河南工程学院第六届程序设计竞赛-A组-题解
更好的阅读体验 \color{red}{更好的阅读体验} 更好的阅读体验
远古时期的签到题
描述:
远古时期奇妙的事情…
远古时期有一个比赛,里面有这样一道签到题:
- 给定一个正整数 N N N
- 求这个整数转化为二进制后的数有多少位是 0 0 0。
输入格式:
共一行,一个正整数 N N N。
输出格式:
共一行,一个整数,表示 N N N 转化为二进制后数位是 0 0 0 的个数。
数据范围:
0 ≤ N ≤ 1 × 1 0 18 0\le N \le 1\times10^{18} 0≤N≤1×1018。
样例输入:
5
样例输出:
1
提示:
对于样例, 5 5 5 的二进制表示为 101 101 101,只有一个 0 0 0。
思想1:
- 签到题。
- 位运算。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int M = 1e7 + 10;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
void solve(){
LL n; cin >> n;
int cnt = 0;
if(n == 0){
cout << 1 << endl;
return ;
}
while(n){
cnt += (n & 1 == 1 ? 0 : 1);
n >>= 1;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
思想2:
- 进制转换。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
//将long long类型的x从10进制转换为p进制,返回值类型为string类型
string to_p(long long x, long long p){
string ans;
if(x == 0) return "0";
while(x){
long long k = x % p; char c;
if(k < 10) c = k + '0';
else c = k + 'A' - 10;
ans = c + ans;
x /= p;
}
return ans;
}
//将string类型的x从p进制转换为10进制,返回值为long long类型
long long to_x(string x, long long p){
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < x .size(); i ++){
long long k = 0;
if(x[i] >= '0' && x[i] <= '9') k = x[i] - '0';
else k = x[i] - 'A' + 10;
ans = ans * p + k;
}
return ans;
}
//将string类型的x从r进制转为p进制,返回值为string类型
string r_to_p(string x, long long r, long long p){
return to_p(to_x(x, r), p);
}
void solve(){
string s; cin >> s;
string p = r_to_p(s, (LL)10, (LL)2);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < p.size(); i ++){
if(p[i] == '0') cnt ++;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
开根
描述:
H F HF HF 告诉 L Y S LYS LYS 说:“我最近学习了二分开根号!!!” L Y S LYS LYS 说:“那我给你出一个开五次方根的题目!” H F HF HF 感觉太简单了,就来找你们解决这个问题。
输入格式;
一行,输入一个整数 n n n
输出格式:
一行,一个浮点数,表示 n n n 开五次方根的结果。(保留六位小数)
数据范围:
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 6 1 \le n \le 10^6 1≤n≤106
样例输入:
32
样例输出:
2.000000
思想:
- 作为一个名副其实的签到题,也不必多说
- 直接用pow函数就可以做了
- 不过有实力的人想用二分也不是不行hh!
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
printf("%.6lf",pow(n,0.2));
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
double l=-1000000,r=1000000;
while(r-l>=1e-8)
{
double mid=(l+r)/2;
if(mid*mid*mid*mid*mid>=n)
{
r=mid;
}
else
l=mid;
}
printf("%.6lf",l);
}
乖乖♂站好
描述:
现在有人组队要来撅我们的野兽仙贝,可是人实在是太多了,野兽仙贝想要这些人排好队,于是他喊道“乖乖♂站好!”

已知在这 N N N 个人编号为 1 ~ N 1\sim N 1~N,编号为 i i i 的人身高为 h i h_i hi?,将这些人按照身高由低到高进行排序,若有相同身高的人,其编号小的排在前面。请你按顺序输出当前排好序的队伍里当前位置所站的人的编号。
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 N N N,代表总人数。
接下来 N N N 个整数 h h h,第 i i i 个整数 h i h_i hi? 代表编号为 i i i 的人的身高。
输出格式:
共一行, N N N 个整数,表示当前位置上的人的编号,每个编号之间空一格。
数据范围:
1 ≤ N ≤ 1 × 1 0 6 , 1 ≤ h ≤ 2 1\le N \le 1\times 10^6,1\le h\le 2 1≤N≤1×106,1≤h≤2。
样例输入:
5
1.1 1.8 1.2 1.1 1.3
样例输出:
1 4 3 5 2
思想:
- 签到题。
- 结构体排序。
- 可能会卡时间,建议
scanf()
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int M = 1e7 + 10;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
struct people{
int x;
double h;
}p[N];
bool cmp(people &p1, people &p2){
if(p1.h == p2.h) return p1.x < p2.x;
return p1.h < p2.h;
}
void solve(){
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
double l; cin >> l;
p[i] = {i + 1, l};
}
sort(p, p + n, cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cout << p[i].x << ' ';
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
毒瘤题
描述:
H F HF HF 与 L Y S LYS LYS 在交流一些灰常复杂的问题,不是别的,就是组合计数问题。在经历了两年半的历练, L Y S LYS LYS 感觉自己的组合计数已经炉火纯青辣,于是 H F HF HF 打算给他加点难度来考验一下 L Y S LYS LYS。

L Y S LYS LYS 的脑瓜转动速度已经大幅超越计算机,他自言说:“我要更难的!组合数太小了(众所周知,后面的组合数灰常的大),我要你在 n n n 大于 24 24 24 时的组合数结果再乘上 7 7 7 的 17 17 17 次方,这样才符合我的计算能力!!!”我奈何不过 L Y S LYS LYS,只能修改题目!
