Python基础进阶7:执行外部命令的五个方法,建议使用第五个
你好,我是kelly,今天分享:Python执行外部命令的五个方法。
在日常开发中,有时需要在Python脚本中执行外部命令,大概有下面几个方法。
案例说明
windows系统,如下图所示,输出指定目录下、包含“file”的文件,即输出文件file1.txt和file2.txt。

一、os.system
这种方法最为简单,输入为完整命令字符串,命令执行结果输出到控制台;执行成功,返回值为0,失败为255。
import os
result = os.system("dir D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files | findstr file")运行结果:

二、os.popen
输入为完整命令字符串,命令执行结果保存在返回值中。
import os
result = os.popen("dir D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files | findstr file")
lines = result.read()
print(lines)运行结果:

下面为os.popen的源码,可知os.popen实际是subprocess.Popen的封装形式:

三、subprocess.run
总体运行效果:执行命令后,运行结果保存在CompletedProcess类实例中,并返回。
不设定stdout参数
import subprocess
result = subprocess.run(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
shell=True,
text=True)
result运行结果:
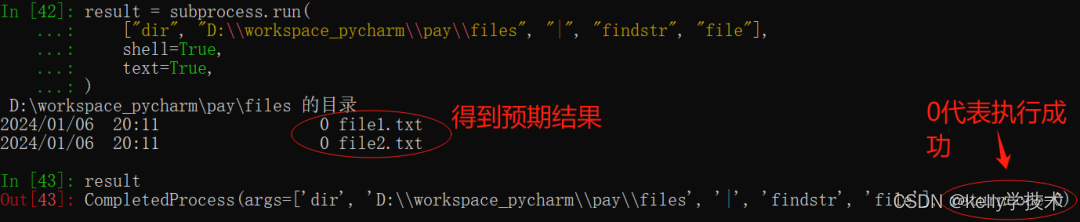
不指定参数stdout时,执行结果直接输出到控制台。
设置stdout参数
result = subprocess.run(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
shell=True,
text=True,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE)运行结果:
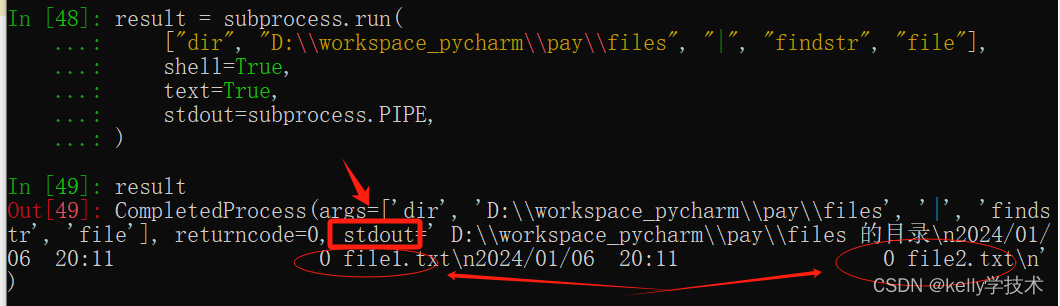
指定stdout为subprocess.PIPE,表示打开标准输出流管道,将命令执行结果以CompleteProcess类实例的方式保存在返回值中,不会直接输出在控制台。
stdout参数也可以设置为外部文件,
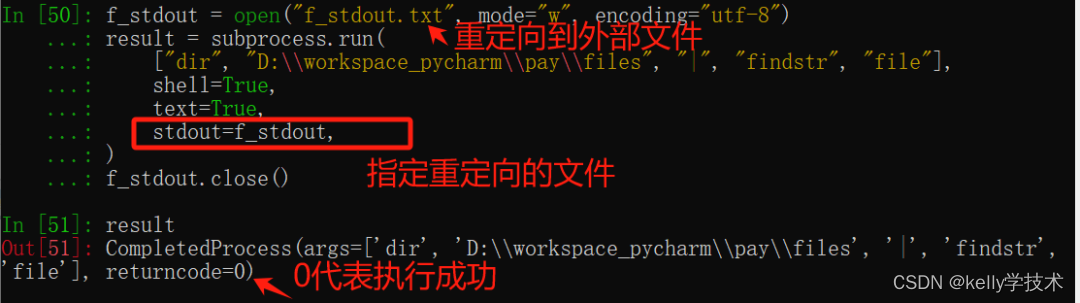
运行结果:

文件f_stdout.txt内容如下:

同理,不设置stderr参数时,外部命令执行失败会直接抛出错误信息,将错误信息输出在控制台;一旦设置,则根据stderr参数进行重定向。
四、subprocess.call
总体运行效果:执行命令后,返回成功或者失败标记,其中成功为0,失败为255。
result = subprocess.call(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
shell=True, text=True)运行结果:

指定stdout参数,可将执行结果重定向到外部文件
with open("stdout2.txt", mode="w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
result = subprocess.call(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
shell=True, text=True, stdout=f)
print(result)生成文件:

生成文件内容:

执行失败,会抛出错误信息
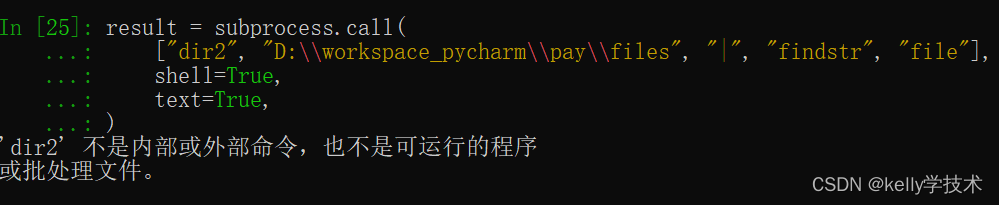
call()的另一个相似用法是check_call,区别主要在于错误信息抛出方式
result = subprocess.check_call(["dir2", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
shell=True, text=True)错误时抛出CalledProcessError类实例,而不是简单错误信息

