手写线程池
2023-12-23 18:01:52
手写线程池
线程池原理
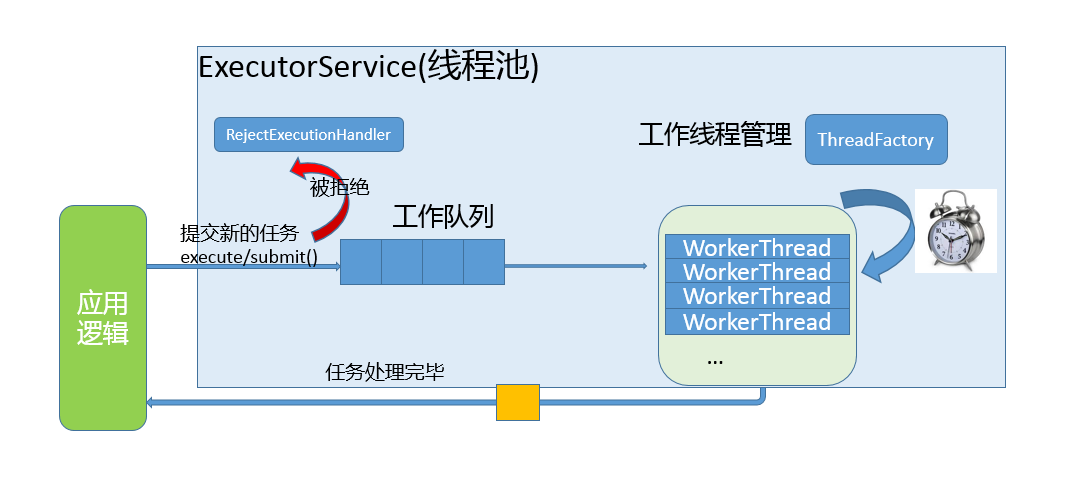
线程池的组成主要分为3个部分,这三部分配合工作就可以得到一个完整的线程池:
- 任务队列,存储需要处理的任务,由工作的线程来处理这些任务
通过线程池提供的API函数,将一个待处理的任务添加到任务队列,或者从任务队列中删除
已处理的任务会被从任务队列中删除
线程池的使用者,也就是调用线程池函数往任务队列中添加任务的线程就是生产者线程 - 工作的线程(任务队列任务的消费者) ,N个
线程池中维护了一定数量的工作线程, 他们的作用是是不停的读任务队列, 从里边取出任务并处理
工作的线程相当于是任务队列的消费者角色,
如果任务队列为空, 工作的线程将会被阻塞 (使用条件变量/信号量阻塞)
如果阻塞之后有了新的任务, 由生产者将阻塞解除, 工作线程开始工作 - 管理者线程(不处理任务队列中的任务),1个
它的任务是周期性的对任务队列中的任务数量以及处于忙状态的工作线程个数进行检测
当任务过多的时候, 可以适当的创建一些新的工作线程
当任务过少的时候, 可以适当的销毁一些工作的线程
1. c语言版
main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "threadpool.h"
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void taskFunc(void* arg){
int num = *(int*)arg;
printf("thread is working, number = %d, tid = %ld\n",num,pthread_self());
usleep(1000);
}
int main(){
// 创建线程池
ThreadPool* pool = threadPoolCreate(3,10,100);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
// threadPoolAdd(pool,taskFunc,&i);
int* num = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*num = i + 100;
threadPoolAdd(pool, taskFunc, num);
}
sleep(30);
threadPoolDestory(pool);
return 0;
}
threadpool.c
#include "threadpool.h"
const int NUMBER = 2;
// 任务结构体
typedef struct Task{
void (*function)(void* arg); //函数指针
void* arg;
}Task;
//线程池结构体
struct ThreadPool{
//任务队列
Task* taskQ;
int queueCapacity; // 容量
int queueSize; //当前任务个数
int queueFront; //队头 ->取数据
int queueRear; //队尾 <-存数据
//管理者线程
pthread_t managerID; //管理者线程ID
//工作线程
pthread_t *threadIDs; //工作的线程ID
int minNum; //最小线程数量
int maxNum; //最大线程数量
int busyNum; //忙的线程个数
int liveNum; //存活的线程个数
int exitNum; //要销毁的线程个数
//互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutexPool; //锁整个的线程池
pthread_mutex_t mutexBusy; //锁busyNum变量
//条件变量
pthread_cond_t notFull; //任务队列是不是满了
pthread_cond_t notEmpty; //任务队列是不是空了
int shutdown; //是不是要销毁线程池,销毁为1,不销毁为0
};
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int min, int max, int queueSize){
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadPool));
do{
if(pool == NULL){
printf("malloc threadpool fail...\n");
break;
}
pool->threadIDs = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * max);
if(pool->threadIDs == NULL){
printf("malloc threadIDS fail...\n");
break;
}
memset(pool->threadIDs,0,sizeof(pthread_t) * max);
//bzero(&pool->threadIDs,sizeof(pthread_t) * max); //清0
pool->minNum = min;
pool->maxNum = max;
pool->busyNum = 0;
pool->liveNum = min; //与最小个数相等
pool->exitNum = 0;
if(pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexBusy,NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutexPool,NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&pool->notEmpty,NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(&pool->notFull,NULL) != 0){
printf("mutex or condition init fail...\n");
break;
}
//任务队列
pool->taskQ = (Task*)malloc(sizeof(Task) * queueSize);
pool->queueCapacity = queueSize;
pool->queueSize = 0;
pool->queueFront = 0;
pool->queueRear = 0;
pool->shutdown = 0;
//创建线程
pthread_create(&pool->managerID,NULL,manager,pool);
for(int i = 0; i < min; i++){
pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i],NULL,worker,pool);
}
return pool;
}while(0);
//释放资源
if(pool && pool->threadIDs){
free(pool->threadIDs);
}
if(pool && pool->taskQ){
free(pool->taskQ);
}
if(pool){
free(pool);
}
return NULL;
}
void threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void(*func)(void*),void* arg){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
while (pool->queueSize == pool->queueCapacity && !pool->shutdown)
{
//阻塞生产者线程(阻塞生产者)
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notFull,&pool->mutexPool);
}
if(pool->shutdown){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return ;
}
// 添加任务
pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].function = func;
pool->taskQ[pool->queueRear].arg = arg;
pool->queueRear = (pool->queueRear + 1) % pool->queueCapacity;
pool->queueSize++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty); //唤醒消费者
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
int threadPoolBusyNum(ThreadPool* pool){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
int busyNum = pool->busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
return busyNum;
}
