VINS-MONO拓展1----手写后端求解器,LM3种阻尼因子策略,DogLeg,构建Hessian矩阵
文章目录
0. 目标及思路
完成VIO课程大作业T1

VINS-MONO使用Ceres的求解器,在factor中实现了Jacobian block的构建,为了探究非线性优化求解过程,我们不使用Ceres,手动完成求解,整体思路如下:
- 非线性优化求解器
- Hessian矩阵构建
- 求解正规方程
- 更新状态
- 迭代求解
- EVO评估结果
以下章节将分别对各个部分进行详细介绍,并在最后给出完整代码。
1. 非线性优化求解器
主要包括LM和DogLeg(DL),本文以LM为主进行讲解,在LM实现的基础上,DL方法按照论文实现即可较容易完成求解。
关于LM的介绍可以参考之前课程Ch3的博客,论文可以参考[1],此处不再赘述。
这里强调一下在实现过程中遇到的最难解的问题:关于
b
b
b的符号问题。
在一次迭代求解中,我们的目标是求解正规方程
H
Δ
x
=
?
b
\begin{align} H\Delta x=-b \end{align}
HΔx=?b??
然后更新
x
=
x
+
Δ
x
\begin{align} x=x+\Delta x \end{align}
x=x+Δx??
关于(1)中右边的
?
b
-b
?b,不同地方对于符号的定义不统一,导致理解有偏差,
b
=
J
T
e
b=J^Te
b=JTe是在marginalization_factor.cpp的MarginalizationInfo::marginalize()最后从Hessian中反解出来的,但是在正规方程中右边是
?
b
-b
?b,所以我们后面再求解(1)之前,构造b之后需要取一下负,否则解出来的
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx要么非常大,要么非常小(1e-30量级的,更新不动
x
x
x),因为之前在这里卡了很久,所以在这里先强调一下,在第2部分中会结合代码讲解具体在哪里操作。
linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();
linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose() * b;
记录一下之前阅读Ceres LM源码debug的记录。
在ceres源码中可以找到答案:在LevenbergMarquardtStrategy::ComputeStep()函数中有注释是这样的:
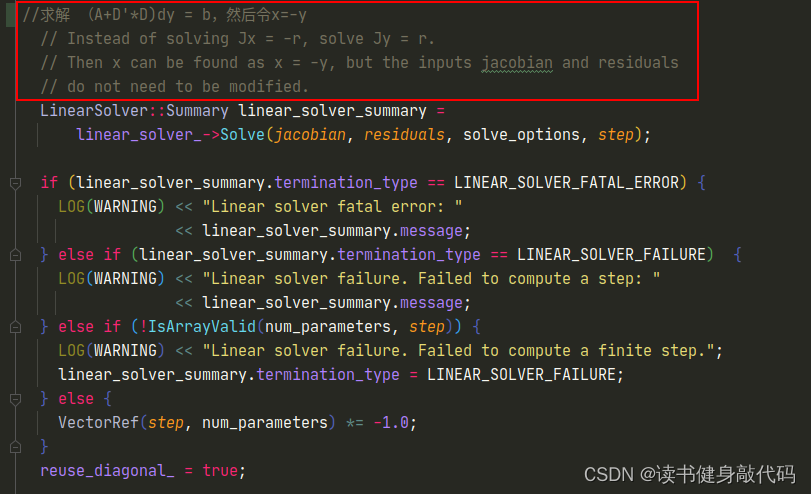
ceres里面只要求传入Jacobian和residual,内部求解的方程
(
A
+
D
′
D
)
d
y
=
b
(A+D'D)dy=b
(A+D′D)dy=b,而不是LM正规方程的形式
(
A
+
λ
I
)
d
x
=
b
(A+\lambda I)dx=b
(A+λI)dx=b(ceres中的
D
D
D是根据Jacobian构建的一个与
λ
\lambda
λ有关的系数阵,叠加到
A
A
A上,这里不做详细介绍,有兴趣的可以看看ceres的源码),而我们自己构建的
b
b
b是
J
T
e
J^Te
JTe
所以之前求解的一直是
?
Δ
x
-\Delta x
?Δx,按照
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx更新给
x
x
x,属于是错误的方向,那么
χ
2
\chi^2
χ2不下降也是正常的,进一步地,
ρ
\rho
ρ也就很那下降,因为
x
x
x更新方向不对。至此,找到了最根本的问题,解决办法是在makeHessian()最后将b取负,那么就是手动求解的正确的正规方程了。
Hessian_ = A;
b_ = -b;
接下来就是LM的一系列调参:
- LM初始化时的 τ \tau τ,设为 1 e ? 15 1e-15 1e?15
- 优化退出条件
delta_x_.squaredNorm() <= 1e-10 || false_cnt > 6 - 优化PCG(预处理共轭梯度法 preconditioned conjugate gradient method)求解速度
- 迭代次数设为
Hessian_.rows()+1 - 迭代停止阈值设为
double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm() - 优化PCG:对角线预处理和不完备的Cholesky预处理(还未做,参考博客)
- 迭代次数设为
2. 基于VINS-MONO的Marginalization框架构建Hessian矩阵
2.1 estimator.cpp移植
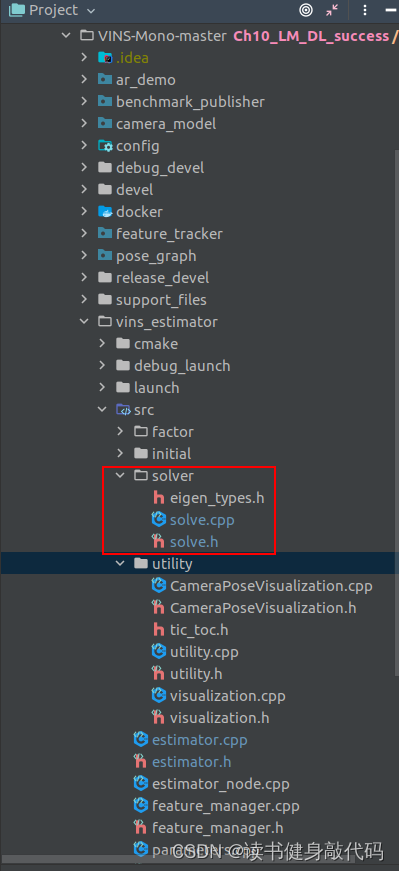
手动构建Hessian的步骤其实在marg时已经有过,所以我们直接借鉴marg部分的代码,将其移植成整个系统的Hessian构建,并加上我们的LM和DL,整个代码结构如下,添加了solver文件夹
marg部分第5篇博客讲过,marg掉的变量实际上就是WINDOW[0]帧相关的待优化变量,包括
P
0
,
V
0
P_0,V_0
P0?,V0?和strat from [0]的landmark的观测,marg的大致流程如下:
- 以factor方式将各个参数块添加到
problem中,包括MarginalizationFactor,IMUFactor,ProjectionTdFactor(ProjectionFactor), - 构建
residual_block_info来待优化参数,同时marg的变量。指定方式是通过drop_set - 调用
addResidualBlockInfo函数将每一个ResidualBlockInfo添加到problem中 - 调用
preMarginalize()函数计算各个factor的Jacobian和residual - 调用
marginalize()函数对待优化变量排序,marg放前面,remain放后面,多线程构建Hessian矩阵,运用Schur compliment执行marg,得到marg后留下的先验,从先验A中反解出该线性化点处的linearized_jacobians和linearized_residuals。 - addr_shift地址映射。
我们需要构建整个系统的Hessian,与VINS-MONO的marg不同的是,我们可以选择marg,也可以选择不marg,重点是需要明白,我们这里求取Hessian的目的与VINS-MONO的marg不同:
- VINS-MONO的marg目的是为了求取marg之后留下的先验,并不需要求解式(1),所以Schur compliment,反解出
linearized_jacobians和linearized_residuals之后,marg的任务就完成了,至于这个线性化点值为多少并不关心(当然也可以(1)求解,(2)更新求出这个线性化点)。 - 而我们现在的目的是为了求解出本次迭代优化之后的线性化点,也就是我们的待优化变量,所以式(1)(2)是我们需要在marg的基础上进一步往下走的。
理清了二者的区别,我们的目标就具体很多了:基于VINS-MONO的margHessian构建框架,我们可以顺利地构建出整个系统的Hessian矩阵,和b,也就完成了式(1)的构建,然后求解式(1)得 Δ x \Delta x Δx,带入式(2)即可完成本次迭代。
接下来的核心任务:
- 完成VINS-MONO的marg框架移植,构建出Hessian矩阵
- 求解式(1)
下面详细讲解marg的移植:(以下内容可根据Appendix中的相关代码来理解)
- 新建
solve.cpp,solve.h,照搬marginalization_factor.cpp/h的所有内容,并封上自己的namespace:solve, - 为了便于对比调试,在
estimator.cpp中加上宏隔离CERES_SOLVE,用于区分使用Ceres求解和我们自己的手动求解。 - 需要注意,我们虽然是照搬marg部分,但是我们修改的是后端求解不分,所以是在求解部分而不是marg部分添加我们的代码,如,ceres部分添加prior residualbolck是
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);
problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);
我们则是
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL, last_marginalization_parameter_blocks, vector<int>{});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
其他factor如法炮制。
需要指出,我们在求解式(1)时有好几种实现方法,其中一种是使用Schur消元,利用Hessian的稀疏性加快式(1)的求解速度,这就意味着我们需要指定需要作为 x m m x_{mm} xmm?的部分,通过drop_set来指定。由于landmark的Jacobian较为稀疏,所以我们这里指定了WINDOW内的landmark为 x m m x_{mm} xmm?,如下所示:
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function, vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]}, vector<int>{3});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
- 为了表意更强,我们将
preMarginalize()和marginalize()改名为preMakeHessian()和makeHessian(),功能大体不变,分别是求J,e和构造H,b。
estimator.cpp总体讲解完毕,下面讲解Hessian的构建。
2.2 solve.cpp/preMakeHessian()
solve::ResidualBlockInfo组织了各个factor的信息,其中最重要的是Evaluate()函数,在Solver::preMakeHessian()会调用,主要通过多态求解各个factor的J,e,每次更新完x之后就需要调用preMakeHessian(),并重新makeHessian()。- 除此之外,由于LM和DLza求解过程中,如果
ρ
<
0
\rho<0
ρ<0,会涉及到参数的回滚,但是频繁地加减会造成精度下降,所以对之前的参数备份进行备份,在
preMakeHessian()中还开了新的数据parameter_block_data_backup(实际上parameter_block_data也是够用的,只是backup表意更强)。
2.3 solve.cpp/makeHessian()
- 整体部分和marg中一样,只是我们这里仅仅只构建Hessian,至于原来marg后面的Schur compliment,我们放到求解中去做。这里需要注意,我们最终构建出来了
Hessian_和b_,这里的b_即 J T e J^Te JTe,跟(1)中差了个负号,所以最后需要取个负,在前面已经强调过了:
Hessian_ = A;
b_ = -b;
LM到这里就可以结束了,但是DOGLEG由于在迭代时需要Jacobian和residual,所以我们需要在这里反解出J,e(反解出J,e在我的机器上大约需要24ms左右,耗时较长,对于DL方法的迭代影响较大。这里应该有办法构建出J和e,但是在VINS-MONO的marg的框架下,我目前没想到太好的办法)
//DOGLEG需反解出J和e
if(method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {
TicToc t_solve_J;
TicToc t_SelfAdjoint;
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes2(A);//这一句24.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_SelfAdjoint cost: %f ms", t_SelfAdjoint.toc());
Eigen::VectorXd S = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_sqrt = S.cwiseSqrt();//开根号
linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv_sqrt = S_inv.cwiseSqrt();
linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().real().transpose() * b;
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_solve_J cost: %f ms", t_solve_J.toc());//25ms
}
3. solve.cpp/solveLinearSystem()求解正规方程
构建完Hessian和b之后,就需要对式(1)进行求解,此部分主要函数:solveLinearSystem()。
3种求解思路:
- 直接
Hessian.inverse() - 使用PCG(预处理共轭梯度法 preconditioned conjugate gradient method)求解式(1)
- Schur消元+PCG求解(采用)
第1种就不讲了,直接调函数即可。
第2种,使用PCG()迭代求解,这里给出PCG的实现,PCG拓展可以看这里
Eigen::MatrixXd Solver::pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter = -1) {
assert(A.rows() == A.cols() && "PCG solver ERROR: A is not a square matrix");
int rows = b.rows();
int n = maxIter < 0 ? rows : maxIter;
VecX x(VecX::Zero(rows));
MatXX M_inv = A.diagonal().asDiagonal().inverse();//取对角线阵的逆矩阵
VecX r0(b); // initial r = b - A*0 = b
VecX z0 = M_inv * r0;
VecX p(z0);
VecX w = A * p;
double r0z0 = r0.dot(z0);
double alpha = r0z0 / p.dot(w);
VecX r1 = r0 - alpha * w;
int i = 0;
double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm(); //比例调大可以提高阈值,放宽停止条件
while (r1.norm() > threshold && i < n) {
i++;
VecX z1 = M_inv * r1;
double r1z1 = r1.dot(z1);
double belta = r1z1 / r0z0;
z0 = z1;
r0z0 = r1z1;
r0 = r1;
p = belta * p + z1;
w = A * p;
alpha = r1z1 / p.dot(w);
x += alpha * p;
r1 -= alpha * w;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nPCG iter times: %d, n: %d, r1.norm(): %f, threshold: %f", i, n, r1.norm(), threshold);
return x;
}
第3种,结合之前ResidualBlockInfo时指定的drop_set,在求解时使用Schur消元求出舒尔补,然后使用PCG求出delta_x_rr,最后求出delta_x_mm,组合即得整体delta_x_,完成式(1)的求解(经试验,方法3的速度最快)。
注意,这里采用Schur compliment的方法要和VINS-MONO的marginalize()中的Schur compliment目的区分开,VINS-MONO那里是为了求出prior information matrix,SelfAdjointEigenSolver部分是为了反解出J,e,而这里是为了在Schur compliment实现消元的基础上进一步求解出整个delta_x_,整体求解代码如下:
/*Solve Hx = b, we can use PCG iterative method or use sparse Cholesky*/
//TODO:使用PCG迭代而非SVD分解求解
void Solver::solveLinearSystem() {
//method1:直接求逆求解
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.inverse() * b_;
// delta_x_ = H.ldlt().solve(b_);
//method2:Schur消元求解,marg掉drop_set中的parameter
#ifdef USE_SCHUR
//step1:Schur消元求
//求解Hx=b,之前marg时不用求出△x,只需要H,所以不用对方程组求解,但现在优化时需要求解出整个△x
TicToc t_Schur_PCG;
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_solver = 0.5 * (Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m) + Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m).transpose());
Eigen::VectorXd bmm_solver = b_.segment(0, m);
Eigen::MatrixXd Amr_solver = Hessian_.block(0, m, m, n);
Eigen::MatrixXd Arm_solver = Hessian_.block(m, 0, n, m);
Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_solver = Hessian_.block(m, m, n, n);
Eigen::VectorXd brr_solver = b_.segment(m, n);
//求Amm_solver^(-1)
TicToc t_Amm_inv;
