顺序表及应用
目录
一. 线性表
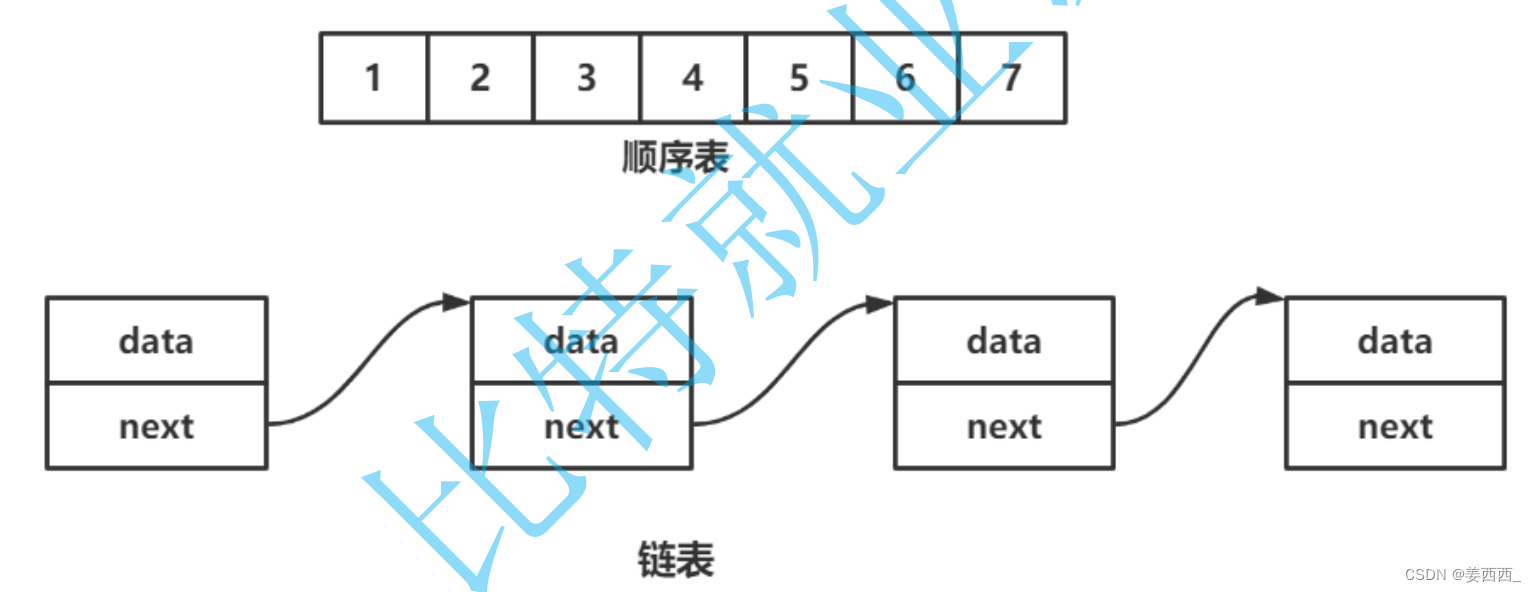
二. 顺序表
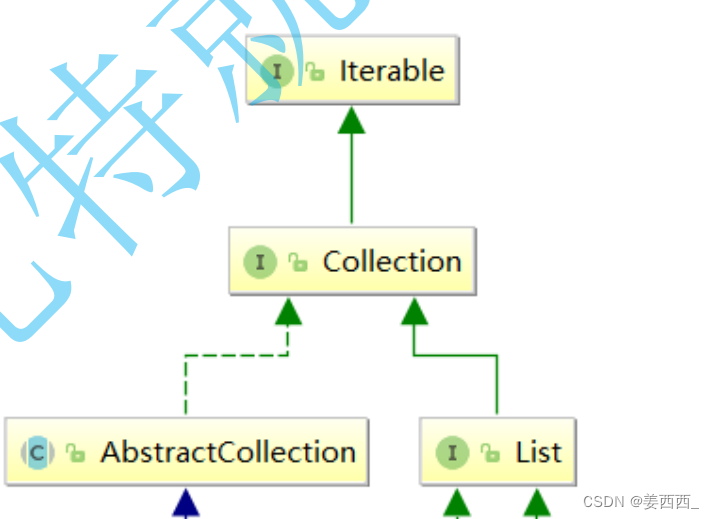
2.1 ArrayList简介
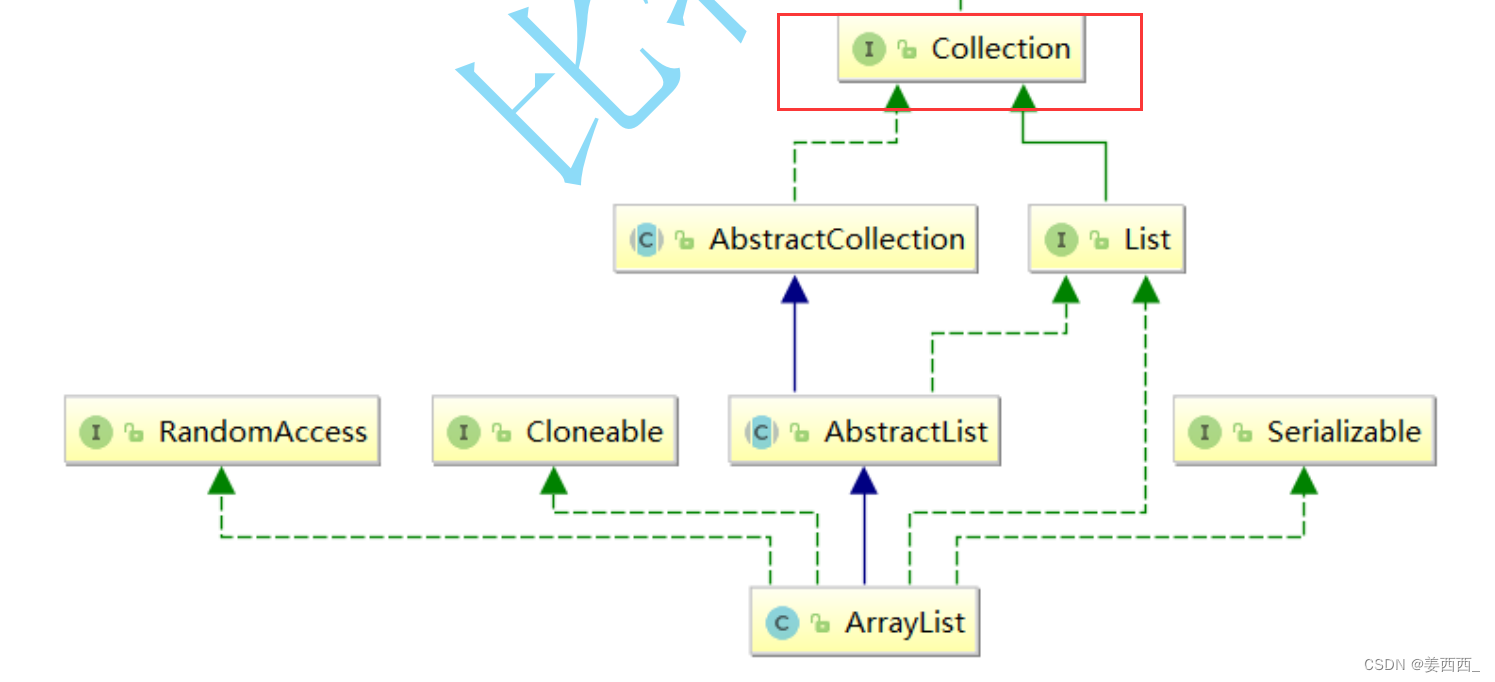
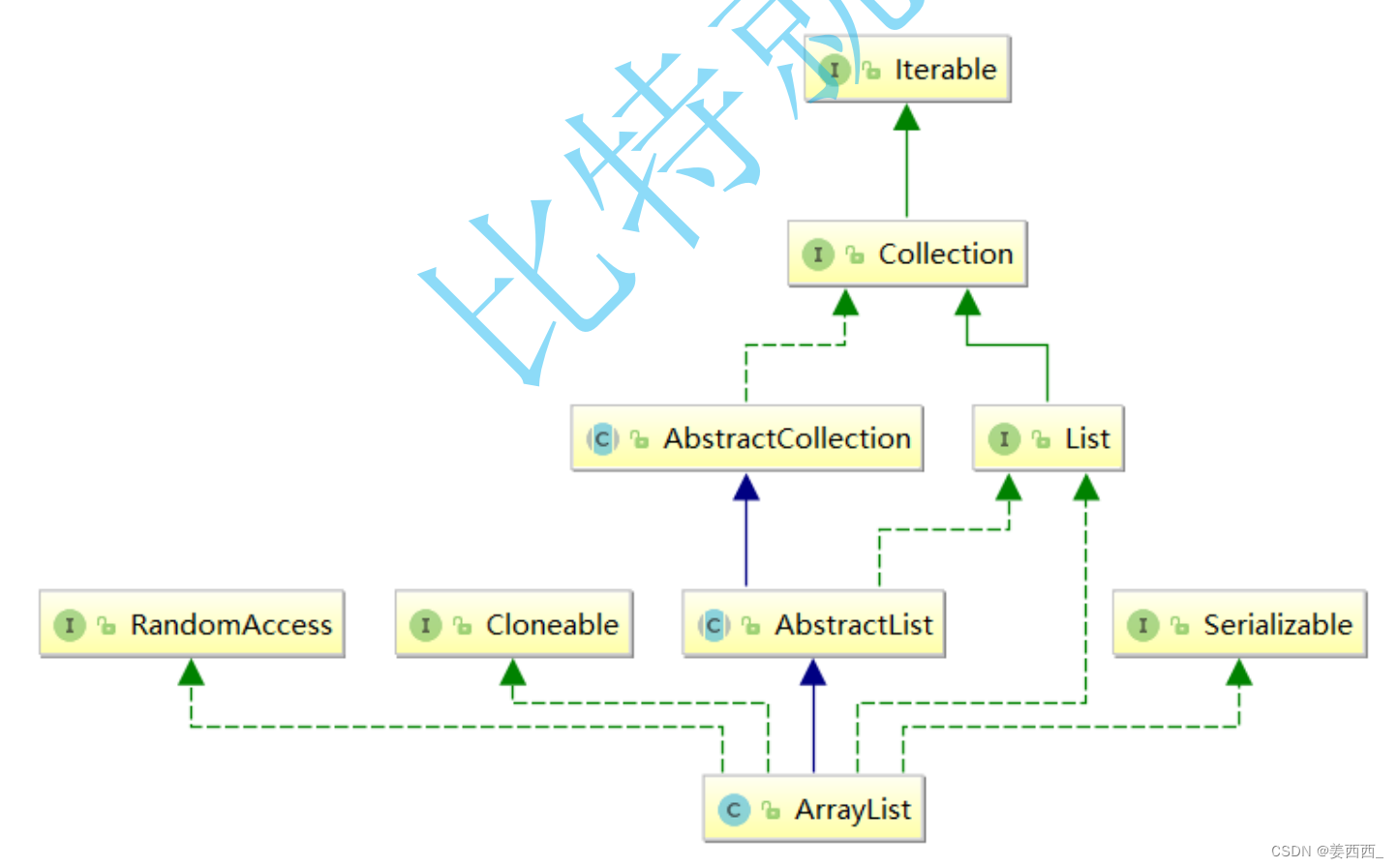
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:
2.2 ArrayList的简单实现
存放整型为例:
?接口:
public interface IList {
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data);
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) ;
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) ;
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) ;
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) ;
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) ;
//删除第一次出现的关键字toRemove
public void remove(int toRemove);
//使用的元素个数
public int size() ;
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() ;
// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display() ;
void isFull(int[] elem);
void isEmpty();
}
自定义异常:
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException(){
super();
}
public EmptyException(String s){
super(s);
}
}public class PosException extends RuntimeException {
public PosException(){
super();
}
public PosException(String s){
super(s);
}
}MyArrayList:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList implements IList{
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 5;
public MyArrayList(){
elem = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
//判断是否为空, 若为空, 扩容
@Override
public void isFull(int[] elem) {
if(usedSize ==elem.length){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
}
@Override
public void add(int data) {
isFull(this.elem);
elem[usedSize] = data;
usedSize++;
}
//适用Add方法:检查pos位置的合法性
public void checkPosOfAdd(int pos){
if(pos<0 || pos>usedSize){//可以是usedSize位置
throw new PosException("pos位置错误");
}
}
@Override
public void add(int pos, int data) {
isFull(this.elem);
checkPosOfAdd(pos);
for (int i = usedSize-1 ; i >= pos; i++) {
elem[i+1] = elem[i];
}
elem[pos] = data;
usedSize++;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//适用于get set方法:检查pos位置的合法性
public void checkPosOfGet(int pos){
if(pos<0 || pos>=usedSize){//pos位置不能为useSize
throw new PosException("pos位置错误");
}
}
//判断是否为空, 若为空, 抛异常
@Override
public void isEmpty() {
if(usedSize==0){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空");
}
}
@Override
public int get(int pos) {
checkPosOfGet(pos);
isEmpty();
return elem[pos];
}
@Override
public void set(int pos, int value) {
checkPosOfGet(pos);
isEmpty();
elem[pos] = value;
}
@Override
public void remove(int toRemove) {
isEmpty();
int index = indexOf(toRemove);
for(int i=index;i< usedSize-1 ;i++){
elem[i] = elem[i+1];
}
usedSize--;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
usedSize = 0;
}
@Override
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
}2.3 ArrayList使用