int threadPoolAliveNum(ThreadPool* pool){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int liveNum = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
return liveNum;
}
int threadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool){
if(pool == NULL){
return -1;
}
// 关闭线程池
pool->shutdown = 1;
// 阻塞回收管理者线程
pthread_join(pool->managerID,NULL);
// 唤醒阻塞的消费者线程
for(int i = 0; i < pool->liveNum; i++){
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
}
if(pool->taskQ){
free(pool->taskQ);
}
if(pool->threadIDs){
free(pool->threadIDs);
}
// 销毁锁和条件变量
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexBusy);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutexPool);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->notEmpty);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->notFull);
free(pool);
pool = NULL;
return 0;
}
// 消费者线程
void* worker(void* arg){
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 当前任务队列是否为空
while (pool->queueSize == 0 && !pool->shutdown)
{
// 阻塞工作线程(阻塞消费者)
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notEmpty,&pool->mutexPool);
// 判断是不是要销毁线程
if(pool->exitNum > 0){
pool->exitNum--;
if(pool->liveNum > pool->minNum){
pool->liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); // 销毁前,先解锁,防止死锁
threadExit(pool);
}
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
// 判断线程池是否被关闭
if(pool->shutdown){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); //防止死锁
threadExit(pool);
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// 从队列中取出一个任务
Task task;
task.function = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].function;
task.arg = pool->taskQ[pool->queueFront].arg;
// 移动头节点
pool->queueFront = (pool->queueFront + 1) % pool->queueCapacity;
pool->queueSize--;
//解锁
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notFull); //唤醒生产者
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
//开始工作
printf("thread %ld start working...\n",pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pool->busyNum++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
//调用任务里的函数
task.function(task.arg); //参数建议传堆内存
//(*task.function)(task.arg); //另一种写法
free(task.arg);
task.arg = NULL;
printf("thread %ld end working...\n",pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pool->busyNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
}
return NULL;
}
void* manager(void* arg){
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(!pool->shutdown){
// 每3s检测一次
sleep(3);
// 取出线程池中日任务的数量和当前线程的数量
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int queueSize = pool->queueSize;
int liveNum = pool->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 取出忙的线程的数量
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
int busyNum = pool->busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
//添加线程
//自定义规则:任务的个数>存活的线程个数 && 存活的线程个数 < 线程的最大个数
if(queueSize > liveNum && liveNum < pool->maxNum){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pool->maxNum && count < NUMBER && pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum; ++i){
if(pool->threadIDs[i] == 0){
pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i],NULL,worker,pool);
count++;
pool->liveNum++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
//销毁线程
//自定义规则:忙的线程*2 < 存活的线程数 && 存活的线程 > 最小线程数
if(busyNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->minNum){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
pool->exitNum = NUMBER;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 让工作的线程自杀
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER; ++i){
// 唤醒工作线程
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool){
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for(int i = 0; i < pool->maxNum; ++i){
if(pool->threadIDs[i] == tid){
pool->threadIDs[i] = 0;
printf("threadExit() called, %ld exiting...\n",tid);
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
threadpool.h
#ifndef _THREADPOOL_H
#define _THREADPOOL_H
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct ThreadPool ThreadPool;
// 创建线程池并初始化
ThreadPool* threadPoolCreate(int min,int max,int queueSize);
// 销毁线程池
int threadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool);
//int threadPoolDestroy(ThreadPool* pool);