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_inv_solver = Amm_solver.inverse();//SelfAdjointEigenSolver和直接求逆速度差不多
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_Amm_inv cost: %f ms", t_Amm_inv.toc());
Eigen::MatrixXd tmpA_solver = Arm_solver * Amm_inv_solver;
//step1: Schur补
Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur = Arr_solver - tmpA_solver * Amr_solver;
Eigen::VectorXd brr_schur = brr_solver - tmpA_solver * bmm_solver;
ROS_DEBUG("here1");
// step2: solve Arr_schur * delta_x_rr = brr_schur
// method1:直接求逆
// Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur_inv = Arr_schur.inverse();
// Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = Arr_schur_inv * brr_schur;
// method2:使用PCG求解
TicToc t_PCG_xrr;
Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = pcgSolver(Arr_schur, brr_schur, Arr_schur.rows()+1); //0.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\n t_PCG_xrr cost %f ms", t_PCG_xrr.toc());
Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_mm = Amm_inv_solver * (bmm_solver - Amr_solver * delta_x_rr);
delta_x_.tail(n) = delta_x_rr;
delta_x_.head(m) = delta_x_mm;
memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组
ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms", t_Schur_PCG.toc());
#else
TicToc t_solve_equation;
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.ldlt().solve(b_);
int pcg_iter_num = Hessian_.rows()+1; // PCG迭代次数,原来给的是rows()*2
delta_x_ = pcgSolver(Hessian_, b_, pcg_iter_num); //0.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms, pcg_iter_num: %d", t_solve_equation.toc(), pcg_iter_num);//15ms
memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组,供状态更新使用
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere3 solve complete, delta_x_.size()=" << delta_x_.size() << ", delta_x_.norm()= "<< delta_x_.norm()
<< ", delta_x_.squaredNorm()=" << delta_x_.squaredNorm() );
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_:" << delta_x_.transpose());
#endif
}
4. 更新状态
完成式(1)的求解之后,需要带入式(2)更新状态,这里难点有2:
- 按照VINS-MONO marg的数据管理方法来更新参数,是pose部分由于有四元数,需要特殊处理。
- LM和DL涉及到状态的回滚和备份。
相关函数:
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight);//weight是LM strategy2时的权重,默认传-1.0,不加权
bool Solver::backupStates();//备份状态,便于后面回滚
bool Solver::rollbackStates();//回滚状态变量
bool Solver::updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta);
主要是一些地址的操作,仔细一些就好,看代码很好理解,这里讲两点:
- 在
rollbackStates()中将状态变量备份到parameter_block_data_backup中,便于后面回滚。 - 注意
memcpy()第3个参数len最好结合数据类型(这里是double)给定,sizeof()地址或者直接给int数值都是不对的。
具体代码:
bool Solver::updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);
//数组转四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);//Jacobian和residual都是按照6维来处理的,但是更新rotation时需要按照四元数来更新
p = _p + dp;
q = (_q * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化
return true;
}
//只更新状态量p,q,v,ba,bg,λ,注意prior不是状态量,虽然在待优化变量中,但是其residual是跟状态量有关,Jacobian在一轮优化中不变,
//这里更新状态的目的是因为计算chi时会用到residual,而residual和状态量有关,而先验的residual更新:f' = f + J*δxp,其中δxp=x-x0,也跟状态量x有关,
//但是因为在先验factor在Evaluate时会计算residual,所以不用手动更新,只需要更新最核心的x即可。其他的factor相同。
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight) {
int array_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;
double used_delta_x[array_size];
if(weight != -1.0)
std::transform(delta_x_array_, delta_x_array_ + array_size, used_delta_x, [weight](double x) { return x * weight; });//对delta_x加权
else
memcpy(used_delta_x, delta_x_array_, sizeof(double) * array_size);
//使用idx来找对应的param
double cur_x_array[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int idx = it.second;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);*/
//保存一份待优化变量,和delta_x进行数量级对比
memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)SIZE_POSE);
if(tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {
updatePose(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), &delta_x_array_[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr));//TODO:这个backup应该可以用parameter_block_data替代
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose after update: " << tmp_pose.transpose());*/
} else {
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{parameter_block_data_backup[addr], tmp_param_block_size};
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x{&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta{reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};
/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters before update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose() << "\ndelta_x: " << delta_x.transpose());*/
x_plus_delta = x + delta_x;
/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters after update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose());*/
}
}
// 初始化Eigen向量
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, m+n);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x: " << cur_x.transpose());
preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residual
return true;
}
//备份状态量
bool Solver::backupStates() {
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
memcpy(parameter_block_data_backup[addr], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
return true;
}
//回滚状态量
bool Solver::rollbackStates() {
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
memcpy(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), parameter_block_data_backup[addr], sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residual
return true;
}
5. 迭代求解
此部分就不赘述,由于前面使用updateStates()已经对状态进行了更新,所以真正的状态更新就更新之后是不回滚,且备份当前状态,简言之,在updateStates(weight)之后调用backupStates()即实现真正的状态更新,循环更新,直至达到迭代停止条件(
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx过小或者cost下降了很多或者其他)。
6. EVO评估结果
完成所有iteration轮的迭代之后就完成了本次后端求解部分,按照optimization()的整理流程,接下来就是marginalization,addr_shift,这些我们就不讲了。
在estimator线程求解完成,参数更新之后,会发送topic给pose_graph线程,在所有数据跑完之后,pose_graph线程会存下待估计参数的值,存为.csv文件,我们使用evo工具、此文件、ground truth文件来对我们的系统进行评估,在评估之前我们需要调整VINS-MONO的输出格式,使其适配EVO,参考以下博客:
参考博客1
参考博客2
虽然更改了VINS的输出格式,但是pose_graph保存的实际上是描述子和特征点,这方面没改,所以仍然可以load pose_graph
- VINS输出数据类型转换:
t n s , t x , t y , t z , R w , R x , R y , R z t_{ns},t_x,t_y, t_z,R_w,R_x,R_y,R_z tns?,tx?,ty?,tz?,Rw?,Rx?,Ry?,Rz?要转换为 t s , t x , t y , t z , R x , R y , R z , R w t_{s},t_x,t_y, t_z,R_x,R_y,R_z,R_w ts?,tx?,ty?,tz?,Rx?,Ry?,Rz?,Rw?
时间戳由 n s ns ns转为 s s s,旋转四元数由 w , x , y , z w,x,y,z w,x,y,z顺序转为 x , y , z , w x,y,z,w x,y,z,w顺序。 - ground truth需要使用以下命令转为tum格式(evo只支持tum格式的绘制)
evo_traj euroc data.csv --save_as_tum
evo评估命令:
evo_ape tum /你的GroundTruth路径/data.tum /你的手写VINS输出路径/vins_result_loop.txt -vap --plot_mode=xyz --align --correct_scale
最终evo的评估如下图所示:
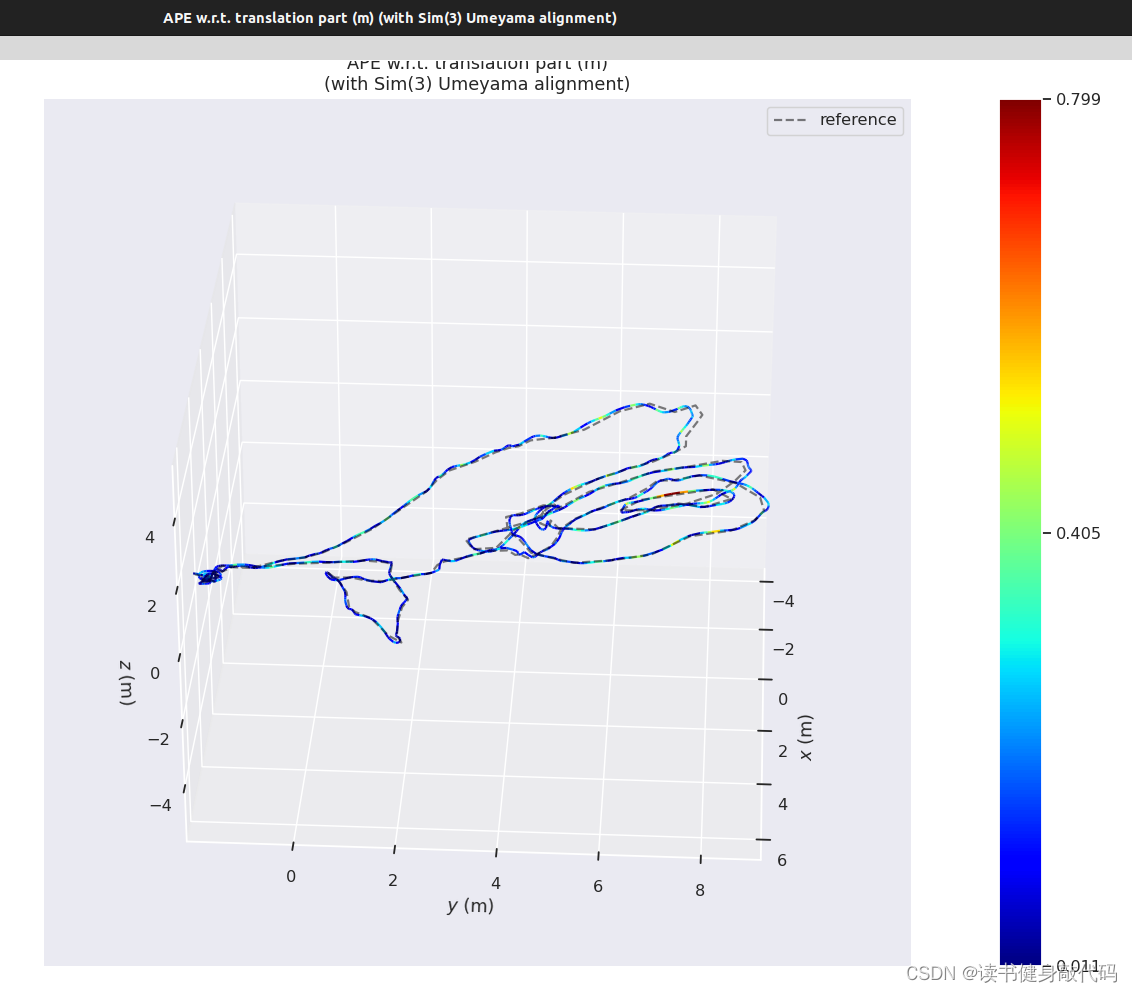
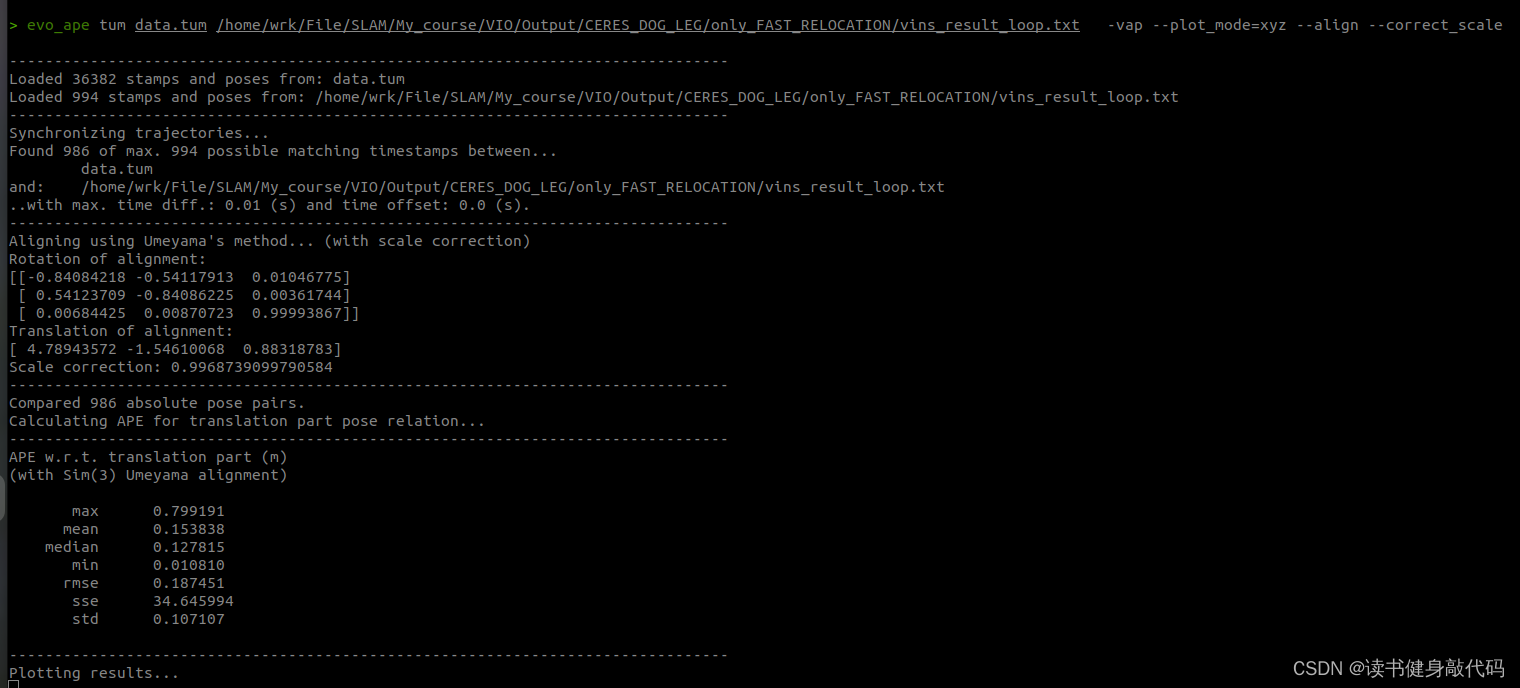
本文实验使用的是MH_01数据集,evo时都有-a,对比结果如下(LM另外两种strategy还没仔细调参,所先挖个坑):
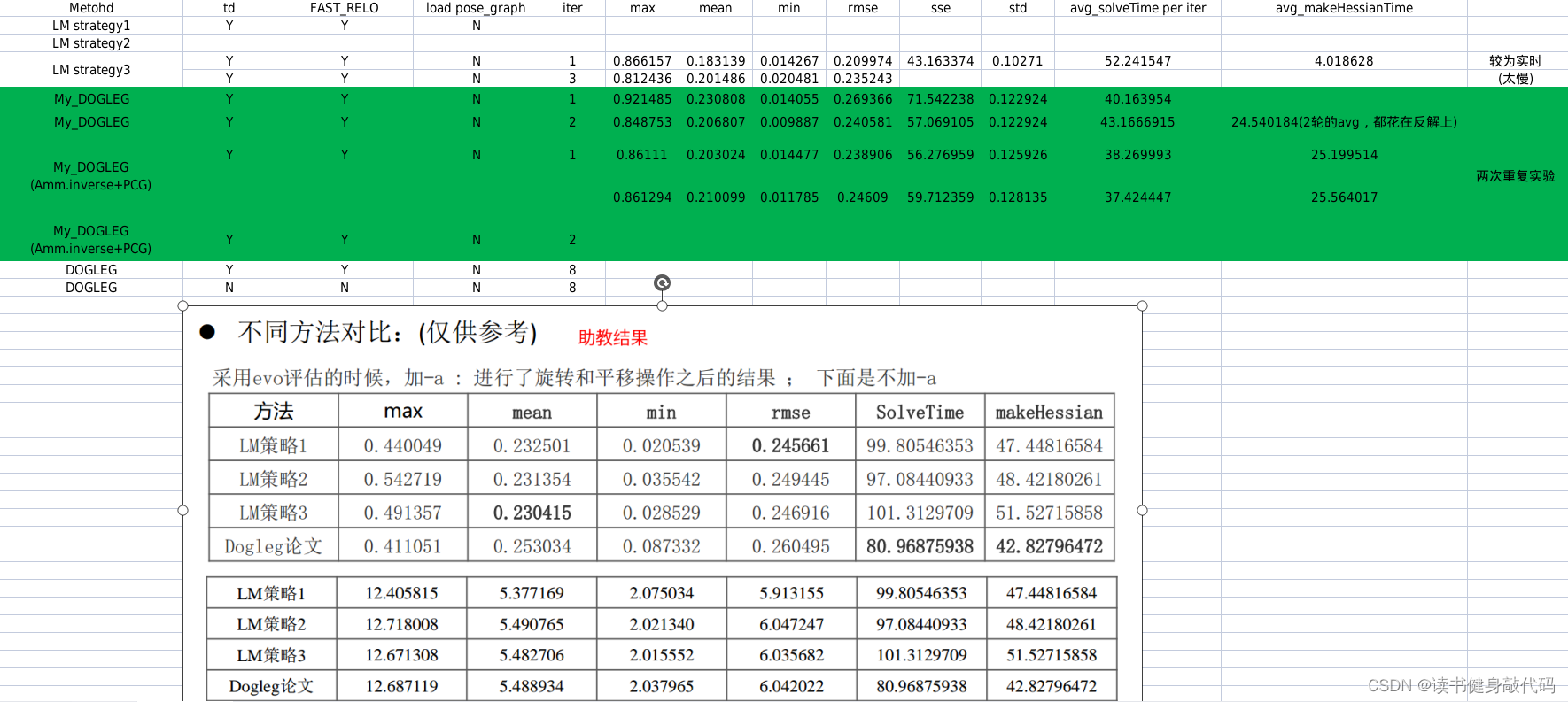
耗时:
- Ceres LM,VINS-MONO迭代8轮耗时约为45ms;
- 手动的LM strategy3的每轮尝试次数为6,1轮6次尝试耗时约为56ms,2轮则输出不实时;
- DL迭代1轮差不多63ms,迭代2轮输出较慢。
精度:整体而言差别不大,手写的DL一轮耗时会稍长,主要原因是没有想到求出J的方法,就使用Ceres的体验来看,DL无论是在速度还是精度方面应该都优于LM。
至于DOGLEG算法的实现,可以完全按照[1]的3.3节来实现,在LM的基础上实现DL很容易,这里就不过多赘述。
至此T1整体工作已完成,部分细节后面再细化。
load pose_graph test:
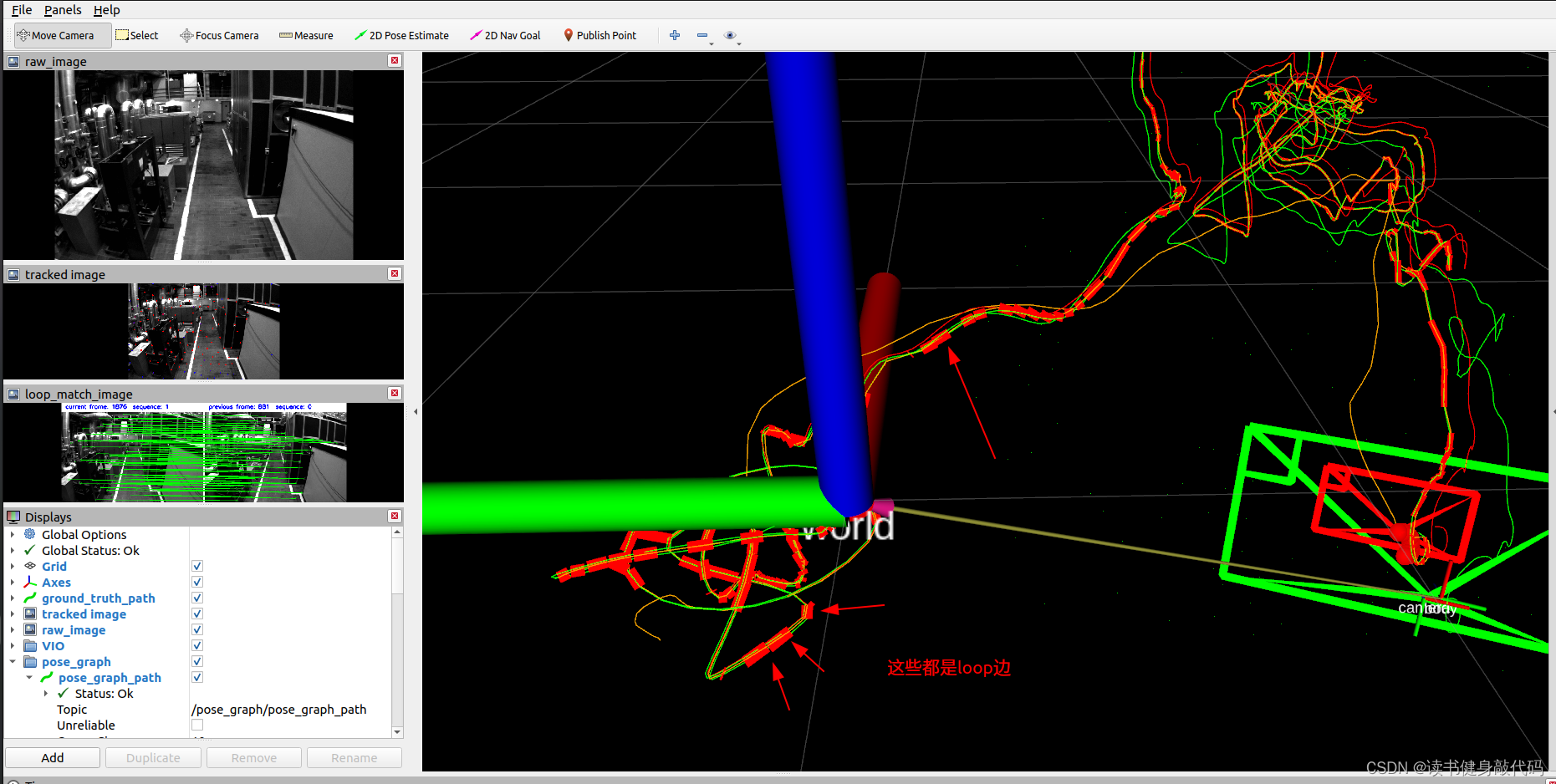
load pose_graph之后发现就很容易产生loop了,因为有了之前的特征和描述子,在rviz中可以看到产生了非常多的loop边,且从一开始就有loop,如果是在同一个地方不同的数据集,这样对于重定位就比较友好。
7. 待填的坑
- LM strategy1,2调参没调完。
- DL反解时间过长,没有想到好/的构建Jacobian的方法。
- PCG的改进
8. Reference
[1] Madsen, K., Nielsen, H. B., & Tingleff, O. (2004). Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems (2nd ed.).
[2] Lourakis, M.I., & Argyros, A.A. (2005). Is Levenberg-Marquardt the most efficient optimization algorithm for implementing bundle adjustment? Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, 2, 1526-1531 Vol. 2.
9. Appendix
整体代码:
9.1 estimator.cpp
#include "estimator.h"
#include "solver/solve.h"
//#define CERES_SOLVE
uint8_t strategy = 3;//先定义为全局变量,后面再优化
Estimator::Estimator(): f_manager{Rs}
{
ROS_INFO("init begins");
clearState();
}
//视觉测量残差的协方差矩阵
void Estimator::setParameter()
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
tic[i] = TIC[i];
ric[i] = RIC[i];
}
f_manager.setRic(ric);
//这里假设标定相机内参时的重投影误差△u=1.5 pixel,(Sigma)^(-1)=(1.5/f * I(2x2))^(-1) = (f/1.5 * I(2x2))
ProjectionFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity();
ProjectionTdFactor::sqrt_info = FOCAL_LENGTH / 1.5 * Matrix2d::Identity();
td = TD;
}
void Estimator::clearState()
{
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE + 1; i++)
{
Rs[i].setIdentity();
