【coco】掩膜mask影像转coco格式txt(含python代码)
????????最近在做实例分割,遇到二值掩膜影像——coco格式txt的实例分割转换问题,困扰很久,不知道怎么转换,转出来的txt没法用代码成功读取。一系列问题,索性记录下自己的结局路程,方便大家python代码自取。
?
目录
📞📞1.coco格式示例
????????coco格式txt文件示例:
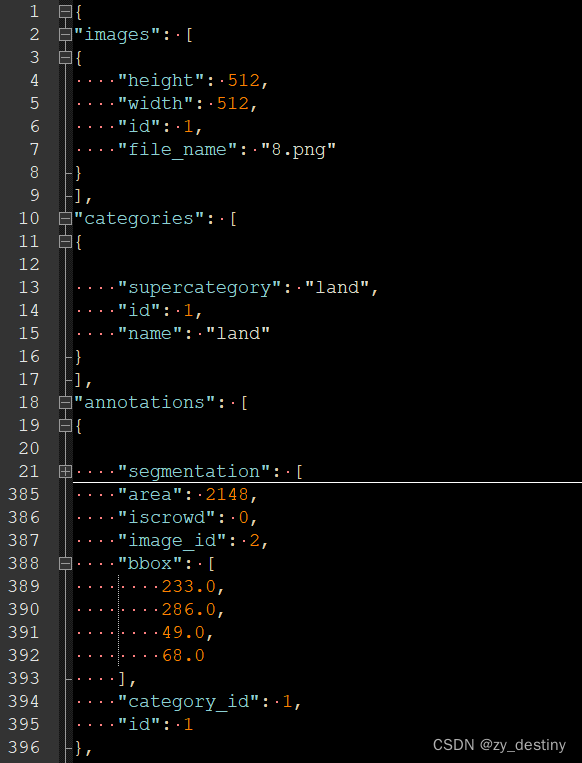
????????主要包含三个模块:
- images
- categories
- annotations
????????其中每个模块都由好多个分块组成,images和categories比较简单。
📗 images模块
????????images里主要记录的是每张image的长宽,id和文件名信息,注意此处的文件名必须是images文件名,labels也得是相同的文件名,不然索引不到。id从1开始,依次向下编号。
images[
{
"height": 512,
"width": 512,
"id": 1,
"file_name": "1.png"
}
...
...
...
{
"height": 512,
"width": 512,
"id": 100,
"file_name": "100.png"
}
]📘 categories模块
????????categories模块记录的是所有样本的类别信息,name为类别名称,id从1开始,依次向下编号,supercategory表示该类别的从属类别,理解起来比较简单,比如name为bus,supercategory就可以为car,name为cat,supercategory就可以为animal。如果没有多级类别,可以将name和supercategory写出相同的,像我下面写的。
"categories": [
{
"supercategory": "land",
"id": 1,
"name": "land"
}
{
"supercategory": "land",
"id": 2,
"name": "land2"
}
...
...
...
{
"supercategory": "land",
"id": n,
"name": "landn"
}
],📙annotation模块
?????????annotation模块主要记录的是label信息,也是最关键的内容,此处以实例分割为例进行讲解,因为coco格式可以做的任务太多,此处仅限实例分割或者语义分割。
annotation模块的一个完整内容包括:
- segmentation记录目标的边界坐标点位置信息,可以是很长但是要记得是双[[...]];
- area记录得是目标得面积信息,这个可以自动计算,后面会细讲;
- iscrowd代表一个目标是否被切分成多块,比如一个猫得身体和尾巴被一只狗头挡住,分开成2部分。0代表没有切分,1代表切分;
- image_id表示这个目标所对应得原始影像得id编号,与images模块里的id是一一对应的关系;
- bbox指这个目标的外界矩形框的位置信息;
- category_id表示这个目标的类别信息,与categories模块里的id是一一对应的关系;
- id代表目标的编号信息,可以与images个数不一致,因为一张图上很可能会有多个目标。
"annotations": [
{
"segmentation": [
[
276,
286,
275,
287,
274,
287,
273,
287,
]
],
"area": 2148,
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": 2,
"bbox": [
233.0,
286.0,
49.0,
68.0
],
"category_id": 1,
"id": 1
},
...