实际上, 我们在使用顺序表时, 不需要自己定义, 我们只需要拿来用即可, 那么我们可以分析一下源码, 方便我们使用:
1.?ArrayList是一个泛型类

?我们看到, ArrayList是一个泛型类, 那么我们在实例化对象时, 写法为:
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
2.? ArrayList中定义的变量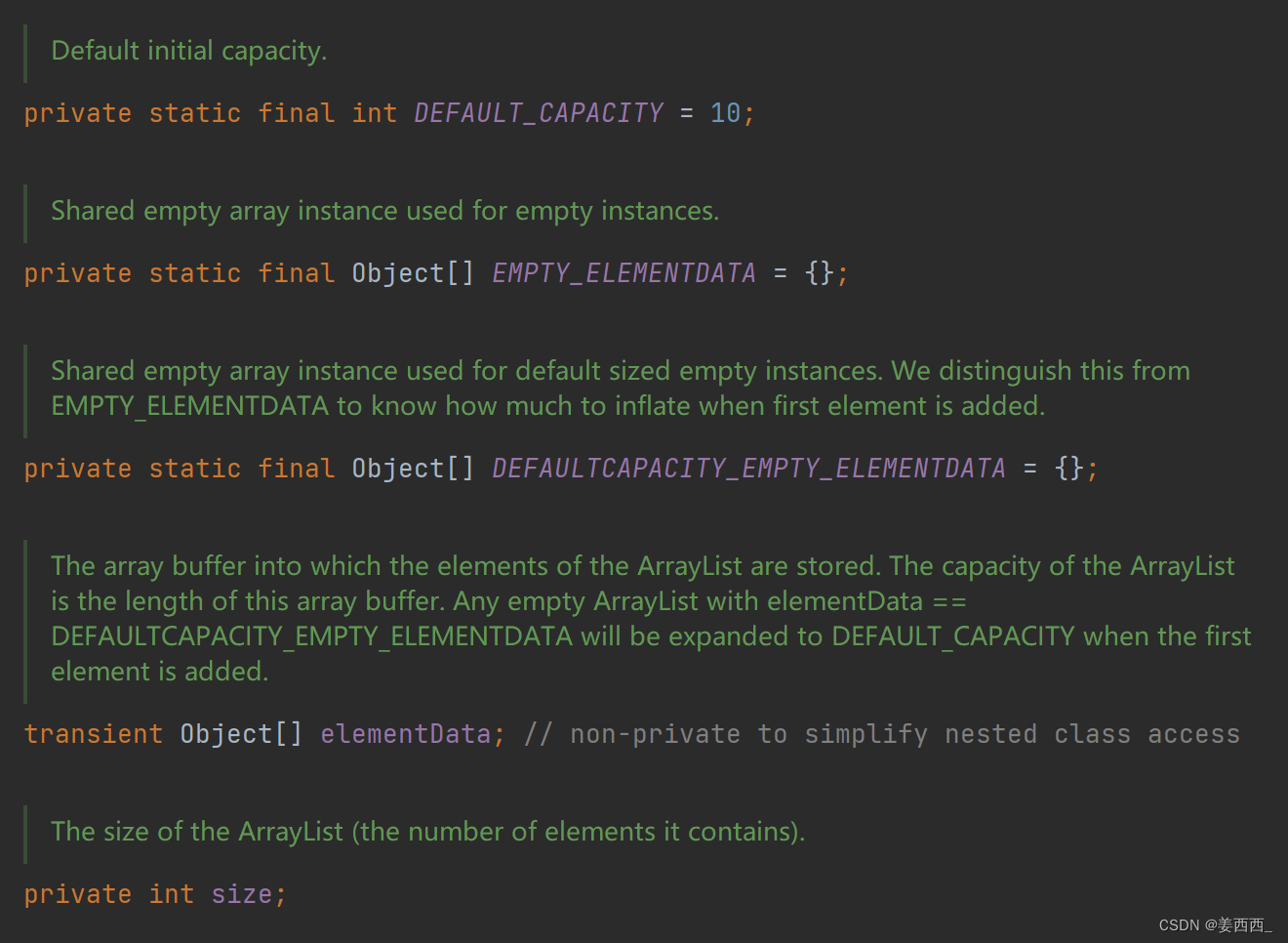
我们大致可以猜出:
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; ---? 默认容量 为10?
size? ?----相当于上述我们定义的usedSize, 数组中使用的个数
其他的我们往下看:
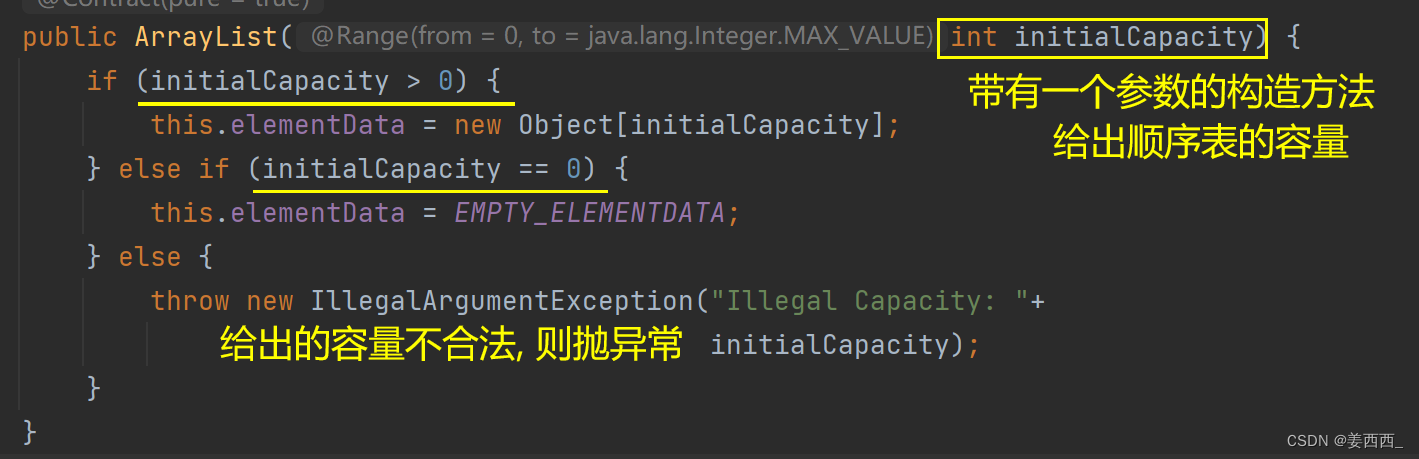
3. ArrayList的构造方法
a. 带有一个容量参数的构造方法
b. 不带参数的构造方法
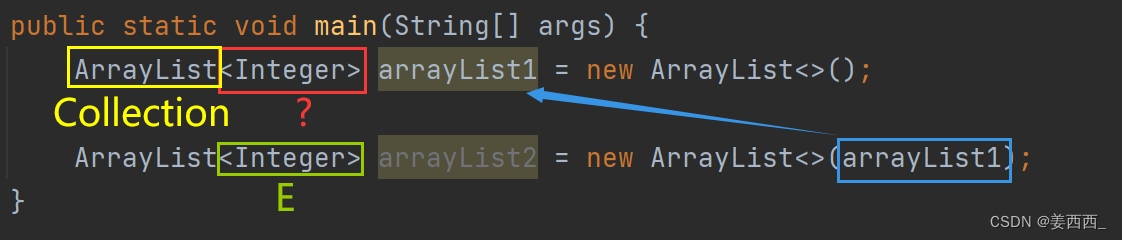
 ?c. 带有一个接口参数的构造方法
?c. 带有一个接口参数的构造方法
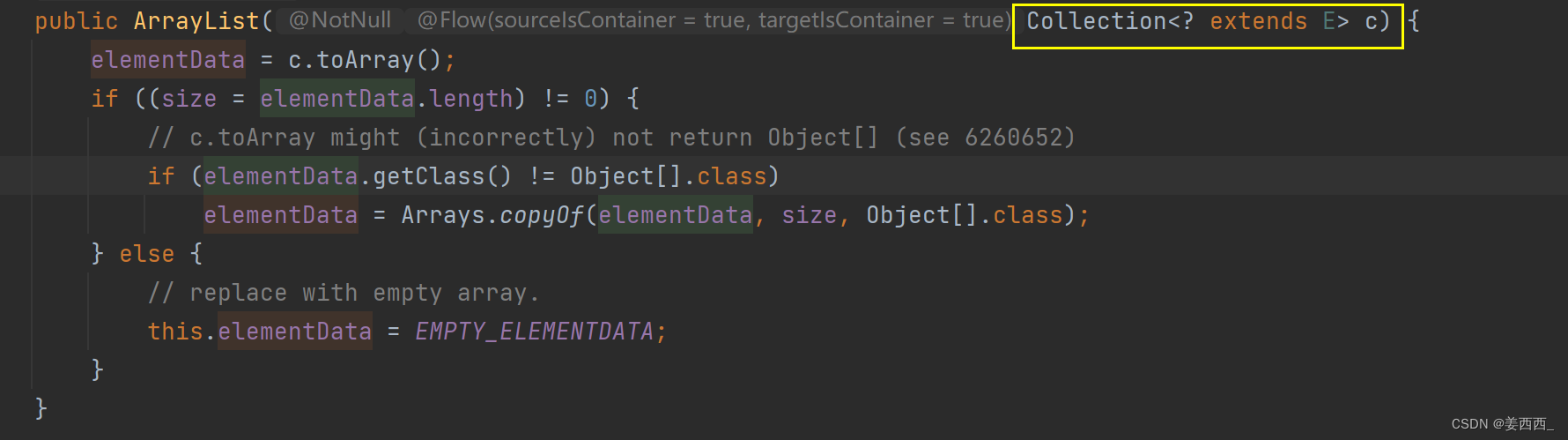
?① Collection< ? extends E> 代表参数的类型
? ? ? c 代表变量
②Collection是一个接口
意味着下面的具体类都能用Collection接收
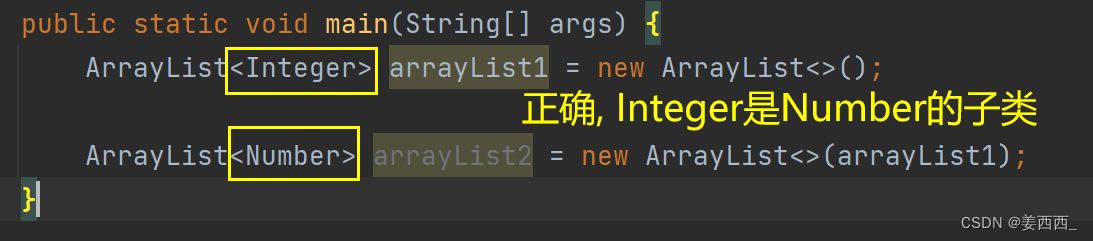
③< ? extends E>? ?? 是一个通配符, 意味着传入的参数必须是E类型或E的子类类型, E表示的是原ArrayList中的参数类型
?举例:
这个构造方法的意义是: 利用另一个集合, 构造当前集合?
例:
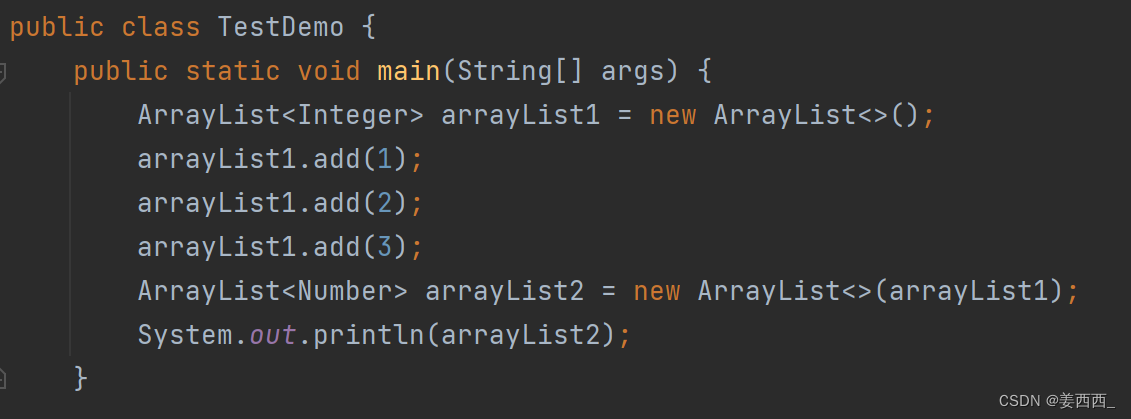
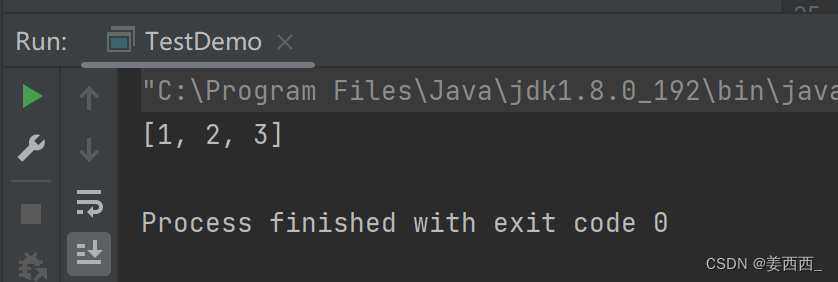
结果为:
?也可对其进行操作:
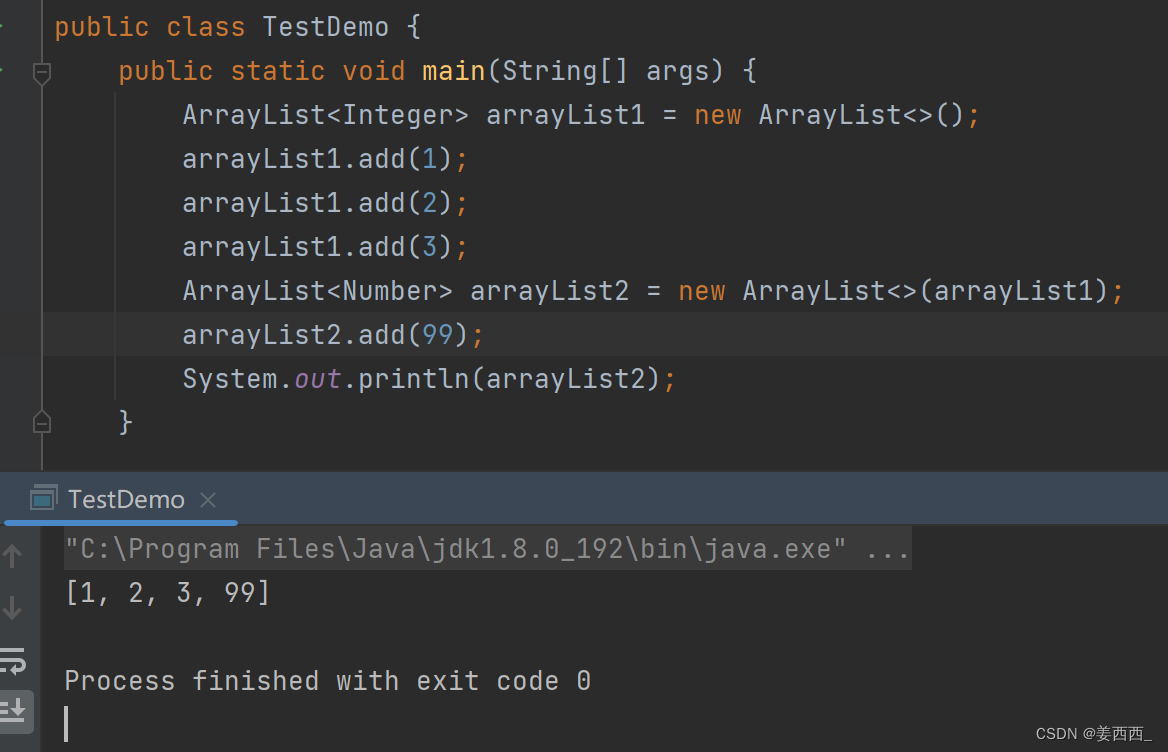
?补充:?
