念:

二、代码实操
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tqdm import tqdm
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
class TeacherModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, num_classes=10):
super(TeacherModel, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 1200)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1200, 1200)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(1200, num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784)
x = self.relu(self.dropout(self.fc1(x)))
x = self.relu(self.dropout(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
class StudentModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, num_classes=10):
super(StudentModel, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 20)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(20, 20)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(20, num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784)
x = self.relu(self.dropout(self.fc1(x)))
x = self.relu(self.dropout(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def teacher(device, train_loader, test_loader):
print('--------------teachermodel start--------------')
model = TeacherModel()
model = model.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
epochs = 6
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
for data, target in tqdm(train_loader):
data = data.to(device)
target = target.to(device)
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_loader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions.eq(y)).sum().item()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = num_correct / num_samples
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Acc:{:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, acc))
torch.save(model, 'teacher.pkl')
print('--------------teachermodel end--------------')
def student(device, train_loader, test_loader):
print('--------------studentmodel start--------------')
model = StudentModel()
model = model.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
epochs = 3
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
for data, target in tqdm(train_loader):
data = data.to(device)
target = target.to(device)
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_loader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
# print(y)
preds = model(x)
# print(preds)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
# print(predictions)
num_correct += (predictions.eq(y)).sum().item()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = num_correct / num_samples
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Acc:{:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, acc))
print('--------------studentmodel prediction end--------------')
def kd(teachermodel, device, train_loader, test_loader):
print('--------------kdmodel start--------------')
teachermodel.eval()
studentmodel = StudentModel()
studentmodel = studentmodel.to(device)
studentmodel.train()
temp = 7 #蒸馏温度
alpha = 0.3
hard_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
soft_loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='batchmean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(studentmodel.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
epochs = 20
for epoch in range(epochs):
for data, target in tqdm(train_loader):
data = data.to(device)
target = target.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_preds = teachermodel(data)
student_preds = studentmodel(data)
student_loss = hard_loss(student_preds, target) #hard_loss
distillation_loss = soft_loss(
F.log_softmax(student_preds / temp, dim=1),
F.softmax(teacher_preds / temp, dim=1)
) #soft_loss
loss = alpha * student_loss + (1 - alpha) * distillation_loss
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
studentmodel.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_loader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = studentmodel(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions.eq(y)).sum().item()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = num_correct / num_samples
studentmodel.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t Acc:{:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, acc))
print('--------------kdmodel end--------------')
if __name__ == '__main__':
torch.manual_seed(0)
device = torch.device("cpu")
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
#加载数据集
X_train = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root="dataset/",
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
X_test = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root="dataset/",
train=False,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=X_train, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=X_test, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
#从头训练教师模型,并预测
teacher(device, train_loader, test_loader)
#从头训练学生模型,并预测
student(device, train_loader, test_loader)
#知识蒸馏训练学生模型
model = torch.load('teacher.pkl')
kd(model, device, train_loader, test_loader)
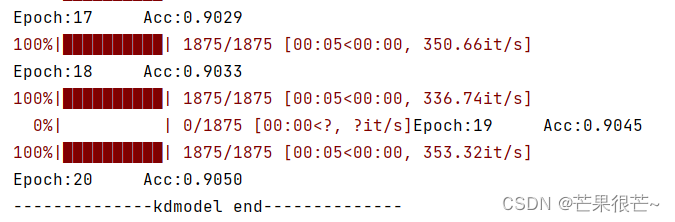
代码结果:
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46458188/article/details/135278993
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!