Ps[i].setZero();
Vs[i].setZero();
Bas[i].setZero();
Bgs[i].setZero();
dt_buf[i].clear();
linear_acceleration_buf[i].clear();
angular_velocity_buf[i].clear();
if (pre_integrations[i] != nullptr)
delete pre_integrations[i];
pre_integrations[i] = nullptr;
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
tic[i] = Vector3d::Zero();
ric[i] = Matrix3d::Identity();
}
for (auto &it : all_image_frame)
{
if (it.second.pre_integration != nullptr)
{
delete it.second.pre_integration;
it.second.pre_integration = nullptr;
}
}
solver_flag = INITIAL;
first_imu = false,
sum_of_back = 0;
sum_of_front = 0;
frame_count = 0;
solver_flag = INITIAL;
initial_timestamp = 0;
all_image_frame.clear();
td = TD;
if (tmp_pre_integration != nullptr)
delete tmp_pre_integration;
if (last_marginalization_info != nullptr)
delete last_marginalization_info;
tmp_pre_integration = nullptr;
last_marginalization_info = nullptr;
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.clear();
f_manager.clearState();
failure_occur = 0;
relocalization_info = 0;
drift_correct_r = Matrix3d::Identity();
drift_correct_t = Vector3d::Zero();
}
//IMU预积分:IntegrationBase类,IMU预积分具体细节
void Estimator::processIMU(double dt, const Vector3d &linear_acceleration, const Vector3d &angular_velocity)
{
if (!first_imu)
{
first_imu = true;
acc_0 = linear_acceleration;//保存本次measurement中的第一帧IMU数据(有啥用?)
gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}
if (!pre_integrations[frame_count])//如果frame_count的积分为空则new一个预积分对象
{
pre_integrations[frame_count] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};
}
if (frame_count != 0)//第0帧[0]没有预积分,第[0]与第[1]帧之间才有预积分
{
pre_integrations[frame_count]->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);//调用IntegrationBase中定义的成员函数push_back,保存变量并propagate预积分
//if(solver_flag != NON_LINEAR)
tmp_pre_integration->push_back(dt, linear_acceleration, angular_velocity);
dt_buf[frame_count].push_back(dt);//保存这两帧IMU之间的时间间隔,用于预积分
linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count].push_back(linear_acceleration);
angular_velocity_buf[frame_count].push_back(angular_velocity);
//IMU预积分(为什么这里要重新再算一遍?push_back里面不是重新算过了吗?为什么不直接把delta_p等结果拿出直接用?)
// 用IMU数据进行积分,当积完一个measurement中所有IMU数据后,就得到了对应图像帧在世界坐标系中的Ps、Vs、Rs(这里为什么是相对于世界坐标系呢?为什么不把关于world系的抽出来呢?)
// 下面这一部分的积分,在没有成功完成初始化时似乎是没有意义的,因为在没有成功初始化时,对IMU数据来说是没有世界坐标系的
// 当成功完成了初始化后,下面这一部分积分才有用,它可以通过IMU积分得到滑动窗口中最新帧在世界坐标系中的P V R
int j = frame_count;//到后面frame_count一直为window_size即10
Vector3d un_acc_0 = Rs[j] * (acc_0 - Bas[j]) - g;//为什么要有重力g?
Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (gyr_0 + angular_velocity) - Bgs[j];
Rs[j] *= Utility::deltaQ(un_gyr * dt).toRotationMatrix();
Vector3d un_acc_1 = Rs[j] * (linear_acceleration - Bas[j]) - g;
Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);//mid-point中值法计算a,w在k~k+1时刻内的测量值
Ps[j] += dt * Vs[j] + 0.5 * dt * dt * un_acc;
Vs[j] += dt * un_acc;
}
acc_0 = linear_acceleration;//更新本次预积分的初始值
gyr_0 = angular_velocity;
}
//实现了视觉与IMU的初始化以及非线性优化的紧耦合
void Estimator::processImage(const map<int, vector<pair<int, Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1>>>> &image, const std_msgs::Header &header)
{
ROS_DEBUG("new image coming ------------------------------------------");
ROS_DEBUG("Adding feature points %lu", image.size());
// 把当前帧图像(frame_count)的特征点添加到f_manager.feature容器中
// 计算第2最新帧与第3最新帧之间的平均视差(当前帧是第1最新帧),判断第2最新帧是否为KF
// 在未完成初始化时,如果窗口没有塞满,那么是否添加关键帧的判定结果不起作用,滑动窗口要塞满
// 只有在滑动窗口塞满后,或者初始化完成之后,才需要滑动窗口,此时才需要做关键帧判别,根据第2最新关键帧是否为关键帧选择相应的边缘化策略
if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image, td))
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;//如果第2新帧是KF则marg掉最老的一帧
else
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;//如果第二新帧不是KF则直接丢掉最新帧的视觉measurement,并对IMU积分propogate
ROS_DEBUG("this frame is--------------------%s", marginalization_flag ? "reject" : "accept");
ROS_DEBUG("%s", marginalization_flag ? "Non-keyframe" : "Keyframe");
ROS_DEBUG("Solving %d", frame_count);
ROS_DEBUG("number of feature: %d", f_manager.getFeatureCount());
Headers[frame_count] = header;
ImageFrame imageframe(image, header.stamp.toSec());
imageframe.pre_integration = tmp_pre_integration;
all_image_frame.insert(make_pair(header.stamp.toSec(), imageframe));
//用于下一个measurement进行积分
tmp_pre_integration = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};
//不知道关于外参的任何info,需要标定
if(ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC == 2)
{
ROS_INFO("calibrating extrinsic param, rotation movement is needed");
if (frame_count != 0)
{
// 找相邻两帧(bk, bk+1)之间的tracking上的点,构建一个pair,所有pair是一个vector,即corres(pondents),first=前一帧的去畸变的归一化平面上的点,second=后一帧的
// 要求it.start_frame <= frame_count_l && it.endFrame() >= frame_count_r
vector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres = f_manager.getCorresponding(frame_count - 1, frame_count);
Matrix3d calib_ric;
//旋转约束+SVD分解求取Ric旋转外参
//delta_q即qbk_bk+1,是从k时刻积分到k+1,所以是qbk_bk+1(从左往右读)
if (initial_ex_rotation.CalibrationExRotation(corres, pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q, calib_ric))
{
ROS_WARN("initial extrinsic rotation calib success");
ROS_WARN_STREAM("initial extrinsic rotation: " << endl << calib_ric);
ric[0] = calib_ric;
RIC[0] = calib_ric;
ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC = 1;
}
}
}
if (solver_flag == INITIAL)// 需要初始化
{
if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)// 滑动窗口中塞满了才进行初始化(初始化并不影响KF的筛选,KF筛选仍然使用:视差>=10和tracked_num<20来判断,满足其一则是KF
{
bool result = false;
if( ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC != 2 && (header.stamp.toSec() - initial_timestamp) > 0.1) //确保有足够的frame参与初始化,有外参,且当前帧时间戳大于初始化时间戳+0.1秒
{
result = initialStructure();//执行视觉惯性联合初始化
initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec();
}
//初始化成功则进行一次非线性优化,不成功则进行滑窗操作
if(result)
{
solver_flag = NON_LINEAR;//求解
solveOdometry();//重新三角化,并后端求解
slideWindow();
ROS_DEBUG("Ps[0] addr: %ld", reinterpret_cast<long>(&Ps[0]));
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!");
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[0];
last_P0 = Ps[0];
}
else
slideWindow();
}
else
frame_count++;//只在这里自增,自增到WINDOW_SIZE(10)之后就不再自增了,后面都是WINDOW_SIZE(10),即后面的优化都是需要进行marg的
}
else//flag==NON_LINEAR,初始化完成,需要求解后端
{
TicToc t_solve;
solveOdometry();
ROS_DEBUG("solver costs: %fms", t_solve.toc());
// 以下5种情况会判定为fail:
// 1,2:ba或bg过大
// 3,4,5:本次WINDOW内和上次WINDOW内的最后一帧pose(Tw_b[k])之间的relative pose的t或z或角度变化过大
// fail之后会clear state并重启系统(重新初始化)
if (failureDetection())
{
ROS_WARN("failure detection!");
failure_occur = 1;
clearState();//所有buff,预积分等都clear,erase,delete
setParameter();//清零外参,time offset
ROS_WARN("system reboot!");
return;
}
TicToc t_margin;
slideWindow();//根据marg flag marg掉old或者2nd,管理优化变量,数据,深度等
ROS_DEBUG("Ps[0] addr: %ld", reinterpret_cast<long>(&Ps[0]));
f_manager.removeFailures();//去掉未三角化出正深度的landmark
ROS_DEBUG("marginalization costs: %fms", t_margin.toc());
// prepare output of VINS(本次优化且划窗之后,保存WINDOW内的所有KF的translation)
key_poses.clear();
//slideWindow后最后两个Ps相同,所以用11个数据无所谓
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]);
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];//保留这一WINDOW内的最新一帧的信息,供下次failureDetection()使用
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[0];
last_P0 = Ps[0];
}
}
//执行视觉惯性联合初始化,包含两部分:1. visual SfM,2.visual和IMU的align(估计gyro bias,scale,重力细化RefineGravity)
bool Estimator::initialStructure()
{
TicToc t_sfm;
//check imu observibility
{
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_it;
Vector3d sum_g;
//遍历window内所有的ImageFrame
for (frame_it = all_image_frame.begin(), frame_it++; frame_it != all_image_frame.end(); frame_it++)
{
double dt = frame_it->second.pre_integration->sum_dt;//该帧总时间
Vector3d tmp_g = frame_it->second.pre_integration->delta_v / dt;//速度/时间=加速度
sum_g += tmp_g;
}
Vector3d aver_g;
aver_g = sum_g * 1.0 / ((int)all_image_frame.size() - 1);//线加速度均值,因为第一帧没有,所以-1
double var = 0;
for (frame_it = all_image_frame.begin(), frame_it++; frame_it != all_image_frame.end(); frame_it++)
{
double dt = frame_it->second.pre_integration->sum_dt;
Vector3d tmp_g = frame_it->second.pre_integration->delta_v / dt;
var += (tmp_g - aver_g).transpose() * (tmp_g - aver_g);
//cout << "frame g " << tmp_g.transpose() << endl;
}
var = sqrt(var / ((int)all_image_frame.size() - 1));//求线加速度的标准差
//ROS_WARN("IMU variation %f!", var);
if(var < 0.25)//如果加速度方差小于0.25,则证明加速度波动较小,证明IMU激励不够(TODO:这个0.25跟标定qcb旋转外参SVD的特征值的那个0.25有关系吗?)