1. 第一次add时, 分配了内存, 大小为10?
2. 当空间不足时需扩容, 以1.5倍扩容, 意味着第二次容量应为15
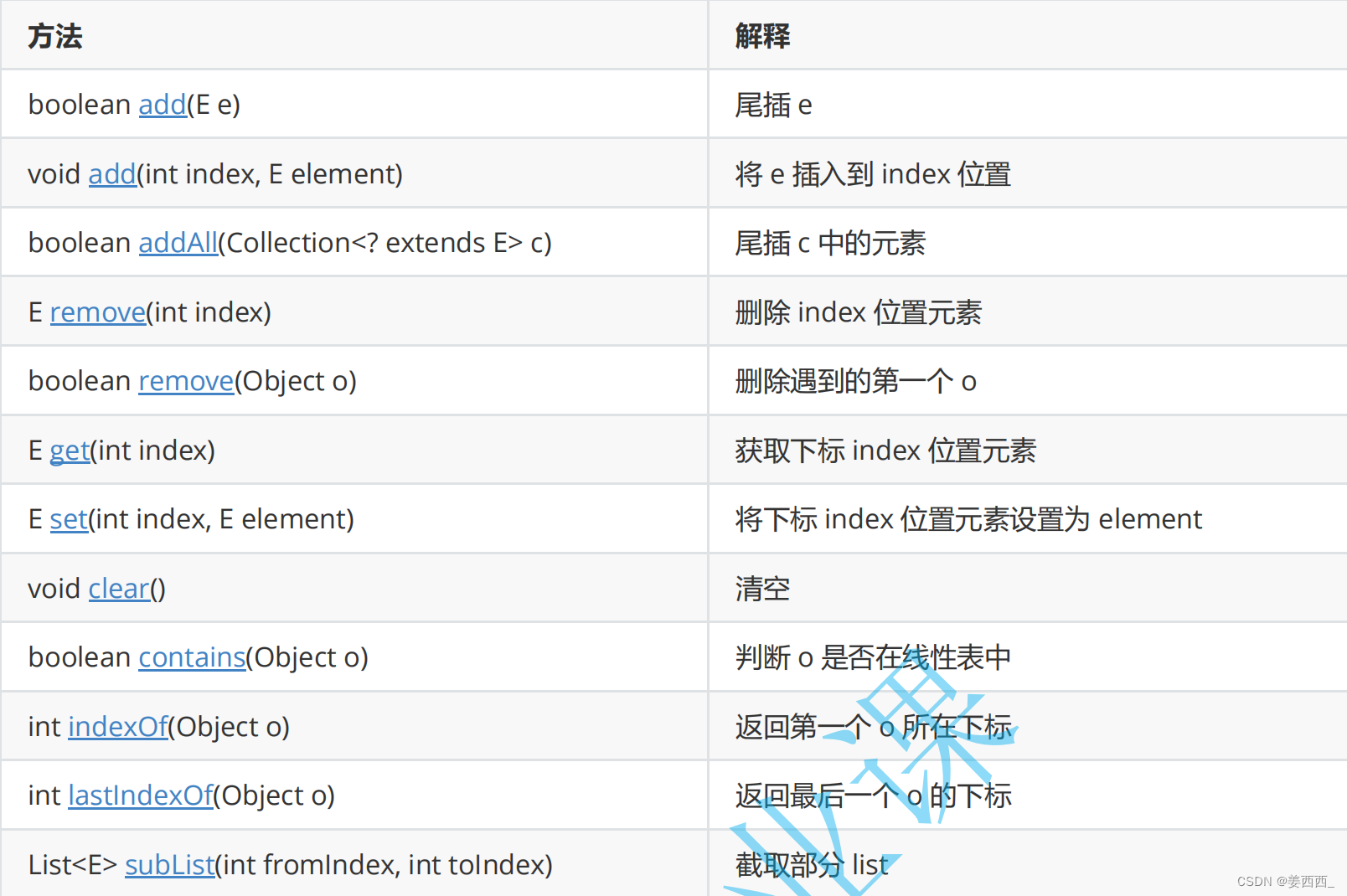
?4. ArrayList常见的方法
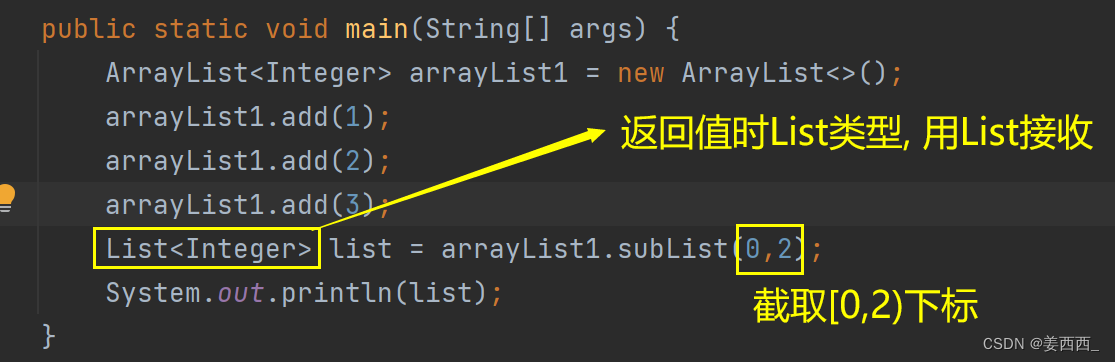
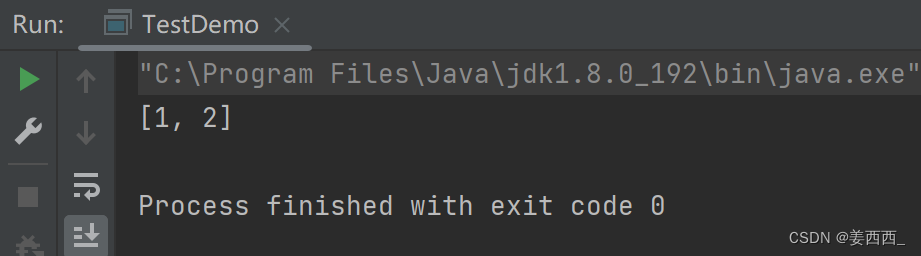
我们来详细了解一下subList方法:
 ?
?