给定 n , m n,m n,m,代表从 n n n 个物品当中选取 m m m 个物品总共有多少种方案。当 n n n 大于 24 24 24 时答案再乘上 7 7 7 的 17 17 17 次方。(由于数据范围过大,答案请对 40353607 40353607 40353607 取余。)
输入格式:
一行,输入两个数,分别为 n n n, m m m
输出格式:
输出一个数,为取余后最终答案
数据范围:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 1 0 9 1\le m \le n \le 10^9 1≤m≤n≤109
样例输入:
8 4
样例输出:
70
思想:
- 作为一个毒瘤题,那必须要有毒瘤的样子
- 本题考的不难,就是对数字的敏感程度,毕竟这种题目在比赛当中还是比较常见的。
- 题目的意思就是求组合数,童叟无欺,只不过就是数据很大,但是观察仔细的话,会发现乘的那个数和取余的那个数是有关系的
- 什么算法也不用,杨辉三角,递归,公式法,lucas 定理都可以来做这个题目,因为当 n 大于 24 24 24 的时候全是 0 0 0
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int C(int n, int m) {
if (n < m) return 0;
if (!m) return 1;
return (C(n - 1, m - 1) + C(n - 1, m)) % 40353607;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
if (n > 24) cout << 0 << endl;
else cout << C(n, m) << endl;
return 0;
}
LYS 拿 HF 的U盘
描述:
众嗦粥汁, H F HF HF 的 U U U 盘里存着许多宝贵的学习资料, L Y S LYS LYS 的学习资料不够了,于是他去找万能 H F HF HF 大佬,可是 H F HF HF 大佬的 U U U 盘实在太多了,这让 L Y S LYS LYS 很是震惊。为了安全起见,在拿 U U U 盘时规定了他只能拿有保护套的 U U U 盘。
已知 H F HF HF 有 N N N 个 U U U 盘,编号为 1 ~ N 1\sim N 1~N, L Y S LYS LYS 可以对这 N N N 个 U U U 盘进行如下操作:
- 若第 i i i 个 U U U 盘有保护套,那么他可以将该 U U U 盘的保护套取下,套给第 i ? 1 i-1 i?1 个 U U U 盘。
- 原本无保护套的 U U U 盘接收其他 U U U 盘的保护套后不能再执行上述操作。
- 原本有保护套的 U U U 盘最多执行一次上述操作,执行上述操作一次后仍可以接收其他 U U U 盘的保护套。
现在给定你一个长度为 N N N 且只包含 0 0 0 和 1 1 1 的字符串 S S S,其中 S i S_i Si? 为 1 1 1 时表示编号为 i i i 的 U U U 盘有保护套,反之则无,第 i i i 个 U U U 盘的含有空间大小为 G i G_i Gi? 的学习资料。由于 L Y S LYS LYS 只能拿走有保护套的 U U U 盘,他想知道对这些 U U U 盘进行如上可行操作之后,可取走的 U U U 盘学习资料的空间之和最大为多少!!!