{
ROS_INFO("IMU excitation not enouth!");
//return false;
}
}
// global sfm
Quaterniond Q[frame_count + 1];//存放window内所有帧相对____的pose T___i
Vector3d T[frame_count + 1];
//把window内所有id对应的所有feature都存到一个vector<SFMFeature>中
map<int, Vector3d> sfm_tracked_points;
vector<SFMFeature> sfm_f;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)//feature是list,元素是装了window内的所有该id的feature的vector,即一个feature_id对应一个vector
{
int imu_j = it_per_id.start_frame - 1;
SFMFeature tmp_feature;
tmp_feature.state = false;//未被三角化
tmp_feature.id = it_per_id.feature_id;
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)//window内该id对应的所有的Matrix<double, 7, 1>
{
imu_j++;
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;
tmp_feature.observation.push_back(make_pair(imu_j, Eigen::Vector2d{pts_j.x(), pts_j.y()}));//observation: 所有观测到该特征点的图像帧ID和图像坐标
}
sfm_f.push_back(tmp_feature);
}
Matrix3d relative_R;
Vector3d relative_T;
int l;
//选择window内第一个满足“tracking数量>20,平均视差>30”的帧(l)与最新帧之间的relative pose,是从最新帧到第l帧Tl_cur,就是下面的Tw_cur
if (!relativePose(relative_R, relative_T, l))
{
ROS_INFO("Not enough features or parallax; Move device around");
return false;
}
l_ = l;//将l赋给成员,便于外面查看l的帧数
//求解SfM问题:对窗口中每个图像帧求解sfm问题,得到所有图像帧相对于参考帧l的旋转四元数Q、平移向量T和特征点坐标sfm_tracked_points。
GlobalSFM sfm;
if(!sfm.construct(frame_count + 1, Q, T, l,
relative_R, relative_T,
sfm_f, sfm_tracked_points))
{
ROS_DEBUG("global SFM failed!");
//如果初始化不成功,就marg掉最老的帧(在all_image_frame中把最老的帧也删掉,但是在MARGIN_SECOND_NEW时就不会删掉all_image_frame中的帧)
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;
return false;
}
//solve pnp for all frame(直接用cv的库函数,没有再使用ceres构建problem)
// 由于并不是第一次视觉初始化就能成功,此时图像帧数目有可能会超过滑动窗口的大小
// 所以再视觉初始化的最后,要求出滑动窗口外的帧的位姿
// 最后把世界坐标系从帧l的相机坐标系,转到帧l的IMU坐标系
// 4.对于非滑动窗口的所有帧,提供一个初始的R,T,然后solve pnp求解pose
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_it;
map<int, Vector3d>::iterator it;
frame_it = all_image_frame.begin( );//时间戳map映射ImgFrame,ImageFrame是里面有的所有id->features的map,features是pair<camera_id, Mat<7,1>>
for (int i = 0; frame_it != all_image_frame.end( ); frame_it++)
{
// provide initial guess
cv::Mat r, rvec, t, D, tmp_r;
if((frame_it->first) == Headers[i].stamp.toSec()) // all_image_frame与滑动窗口中对应的帧,SfM阶段已经计算过,无需再次计算
{
frame_it->second.is_key_frame = true;// 滑动窗口中所有帧都是关键帧
frame_it->second.R = Q[i].toRotationMatrix() * RIC[0].transpose();// 根据各帧相机坐标系的姿态和外参,得到用各帧IMU坐标系的姿态(对应VINS Mono论文(2018年的期刊版论文)中的公式(6))。
frame_it->second.T = T[i];
i++;
continue;
}
if((frame_it->first) > Headers[i].stamp.toSec())
{
i++;
}
// 为滑动窗口外的帧提供一个初始位姿
Matrix3d R_inital = (Q[i].inverse()).toRotationMatrix();//qwc^(-1)=qcw
Vector3d P_inital = - R_inital * T[i];
cv::eigen2cv(R_inital, tmp_r);
cv::Rodrigues(tmp_r, rvec);
cv::eigen2cv(P_inital, t);
frame_it->second.is_key_frame = false;// 初始化时位于滑动窗口外的帧是非关键帧
vector<cv::Point3f> pts_3_vector;// 用于pnp解算的3D点
vector<cv::Point2f> pts_2_vector;// 用于pnp解算的2D点
for (auto &id_pts : frame_it->second.points) // 对于该帧中的特征点
{
int feature_id = id_pts.first;// 特征点id
for (auto &i_p : id_pts.second)// 由于可能有多个相机,所以需要遍历。i_p对应着一个相机所拍图像帧的特征点信息
{
it = sfm_tracked_points.find(feature_id);
if(it != sfm_tracked_points.end())//如果找到了已经Triangulation的,说明在sfm_tracked_points中找到了相应的3D点
{
// 记录该已被Triangulated的id特征点的3D位置
Vector3d world_pts = it->second;
cv::Point3f pts_3(world_pts(0), world_pts(1), world_pts(2));
pts_3_vector.push_back(pts_3);
// 记录该id的特征点在该帧图像中的2D位置
Vector2d img_pts = i_p.second.head<2>();
cv::Point2f pts_2(img_pts(0), img_pts(1));
pts_2_vector.push_back(pts_2);
}
}
}
cv::Mat K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1);
if(pts_3_vector.size() < 6)
{
cout << "pts_3_vector size " << pts_3_vector.size() << endl;
ROS_DEBUG("Not enough points for solve pnp !");
return false;
}
if (! cv::solvePnP(pts_3_vector, pts_2_vector, K, D, rvec, t, 1)) // pnp求解失败
{
ROS_DEBUG("solve pnp fail!");
return false;
}
cv::Rodrigues(rvec, r);
MatrixXd R_pnp,tmp_R_pnp;
cv::cv2eigen(r, tmp_R_pnp);
R_pnp = tmp_R_pnp.transpose();//qwc = qcw^(-1)
MatrixXd T_pnp;
cv::cv2eigen(t, T_pnp);
T_pnp = R_pnp * (-T_pnp);
frame_it->second.R = R_pnp * RIC[0].transpose(); // Tc0_ck * Tbc^(-1) = Tc0_bk转到c0系下看bk
frame_it->second.T = T_pnp;
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere l_: " << l_ << "\nKF[0] Rs[0]:\n" << all_image_frame[Headers[0].stamp.toSec()].R);
if (visualInitialAlign())//视觉惯性对齐:bg,gc0,s,v的估计
return true;
else
{
ROS_INFO("misalign visual structure with IMU");
return false;
}
}
bool Estimator::visualInitialAlign()
{
TicToc t_g;
VectorXd x;//待优化变量[vk,vk+1,w,s],维度是(all_image_frame.size() * 3 + 2 + 1)
//估计陀螺仪的偏置,速度、重力和尺度初始化,重力细化
bool result = VisualIMUAlignment(all_image_frame, Bgs, g, x);
if(!result)
{
ROS_DEBUG("solve g failed!");
return false;
}
//原文:we can get the rotation qw c0 between the world frame and the
//camera frame c0 by rotating the gravity to the z-axis. We then
//rotate all variables from the reference frame (·)c0 to the world
//frame (·)w.
// change state(以下仅对WINDOW内的frame进行操作)
for (int i = 0; i <= frame_count; i++)
{
Matrix3d Ri = all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].R;//IMU相对于world(即c0,此时还是l帧)的pose:Tc0_b[k]
Vector3d Pi = all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].T;//Rc0_b[k]
Ps[i] = Pi;
Rs[i] = Ri;
all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].is_key_frame = true;
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere l_: " << l_
<< "\nKF Rs[0]:\n" << Rs[0]);
//1.梳理一下:此时all_image_frame[Headers[i].stamp.toSec()].R,T都是Tc0_bk
//所以Ps,Rs也都是Tc0_bk
//将三角化出的深度均设为-1,重新三角化
VectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();//获取WINDOW内所有成功Triangulated出深度的landmark,求其逆深度
for (int i = 0; i < dep.size(); i++)
dep[i] = -1;
f_manager.clearDepth(dep);//重新赋深度(都是-1)
//triangulat on cam pose , no tic
//平移tic未标定,设为0
Vector3d TIC_TMP[NUM_OF_CAM];
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
TIC_TMP[i].setZero();
ric[0] = RIC[0];
f_manager.setRic(ric);
f_manager.triangulate(Ps, &(TIC_TMP[0]), &(RIC[0]));//Ps是tc0_bk(里面要转为tc_ck使用)
double s = (x.tail<1>())(0);//取优化出的scale
//gyro bias bg改变了,需要重新IMU预积分
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
//对每两帧camera之间的IMU数据重新进行积分(每次积分的观测初值(acc_0,gyro_0)仍然使用之前保存的linearized_acc, linearized_gyro)
pre_integrations[i]->repropagate(Vector3d::Zero(), Bgs[i]);
}
ROS_INFO_STREAM("TIC[0]:\n" << TIC[0].transpose());
//2.这里将Ps转换为(c0)tb0_bk
for (int i = frame_count; i >= 0; i--) {
//论文式(6),看起来Rs应该是Rc0_bk(这个时候c0应该还没变为world,所以应该是在恢复米制单位)
Ps[i] = s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0] - (s * Ps[0] - Rs[0] * TIC[0]);//这里输入的Ps还是tc0_bk,输出的Ps是(c0)tb0_bk,是在c0系下看的这个translation
//TIC[0]为0代表第一项 s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]=s*Ps[i],即s*tc0_b[k]=s*tc0_c[k](因为此时Ps=tc0_b[k])
ROS_INFO_STREAM("TIC[0]:" << TIC[0].transpose()
<< "\ns * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]: " << (s * Ps[i] - Rs[i] * TIC[0]).transpose()
<< "\ns * Ps[i]: " << (s * Ps[i]).transpose()
<< "\nl_: " << l_
<< "\nPs[0]: " << Ps[0].transpose()//看他是否为0,如果不是0则证明我把c0和c[0]弄混了
<< "\ns * Ps[0]: " << (s * Ps[0]).transpose());
}
//速度,深度处理
int kv = -1;
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_i;
for (frame_i = all_image_frame.begin(); frame_i != all_image_frame.end(); frame_i++)
{
if(frame_i->second.is_key_frame)
{
kv++;
Vs[kv] = frame_i->second.R * x.segment<3>(kv * 3);//更新bk系下的速度:Rc0_bk * (bk)vk = (c0)vk
}
}
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
it_per_id.estimated_depth *= s;//恢复真实世界下尺度的深度
}
//g是world系下的重力向量,Rs[0]是Rc0_b[0]
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nRs[0] is Rc0_b0:\n" << Rs[0]
<<"\nRbc^T:\n" << RIC[0].transpose());
Matrix3d R0 = Utility::g2R(g);//求出gc0->gw(0,0,1)的pitch和roll方向的旋转R0
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere1 R0.yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(R0).x());
Eigen::Vector3d here1_Rs0_ypr = Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]);
double here1_Rs0_yaw = here1_Rs0_ypr.x();//Rs[0].yaw
double yaw = Utility::R2ypr(R0 * Rs[0]).x();//和transformed_yaw相等,说明不是运算精度的问题,可能就是旋转之后yaw会受到影响
R0 = Utility::ypr2R(Eigen::Vector3d{-yaw, 0, 0}) * R0;
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere2 yaw = :\n" << yaw <<
"\nRs[0].yaw = :\n" << here1_Rs0_yaw <<
"\neventually, R0.yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(R0).x());
g = R0 * g;//将估计的重力g旋转到world系:yaw * Rwc0*g^(c0)=g^w,
//Matrix3d rot_diff = R0 * Rs[0].transpose();
Matrix3d rot_diff = R0;//rotdiff最后使得在world系下,b[0]真的yaw为0°
//(PRV)w_b[k] = Rw_b[0] * (PRV)c0_b[k]
for (int i = 0; i <= frame_count; i++)
{
Ps[i] = rot_diff * Ps[i];
Rs[i] = rot_diff * Rs[i];//(w)vb0_bk
Vs[i] = rot_diff * Vs[i];//(w)vb0_bk
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ni=" << i <<" Rs[i].yaw = \n" << Utility::R2ypr(Rs[i]).x());
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("g0 " << g.transpose());
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("my R0 " << Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]).transpose());
return true;
}
//选择window内第一个满足tracking数量>20,平均视差>30的帧(l)与最新帧之间的relative pose,是从最新帧到第l帧
bool Estimator::relativePose(Matrix3d &relative_R, Vector3d &relative_T, int &l)
{
// find previous frame which contians enough correspondance and parallex with newest frame
//对应论文V.A节
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
vector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres;
// 找第i帧和buffer内最后一帧,(i, WINDOW_SIZE),之间的tracking上的点,构建一个pair,
// 所有pair是一个vector,即corres(pondents),first=前一帧的去畸变的归一化平面上的点,second=后一帧的
corres = f_manager.getCorresponding(i, WINDOW_SIZE);
if (corres.size() > 20)//要求两帧的共视点大于20对
{
double sum_parallax = 0;
double average_parallax;
for (int j = 0; j < int(corres.size()); j++)
{
Vector2d pts_0(corres[j].first(0), corres[j].first(1));
Vector2d pts_1(corres[j].second(0), corres[j].second(1));
double parallax = (pts_0 - pts_1).norm();//计算共视点的视差(欧氏距离)
sum_parallax = sum_parallax + parallax;
}
average_parallax = 1.0 * sum_parallax / int(corres.size());//平均视差
//用内参将归一化平面上的点转化到像素平面fx*X/Z + cx,cx相减抵消,z=1,所以直接就是fx*X
//求的Rt是当前帧([WINDOW_SIZE]帧)到第l帧的坐标系变换Rl_[WINDOW_SIZE]
if(average_parallax * 460 > 30 && m_estimator.solveRelativeRT(corres, relative_R, relative_T))
{
l = i;
// l = l+2;
// ROS_DEBUG("change l to l+2 = %d", l);
ROS_DEBUG("average_parallax %f choose l %d and newest frame to triangulate the whole structure", average_parallax * 460, l);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void Estimator::solveOdometry()
{
//需要在WINDOW满之后才进行求解,没满之前,初始化阶段pose由sfm等求解
if (frame_count < WINDOW_SIZE)
return;
//
if (solver_flag == NON_LINEAR)
{
TicToc t_tri;
//在optimize和marg,在新的start_frame上重新三角化landmark
f_manager.triangulate(Ps, tic, ric);
ROS_DEBUG("triangulation costs %f", t_tri.toc());
optimization();
}
}
//vector转换成double数组,因为ceres使用数值数组
//Ps、Rs转变成para_Pose,Vs、Bas、Bgs转变成para_SpeedBias
void Estimator::vector2double()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
para_Pose[i][0] = Ps[i].x();
para_Pose[i][1] = Ps[i].y();
para_Pose[i][2] = Ps[i].z();
Quaterniond q{Rs[i]};
para_Pose[i][3] = q.x();
para_Pose[i][4] = q.y();
para_Pose[i][5] = q.z();
para_Pose[i][6] = q.w();
para_SpeedBias[i][0] = Vs[i].x();
para_SpeedBias[i][1] = Vs[i].y();
para_SpeedBias[i][2] = Vs[i].z();
para_SpeedBias[i][3] = Bas[i].x();
para_SpeedBias[i][4] = Bas[i].y();
para_SpeedBias[i][5] = Bas[i].z();
para_SpeedBias[i][6] = Bgs[i].x();
para_SpeedBias[i][7] = Bgs[i].y();
para_SpeedBias[i][8] = Bgs[i].z();
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
para_Ex_Pose[i][0] = tic[i].x();
para_Ex_Pose[i][1] = tic[i].y();
para_Ex_Pose[i][2] = tic[i].z();
Quaterniond q{ric[i]};
para_Ex_Pose[i][3] = q.x();
para_Ex_Pose[i][4] = q.y();
para_Ex_Pose[i][5] = q.z();
para_Ex_Pose[i][6] = q.w();
}
VectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();
for (int i = 0; i < f_manager.getFeatureCount(); i++)
para_Feature[i][0] = dep(i);
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
para_Td[0][0] = td;
}
// 优化一次之后,求出优化前后的第一帧的T,用于后面作用到所有的轨迹上去
// 数据转换,vector2double的相反过程
// 同时这里为防止优化结果往零空间变化,会根据优化前后第一帧的位姿差进行修正。
void Estimator::double2vector()
{
//窗口第一帧优化前的位姿
Vector3d origin_R0 = Utility::R2ypr(Rs[0]);//R[0]
Vector3d origin_P0 = Ps[0];
if (failure_occur)
{
origin_R0 = Utility::R2ypr(last_R0);
origin_P0 = last_P0;
failure_occur = 0;
}
//窗口第一帧优化后的位姿 q(wxyz)
Vector3d origin_R00 = Utility::R2ypr(Quaterniond(para_Pose[0][6],
para_Pose[0][3],
para_Pose[0][4],
para_Pose[0][5]).toRotationMatrix());
//(R_before_after).yaw(转到被减,变换到before)
//TODO:确定到底是哪个 若是R_after_before.x()则下面使用rot_diff做的矫正就不对了,para_Pose肯定是after的
double y_diff = origin_R0.x() - origin_R00.x();
//TODO:了解欧拉角奇异点
Matrix3d rot_diff = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(y_diff, 0, 0));
if (abs(abs(origin_R0.y()) - 90) < 1.0 || abs(abs(origin_R00.y()) - 90) < 1.0)
{
ROS_DEBUG("euler singular point!");
rot_diff = Rs[0] * Quaterniond(para_Pose[0][6],
para_Pose[0][3],
para_Pose[0][4],
para_Pose[0][5]).toRotationMatrix().transpose();
}
// 根据位姿差做修正,即保证第一帧优化前后位姿不变(似乎只是yaw不变,那tilt呢?)
