代码随想录算法训练营第十五天| 二叉树 513. 找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
513. 找树左下角的值
层序遍历
本题用层序遍历可以直接秒了,直接提取每一层中最左边的元素(i=0),然后保存到最后一层即可。
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int res;
if(!root)return res;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* node=que.front();
que.pop();
if(i==0)res=node->val;
if(node->left)que.push(node->left);
if(node->right)que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};迭代遍历
首先先要明确使用递归法,如何判断最后一行,就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。因此需要本题定义一个全局参数用于记录当前的行。
确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 前面做题的时候一直卡在函数需要int类型的返回值上,其实可以不需要。本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxDepth用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
确定终止条件:当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。然后如果是目前的最大深度,可以使用result保存。
确定单层递归的逻辑:在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯,理解回溯过程:首先进入leftNum函数的时候肯定回答道最左边最左下脚那一个数字,此时depth记录的是当时的深度,但是最左边最左下角那个不一定是底层,可以先返回上一层,看一看他的右子树是否更深,需将depth-1.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
int result;
void leftNum(TreeNode* node,int depth){
if(!node->left&&!node->right){
if(depth>maxDepth){
maxDepth=depth;
result=node->val;
}
return;
}
if(node->left){
depth++;
leftNum(node->left,depth);
depth--;
}
if(node->right){
depth++;
leftNum(node->right,depth);
depth--;
}
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
int depth{0};
leftNum(root,depth);
return result;
}
};112. 路径总和
确定递归函数的参数和返回类型:需要二叉树的根节点,还需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。本题需要找到是否有这么一条路径,因此函数类型为bool。
确定终止条件:如果到达叶子节点且count==0,此时可以返回true,否则返回false。当然也可以设置一个值然后与目标值去比对,但是此时会很麻烦,需要多穿一个参数,因此还是直接将目标值减去根结点到叶子节点的值是否为0比较好。
确定单层递归的逻辑:因为终止条件是判断叶子节点,所以递归的过程中就不要让空节点进入递归了。递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。(前面忽略了函数的返回是否为true)
出现错误:
1.忽略了root为空指针的情况
2.在主函数中,原先写成getsum(root,targetSum),此时没有减去初始值
3.由于设置的函数是bool类型的,在迭代的过程中。没有用到迭代,当结点为true的时候,就没有必要继续运行了。
class Solution {
public:
bool getsum(TreeNode* node, int count){
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
if(!count)return true;
else return false;
}
if(node->left){
count-=node->left->val;
if(getsum(node->left,count)) return true;
count+=node->left->val;
}
if(node->right){
count-=node->right->val;
if(getsum(node->right,count)) return true;
count+=node->right->val;
}
return false;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) return false;
return getsum(root,targetSum-root->val);
}
};106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
这题是真不会,直接看视频和题解的思路。
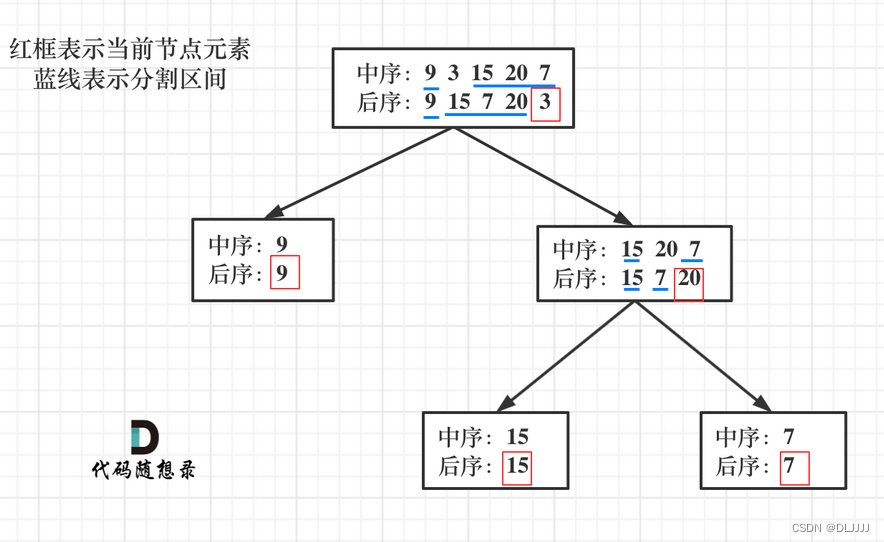
共分六步:
-
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
-
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
-
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
-
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
-
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
-
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
确定递归函数的参数和返回类型:题目需要得到结点,因此设置类型也应该是结点,然后参数为中序数组以及后续数组。
确定终止条件:当后序数组(中序数组)大小为0时,说明搜索完毕了。
确定单层递归的逻辑:参考前面的六步
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* travelsal(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){
if(postorder.size()==0)return NULL;
int postval=postorder[postorder.size()-1];
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(postval);
// 叶子节点
if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;
//找到中序数组需要切割的地方
int index=0;
for(;index<inorder.size();index++)
{
if(inorder[index]==postval)break;
}
vector<int> inleft(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+index);
vector<int> inright(inorder.begin()+index+1,inorder.end());
// postorder 舍弃末尾元素,因为这个元素就是中间节点,已经用过了
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);
vector<int> postleft(postorder.begin(),postorder.begin()+index);
//这里不需要+1,因为这是后序数组,左右是连着的
vector<int> postright(postorder.begin()+index,postorder.end());
root->left=travelsal(inleft,postleft);
root->right=travelsal(inright,postright);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
return travelsal(inorder, postorder);
}
};本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!