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 N N N,表示 U U U 盘数量。
第二行,一个长度为 N N N 的只包含 0 0 0 和 1 1 1 的字符串 S S S。
第三行,共 N N N 个整数 G G G,第 i i i 个整数 G i G_i Gi? 表示编号为 i i i 的 U U U 盘所含学习资料的空间大小。
输出格式:
共一行,输出可取走的 U U U 盘学习资料的空间之和的最大值。
数据范围:
1 ≤ N ≤ 1 × 1 0 6 , 1 ≤ G ≤ 1 × 1 0 9 1\le N \le 1\times 10^6,1\le G\le 1\times 10^9 1≤N≤1×106,1≤G≤1×109。
样例输入:
5
10011
1 5 4 3 2
样例输出:
8
提示:
对于样例,我们将编号为 4 4 4 的 U U U 盘的保护套取下,套给编号 3 3 3,然后将编号为 5 5 5 的 U U U 盘保护套取下,套给编号 4 4 4。编号 3 3 3 的 U U U 盘原本无保护套,所以不能执行操作。最终可以拿走编号为 1 , 3 , 4 1,3,4 1,3,4 的 U U U 盘,使得学习资料空间总和最大为 8 8 8。
思想:
- 贪心。
- 对于某个连续的 1 1 1 的区间 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j),我们可以移动的保护套范围在 ( i ? 1 , j ) (i-1,j) (i?1,j)。
- 那么在区间 ( i ? 1 , j ) (i-1,j) (i?1,j) 中必然存在一个 U U U 盘没有保护套。
- 故需要将区间 ( i ? 1 , j ) (i-1,j) (i?1,j) 中所含学习资料空间最少的 U U U 盘的保护套移除,提供给没有保护套的 U U U 盘。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
int a[N];
void solve(){
int n; cin >> n;
string s; cin >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
LL sum = 0;
int pos = s.find("1");
if(pos == -1){
cout << 0 << endl;
return ;
}
for(int i = pos; i < n; i ++){
if(s[i] == '1'){
int cnt = 1;
int t = a[i];
sum += t;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j ++){
if(s[j] == '0') break;
else cnt ++;
t = min(t, a[j]);
sum += a[j];
}
if(i - 1 >= 0){
int p = a[i - 1];
if(p > t) sum += p - t;
}
i += cnt - 1;
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
步数
描述:
在河工院当中有编号由 1 ~ n 1 \sim n 1~n 的 n n n 栋硕大的教学楼,这些教学楼之间有着非常的神奇道路,神奇到这些道路只需要一步就可以走完。
这是因为法力超强的超凡giegie制作的法力场。
河工院在设计这些教学楼之间的道路的时候为了考验学生的数学能力,每个教学楼能到达的教学楼只能是其编号的约数之和(约数之和不包含本身)并且要比其编号小的的教学楼。
即 4 4 4 号教学楼可以到达 3 3 3 号教学楼,因为 4 4 4 的约数之和为 3 3 3,并且 3 < 4 3 \lt 4 3<4。(同样 3 3 3 号也可以到 4 4 4 号教学楼,因为道路是双向的)
今日 L Y S LYS LYS 大佬闲来无事想去领略一下校园的风景,他可以从任何一栋教学楼出发,他想知道他可以走的最多步数。(因为 L Y S LYS LYS 大佬太强了不想自己算,就来考验一下你们啦)
输入格式:
输入一个数 n n n,代表有 n n n 所教学楼。
输出格式:
输出一个数,为最多步数。
数据范围:
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 6 1 \le n \le 10^6 1≤n≤106
样例输入:
3
样例输出:
2
提示:

思想:
-
本题比前面的题稍微复杂了那么一点点,一共有两个难点。
-
怎么建图
-
怎么求树的最长链
-
-
在这里不能直接去暴力建图,需要先预处理出来一个数组来存储每个数的约数之和。
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=2;j<=n/i;j++)
{
sum[i*j]+=i;
}
}
-
这样就可以直接来建图了。
-
第二个难点的话,就是怎么来求树的最长链,很直白的做法就是用树形DP来求,不过可以发现每条路的边权只有1,所以也可以直接用DFS或者BFS来求。
-
任意找一个点u,距离u最远距离的那个点v,再找距离v点最远的点z,v到z的距离就是最长链。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int he[2000010],ne[2000010],e[2000010],ver[2000010];
int d[2000010],tot=0,st[2000010];
void add(int x,int y,int z)
{
ver[++tot]=y;
e[tot]=z;
ne[tot]=he[x];
he[x]=tot;
}
int ans=0,p;