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
Rs[i] = rot_diff * Quaterniond(para_Pose[i][6], para_Pose[i][3], para_Pose[i][4], para_Pose[i][5]).normalized().toRotationMatrix();
Ps[i] = rot_diff * Vector3d(para_Pose[i][0] - para_Pose[0][0],
para_Pose[i][1] - para_Pose[0][1],
para_Pose[i][2] - para_Pose[0][2]) + origin_P0;
Vs[i] = rot_diff * Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][0],
para_SpeedBias[i][1],
para_SpeedBias[i][2]);
Bas[i] = Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][3],
para_SpeedBias[i][4],
para_SpeedBias[i][5]);
Bgs[i] = Vector3d(para_SpeedBias[i][6],
para_SpeedBias[i][7],
para_SpeedBias[i][8]);
}
//外参
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
tic[i] = Vector3d(para_Ex_Pose[i][0],
para_Ex_Pose[i][1],
para_Ex_Pose[i][2]);
ric[i] = Quaterniond(para_Ex_Pose[i][6],
para_Ex_Pose[i][3],
para_Ex_Pose[i][4],
para_Ex_Pose[i][5]).toRotationMatrix();
}
//转为逆深度,并置flag
VectorXd dep = f_manager.getDepthVector();
for (int i = 0; i < f_manager.getFeatureCount(); i++)
dep(i) = para_Feature[i][0];
f_manager.setDepth(dep);
//time offset
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
td = para_Td[0][0];
// relative info between two loop frame
if(relocalization_info)
{
//按照WINDOW内第一帧的yaw角变化对j帧进行矫正
Matrix3d relo_r;//j帧矫正之后的T
Vector3d relo_t;
relo_r = rot_diff * Quaterniond(relo_Pose[6], relo_Pose[3], relo_Pose[4], relo_Pose[5]).normalized().toRotationMatrix();
relo_t = rot_diff * Vector3d(relo_Pose[0] - para_Pose[0][0],
relo_Pose[1] - para_Pose[0][1],
relo_Pose[2] - para_Pose[0][2]) + origin_P0;//保证第[0]帧不变之后,+origin_P0转为世界系下的t
//由于pitch和roll是可观的,所以我们在BA中一直都在优化pitch和roll,但由于yaw不可观,
//所以即使漂了,可能还是满足我们BA的最优解,所以需要手动进行矫正
//prev_relo_r=Tw1_bi, relo_Pose=Tw2_bi,这两个pose间的yaw和t的漂移Rw1_w2,tw1_w2
double drift_correct_yaw;
//yaw drift, Rw1_bi.yaw() - Rw2_bi.yaw=Rw1_w2.yaw()
drift_correct_yaw = Utility::R2ypr(prev_relo_r).x() - Utility::R2ypr(relo_r).x();
drift_correct_r = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(drift_correct_yaw, 0, 0));
//tw1_w2
drift_correct_t = prev_relo_t - drift_correct_r * relo_t;
//Tw2_bi^(-1) * Tw2_bj = Tbi_bj
relo_relative_t = relo_r.transpose() * (Ps[relo_frame_local_index] - relo_t);
relo_relative_q = relo_r.transpose() * Rs[relo_frame_local_index];
//Rw2_bj.yaw() - Rw2_bi.yaw() = Rbi_bj.yaw()
relo_relative_yaw = Utility::normalizeAngle(Utility::R2ypr(Rs[relo_frame_local_index]).x() - Utility::R2ypr(relo_r).x());
/* //验证Tw1w2是否正确。 结果不一样,不知道为啥。
//1.计算Rw1_w2 = Rw1_bi * Rw2_bi^(-1)
Matrix3d Rw1_w2 = prev_relo_r * relo_r;
//2. 计算Tw1_w2中的Rw1_w2 = Tw1_bi.R * Tbi_bj.R * Rw2_bj^(-1)
Matrix3d Rw1_w2_prime = prev_relo_r * relo_relative_q.toRotationMatrix() * Rs[relo_frame_local_index].transpose();
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncheck Rw1_w2:\n" << Rw1_w2 << "\nRw1_w2_prime:\n" << Rw1_w2_prime);*/
//cout << "vins relo " << endl;
//cout << "vins relative_t " << relo_relative_t.transpose() << endl;
//cout << "vins relative_yaw " <<relo_relative_yaw << endl;
relocalization_info = 0;
}
}
bool Estimator::failureDetection()
{
//最后一帧tracking上的点的数量是否足够多
if (f_manager.last_track_num < 2)
{
ROS_INFO(" little feature %d", f_manager.last_track_num);
//return true;
}
//ba和bg都不应过大
if (Bas[WINDOW_SIZE].norm() > 2.5)
{
ROS_INFO(" big IMU acc bias estimation %f", Bas[WINDOW_SIZE].norm());
return true;
}
if (Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE].norm() > 1.0)
{
ROS_INFO(" big IMU gyr bias estimation %f", Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE].norm());
return true;
}
/*
if (tic(0) > 1)
{
ROS_INFO(" big extri param estimation %d", tic(0) > 1);
return true;
}
*/
//在world系下的pose的t和z变化如果过大则认为fail
Vector3d tmp_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
if ((tmp_P - last_P).norm() > 5)
{
ROS_INFO(" big translation");
return true;
}
if (abs(tmp_P.z() - last_P.z()) > 1)
{
ROS_INFO(" big z translation");
return true;
}
//relative pose过大则fail
//求误差的角度大小,对四元数表示的旋转,delta q有
//delta q = [1, 1/2 delta theta]
//delta theta = [delta q]_xyz * 2,弧度制,视情况转为degree
Matrix3d tmp_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
Matrix3d delta_R = tmp_R.transpose() * last_R;
Quaterniond delta_Q(delta_R);
double delta_angle;
delta_angle = acos(delta_Q.w()) * 2.0 / 3.14 * 180.0;//转为degree
if (delta_angle > 50)
{
ROS_INFO(" big delta_angle ");
//return true;
}
return false;
}
//获得当前优化参数,按照自定义solver中的排列方式排列
static void get_cur_parameter(solve::Solver& solver, double* cur_x_array) {
for (auto it : solver.parameter_block_idx) {
const long addr = it.first;
const int idx = it.second;
const int tmp_param_block_size = solver.parameter_block_size[addr];
ROS_ASSERT_MSG(tmp_param_block_size > 0, "tmp_param_block_size = %d", tmp_param_block_size);
memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
}
static bool updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);
Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);
p = -_p + dp ;
q = (_q.inverse() * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化
return true;
}
//计算ceres优化iteration轮之后的delta_x, solver要传引用,否则会调用析构函数
static void cal_delta_x(solve::Solver& solver, double* x_before, double* x_after, double* delta_x) {
for (auto it : solver.parameter_block_idx) {
const long addr = it.first;
const int idx = it.second;
const int tmp_param_block_size = solver.parameter_block_size[addr];
double tmp_delta_pose_array[SIZE_POSE];
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x size: " << delta_x.size());
if (tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {
updatePose(&x_after[idx], &x_before[idx], &delta_x[idx]);
} else {
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x_map(&x_before[idx], tmp_param_block_size);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta_map(&x_after[idx], tmp_param_block_size);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_map(&delta_x[idx], tmp_param_block_size);
delta_x_map = x_plus_delta_map - x_map;
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_map: " << delta_x_map.transpose());
}
}
}
//后端非线性优化
//大作业T1.a思路 这里要添加自己的makehessian的代码AddResidualBlockSolver()//类似于marg一样管理所有的factor,只不过,这里的m是WINDOW内所有的landmark,n是所有的P,V,Tbc,td,relopose
//管理方式也是地址->idx,地址->size一样,在添加的时候指定landmark的drop_set为valid,剩下的为非valid
//在最后求解出整个delta x,在solve中用LM评估迭代效果并继续迭代
void Estimator::optimization()
{
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;
//loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);//Huber损失函数
loss_function = new ceres::CauchyLoss(1.0);//柯西损失函数
ceres::Problem problem;
//自己写的solver
solve::Solver solver(strategy);
solver.method_ = solve::Solver::kDOGLEG;
solver.iterations_ = NUM_ITERATIONS;
solver.makeHessian_time_sum_ = &(makeHessian_time_sum_);
solver.makeHessian_times_ = &makeHessian_times_;
if(solver.method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {
solver.epsilon_1_ = 1e-10;
solver.epsilon_2_ = 1e-6;//h_dl和radius_减小的倍数阈值
solver.epsilon_3_ = 1e-10;
}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
//添加ceres参数块
//因为ceres用的是double数组,所以在下面用vector2double做类型装换
//Ps、Rs转变成para_Pose,Vs、Bas、Bgs转变成para_SpeedBias
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE + 1; i++)
{
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);//ceres里叫参数块,g2o里是顶点和边
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_SpeedBias[i], SIZE_SPEEDBIAS);
}
//ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC!=0则camera到IMU的外参也添加到估计
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Ex_Pose[i], SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
if (!ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC)
{
ROS_DEBUG("fix extinsic param");
problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(para_Ex_Pose[i]);
}
else
ROS_DEBUG("estimate extinsic param");
}
//相机和IMU硬件不同步时估计两者的时间偏差
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_Td[0], 1);
//problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(para_Td[0]);
}
#else
//自己写的solver如何固定住外参呢?不加入ResidualBlockInfo即可
#endif
TicToc t_whole, t_prepare;
vector2double();
//用于check维度
std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> param_addr_check;//所有param维度
std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> landmark_addr_check;//landmark维度
//1.添加边缘化残差(先验部分)
size_t size_1=0;
if (last_marginalization_info)
{
// construct new marginlization_factor
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);//里面设置了上次先验的什么size,现在还不懂
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);
// /*用于check维度是否正确*/
for(int i=0; i<last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size(); ++i) {
size_t tmp_size = last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])];
tmp_size = tmp_size==7 ? 6: tmp_size;
//这个double*的地址代表的待优化变量的local_size,把每个地址都记录在map中,分配给待优化变量的地址都是连续的
for(int j=0; j<tmp_size; ++j) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i]) + (double)j * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
//打印prior的Jacobian维度
ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)",
last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.rows(), last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.cols());
size_1 = param_addr_check.size();//76
ROS_DEBUG("\nprior size1=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_1, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
#else
//dropset用于指定求解时需要Schur消元的变量,即landmark
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,
vector<int>{});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif
}
//2.添加IMU残差
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
int j = i + 1;
//两帧KF之间IMU积分时间过长的不进行优化(可能lost?)