当我们修改list的值, 发现:
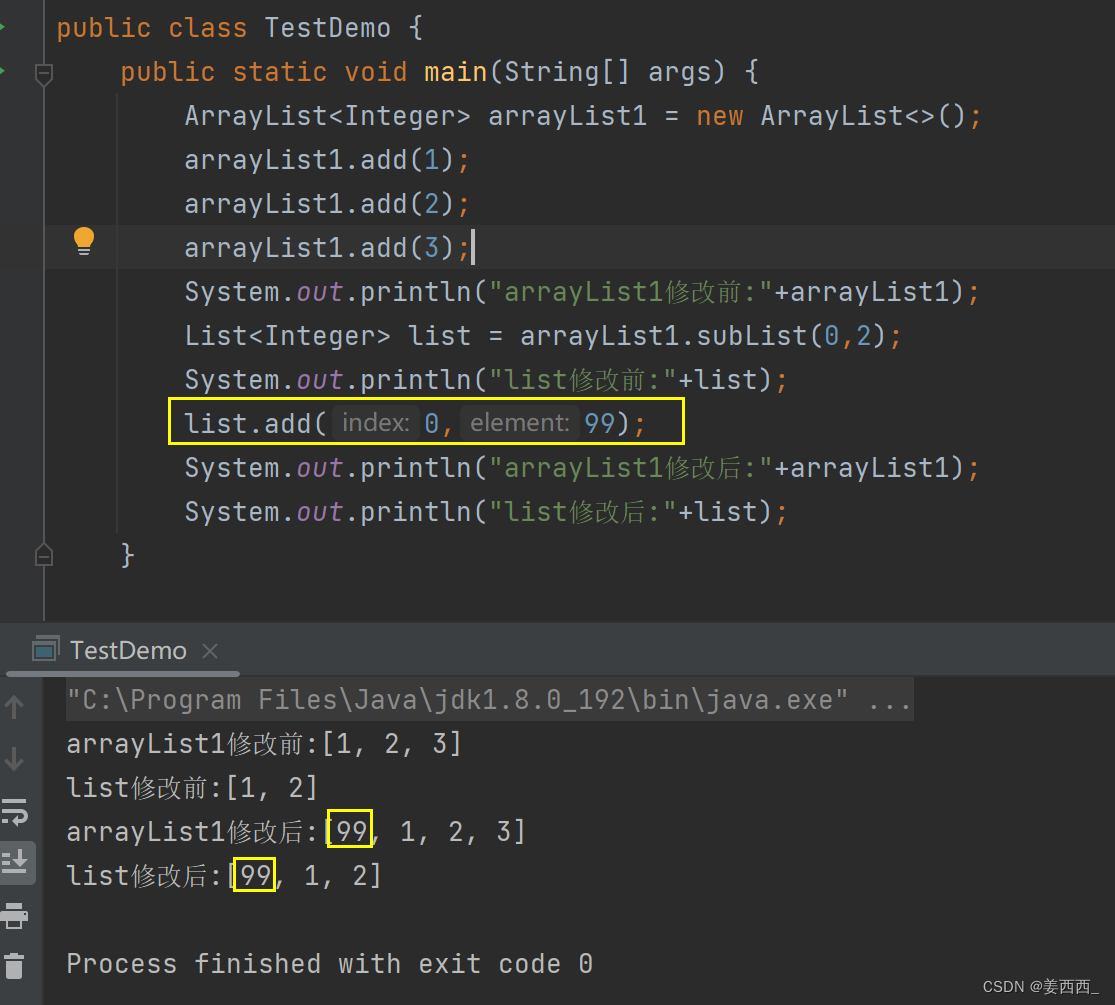 ?arrayList1的值也被修改了.
?arrayList1的值也被修改了.
实际上, subList方法, 截取时, 不是产生了新的对象, 只是指向了原顺序表的某个下标.
2.4 ArrayList的遍历
第一种:for循环
// 使用下标 +for 遍历for ( int i = 0 ; i < arrayL ist . size (); i ++ ) {????????System . out . print (arrayL ist . get ( i ) + " " );}
?第二种: for-each
// 借助 foreach 遍历for ( Integer x ? : arrayList ) {????????System . out . print ( integer + " " );}System . out . println ();
第三种: 使用迭代器
可以使用迭代器的原因是: 继承了Iterable接口
从前往后:?
Iterator < Integer > it = arrayList .iterator ();while ( it . hasNext ()){????????System . out . print ( it . next () + " " );}
或
ListIterator < Integer > it = arrayList .l istIterator ();while ( it . hasNext ()){????????System . out . print ( it . next () + " " );}
注: ListIterator是Iterator的子类
?从后往前:
ListIterator < Integer > it = arrayList .l istIterator ();while ( it . hasPrevious ()){????????System . out . print ( it .previous () + " " );}
?2.5 ArrayList的扩容机制
源码了解即可, 就不在这里展示
面试题:
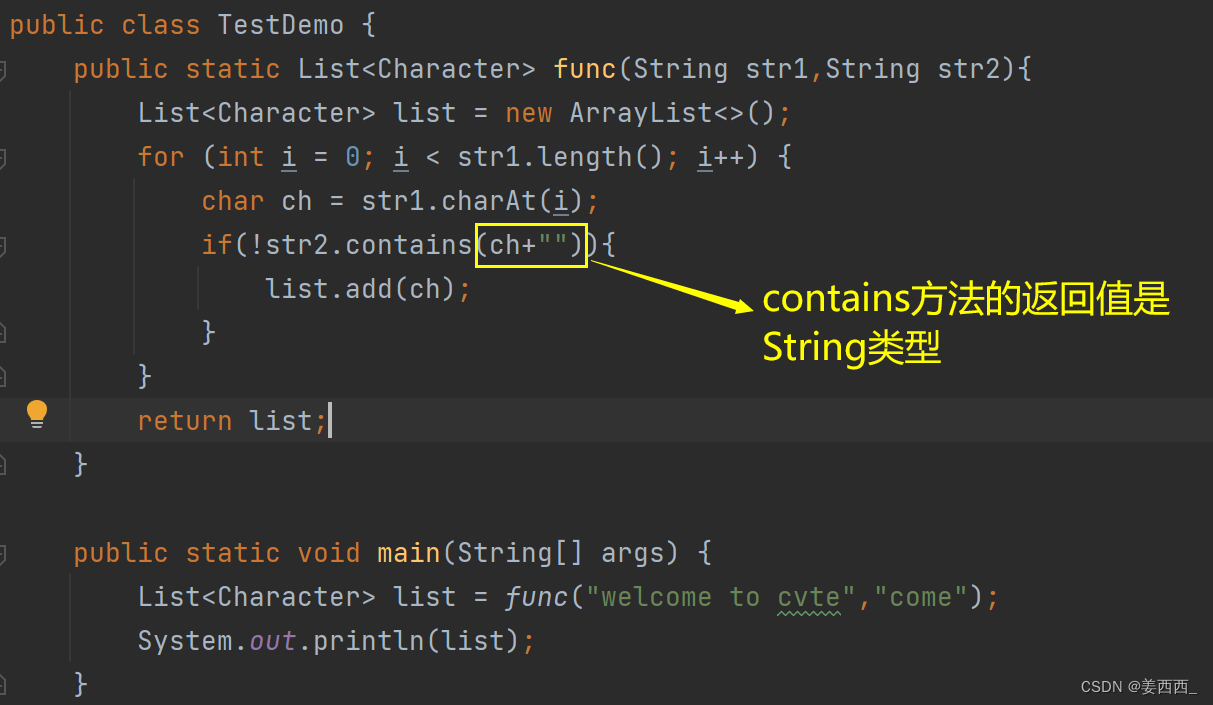
给出两个字符串, 将字符串1中的和字符串2相同的字符删掉, 例:? str1 = "welcome to cvte" str2 = "come"
思路: 遍历str1, 判断此字符是否出现在str2中, 若没出现, 将此字符串存到顺序表中.