{
"segmentation": [
[
276,
286,
275,
287,
274,
287,
273,
287,
]
],
"area": 248,
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": 5,
"bbox": [
233.0,
286.0,
49.0,
68.0
],
"category_id": 2,
"id":100
},
📷📷2.环境准备
????????代码所需环境包有:json、numpy、pycocotools、OpenCV、os、sys。
????????包导入命令:
import json
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask
import cv2
import os
import sys📢📢3.maskToanno函数定义
输入:round_truth_binary_mask, ann_count, category_id
输出:annotations
????????python代码如下:
def maskToanno(ground_truth_binary_mask, ann_count, category_id):
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(ground_truth_binary_mask, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 根据二值图找轮廓
annotations = [] #一幅图片所有的annotatons
global segmentation_id
# print(ann_count)
# 对每个实例进行处理
for i in range(len(contours)):
# print(i)
# 生成二值的黑色图片
x = np.zeros((512, 512))
cv2.drawContours(x, contours, i, (1, 1, 1), -1) # 将单个mask表示为二值图的形式
ground_truth_binary_mask_id = np.array(x, dtype=object).astype(np.uint8)
fortran_ground_truth_binary_mask = np.asfortranarray(ground_truth_binary_mask_id)
# 求每个mask的面积和框
encoded_ground_truth = mask.encode(fortran_ground_truth_binary_mask)
ground_truth_area = mask.area(encoded_ground_truth)
ground_truth_bounding_box = mask.toBbox(encoded_ground_truth)
contour, _ = cv2.findContours(ground_truth_binary_mask_id, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# contour = measure.find_contours(ground_truth_binary_mask_id, 0.5)
# print(contour)
annotation = {
"segmentation": [],
"area": ground_truth_area.tolist(),
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": ann_count,
"bbox": ground_truth_bounding_box.tolist(),
"category_id": category_id,
"id": segmentation_id
}
#print(contour)
# 求segmentation部分
contour = np.flip(contour, axis=0)
segmentation = contour.ravel().tolist()
if len(segmentation)<=4:
continue
annotation["segmentation"].append(segmentation)
annotations.append(annotation)
segmentation_id = segmentation_id + 1
return annotations??4.images模块内容写入txt
输入:jsonpath
输出:jsonpath
????????将jsonpath路径下的txt文件打开,若image存在且对应文件名的label文件存在,就可以写image的images模块信息,python代码如下:
with io.open(jsonPath, 'w', encoding='utf8') as output:
# 那就全部写在一个文件夹好了
# 先写images的信息
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
output.write(unicode('"images": [\n'))
for image in rgb_image_files:
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(block_mask_path, image)):
output.write(unicode('{'))
annotation = {
"height": 512,
"width": 512,
"id": imageCount,
"file_name": image
}
str_ = json.dumps(annotation, indent=4)
str_ = str_[1:-1]
if len(str_) > 0:
output.write(unicode(str_))
imageCount = imageCount + 1
if (image == rgb_image_files[-1]):
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
else:
output.write(unicode('},\n'))📡📡5.categories模块内容写入txt
输入:jsonpath
输出:jsonpath
????????将jsonpath路径下的txt文件打开,将categories模块里的supercategory、id、name信息写入txt,此处的categories信息只是示例,可以根据自己的类别信息修改,python代码如下:
with io.open(jsonPath, 'w', encoding='utf8') as output:
output.write(unicode('"categories": [\n'))
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
categories = {
"supercategory": "land",
"id": 1,
"name": "land"
}
str_ = json.dumps(categories, indent=4)
str_ = str_[1:-1]
if len(str_) > 0:
output.write(unicode(str_))
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
output.write(unicode('],\n'))🛁🛁6.annotation模块内容写入txt
输入:jsonpath
输出:jsonpath
????????将jsonpath路径下的txt文件打开,若label存在且对应文件名的image文件存在,就可以把annotation模块里的信息写入txt,python代码如下:
with io.open(jsonPath, 'w', encoding='utf8') as output:
output.write(unicode('"annotations": [\n'))
for i in range(len(block_mask_image_files)):
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(path, block_mask_image_files[i])):
block_image = block_mask_image_files[i]
# 读取二值图像
block_im = cv2.imread(os.path.join(block_mask_path, block_image), 0)
_, block_im = cv2.threshold(block_im, 100, 1, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if not block_im is None:
block_im = np.array(block_im, dtype=object).astype(np.uint8)
block_anno = maskToanno(block_im, annCount, 1)
for b in block_anno:
str_block = json.dumps(b, indent=4)
str_block = str_block[1:-1]
if len(str_block) > 0:
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
output.write(unicode(str_block))
if (block_image == rgb_image_files[-1] and b == block_anno[-1]):
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