if (pre_integrations[j]->sum_dt > 10.0)
continue;
IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[j]);//这里的factor就是残差residual,ceres里面叫factor
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
problem.AddResidualBlock(imu_factor, NULL, para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]);
//check维度
long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_Pose[%d]", i);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", i);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[j]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_Pose[%d]", j);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[j]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", j);
for (int k = 0; k < SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
#else
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info =
new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(imu_factor, NULL,
vector<double *>{para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]},
vector<int>{});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif
}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
size_t size_2 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1;//96
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU size2=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_2, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
#endif
//3.添加视觉残差
int f_m_cnt = 0;
int feature_index = -1;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
//!(至少两次tracking,且最新帧1st的tracking不能算(因为1st可能被marg掉),start_frame最大是[7])
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
++feature_index;
int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;
//这个id的feature的第一帧和后面所有的帧分别构建residual block
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)
{
imu_j++;
if (imu_i == imu_j)
{
continue;
}
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;
//是否要time offset
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
//对于一个feature,都跟[it_per_id.start_frame]帧进行优化
ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
problem.AddResidualBlock(f_td, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]);
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = 1;
/*
double **para = new double *[5];
para[0] = para_Pose[imu_i];
para[1] = para_Pose[imu_j];
para[2] = para_Ex_Pose[0];
para[3] = para_Feature[feature_index];
para[4] = para_Td[0];
f_td->check(para);
*/
#else
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f_td, loss_function,
vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]},
vector<int>{3});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif
}
else
{
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
#else
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,
vector<double*>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},
vector<int>{3});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif
}
f_m_cnt++;
}
}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
size_t size_3 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2;//应该和landmark_addr_check.size一样
ROS_DEBUG("\nvisual size3=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_3, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
#endif
ROS_DEBUG("visual measurement count: %d", f_m_cnt);//总的视觉观测个数,观测可能是在不同帧对同一个landmark进行观测,所以可能查过1000,注意与landmark个数进行区分
ROS_DEBUG("prepare for ceres: %f", t_prepare.toc());
//4.添加闭环检测残差,计算滑动窗口中与每一个闭环关键帧的相对位姿,这个相对位置是为后面的图优化(pose graph)准备 或者是 快速重定位(崔华坤PDF7.2节)
//这里注意relo_pose是Tw2_bi = Tw2_w1 * Tw1_bi
if(relocalization_info)
{
ROS_DEBUG("\nhas relocation blocks");
//printf("set relocalization factor! \n");
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(relo_Pose, SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
#endif
int retrive_feature_index = 0;
int feature_index = -1;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
ROS_DEBUG("\nfeature_id: %d", it_per_id.feature_id);
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
++feature_index;
int start = it_per_id.start_frame;
ROS_DEBUG("\nmatch_points size: %lu, retrive_feature_index: %d", match_points.size(), retrive_feature_index);
if(start <= relo_frame_local_index)//必须之前看到过
{
//1.先在i中match的点中找到可能是现在这个feature的id的index
while((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() < it_per_id.feature_id && retrive_feature_index <= match_points.size()-2)//.z()存的是i,j两帧match上的feature的id
{
retrive_feature_index++;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here1, retrive_feature_index: %d", retrive_feature_index);
//2.如果是,则WINDOW内的it_per_id.feature_id这个id的landmark就是被loop上的landmark,取归一化坐标,
if((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() == it_per_id.feature_id)
{
//pts_j是i帧的归一化平面上的点,这里理解relo_Pose及其重要,relo_Pose实际上是Tw2_bi,视觉重投影是从WINDOW内的start帧的camera(在w2系下),投影到i帧(在w1系下),耦合了Tw1_w2
Vector3d pts_j = Vector3d(match_points[retrive_feature_index].x(), match_points[retrive_feature_index].y(), 1.0);
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//start中的点
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
//relo_Pose是Tw2_bi
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[start]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(relo_Pose) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
#else
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here2");
solve::ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new solve::ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,
vector<double*>{para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},
vector<int>{});
solver.addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
#endif
retrive_feature_index++;
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here3");
}
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelo here4");
}
#ifdef CERES_SOLVE
size_t size_4 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2 - size_3;//没有loop时应该为0
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelocation size_4=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_4, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_SCHUR;
//options.num_threads = 2;
// options.trust_region_strategy_type = ceres::DOGLEG;//狗腿算法,与LM较为接近
options.trust_region_strategy_type = ceres::LEVENBERG_MARQUARDT;//LM
options.max_num_iterations = NUM_ITERATIONS;
//options.use_explicit_schur_complement = true;
//options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
//options.use_nonmonotonic_steps = true;
if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)
options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME * 4.0 / 5.0;
else
options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME;
TicToc t_solver;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
/* //获得idx和data
solver.preMakeHessian();
solver.makeHessian();
ROS_DEBUG("delta1");
int cur_x_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;
double cur_x_array[cur_x_size], cur_x_array_before[cur_x_size];
get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);
memcpy(cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, sizeof(double) * cur_x_size);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, solver.m + solver.n);//cur_x_array变了,cur_x才会变
const Eigen::VectorXd cur_x_before = cur_x;*/
ROS_DEBUG("delta2");
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
ROS_DEBUG("delta3");
/* get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);
double delta_x_ceres[cur_x_size];
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_ceres_map(delta_x_ceres, solver.m + solver.n);
cal_delta_x(solver, cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, delta_x_ceres);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x before: " << cur_x_before.transpose() <<
"\ncur_x after: " << cur_x.transpose() <<
"\ndelta_x_ceres: "<< delta_x_ceres_map.transpose() <<
"\ndelta_x_ceres.norm(): " << delta_x_ceres_map.norm() <<
", delta_x_ceres.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_ceres_map.squaredNorm());*/
//cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl;
ROS_DEBUG("\nIterations : %d", static_cast<int>(summary.iterations.size()));
#else //手写求解器求解
ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta0");
solver.preMakeHessian();
solver.makeHessian();
ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta1");
int cur_x_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;
double cur_x_array[cur_x_size], cur_x_array_before[cur_x_size];
get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);
memcpy(cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, sizeof(double) * cur_x_size);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, solver.m + solver.n);//cur_x_array变了,cur_x才会变
const Eigen::VectorXd cur_x_before = cur_x;
ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta2");
TicToc t_solver;
solver.solve();
double vins_finish_time = t_solver.toc();
solver_time_sum_ += vins_finish_time;
++solve_times_;
ROS_DEBUG("\nmy solver costs: %f ms, iter nums: %d, avg_solve_time: %f ms, solver_time_sum_: %f, solve_times_: %f",
vins_finish_time, NUM_ITERATIONS, solver_time_sum_/solve_times_, solver_time_sum_, solve_times_);
get_cur_parameter(solver, cur_x_array);
double delta_x[cur_x_size];
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x_map(delta_x, solver.m + solver.n);
ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta3");
cal_delta_x(solver, cur_x_array_before, cur_x_array, delta_x);
TicToc t_print;
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM(
// "\ncur_x before: " << cur_x_before.transpose() <<
// "\ncur_x after: " << cur_x.transpose() <<
"\ndelta_x: "<< delta_x_map.transpose() <<
"\ndelta_x.norm(): " << delta_x_map.norm() <<
", delta_x.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_map.squaredNorm());
ROS_DEBUG("\nprint costs: %f ms", t_print.toc());
#endif
// 防止优化结果在零空间变化,通过固定第一帧的位姿(如何固定,free,gauge,fix?)
double2vector();
//边缘化处理
//如果次新帧是关键帧,将边缘化最老帧,及其看到的路标点和IMU数据,将其转化为先验:
TicToc t_whole_marginalization;//如marg掉xi_2,则需要处理跟xi_2相关的先验信息,IMU信息,视觉信息
//1. marg 最老帧[0]
if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)
{
//new_marg_info,编译器生成默认构造函数
MarginalizationInfo *marginalization_info = new MarginalizationInfo();
vector2double();
//1) 把上一次先验项中的残差项(尺寸为 n) 传递给当前先验项,并从中取出需要丢弃的状态量;
// (这一步不是多此一举?第2步中的parameter_block不会保证marg掉para_Pose[0]和para_SpeedBias[0]吗?)
//并不是,因为里面要求Jacobian,所以必须按照标准的格式传入才能求出正确的Jacobian
if (last_marginalization_info)//如果不是第一帧(因为第一帧没有marg掉之后生成的先验matrix)
{
//如果上次的先验中有本次需要marg的变量,则添加到drop_set中
vector<int> drop_set;//本次被marg的参数的idx
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
if (last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_Pose[0] ||
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_SpeedBias[0])
drop_set.push_back(i);
}
// construct new marginlization_factor
// 用上次marg的info初始化这次的marg_factor,再加到这次的info中,info管理marg的操作,
// ceres只管调用marg_factor,不直接管info(当然factor需要info来初始化,所以是marg_factor管info,而不是ceres)
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);
ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,
drop_set);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd MARGIN_OLD last_marginalization_info\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << marginalization_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << marginalization_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
}
//2) 将滑窗内第 0 帧和第 1 帧间的 IMU 预积分因子( pre_integrations[1])放到marginalization_info 中
// (不理解为什么para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]也要marg)
{
if (pre_integrations[1]->sum_dt < 10.0)//两帧间时间间隔少于10s,过长时间间隔的不进行marg
{
IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[1]);
//drop_set表示只marg掉[0][1],即P0,V0(虽然只drop[0][1],但是evaluate需要所有的变量来计算Jacobian,所以还是全部传进去)
ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(imu_factor, NULL,
vector<double *>{para_Pose[0], para_SpeedBias[0], para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]},
vector<int>{0, 1});
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd imu_factor\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << imu_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << imu_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());
}
}
//3) 挑 选 出 第 一 次 观 测 帧 为 第 0 帧 的 路 标 点 , 将 对 应 的 多 组 视 觉 观 测 放 到marginalization_info 中,
{
int feature_index = -1;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
++feature_index;
int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;
if (imu_i != 0)//只选择从[0]开始tracking的点
continue;
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//old中的2d坐标
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)
{
imu_j++;
if (imu_i == imu_j)
continue;
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());
ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(f_td, loss_function,
vector<double *>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]},
vector<int>{0, 3});//只drop掉[0](P0)和[3](tracking始于old的landmark)
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
}
else
{
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(f, loss_function,
vector<double *>{para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]},
vector<int>{0, 3});
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nadd ProjectionFactor\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << f->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << f->parameter_block_sizes().size());
}
}
}
}
//得到 上次的先验、IMU测量、视觉观测(都是factor)对应的参数块(parameter_blocks)、雅可比矩阵(jacobians)、残差值(residuals),
//与[0]有关的待优化变量存放于parameter_block_data中
TicToc t_pre_margin;
marginalization_info->preMarginalize();
ROS_DEBUG("\npre marginalization %f ms", t_pre_margin.toc());
//多线程计算在X0处的整个先验项的参数块,雅可比矩阵和残差值
//5、多线程构造先验项舒尔补AX=b的结构,在X0处线性化计算Jacobian和残差
TicToc t_margin;
marginalization_info->marginalize();
ROS_DEBUG("\nmarginalization %f ms", t_margin.toc());
//用marg之后的待优化参数去生成新的last_marg_info和last_marg_parameter_blocks供下一次使用
//6.调整参数块在下一次窗口中对应的位置(往前移一格),注意这里是指针,后面slideWindow中会赋新值,这里只是提前占座
std::unordered_map<long, double *> addr_shift;
for (int i = 1; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
//让指针指向
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i - 1];
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i - 1];
double* tmp_para_ptr = para_Pose[i-1];
double* tmp_ptr = addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])];
// for(int j=0; j<7; ++j) {
// ROS_DEBUG("\npara_Pose[%d] data: %f", i, *tmp_para_ptr);
// ++tmp_para_ptr;
// ROS_DEBUG("\naddr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[%d])] data: %f", i, *tmp_ptr);
// ++tmp_ptr;
// }
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[i])] = para_Ex_Pose[i];
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = para_Td[0];
}
vector<double *> parameter_blocks = marginalization_info->getParameterBlocks(addr_shift);
if (last_marginalization_info)
delete last_marginalization_info;
last_marginalization_info = marginalization_info;//保存此次marg info
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks = parameter_blocks;
}
//2. marg最新帧1st:仅marg掉视觉pose
else
{
if (last_marginalization_info &&
std::count(std::begin(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks), std::end(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks), para_Pose[WINDOW_SIZE - 1]))
{
MarginalizationInfo *marginalization_info = new MarginalizationInfo();
vector2double();
if (last_marginalization_info)
{
//只drop掉2nd的视觉pose(IMU部分是在slideWindow内继承和delete的)
vector<int> drop_set;
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
ROS_ASSERT(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] != para_SpeedBias[WINDOW_SIZE - 1]);
if (last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i] == para_Pose[WINDOW_SIZE - 1])
drop_set.push_back(i);
}
// construct new marginlization_factor
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);
ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info = new ResidualBlockInfo(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks,
drop_set);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nin MARGIN_SECOND_NEW add last_marginalization_info\n " <<
// "\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << marginalization_factor->num_residuals() <<
// "\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << marginalization_factor->parameter_block_sizes().size());
marginalization_info->addResidualBlockInfo(residual_block_info);
}
TicToc t_pre_margin;
ROS_DEBUG("begin marginalization");
marginalization_info->preMarginalize();
ROS_DEBUG("end pre marginalization, %f ms", t_pre_margin.toc());
TicToc t_margin;
ROS_DEBUG("begin marginalization");
marginalization_info->marginalize();
ROS_DEBUG("end marginalization, %f ms", t_margin.toc());
std::unordered_map<long, double *> addr_shift;
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
if (i == WINDOW_SIZE - 1)
continue;
else if (i == WINDOW_SIZE)
{
//看不懂啥意思,后面不是还要操作slideWindow吗,这里搞地址干什么?
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i - 1];
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i - 1];
}
else
{
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i])] = para_Pose[i];
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i])] = para_SpeedBias[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[i])] = para_Ex_Pose[i];
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
addr_shift[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = para_Td[0];
}
vector<double *> parameter_blocks = marginalization_info->getParameterBlocks(addr_shift);
if (last_marginalization_info)
delete last_marginalization_info;
last_marginalization_info = marginalization_info;
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks = parameter_blocks;
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("whole marginalization costs: %f ms", t_whole_marginalization.toc());
ROS_DEBUG("whole time for ceres: %f ms", t_whole.toc());
}
//滑窗之后,WINDOW的最后两个Ps,Vs,Rs,Bas,Bgs相同,无论是old还是new,
//因为后面预积分要用最新的预积分初值,所以为了保证窗口内有11个观测,使最后两个相同
void Estimator::slideWindow()
{
TicToc t_margin;
//把最老的帧冒泡移到最右边,然后delete掉,在new一个新的对象出来
if (marginalization_flag == MARGIN_OLD)
{
double t_0 = Headers[0].stamp.toSec();
back_R0 = Rs[0];//
back_P0 = Ps[0];
if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)
{
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)//循环完成也就冒泡完成到最右侧
{
Rs[i].swap(Rs[i + 1]);//世界系下old冒泡
std::swap(pre_integrations[i], pre_integrations[i + 1]);//每一帧的预积分old冒泡
dt_buf[i].swap(dt_buf[i + 1]);//各种buf也冒泡
linear_acceleration_buf[i].swap(linear_acceleration_buf[i + 1]);
angular_velocity_buf[i].swap(angular_velocity_buf[i + 1]);
Headers[i] = Headers[i + 1];//最后一个是 Headers[WINDOW_SIZE-1] = Headers[WINDOW_SIZE]
Ps[i].swap(Ps[i + 1]);
Vs[i].swap(Vs[i + 1]);
Bas[i].swap(Bas[i + 1]);
Bgs[i].swap(Bgs[i + 1]);
}
//这一步是为了 new IntegrationBase时传入最新的预积分的初值acc_0, gyr_0,ba,bg,所以必须要强制等于最新的
Headers[WINDOW_SIZE] = Headers[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
Ps[WINDOW_SIZE] = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
Vs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Vs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
Rs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
Bas[WINDOW_SIZE] = Bas[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE] = Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE - 1];
//冒泡到最右边之后把对应的都delete&new或者clear掉
delete pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE];//delete掉,并new新的预积分对象出来
pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[WINDOW_SIZE], Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE]};
dt_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
linear_acceleration_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
angular_velocity_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, before marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);
if (true || solver_flag == INITIAL)
{
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator it_0;
it_0 = all_image_frame.find(t_0);//t_0是最老帧的时间戳,marg_old时删掉了帧,但是marg2nd的时候没有动,但是在process时候加进来了,说明all_image_frame应该是在增长的
delete it_0->second.pre_integration;
it_0->second.pre_integration = nullptr;
for (map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator it = all_image_frame.begin(); it != it_0; ++it)
{
if (it->second.pre_integration)
delete it->second.pre_integration;
it->second.pre_integration = NULL;
}
all_image_frame.erase(all_image_frame.begin(), it_0);//erase掉从开始到被marg掉的old之间所有的帧[begin(), it_0)
all_image_frame.erase(t_0);//erase掉old帧
}
slideWindowOld();//管理feature(landmark)
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, after marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);
}
}
//如果2nd不是KF则直接扔掉1st的visual测量,并在2nd基础上对1st的IMU进行预积分,window前面的都不动
else
{
if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)
{
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, before marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < dt_buf[frame_count].size(); i++)//对最新帧的img对应的imu数据进行循环
{
double tmp_dt = dt_buf[frame_count][i];
Vector3d tmp_linear_acceleration = linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count][i];
Vector3d tmp_angular_velocity = angular_velocity_buf[frame_count][i];
pre_integrations[frame_count - 1]->push_back(tmp_dt, tmp_linear_acceleration, tmp_angular_velocity);//2nd对1st进行IMU预积分
//imu数据保存,相当于一个较长的KF,eg:
// |-|-|-|-|-----|
// ↑
// 这段img为1st时,2nd不是KF,扔掉了这个2nd的img,但buf了IMU数据,所以这段imu数据较长
dt_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_dt);
linear_acceleration_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_linear_acceleration);
angular_velocity_buf[frame_count - 1].push_back(tmp_angular_velocity);
}
//相对世界系的预积分需要继承过来
Headers[frame_count - 1] = Headers[frame_count];
Ps[frame_count - 1] = Ps[frame_count];
Vs[frame_count - 1] = Vs[frame_count];
Rs[frame_count - 1] = Rs[frame_count];
Bas[frame_count - 1] = Bas[frame_count];
Bgs[frame_count - 1] = Bgs[frame_count];
delete pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE];
pre_integrations[WINDOW_SIZE] = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[WINDOW_SIZE], Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE]};
dt_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
linear_acceleration_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
angular_velocity_buf[WINDOW_SIZE].clear();
slideWindowNew();
// ROS_DEBUG("marg_flag: %d, after marg, all_image_frame.size(): %lu, WINDOW_SIZE: %d",
// marginalization_flag, all_image_frame.size(), WINDOW_SIZE);
}
}
}
// real marginalization is removed in solve_ceres()
void Estimator::slideWindowNew()
{
sum_of_front++;
f_manager.removeFront(frame_count);
}
// real marginalization is removed in solve_ceres()
void Estimator::slideWindowOld()
{
sum_of_back++;
bool shift_depth = solver_flag == NON_LINEAR ? true : false;
if (shift_depth)
{
Matrix3d R0, R1;
Vector3d P0, P1;
//Twb * Tbc = Twc
//0:被marg掉的T_marg,1:新的第[0]帧的T_new
R0 = back_R0 * ric[0];
R1 = Rs[0] * ric[0];
P0 = back_P0 + back_R0 * tic[0];
P1 = Ps[0] + Rs[0] * tic[0];
f_manager.removeBackShiftDepth(R0, P0, R1, P1);//为什么要转移深度?landmark不是删除了吗?