int sum[1000010];
void dfs(int x,int y,int z)
{
if(ans<z)
{
ans=z;
p=x;
}
st[x]=1;
for(int i=he[x];i;i=ne[i])
{
if(ver[i]==y)
continue;
dfs(ver[i],x,z+e[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=2;j<=n/i;j++)
{
sum[i*j]+=i;
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i>sum[i])
{
add(sum[i],i,1);
add(i,sum[i],1);
}
}
int anss=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
ans=0;
dfs(i,0,0);
dfs(p,0,0);
anss=max(anss,ans);
}
}
cout<<anss;
}
到达龙湖最美大学
描述:
到达龙湖最美大学——河南工程学院,太美丽啦河南工程学院。哎哟这不 H F HF HF 嘛,再看一下远处的图书馆吧家人们…
H F HF HF 现在想要爬到图书馆楼顶,已知图书馆有 N N N 级台阶,编号为 1 ~ N 1\sim N 1~N,他的腿长度为 h h h,第 i i i 级台阶相较第 i ? 1 i-1 i?1 级台阶的高度 d i d_i di?:
- H F HF HF 最开始所处的高度为 H = 0 H = 0 H=0。
- 当且仅当 h ≥ d i h\ge d_i h≥di? 时, H F HF HF 可以爬上第 i i i 级台阶。
- 若 H F HF HF 能够爬上第 i i i 级台阶,他所处的高度 H H H 就会变为 H + d i H+d_i H+di?。
- H F HF HF 只能按照台阶顺序来爬,不能跨编号爬台阶。
接下来给出 N N N 个台阶的高度 d d d 以及 M M M 次询问,对于每次询问包含 M M M 个腿长 h h h,求对于每一次询问在遵循上述规则的条件下, H F HF HF 最高能到达的高度 H H H。
输入格式:
第一行,两个整数 N N N 和 M M M,分别表示台阶个数和询问次数。
第二行, N N N 个整数 d d d, d i d_i di? 表示第 i i i 级台阶相较第 i ? 1 i-1 i?1 级台阶的高度。
第三行, M M M 个整数 h h h, h i h_i hi? 表示第 i i i 次询问的腿长。
输出格式:
共一行,每行输出在对应的询问下能到达的最大高度 H H H。
数据范围:
1 ≤ N , M ≤ 1 × 1 0 6 , 0 ≤ d , h ≤ 1 0 9 1\le N,M \le 1\times 10^6,0\le d,h\le 10^9 1≤N,M≤1×106,0≤d,h≤109。
样例输入:
6 4
1 2 1 4 4 3
1 2 3 4
样例输出:
1 4 4 15
提示:
- 对于样例:
- 当 h = 1 h = 1 h=1 时,最高可以上到 1 1 1 号台阶,最后高度 H = 1 H = 1 H=1;
- 当 h = 2 , 3 h = 2,3 h=2,3 时,最高可以上到 1 , 2 , 3 1,2,3 1,2,3 号台阶,最后高度 H = 4 H = 4 H=4;
- 当 h = 4 h = 4 h=4 时,最高可以上到 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 1,2,3,4,5,6 1,2,3,4,5,6 号台阶,最后高度 H = 15 H = 15 H=15。
思想:
- 前缀和,二分。
- 查询次数频繁,考虑前缀和存储能够上到前 i i i 级阶梯的高度。
- 预处理出上到第 i i i 个台阶所需的腿长,即对于前 i i i 级台阶,预处理出最大的高度差。
- 在询问时,对于每个腿长,二分即可快速找到最大能达到的台阶编号。
- 综上,利用前缀和处理能够上到第 i i i 个台阶时的高度,同时出预处理到达第 i i i 个台阶之前最高的台阶高度,最后二分处理每一次询问即可,时间复杂度 O ( M log ? N ) \mathcal{O}(M\log{N}) O(MlogN)。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
LL a[N], b[N];
void solve(){
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
LL flag = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
cin >> a[i];
flag = max(flag, a[i]);
a[i] += a[i - 1];
b[i] = flag;
}
while(m --){
int x; cin >> x;
if(x == 0){
cout << 0 << ' ';
continue;
}
int pos = upper_bound(b, b + n, x) - b;
if(b[pos] > x) pos --;
cout << a[pos] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
// cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
LYS 的小小游戏
描述:
L Y S LYS LYS 给 H F HF HF 突然提到了一个他很久很久之前发明的一个小小游戏,这个游戏需要两个人来配合,于是就和 H F HF HF 开心的玩了起来。