// 给线程池添加任务
void threadPoolAdd(ThreadPool* pool, void(*func)(void*),void* arg);
// 获取线程池中工作的线程的个数
int threadPoolBusyNum(ThreadPool* pool);
// 获取线程池中活着的线程的个数
int threadPoolAliveNum(ThreadPool* pool);
//
void* worker(void* arg);
void* manager(void* arg);
void threadExit(ThreadPool* pool);
//
#endif
2. c++版
main.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<unistd.h>
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include "ThreadPool.cpp"
using namespace std;
void taskFunc(void* arg){
int num = *(int*)arg;
printf("thread is working, number = %d, tid = %ld\n",num,pthread_self());
usleep(1000);
}
int main(){
// 创建线程池
ThreadPool<int> pool(3,10);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
// threadPoolAdd(pool,taskFunc,&i);
int* num = new int(i + 100);
pool.threadPoolAddTask(Task<int>(taskFunc,num));
}
sleep(30);
return 0;
}
TaskQueue.cpp
#include "TaskQueue.h"
template <typename T>
TaskQueue<T>::TaskQueue(){
pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex,NULL);
}
template <typename T>
TaskQueue<T>::~TaskQueue(){
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex);
}
template <typename T>
void TaskQueue<T>::addTask(Task<T>& task){
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
m_taskQ.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
}
template <typename T>
void TaskQueue<T>::addTask(callback f, void* arg){
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
m_taskQ.push(Task<T>(f,arg));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
}
template <typename T>
Task<T> TaskQueue<T>::getTask(){
Task<T> task;
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
if(m_taskQ.empty()){
return task;
}
task = m_taskQ.front();
m_taskQ.pop();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
return task;
}
TaskQueue.h
#pragma once
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
using namespace std;
using callback = void (*)(void*);
// 任务结构体
template <typename T>
struct Task{
Task<T>(){
function = nullptr;
arg = nullptr;
}
Task<T>(callback f, void* arg){
function = f;
this->arg = (T*)arg;
}
callback function;
T* arg;
};
template <typename T>
class TaskQueue{
public:
TaskQueue();
~TaskQueue();
// 取出一个任务
Task<T> getTask();
// 添加一个任务
void addTask(Task<T>& task);
void addTask(callback f, void* arg); //重载
inline int taskNumber(){
return m_taskQ.size();
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t m_mutex;
queue<Task<T>> m_taskQ;
};
ThreadPool.cpp
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
ThreadPool<T>::ThreadPool(int min, int max)
{
do{
// 实例化任务对列
taskQ = new TaskQueue<T>;
if(taskQ == nullptr){
cout<<"malloc taskQ fail..."<<endl;
break;
}
minNum = min;
maxNum = max;
busyNum = 0;
liveNum = min; //与最小个数相等
exitNum = 0;
threadIDs = new pthread_t[max];
if(threadIDs == nullptr){
cout<<"malloc threadIDS fail..."<<endl;
break;
}
if(pthread_mutex_init(&mutexPool,NULL) != 0 || pthread_cond_init(¬Empty,NULL) != 0){
printf("mutex or condition init fail...\n");
break;
}
shutdown = false;
//创建线程
pthread_create(&managerID,NULL,manager,this);
for(int i = 0; i < min; i++){
pthread_create(&threadIDs[i],NULL,worker,this);
}
}while(0);
}
template <typename T>
ThreadPool<T>::~ThreadPool()
{
// 关闭线程池
shutdown = 1;
// 阻塞回收管理者线程(销毁管理者线程)
pthread_join(managerID,NULL);
// 唤醒阻塞的消费者线程
for(int i = 0; i < liveNum; i++){
pthread_cond_signal(¬Empty);
}
if(taskQ){
delete taskQ;
}
if(threadIDs){
delete[] threadIDs;
}
// 销毁锁和条件变量
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutexPool);
pthread_cond_destroy(¬Empty);
}
template <typename T>
void ThreadPool<T>::threadPoolAddTask(Task<T> task){
if(shutdown){
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutexPool);
return ;
}
// 添加任务
taskQ->addTask(task);
// 唤醒工作的线程
pthread_cond_signal(¬Empty);
}
template <typename T>
int ThreadPool<T>::getBusyNum(){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutexPool);
int busyNum = this->busyNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutexPool);
return busyNum;
}
template <typename T>
int ThreadPool<T>::getAliveNum(){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutexPool);
int liveNum = this->liveNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutexPool);