}
else
f_manager.removeBack();
}
void Estimator::setReloFrame(double _frame_stamp, int _frame_index, vector<Vector3d> &_match_points, Vector3d _relo_t, Matrix3d _relo_r)
{
relo_frame_stamp = _frame_stamp;//与old frame loop上的WINDOW内的帧(j帧)的时间戳
relo_frame_index = _frame_index;//j帧的帧号
match_points.clear();
match_points = _match_points;//i帧中与j帧中match上的点在i帧中的归一化(x,y,id)
//Tw1_bi=Tw1_b_old
prev_relo_t = _relo_t;//i帧pose
prev_relo_r = _relo_r;
for(int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
if(relo_frame_stamp == Headers[i].stamp.toSec())
{
relo_frame_local_index = i;//j帧在WINDOW中的下标
relocalization_info = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE_POSE; j++)
//注意,这不是赋地址,而是new了一个新的优化变量的内存,relo_Pose虽然赋初值时为Tw2_bj,但是实际上作用是Tw2_bi
relo_Pose[j] = para_Pose[i][j];
}
}
}
9.2 solve.cpp
//
// Created by wrk on 2023/12/22.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "solve.h"
#include "../parameters.h"
#define USE_SCHUR
namespace solve{
/*solver_info相关函数*/
//计算每个残差,对应的Jacobian,并更新 parameter_block_data
void ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()
{
//每个factor的残差块总维度 和 残差块具体size
//residual总维度,先验=last n=76,IMU=15,Visual=2
residuals.resize(cost_function->num_residuals());
//有td时,先验factor为13(9*1+6*10+6+1),IMU factor为4(7,9,7,9),每个feature factor size=5(7,7,7,1)
//无td时 12 4 4
std::vector<int> block_sizes = cost_function->parameter_block_sizes();
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncost_function->num_residuals(): " << cost_function->num_residuals() <<
"\ncost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size: " << cost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size());
for(int i=0; i<cost_function->parameter_block_sizes().size(); ++i) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nparameter_block_sizes()[%d]: %d", i, cost_function->parameter_block_sizes()[i]);
}*/
raw_jacobians = new double *[block_sizes.size()];//二重指针,指针数组
jacobians.resize(block_sizes.size());
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(block_sizes.size()); i++)
{
jacobians[i].resize(cost_function->num_residuals(), block_sizes[i]);
raw_jacobians[i] = jacobians[i].data();//二重指针,是为了配合ceres的形参 double** jacobians,看不懂,给data还能够操作地址??
//dim += block_sizes[i] == 7 ? 6 : block_sizes[i];
}
//虚函数,调用的是基类自己实现的Evaluate,即分别是MarginalizationFactor、IMUFactor 和 ProjectionTdFactor(或ProjectionFactor)的Evaluate()函数
cost_function->Evaluate(parameter_blocks.data(), residuals.data(), raw_jacobians);
//std::vector<int> tmp_idx(block_sizes.size());
//Eigen::MatrixXd tmp(dim, dim);
//for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
//{
// int size_i = localSize(block_sizes[i]);
// Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);
// for (int j = 0, sub_idx = 0; j < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); sub_idx += block_sizes[j] == 7 ? 6 : block_sizes[j], j++)
// {
// int size_j = localSize(block_sizes[j]);
// Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);
// tmp_idx[j] = sub_idx;
// tmp.block(tmp_idx[i], tmp_idx[j], size_i, size_j) = jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
// }
//}
//Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes(tmp);
//std::cout << saes.eigenvalues() << std::endl;
//ROS_ASSERT(saes.eigenvalues().minCoeff() >= -1e-6);
//这里使用的是CauchyLoss(应该是计算一个scale对residuals进行加权,先不细看,TODO:了解CauchyLoss等loss函数的意义)
if (loss_function)
{
double residual_scaling_, alpha_sq_norm_;
double sq_norm, rho[3];
sq_norm = residuals.squaredNorm();
//loss_function 为 robust kernel function,in:sq_norm, out:rho out[0] = rho(sq_norm),out[1] = rho'(sq_norm), out[2] = rho''(sq_norm),
loss_function->Evaluate(sq_norm, rho);//求取鲁棒核函数关于||f(x)||^2的一二阶导数
//printf("sq_norm: %f, rho[0]: %f, rho[1]: %f, rho[2]: %f\n", sq_norm, rho[0], rho[1], rho[2]);
double sqrt_rho1_ = sqrt(rho[1]);
if ((sq_norm == 0.0) || (rho[2] <= 0.0))
{
residual_scaling_ = sqrt_rho1_;
alpha_sq_norm_ = 0.0;
}
else
{
const double D = 1.0 + 2.0 * sq_norm * rho[2] / rho[1];
const double alpha = 1.0 - sqrt(D);//求根公式求方程的根
residual_scaling_ = sqrt_rho1_ / (1 - alpha);
alpha_sq_norm_ = alpha / sq_norm;
}
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
jacobians[i] = sqrt_rho1_ * (jacobians[i] - alpha_sq_norm_ * residuals * (residuals.transpose() * jacobians[i]));
}
residuals *= residual_scaling_;
}
}
Solver::~Solver()
{
ROS_DEBUG("destractor here1");
//new出来的是在堆上的内存,需要手动delete释放;malloc的内存使用free来释放
if(mem_allocated_) {
for (auto it = parameter_block_data.begin(); it != parameter_block_data.end(); ++it)
delete[] it->second;
ROS_DEBUG("destractor here2");
for (auto it = parameter_block_data_backup.begin(); it != parameter_block_data_backup.end(); ++it)
delete[] it->second;
}
ROS_DEBUG("destractor here3");
//这个不能在这delete放,因为ceres要用
// for (int i = 0; i < (int)factors.size(); i++)
// {
//
// delete[] factors[i]->raw_jacobians;
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here31");
// delete[] factors[i]->cost_function;
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here32");
// delete[] factors[i];
// ROS_DEBUG("destractor here33");
// }
ROS_DEBUG("destractor here4");
}
void Solver::addResidualBlockInfo(ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info)
{
factors.emplace_back(residual_block_info);
std::vector<double *> ¶meter_blocks = residual_block_info->parameter_blocks;//每个factor的待优化变量的地址
std::vector<int> parameter_block_sizes = residual_block_info->cost_function->parameter_block_sizes();//待优化变量的维度
//parameter_blocks.size
//有td时,先验factor为13(9*1+6*10+6+1),IMU factor为4(7,9,7,9),每个feature factor size=5(7,7,7,1)
//无td时 12 4 4
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(residual_block_info->parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
double *addr = parameter_blocks[i];
int size = parameter_block_sizes[i];//待优化变量的维度
//map没有key时会新建key-value对
parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = size;//global size <优化变量内存地址,localSize>
// ROS_DEBUG("in addResidualBlockInfo size: %d", size);
}
//需要 marg 掉的变量
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(residual_block_info->drop_set.size()); i++)
{
double *addr = parameter_blocks[residual_block_info->drop_set[i]];//获得待marg变量的地址
//要marg的变量先占个key的座,marg之前将m放在一起,n放在一起
parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = 0;//local size <待边缘化的优化变量内存地址,在parameter_block_size中的id>,
}
}
void Solver::preMakeHessian()
{
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nfactors.size(): " << factors.size());
int i=0;
ROS_DEBUG("factors size=%lu, landmark size=%lu", factors.size(), factors.size()-2); //始于[0]帧的landmark
for (auto it : factors)
{
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nin preMarginalize i: "<< ++i); //很大,能到900多,说明[0]观测到了很多landmark
it->Evaluate();//计算每个factor的residual和Jacobian
//如果完成过就只计算Jacobian和residual(里面已经耦合了sqrt_info,所以直接H=J^T*J,不用J^T*W*J),不用再new内存,重复调用只是为了计算新的Jacobian和residual
if(mem_allocated_) {
continue;
}
std::vector<int> block_sizes = it->cost_function->parameter_block_sizes(); //residual总维度,先验=last n=76,IMU=15,Visual=2
/* 测试地址转换之后还能否转换回来
long tmp_addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[0]);
double* tmp_pt = reinterpret_cast<double *>(tmp_addr);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nraw double* = " << it->parameter_blocks[0] << ", cast to long= " << tmp_addr << ", back to double* = " << tmp_pt);*/
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(block_sizes.size()); i++)
{
long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i]);//parameter_blocks是vector<double *>,存放的是数据的地址
int size = block_sizes[i];
//如果优化变量中没有这个数据就new一片内存放置
if (parameter_block_data.find(addr) == parameter_block_data.end())
{
double *data = new double[size];
//dst,src
memcpy(data, it->parameter_blocks[i], sizeof(double) * size);
parameter_block_data[addr] = data;
//数据备份
double *data_backup = new double[size];
memcpy(data_backup, it->parameter_blocks[i], sizeof(double) * size);
parameter_block_data_backup[addr] = data_backup;
}
}
}
mem_allocated_ = true;
}
int Solver::localSize(int size) const
{
return size == 7 ? 6 : size;
}
int Solver::globalSize(int size) const
{
return size == 6 ? 7 : size;
}
//线程函数
static void* ThreadsConstructA(void* threadsstruct)
{
ThreadsStruct* p = ((ThreadsStruct*)threadsstruct);
//遍历该线程分配的所有factors,这factor可能是任何一个factor
for (auto it : p->sub_factors)
{
//遍历该factor中的所有参数块,比如IMU factor传入的是vector<double *>{para_Pose[0], para_SpeedBias[0], para_Pose[1], para_SpeedBias[1]}
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
int idx_i = p->parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];
int size_i = p->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];
if (size_i == 7) //对于pose来说,是7维的,最后一维为0,这里取左边6
size_i = 6;
//只提取local size部分,对于pose来说,是7维的,最后一维为0,这里取左边6维;对于其他待优化变量,size_i不变,取全部jacobian
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = it->jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);
for (int j = i; j < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); j++)
{
int idx_j = p->parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];
int size_j = p->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];
if (size_j == 7)
size_j = 6;
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = it->jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);
//主对角线
if (i == j)
p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
//非主对角线
else
{
p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
p->A.block(idx_j, idx_i, size_j, size_i) = p->A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j).transpose();
}
}
p->b.segment(idx_i, size_i) += jacobian_i.transpose() * it->residuals;
}
}
return threadsstruct;
}
static bool updatePose(const double *x, const double *delta, double *x_plus_delta)
{
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> _p(x);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Quaterniond> _q(x + 3);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d> dp(delta);
//数组转四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond dq = Utility::deltaQ(Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Vector3d>(delta + 3));
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d> p(x_plus_delta);
Eigen::Map<Eigen::Quaterniond> q(x_plus_delta + 3);//Jacobian和residual都是按照6维来处理的,但是更新rotation时需要按照四元数来更新
p = _p + dp;
q = (_q * dq).normalized();//四元数乘法并归一化
return true;
}
void Solver::makeHessian()
{
int pos = 0;//Hessian矩阵整体维度
//it.first是要被marg掉的变量的地址,将其size累加起来就得到了所有被marg的变量的总localSize=m
//marg的放一起,共m维,remain放一起,共n维
for (auto &it : parameter_block_idx)
{
it.second = pos;//也算是排序1
pos += localSize(parameter_block_size[it.first]);//PQ7为改为6维
}
m = pos;//要被marg的变量的总维度
int tmp_n = 0;
//与[0]相关总维度
for (const auto &it : parameter_block_size)
{
if (parameter_block_idx.find(it.first) == parameter_block_idx.end())//将不在drop_set中的剩下的维度加起来,这一步实际上算的就是n
{
parameter_block_idx[it.first] = pos;//排序2
tmp_n += localSize(it.second);
pos += localSize(it.second);
}
}
n = pos - m;//remain变量的总维度,这样写建立了n和m间的关系,表意更强
ROS_DEBUG("\nn: %d, tmp_n: %d", n, tmp_n);
ROS_DEBUG("\nSolver, pos: %d, m: %d, n: %d, size: %d", pos, m, n, (int)parameter_block_idx.size());
TicToc t_summing;
Eigen::MatrixXd A(pos, pos);//总系数矩阵
Eigen::VectorXd b(pos);//总误差项
A.setZero();
b.setZero();
Hessian_.resize(pos,pos);
b_.resize(pos);
delta_x_.resize(pos);
//构建信息矩阵可以多线程构建
/* //single thread
for (auto it : factors)
{
//J^T*J
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
int idx_i = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];//要被marg的second=0
int size_i = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])]);
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = it->jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);//remain变量的初始jacobian
for (int j = i; j < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); j++)
{
int idx_j = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];
int size_j = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])]);
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = it->jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);//marg变量的初始jacobian
//主对角线,注意这里是+=,可能之前别的变量在这个地方已经有过值了,所以要+=
if (i == j)
A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
//非主对角线
else
{
A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
A.block(idx_j, idx_i, size_j, size_i) = A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j).transpose();
}
}
b.segment(idx_i, size_i) += jacobian_i.transpose() * it->residuals;//J^T*e
}
}
ROS_INFO("summing up costs %f ms", t_summing.toc());*/
//multi thread
TicToc t_thread_summing;
pthread_t tids[NUM_THREADS];//4个线程构建
//携带每个线程的输入输出信息
ThreadsStruct threadsstruct[NUM_THREADS];
//将先验约束因子平均分配到4个线程中
int i = 0;
for (auto it : factors)
{
threadsstruct[i].sub_factors.push_back(it);
i++;
i = i % NUM_THREADS;
}
//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
{
TicToc zero_matrix;
threadsstruct[i].A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(pos,pos);
threadsstruct[i].b = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(pos);
threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_size = parameter_block_size;//marg里的block_size,4个线程共享
threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_idx = parameter_block_idx;
int ret = pthread_create( &tids[i], NULL, ThreadsConstructA ,(void*)&(threadsstruct[i]));//参数4是arg,void*类型,取其地址并强制类型转换
if (ret != 0)
{
ROS_WARN("pthread_create error");
ROS_BREAK();
}
}
//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来
for( int i = NUM_THREADS - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
pthread_join( tids[i], NULL );//阻塞等待线程完成,这里的A和b的+=操作在主线程中是阻塞的,+=的顺序是pthread_join的顺序
A += threadsstruct[i].A;
b += threadsstruct[i].b;
}
//ROS_DEBUG("thread summing up costs %f ms", t_thread_summing.toc());
//ROS_INFO("A diff %f , b diff %f ", (A - tmp_A).sum(), (b - tmp_b).sum());
Hessian_ = A;
b_ = -b;
//反解出J和e
TicToc t_solve_J;
TicToc t_SelfAdjoint;
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes2(A);//这一句24.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_SelfAdjoint cost: %f ms", t_SelfAdjoint.toc());
Eigen::VectorXd S = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_sqrt = S.cwiseSqrt();//开根号
linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv_sqrt = S_inv.cwiseSqrt();
linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().real().transpose() * b;
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_solve_J cost: %f ms", t_solve_J.toc());//25ms
}
std::vector<double *> Solver::getParameterBlocks(std::unordered_map<long, double *> &addr_shift)
{
std::vector<double *> keep_block_addr;//remain的优化变量的地址
keep_block_size.clear();
keep_block_idx.clear();
keep_block_data.clear();
for (const auto &it : parameter_block_idx)
{
if (it.second >= m)//如果是remain部分
{
keep_block_size.push_back(parameter_block_size[it.first]);
keep_block_idx.push_back(parameter_block_idx[it.first]);
keep_block_data.push_back(parameter_block_data[it.first]);
keep_block_addr.push_back(addr_shift[it.first]);//待优化变量的首地址需要不变,但是首地址对应的变量是P0,需要在slideWindow中被冒泡到后面delete掉
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("keep_block_addr[0] long addr: %ld, [1] long addr: %ld",