此外,call的第二个相似函数check_output,与check_call的区别如下:
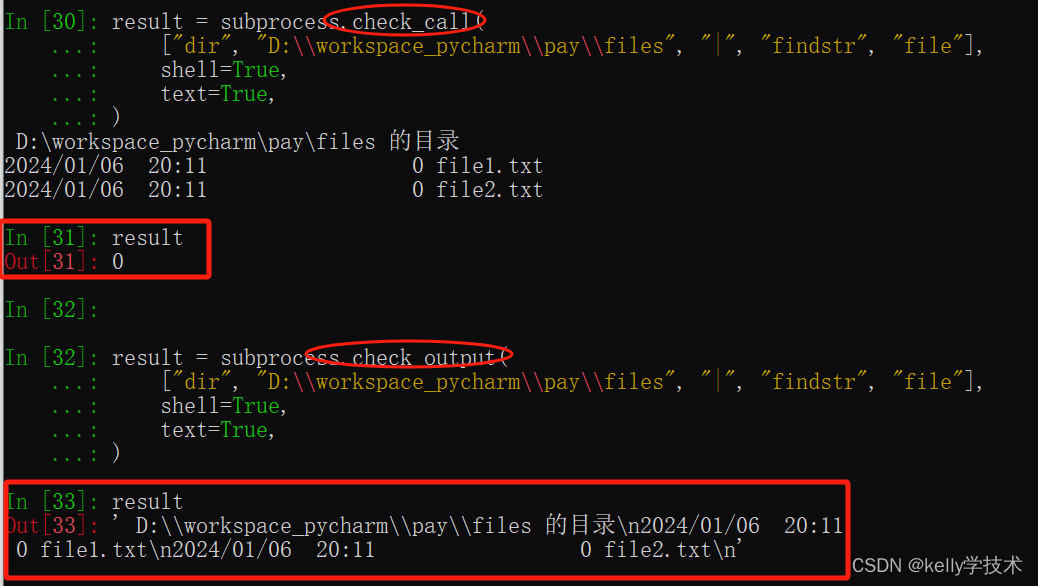
check_call成功执行后返回值为0,而check_output成功执行后返回值为执行结果。
五、subprocess.Popen
总体运行效果:先创建一个Popen对象,再调用communicate函数进行执行,得到输出和错误信息。
5.1 执行命令放在同一个Popen对象中,
5.1.1 没有指定参数stdout和stderr
process = subprocess.Popen(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
text=True, shell=True)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()运行结果:

执行结果直接输出,返回变量stdout不保存执行结果,
5.1.2 指定参数stdout和stderr
process = subprocess.Popen(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files", "|", "findstr", "file"],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True, shell=True)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()运行结果:
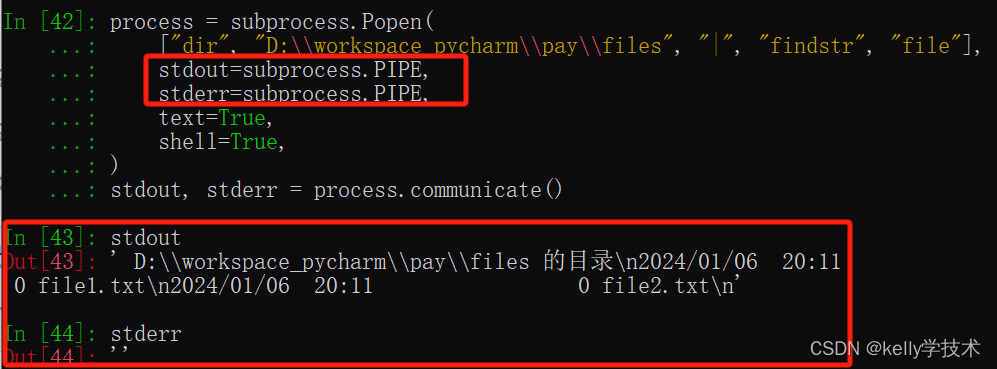
指定参数stdout为subprocess.PIPE,则将执行结果重定向到stdout变量中,stdout变量保存执行结果。
5.2 执行命令,拆分为两个子执行命令,通过stdin的方式进行联合
process1 = subprocess.Popen(["dir", "D:\\workspace_pycharm\\pay\\files"],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
shell=True)
process2 = subprocess.Popen(["findstr", "file"],
stdin=process1.stdout,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
shell=True)
stdout, stderr = process2.communicate()运行结果:

这种方式,更符合常见操作习惯。
总结一下:
-
1)os.system:使用最简单,输入为字符串形式,完整的外部命令。
-
2)os.popen:输入与os.system相同,实际是subprocess.Popen的封装。
-
3)subprocess.run:输入为列表形式,为外部命令的拆分,返回值为CompletedProcess实例。
-
4)subprocess.call:输入同上,返回值为状态码。
-
5)subprocess.Popen:输入同上,返回值为执行结果和错误信息。
好了,今天的分享就到这里。
本文原始版本发表链接:
kelly会在公众号「kelly学技术」不定期更新文章,感兴趣的朋友可以关注一下,期待与您交流。
--over--
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!