else:
output.write(unicode('},\n'))
annCount = annCount + 1
else:
print(block_image)🔋🔋7.完整python代码
????????二值掩膜mask影像转coco格式的实例分割txt完整python代码如下:
import json
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask
import cv2
import os
import sys
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
unicode = str
import io
# 实例的id,每个图像有多个物体每个物体的唯一id
global segmentation_id
segmentation_id = 1
# annotations部分的实现
def maskToanno(ground_truth_binary_mask, ann_count, category_id):
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(ground_truth_binary_mask, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 根据二值图找轮廓
annotations = [] #一幅图片所有的annotatons
global segmentation_id
# print(ann_count)
# 对每个实例进行处理
for i in range(len(contours)):
# print(i)
# 生成二值的黑色图片
x = np.zeros((512, 512))
cv2.drawContours(x, contours, i, (1, 1, 1), -1) # 将单个mask表示为二值图的形式
ground_truth_binary_mask_id = np.array(x, dtype=object).astype(np.uint8)
fortran_ground_truth_binary_mask = np.asfortranarray(ground_truth_binary_mask_id)
# 求每个mask的面积和框
encoded_ground_truth = mask.encode(fortran_ground_truth_binary_mask)
ground_truth_area = mask.area(encoded_ground_truth)
ground_truth_bounding_box = mask.toBbox(encoded_ground_truth)
contour, _ = cv2.findContours(ground_truth_binary_mask_id, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# contour = measure.find_contours(ground_truth_binary_mask_id, 0.5)
# print(contour)
annotation = {
"segmentation": [],
"area": ground_truth_area.tolist(),
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": ann_count,
"bbox": ground_truth_bounding_box.tolist(),
"category_id": category_id,
"id": segmentation_id
}
#print(contour)
# 求segmentation部分
contour = np.flip(contour, axis=0)
segmentation = contour.ravel().tolist()
if len(segmentation)<=4:
continue
annotation["segmentation"].append(segmentation)
annotations.append(annotation)
segmentation_id = segmentation_id + 1
return annotations
# mask图像路径
block_mask_path = '/labels_512'
block_mask_image_files = sorted(os.listdir(block_mask_path))
# coco json保存的位置
jsonPath = "/data/temp.json"
annCount = 1
imageCount = 1
# 原图像的路径, 原图像和mask图像的名称是一致的。
path = "/images_512"
rgb_image_files = sorted(os.listdir(path))
with io.open(jsonPath, 'w', encoding='utf8') as output:
# 那就全部写在一个文件夹好了
# 先写images的信息
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
output.write(unicode('"images": [\n'))
for image in rgb_image_files:
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(block_mask_path, image)):
output.write(unicode('{'))
annotation = {
"height": 512,
"width": 512,
"id": imageCount,
"file_name": image
}
str_ = json.dumps(annotation, indent=4)
str_ = str_[1:-1]
if len(str_) > 0:
output.write(unicode(str_))
imageCount = imageCount + 1
if (image == rgb_image_files[-1]):
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
else:
output.write(unicode('},\n'))
output.write(unicode('],\n'))
# 接下来写cate
output.write(unicode('"categories": [\n'))
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
categories = {
"supercategory": "land",
"id": 1,
"name": "land"
}
str_ = json.dumps(categories, indent=4)
str_ = str_[1:-1]
if len(str_) > 0:
output.write(unicode(str_))
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
output.write(unicode('],\n'))
# 写annotations
output.write(unicode('"annotations": [\n'))
for i in range(len(block_mask_image_files)):
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(path, block_mask_image_files[i])):
block_image = block_mask_image_files[i]
# 读取二值图像
block_im = cv2.imread(os.path.join(block_mask_path, block_image), 0)
_, block_im = cv2.threshold(block_im, 100, 1, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if not block_im is None:
block_im = np.array(block_im, dtype=object).astype(np.uint8)
block_anno = maskToanno(block_im, annCount, 1)
for b in block_anno:
str_block = json.dumps(b, indent=4)
str_block = str_block[1:-1]
if len(str_block) > 0:
output.write(unicode('{\n'))
output.write(unicode(str_block))
if (block_image == rgb_image_files[-1] and b == block_anno[-1]):
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
else:
output.write(unicode('},\n'))
annCount = annCount + 1
else:
print(block_image)
output.write(unicode(']\n'))
output.write(unicode('}\n'))
有问题,欢迎评论区交流~~~
整理不易,欢迎一键三连!!!
送你们一条美丽的--分割线--
🌷🌷🍀🍀🌾🌾🍓🍓🍂🍂🙋🙋🐸🐸🙋🙋💖💖🍌🍌🔔🔔🍉🍉🍭🍭🍋🍋🍇🍇🏆🏆📸📸????🍎🍎👍👍🌷🌷
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!