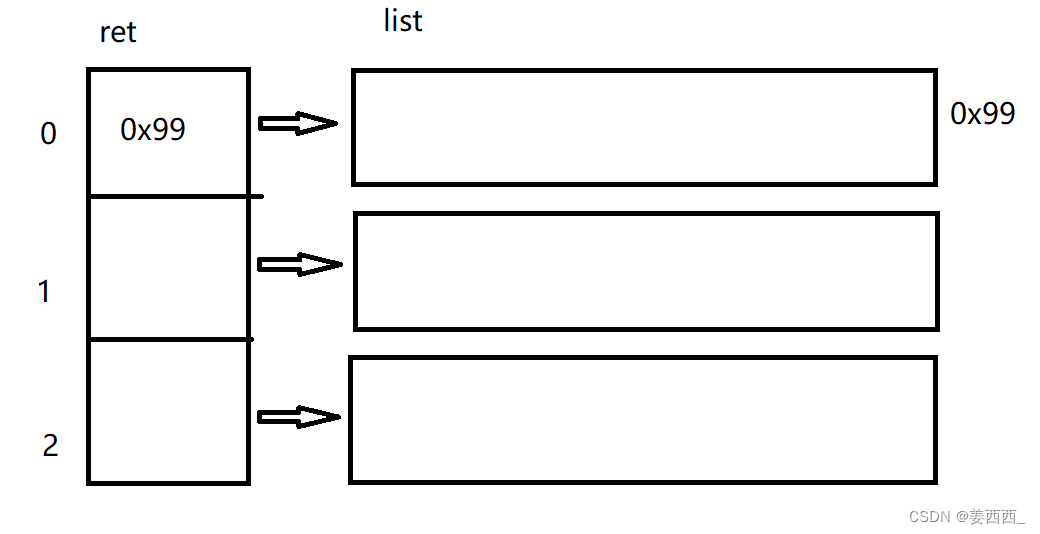
2.6 二维顺序表
?语法结构:
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
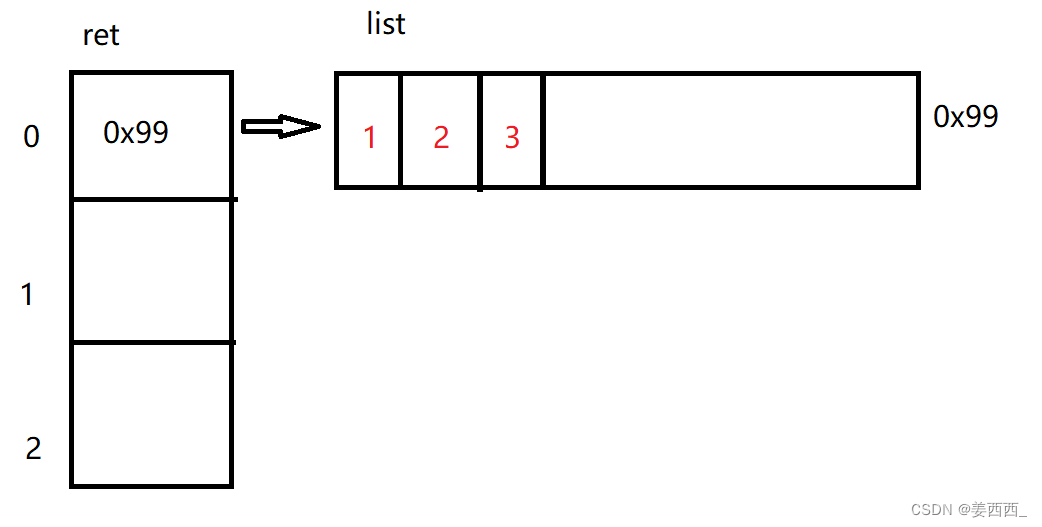
画图理解:
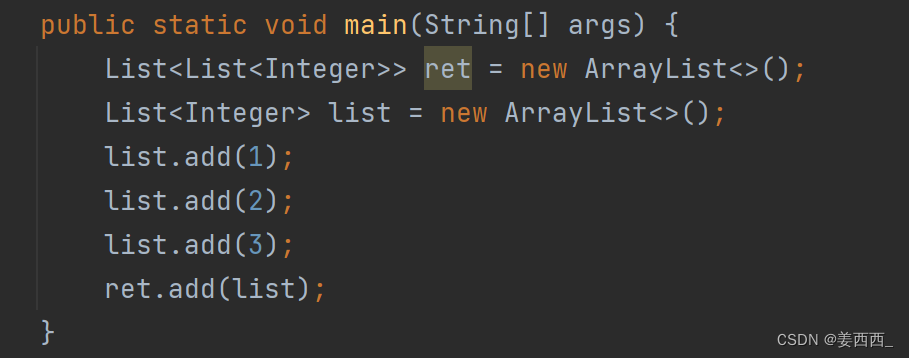
?添加元素:
实例:
?杨辉三角
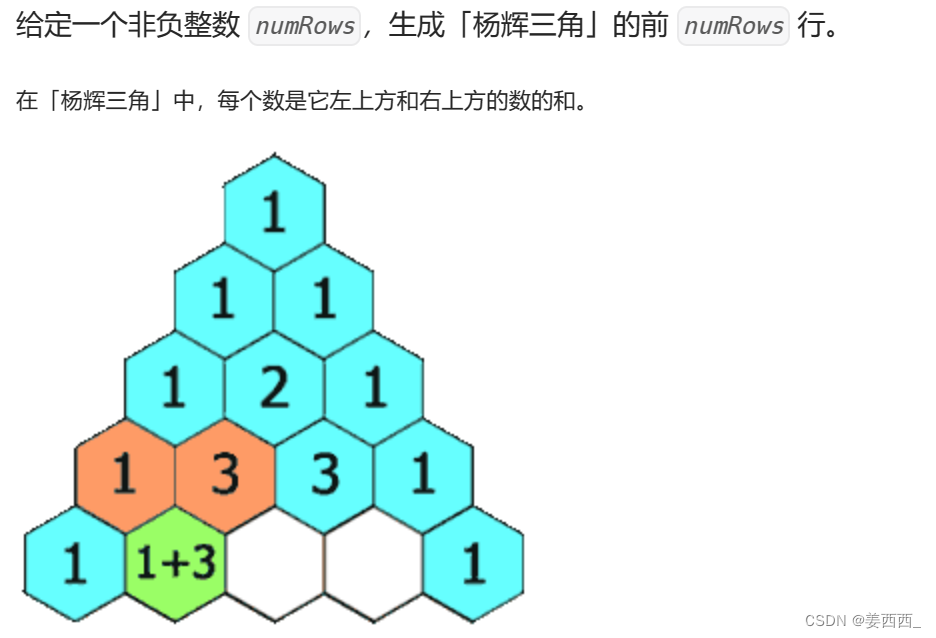
思路:
1. 每一行的第一个数字和最后一个数是1?