这个游戏就是 H F HF HF 给定一个 n n n,代表矩阵的大小是 n × n n \times n n×n 的蛇形矩阵,这个名字一定不为陌生,就是像蛇一样顺时针盘旋成一个矩阵,每一圈的数字都是顺时针排列的。就像下图一样:

不过 L Y S LYS LYS 这个小小游戏比较像这个,但又不太一样。(我称之为回字拐弯矩阵)蛇形矩阵一个人就可以玩,但是这个小小游戏需要两个人,因为需要另一个人发出指令。指令只有 1 1 1 或者 ? 1 -1 ?1,如果为 1 1 1,代表当前圈顺时针排列,如果是 ? 1 -1 ?1,就要变成逆时针排列。(具体可以看样例解释)
输入格式:
一个整数 n n n,代表矩阵的边长
第二行 ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 个整数,分别为 1 1 1 或 ? 1 -1 ?1,代表当前圈顺时针还是逆时针。
输出格式:
输出这个回字拐弯矩阵
数据范围:
1 ≤ n ≤ 1000 1 \le n \le 1000 1≤n≤1000
样例输入:
7
1 -1 -1 1
样例输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
24 25 40 39 38 37 8
23 26 41 48 47 36 9
22 27 42 49 46 35 10
21 28 43 44 45 34 11
20 29 30 31 32 33 12
19 18 17 16 15 14 13
提示:
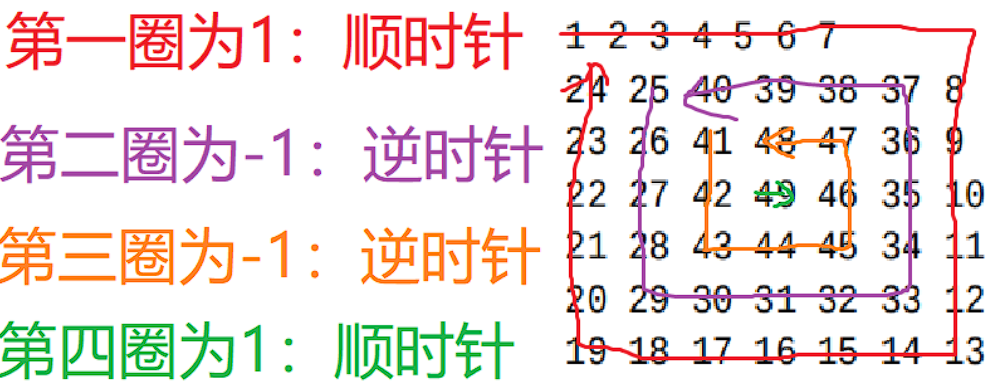
思想:
- 本题是一个模拟题,作为次签到题也是可以的。
- 直接根据题目的描述直接for循环模拟就行了,问题不大。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[1100][1100],n;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
int ll=(n+1)/2;
int cnt=0,pp=1;
int oo=n;
for(int i=1;i<=ll;i++)
{
cnt++;
int x;
cin>>x;
if(x==1)
{
for(int j=cnt;j<=n;j++)
{
a[cnt][j]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=cnt+1;j<=n;j++)
{
a[j][n]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=n-1;j>=cnt;j--)
{
a[n][j]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=n-1;j>cnt;j--)
{
a[j][cnt]=pp;
pp++;
}
}
if(x==-1)
{
for(int j=cnt;j<=n;j++)
{
a[j][cnt]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=cnt+1;j<=n;j++)
{
a[n][j]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=n-1;j>=cnt;j--)
{
a[j][n]=pp;
pp++;
}
for(int j=n-1;j>cnt;j--)
{
a[cnt][j]=pp;
pp++;
}
}
n--;
}
for(int i=1;i<=oo;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=oo;j++)
cout<<a[i][j]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
}
欧拉幻树
描述:
那一天, L Y S LYS LYS 再次回忆起了被 H F HF HF 出的真·毒瘤题——欧拉幻方支配的恐惧,这使得 L Y S LYS LYS 彻底疯狂。
奕前是奕前,仙在是仙在,奕悟之后的 L Y S LYS LYS 给出了一个长度为 n n n 的排列 p p p,要求 H F HF HF 根据 p p p 构建出他想要的欧拉幻树。
给出欧拉幻树的定义:
- 该树是一颗含有 n n n 个节点的有根树
- 对于排列 p p p,满足所有的 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n 1\le i < j \le n 1≤i<j≤n 中,使得 p i p_i pi? 到根的距离小于点 p j p_j pj? 到根的距离
H F HF HF 大喜,这一看就肥肠煎蛋,于是很自然地交给了你来解决。
请你对树上的边赋权,使得满足欧拉幻树的定义。若无解,输出 ? 1 -1 ?1 ;否则输出 n n n 个整数,第 i i i 个整数 v i v_i vi? 表示点 i i i 到其父亲的边权为 v i v_i vi?,特别地,根到其父亲的边权为 0 0 0 ,其他的边权至少为 1 1 1。
输入格式:
第一行输入数据包含一个整数 t t t 测试中输入数据集的数量。
每个测试用例由三行组成。
第一行包含一个整数 n n n,表示树的顶点数。
第二行包含 n n n 个整数 b 1 , b 2 , . . . , b n ( 1 ≤ b i ≤ n ) b_1,b_2,...,b_n(1\le b_i \le n) b1?,b2?,...,bn?(1≤bi?≤n) 表示 i i i 的父亲,保证是一颗有根树。
第三行包含给定的排列 p p p , n n n 个不同的整数 p i ( 1 ≤ p i ≤ n ) p_i(1\le p_i \le n) pi?(1≤pi?≤n)。
输出格式:
对于每组输入数据,将答案输出在单独的一行上。