return liveNum;
}
template <typename T>
// 消费者线程
void* ThreadPool<T>::worker(void* arg){
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 当前任务队列是否为空
while (pool->taskQ->taskNumber() == 0 && !pool->shutdown)
{
// 阻塞工作线程(阻塞消费者)
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notEmpty,&pool->mutexPool);
// 判断是不是要销毁线程
if(pool->exitNum > 0){
pool->exitNum--;
if(pool->liveNum > pool->minNum){
pool->liveNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); // 销毁前,先解锁,防止死锁
pool->threadExit();
}
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
// 判断线程池是否被关闭
if(pool->shutdown){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool); //防止死锁
pool->threadExit();
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// 从队列中取出一个任务
Task<T> task = pool->taskQ->getTask();
//解锁
// pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notFull); //唤醒生产者
//开始工作
printf("thread %ld start working...\n",pthread_self());
// pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pool->busyNum++;
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
//调用任务里的函数
task.function(task.arg); //参数建议传堆内存
//(*task.function)(task.arg); //另一种写法
delete task.arg;
task.arg = nullptr;
printf("thread %ld end working...\n",pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
pool->busyNum--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
return NULL;
}
template <typename T>
void* ThreadPool<T>::manager(void* arg){
ThreadPool* pool = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(!pool->shutdown){
// 每3s检测一次
sleep(3);
// 取出线程池中日任务的数量和当前线程的数量
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int queueSize = pool->taskQ->taskNumber();
int liveNum = pool->liveNum;
// 取出忙的线程的数量
// pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexBusy);
int busyNum = pool->busyNum;
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexBusy);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
//添加线程
//自定义规则:任务的个数>存活的线程个数 && 存活的线程个数 < 线程的最大个数
if(queueSize > liveNum && liveNum < pool->maxNum){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pool->maxNum && count < NUMBER && pool->liveNum < pool->maxNum; ++i){
if(pool->threadIDs[i] == 0){
pthread_create(&pool->threadIDs[i],NULL,worker,pool);
count++;
pool->liveNum++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
}
//销毁线程
//自定义规则:忙的线程*2 < 存活的线程数 && 存活的线程 > 最小线程数
if(busyNum * 2 < liveNum && liveNum > pool->minNum){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutexPool);
pool->exitNum = NUMBER;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutexPool);
// 让工作的线程自杀
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER; ++i){
// 唤醒工作线程
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notEmpty);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
template <typename T>
// 线程退出
void ThreadPool<T>::threadExit()
{
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for (int i = 0; i < maxNum; ++i)
{
if (threadIDs[i] == tid)
{
cout << "threadExit() function: thread "
<< to_string(pthread_self()) << " exiting..." << endl;
threadIDs[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
ThreadPool.h
#pragma once
#include "TaskQueue.h"
#include "TaskQueue.cpp"
template <typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
public:
// 创建线程池并初始化
ThreadPool(int min, int max);
// 销毁线程池
~ThreadPool();
// 给线程池添加任务
void threadPoolAddTask(Task<T> task);
// 获取线程池中工作的线程的个数
int getBusyNum();
// 获取线程池中活着的线程的个数
int getAliveNum();
//
private:
static void* worker(void* arg);
static void* manager(void* arg);
void threadExit();
//
private:
//任务队列
TaskQueue<T> *taskQ;
//管理者线程
pthread_t managerID; //管理者线程ID
//工作线程
pthread_t *threadIDs; //工作的线程ID
int minNum; //最小线程数量
int maxNum; //最大线程数量
int busyNum; //忙的线程个数
int liveNum; //存活的线程个数
int exitNum; //要销毁的线程个数
//互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutexPool; //锁整个的线程池
//条件变量
pthread_cond_t notEmpty; //任务队列是不是空了
bool shutdown = false; //是不是要销毁线程池,销毁为1,不销毁为0
static const int NUMBER = 2;
};
参考:手写线程池 - C语言版 | 爱编程的大丙 (subingwen.cn)和手写线程池 - C改C++版 | 爱编程的大丙 (subingwen.cn)
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43784519/article/details/135169623
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!