2. 每一行中间的数字 假设这个数字在[ i ][ j ]位置, 那么[ i ][ j ] =?[ i -1 ][ j ] +[ i -1 ][ j -1 ]
首先定义一个二维顺序表, 先将第一个数和最后一个数加入
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//1. 第一个元素设为1
list.add(1);
//2. 中间元素
//3. 最后一个元素设为1
list.add(1);
ret.set(i,list);
}
}?中间元素, 首先我们要创建列下标, 并找到第i-1行, 进行[ i ][ j ] =?[ i -1 ][ j ] +[ i -1 ][ j -1 ]
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
ret.add(list);
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
//1. 第一个元素设为1
curList.add(1);
//2. 中间元素
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
List<Integer> prevList = ret.get(i-1);
int x = prevList.get(j-1)+prevList.get(j);
prevList.add(x);
}
//3. 最后一个元素设为1
curList.add(1);
ret.add(curList);
}
return ret;
}?2.7 ArrayList的使用
简单的洗牌算法
(一副扑克牌, 不包含大小王, 共4个花色, 13个数字?)
首先我们要创建一个牌对象Card, 并提供构造方法, 重写toString方法
public class Card {
public String suit;//花色
public int rank;//数字
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Card{" +
"suit='" + suit + '\'' +
", rank=" + rank +
'}';
//若不想要本方法打印输出, 可以自定义,如:
// return suit+rank+" ";
}
public Card(String suit, int rank) {
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
}
?
下面创建一个CardGame类, 来实现对牌的操作
public class CardGame {
public static final String[] suits = {"?","?","?","?"};
}
?
再创建一个Main类, 用来放main方法, 进行运行测试代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}?
下面实现一个买牌的操作, 即创建一副扑克牌
//CardGame
public List<Card> butCard(){
List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>();//创建一个顺序表用来存放Card,构成一副牌
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {//四个花色
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {//13个数字
String suit = suits[i];
Card card = new Card(suit,j);//实例化一张牌
cardList.add(card);//添加到顺序表中
}
}
return cardList;
}?
下面实现一个洗牌的操作, 通过交换的方式, 每一个下标的数据和其他下标的数据进行交换
生成0~100的随机数(不包括100)
Random random = new Random(); int index = random.nextInt(100);
public void shuffle(List<Card> cardList){
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = cardList.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
//从后往前遍历, 让i位置和0~i的随机数位置进行交换数据
int index = random.nextInt(i);
swap(cardList, i,index);
}
}
private static void swap(List<Card> cardList,int i,int j ){
Card tmp = cardList.get(i);
cardList.set(i,cardList.get(j));
cardList.set(j,tmp);
}?
?下面实现一个抓牌的操作, 共三个人, 轮流抓牌, 每人抓5张
可以用二维顺序表来实现, 定义一个person顺序表, 共三个数据, 每个数据指向一个CardList
public List<List<Card>> getCard(List<Card> cardList){
List<Card> person1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> person = new ArrayList<>();
person.add(person1);
person.add(person2);
person.add(person3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cardList.remove(0);//没抓一张牌代表删去顺序表的第一个数据
person.get(j).add(card);
}
}
return person;
}完整代码+实现:
//Card.java
public class Card {
public String suit;//花色
public int rank;//数字
@Override
public String toString() {
/* return "Card{" +
"suit='" + suit + '\'' +
", rank=" + rank +
'}';*/
return suit+rank+" ";
}
public Card(String suit, int rank) {
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
}
//CardGame.java
public class CardGame {
public static final String[] suits = {"?","?","?","?"};
public List<Card> butCard(){
List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
String suit = suits[i];
Card card = new Card(suit,j);
cardList.add(card);
// cardList.add(new Card(suits[i],j)); 匿名对象
}
}
return cardList;
}
public void shuffle(List<Card> cardList){
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = cardList.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
int index = random.nextInt(i);
swap(cardList, i,index);
}
}
private static void swap(List<Card> cardList,int i,int j ){
Card tmp = cardList.get(i);
cardList.set(i,cardList.get(j));
cardList.set(j,tmp);
}
public List<List<Card>> getCard(List<Card> cardList){
List<Card> person1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> person = new ArrayList<>();
person.add(person1);
person.add(person2);
person.add(person3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cardList.remove(0);
person.get(j).add(card);
}
}
return person;
}
}
//Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CardGame cardGame = new CardGame();
List<Card> ret = cardGame.butCard();
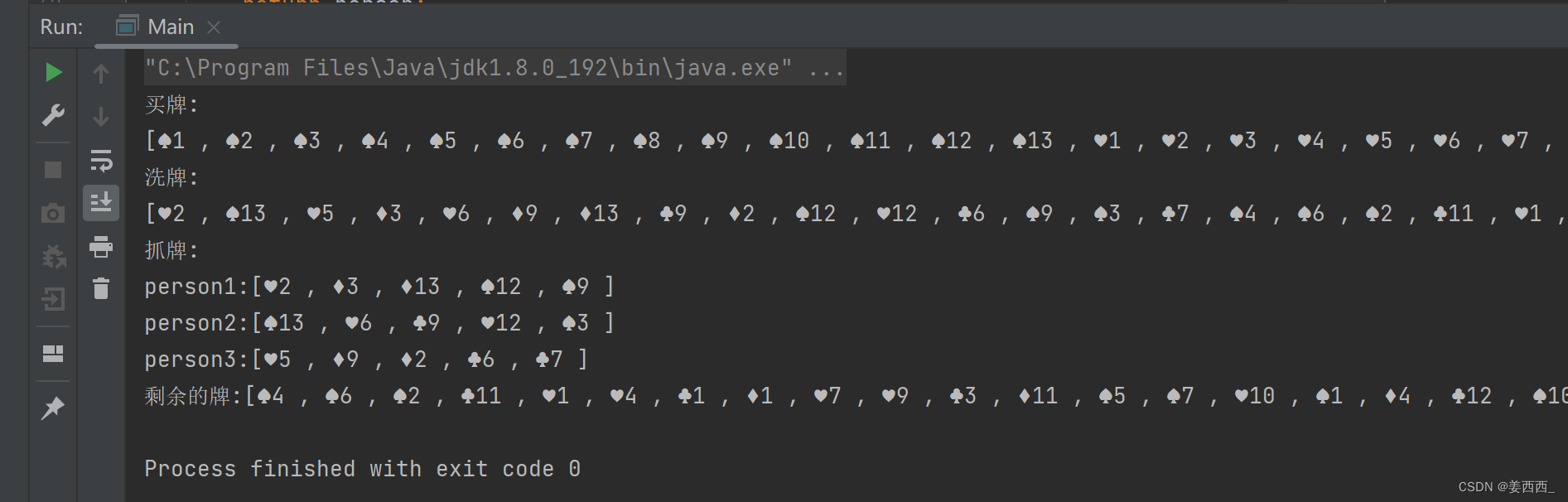
System.out.println("买牌:");
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println("洗牌:");
cardGame.shuffle(ret);
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println("抓牌:");
List<List<Card>> person = cardGame.getCard(ret);
for (int i = 0; i < person.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("person"+(i+1)+":"+ person.get(i));
}
System.out.println("剩余的牌:"+ret);
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!