如果存在解,则输出 n n n 个整数 v 1 , v 2 , . . . , v n v_1 ,v_2,...,v_n v1?,v2?,...,vn? 表示 b i b_i bi? 到 i i i 这条边的权重,特别地,对于根顶点边权为 0 0 0
如果有多个答案,请输出字典序最小的答案序列。
数据范围:
1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1\le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104
$1 \le n \le 2\times 10^5 , \sum n \le 5\times 10^5 $
样例输入:
4
5
3 1 3 3 1
3 1 2 5 4
3
1 1 2
3 1 2
7
1 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
6
4 4 4 4 1 1
4 2 1 5 6 3
样例输出:
1 1 0 4 2
-1
0 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 5 0 1 2
思想:
- 首先,判断是否存在解:
- 如果一个点的某个儿子到根的距离比自己短那么一定是不合法的,其他情况都是合法的
- 遍历每个节点,对于每个节点 x x x,检查其所有子节点 y y y,如果存在一个子节点 y y y,使得 y y y 到根的距离比 x x x 到根的距离更短,那么该排列没有解,输出 ? 1 -1 ?1
- 如果存在解:
- 则按照字典序最小的方式给每个节点赋值。
- 将排列 p p p 中的节点按照从小到大的顺序遍历,对于排列中的第 i i i 个节点 p i p_i pi?,将其赋值为 i i i
- 赋值完成后,再 DFS 一遍给每条边赋值:
- 从根节点开始,对于每个节点 x x x,遍历其所有子节点 y y y,将边 ( x , y ) (x, y) (x,y) 的权值设为 p y ? p x p_y - p_x py??px? 即可
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define re register
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
const int N = 1e6 + 3;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1);
vector<vector<int>> tree; // 存储树的邻接表
vector<int> ans; // 存储每个节点到其父节点的边权
vector<int> vis; // 存储每个节点在排列中的位置
vector<int> res; // 存储排列
int n, flag = 1; // n为节点个数,flag用于判断是否满足欧拉幻树的定义
// 检查是否满足欧拉幻树的定义
void check(int x, int fa) {
for (auto y : tree[x]) {
if (y == fa) continue;
if (res[y] < res[x]) flag = 0; // 如果存在满足条件的边,则不满足欧拉幻树的定义
check(y, x);
}
}
// 深度优先搜索构建欧拉幻树
void dfs(int x, int fa, int deep) {
ans[x] = vis[x] - deep; // 节点x到其父节点的边权为节点在排列中的位置减去当前深度
for (auto y : tree[x]) {
if (y == fa) continue;
dfs(y, x, deep + ans[x]);
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> n;
tree = vector<vector<int>>(n);
int root = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
int x; cin >> x;
x --;
if (x == i) {
root = x; // 找到根节点
continue;
}
tree[x].push_back(i);
tree[i].push_back(x);
}
res = vector<int>(n);
vector<int> st(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> st[i];
st[i]--; res[st[i]] = i; // 将排列中的位置记录在res数组中
}
flag = 1;
check(root, -1); // 检查是否满足欧拉幻树的定义
ans = vector<int>(n);
if (!flag) {
cout << -1 << "\n"; // 如果不满足欧拉幻树的定义,则输出-1
return;
}
vis = vector<int>(n);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) vis[st[i]] = cnt ++; // 将排列中的位置映射到节点编号
dfs(root, -1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == n - 1]; // 输出每个节点到其父节点的边权
}
int main(){
IOS;
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while(_ --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!