reinterpret_cast<long>(keep_block_addr[0]), reinterpret_cast<long>(keep_block_addr[1]));
sum_block_size = std::accumulate(std::begin(keep_block_size), std::end(keep_block_size), 0);
return keep_block_addr;
}
//只更新状态量p,q,v,ba,bg,λ,注意prior不是状态量,虽然在待优化变量中,但是其residual是跟状态量有关,Jacobian在一轮优化中不变,
//这里更新状态的目的是因为计算chi时会用到residual,而residual和状态量有关,而先验的residual更新:f' = f + J*δxp,其中δxp=x-x0,也跟状态量x有关,
//但是因为在先验factor在Evaluate时会计算residual,所以不用手动更新,只需要更新最核心的x即可。其他的factor相同。
bool Solver::updateStates(double weight) {
int array_size = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;
double used_delta_x[array_size];
if(weight != -1.0)
std::transform(delta_x_array_, delta_x_array_ + array_size, used_delta_x, [weight](double x) { return x * weight; });//对delta_x加权
else
memcpy(used_delta_x, delta_x_array_, sizeof(double) * array_size);
//使用idx来找对应的param
double cur_x_array[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int idx = it.second;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nidx: " << idx << ", tmp_param_block_size: " << tmp_param_block_size);*/
//保存一份待优化变量,和delta_x进行数量级对比
memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)SIZE_POSE);
if(tmp_param_block_size == SIZE_POSE) {
/* Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> delta_pose {&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> tmp_pose {reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};
for(int i=0;i<tmp_param_block_size;++i){
tmp_pose[i] = *(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr + sizeof(double)*i));
delta_pose[i] = delta_x_array_[idx+i];
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose before update: " << tmp_pose.transpose() << "\ndelta_pose: " << delta_pose.transpose());*/
updatePose(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), &delta_x_array_[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr));//TODO:这个backup应该可以用parameter_block_data替代
/* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\npose after update: " << tmp_pose.transpose());*/
} else {
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{parameter_block_data_backup[addr], tmp_param_block_size};
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> delta_x{&delta_x_array_[idx], tmp_param_block_size};
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> x_plus_delta{reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), tmp_param_block_size};
/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters before update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose() << "\ndelta_x: " << delta_x.transpose());*/
x_plus_delta = x + delta_x;
/*ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother parameters after update: " << x_plus_delta.transpose());*/
}
}
// 初始化Eigen向量
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> cur_x(cur_x_array, m+n);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ncur_x: " << cur_x.transpose());
preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residual
return true;
}
//备份状态量
bool Solver::backupStates() {
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
memcpy(parameter_block_data_backup[addr], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
return true;
}
//回滚状态量
bool Solver::rollbackStates() {
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx){
const long addr = it.first;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
memcpy(reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), parameter_block_data_backup[addr], sizeof(double) * (int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
preMakeHessian();//计算更新后的Jacobian和residual
return true;
}
bool Solver::get_cur_parameter(double* cur_x_array) {
for (auto it : parameter_block_idx) {
const long addr = it.first;
const int idx = it.second;
const int tmp_param_block_size = parameter_block_size[addr];
ROS_ASSERT_MSG(tmp_param_block_size > 0, "tmp_param_block_size = %d", tmp_param_block_size);
memcpy( &cur_x_array[idx], reinterpret_cast<double *>(addr), sizeof(double) *(int)tmp_param_block_size);
}
return true;
}
//在ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()中调用的多态Evaluate()函数后已经考虑了loss_function对Jacobian和residual的加权
//分别计算先验和其他factor的chi
double Solver::computeChi() const{
//先验的residual维度
size_t prior_dim = SIZE_SPEEDBIAS + (SIZE_POSE-1) * WINDOW_SIZE + (SIZE_POSE-1);
if(ESTIMATE_TD){
prior_dim+=1;
}
double tmpChi = 0;
for (auto it : factors){
//TODO:先验的也改成正常更新,按照参数也是PQV来理解先验的话,就应该是正常更新,而不是使用norm(),后面看看对不对
double this_Chi = it->residuals.transpose() * it->residuals;
tmpChi += this_Chi;
// if(it->residuals.size()==prior_dim) {
// double this_Chi = it->residuals.norm();
// tmpChi += this_Chi;
///* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nprior factor, this_Chi= " << this_Chi
// << ", residuals size: " << it->residuals.size()
// << ", residuals: " << it->residuals.transpose());*/
// } else {
// double this_Chi = it->residuals.transpose() * it->residuals;
// tmpChi += this_Chi;
///* ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nother factor, this_Chi= " << this_Chi
// << ", residuals size: " << it->residuals.size()
// << ", residuals: " << it->residuals.transpose());*/
// }
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere tmpChi= " << tmpChi);
return tmpChi;
}
/// LM
void Solver::computeLambdaInitLM() {
if(strategy_ == 1) {
currentChi_ = computeChi();
double maxDiagonal = 0;
ulong size = Hessian_.cols();
assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");
for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
maxDiagonal = std::max(fabs(Hessian_(i, i)), maxDiagonal);//取H矩阵的最大值,然后*涛
}
double tau = 1e1;//[1e-8,1] tau越小,△x越大
currentLambda_ = tau * maxDiagonal;
} else if(strategy_ == 2) {
// set a large value, so that first updates are small steps in the steepest-descent direction
currentChi_ = computeChi();
currentLambda_ = 1e16;
// currentLambda_ = 1e-3;
} else if(strategy_ == 3) {
ni_ = 2.;
currentLambda_ = -1.;
currentChi_ = computeChi();
stopThresholdLM_ = 1e-6 * currentChi_; // 迭代条件为 误差下降 1e-6 倍
double maxDiagonal = 0;
ulong size = Hessian_.cols();
assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");
for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
maxDiagonal = std::max(fabs(Hessian_(i, i)), maxDiagonal);//取H矩阵的最大值,然后*涛
}
// double tau = 1e-5;
double tau = 1e-15;//[1e-8,1] tau越小,△x越大//
currentLambda_ = tau * maxDiagonal;
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nin computeLambdaInitLM currentChi_= " << currentChi_
<< ", init currentLambda_=" << currentLambda_
<< ", maxDiagonal=" << maxDiagonal);
}
}
void Solver::addLambdatoHessianLM() {
ulong size = Hessian_.cols();
assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");
for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if(strategy_==1) {
Hessian_(i, i) += currentLambda_ * Hessian_(i, i); //理解: H(k+1) = H(k) + λ H(k) = (1+λ) H(k) 策略1
} else if(strategy_==2 || strategy_==3) {
Hessian_(i, i) += currentLambda_;
}
}
}
void Solver::removeLambdaHessianLM() {
ulong size = Hessian_.cols();
assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");
// TODO:: 这里不应该减去一个,数值的反复加减容易造成数值精度出问题?而应该保存叠加lambda前的值,在这里直接赋值
for (ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if(strategy_==1) {
Hessian_(i, i) /= 1.0 + currentLambda_;//H回退: H(k) = 1/(1+λ) * H(k+1),策略1
} else if(strategy_==2 || strategy_==3) {
Hessian_(i, i) -= currentLambda_;
}
}
}
//Nielsen的方法,分母直接为L,判断\rho的符号
bool Solver::isGoodStepInLM() {
bool ret = false;
assert(Hessian_.rows() == Hessian_.cols() && "Hessian is not square");
if(strategy_==1) {
double tempChi = computeChi();
ulong size = Hessian_.cols();
MatXX diag_hessian(MatXX::Zero(size, size));
for(ulong i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
diag_hessian(i, i) = Hessian_(i, i);
}
double scale = delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * diag_hessian * delta_x_ + b_);//scale就是rho的分母
double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;//计算rho
// update currentLambda_
double epsilon = 0.75;
double L_down = 9.0;
double L_up = 11.0;
if(rho > epsilon && isfinite(tempChi)) {
currentLambda_ = std::max(currentLambda_ / L_down, 1e-7);
currentChi_ = tempChi;
ret = true;
ROS_DEBUG("choose L_down");
} else {
currentLambda_ = std::min(currentLambda_ * L_up, 1e7);
ret = false;
ROS_DEBUG("choose L_up");
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy1: currentLambda_: %e,rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, scale: %e",
currentLambda_, rho, currentChi_, tempChi, scale);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho <<
", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() <<
", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() );
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nb_: " << b_.transpose());
} else if(strategy_==2) {
// 统计所有的残差
double tempChi_p_h = 0.0, tempChi_p_alpha_h = 0.0;
tempChi_p_h = computeChi();
double alpha_up = b_.transpose() * delta_x_;
double alpha_down = (tempChi_p_h - currentChi_) / 2. + 2. * alpha_up;
double alpha_tmp = alpha_up / alpha_down;
double scale = 0;
scale = fabs((alpha_tmp * delta_x_).transpose() * (currentLambda_ * (alpha_tmp * delta_x_) + b_));
scale += 1e-3; // make sure it's non-zero :)
//回滚刚才更新的x=x+△x,使用α重新更新x=x + α*△x,并重新计算残差和chi
rollbackStates();
updateStates(alpha_tmp);
preMakeHessian();//更新状态之后就要更新reidual
tempChi_p_alpha_h = computeChi();
double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi_p_alpha_h) / scale;
if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi_p_alpha_h)) { // last step was good, 误差在下降
currentLambda_ = std::max(currentLambda_ / (1 + alpha_tmp), 1e-7);
lm_alpha_ = alpha_tmp;
currentChi_ = tempChi_p_alpha_h;
ret = true;
} else {
currentLambda_ = currentLambda_ + fabs(tempChi_p_alpha_h - currentChi_) / (2 * alpha_tmp);
ret = false;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy2: currentLambda_: %e,alpha_tmp: %e, rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi_p_h: %e, tempChi_p_alpha_h: %e, scale: %e",
currentLambda_, alpha_tmp, rho, currentChi_, tempChi_p_h, tempChi_p_alpha_h, scale);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho <<
", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()
<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());
} else if(strategy_==3) {
double scale = 0;
scale = fabs(delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * delta_x_ + b_));
scale += 1e-3; // make sure it's non-zero :)
// 统计更新后的所有的chi()
double tempChi = computeChi();
double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;
if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi)) // last step was good, 误差在下降
{
double alpha = 1. - pow((2 * rho - 1), 3);//更新策略跟课件里面一样
//TODO:这个ceres里面没有限制上限为2/3
alpha = std::min(alpha, 2. / 3.);
double scaleFactor = (std::max)(1. / 3., alpha);
currentLambda_ *= scaleFactor;//课程里面应该是μ,需要绘制曲线
ni_ = 2; //v
currentChi_ = tempChi;
ret = true;
} else {//如果\rho<0则增大阻尼μ,减小步长
currentLambda_ *= ni_;
ni_ *= 2;//2这个值越大,λ增长越快
ret = false;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy3: currentLambda_: %e, ni_: %e, rho: %f, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, scale: %e",
currentLambda_, ni_, rho, currentChi_, tempChi, scale);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nret = " << ret <<", rho>0 = " << (rho>0) <<", rho: " << rho << ", delta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()
<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());
/* FILE *fp_lambda = fopen(file_name_.data(), "a");
fprintf(fp_lambda, "%d, %f\n", try_iter_, currentLambda_);
fflush(fp_lambda);
fclose(fp_lambda);*/
}
ROS_DEBUG("\n%d record lambda finish\n", try_iter_);
return ret;
}
/*
* @brief conjugate gradient with perconditioning
*
* the jacobi PCG method 共轭梯度法
* 知乎有一篇帖子是针对PCG进行改进的,能减少迭代次数:对角线预处理和不完备的Cholesky预处理
* https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/521753443
*/
Eigen::MatrixXd Solver::pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter = -1) {
assert(A.rows() == A.cols() && "PCG solver ERROR: A is not a square matrix");
int rows = b.rows();
int n = maxIter < 0 ? rows : maxIter;
VecX x(VecX::Zero(rows));
MatXX M_inv = A.diagonal().asDiagonal().inverse();//取对角线阵的逆矩阵
VecX r0(b); // initial r = b - A*0 = b
VecX z0 = M_inv * r0;
VecX p(z0);
VecX w = A * p;
double r0z0 = r0.dot(z0);
double alpha = r0z0 / p.dot(w);
VecX r1 = r0 - alpha * w;
int i = 0;
double threshold = 1e-5 * r0.norm(); //比例调大可以提高阈值,放宽停止条件
while (r1.norm() > threshold && i < n) {
i++;
VecX z1 = M_inv * r1;
double r1z1 = r1.dot(z1);
double belta = r1z1 / r0z0;
z0 = z1;
r0z0 = r1z1;
r0 = r1;
p = belta * p + z1;
w = A * p;
alpha = r1z1 / p.dot(w);
x += alpha * p;
r1 -= alpha * w;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nPCG iter times: %d, n: %d, r1.norm(): %f, threshold: %f", i, n, r1.norm(), threshold);
return x;
}
/*Solve Hx = b, we can use PCG iterative method or use sparse Cholesky*/
//TODO:使用PCG迭代而非SVD分解求解
void Solver::solveLinearSystem() {
//method1:直接求逆求解
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.inverse() * b_;
// delta_x_ = H.ldlt().solve(b_);
//method2:Schur消元求解,marg掉drop_set中的parameter
#ifdef USE_SCHUR
//step1:Schur消元求
//求解Hx=b,之前marg时不用求出△x,只需要H,所以不用对方程组求解,但现在优化时需要求解出整个△x
TicToc t_Schur_PCG;
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_solver = 0.5 * (Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m) + Hessian_.block(0, 0, m, m).transpose());
Eigen::VectorXd bmm_solver = b_.segment(0, m);
Eigen::MatrixXd Amr_solver = Hessian_.block(0, m, m, n);
Eigen::MatrixXd Arm_solver = Hessian_.block(m, 0, n, m);
Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_solver = Hessian_.block(m, m, n, n);
Eigen::VectorXd brr_solver = b_.segment(m, n);
//求Amm_solver^(-1)
TicToc t_Amm_inv;
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_inv_solver = Amm_solver.inverse();//SelfAdjointEigenSolver和直接求逆速度差不多
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_Amm_inv cost: %f ms", t_Amm_inv.toc());
Eigen::MatrixXd tmpA_solver = Arm_solver * Amm_inv_solver;
//step1: Schur补
Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur = Arr_solver - tmpA_solver * Amr_solver;
Eigen::VectorXd brr_schur = brr_solver - tmpA_solver * bmm_solver;
ROS_DEBUG("here1");
// step2: solve Arr_schur * delta_x_rr = brr_schur
// method1:直接求逆
// Eigen::MatrixXd Arr_schur_inv = Arr_schur.inverse();
// Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = Arr_schur_inv * brr_schur;
// method2:使用PCG求解
TicToc t_PCG_xrr;
Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_rr = pcgSolver(Arr_schur, brr_schur, Arr_schur.rows()+1); //0.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\n t_PCG_xrr cost %f ms", t_PCG_xrr.toc());
Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_mm = Amm_inv_solver * (bmm_solver - Amr_solver * delta_x_rr);
delta_x_.tail(n) = delta_x_rr;
delta_x_.head(m) = delta_x_mm;
memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组
ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms", t_Schur_PCG.toc());
#else
TicToc t_solve_equation;
// delta_x_ = Hessian_.ldlt().solve(b_);
int pcg_iter_num = Hessian_.rows()+1; // PCG迭代次数,原来给的是rows()*2
delta_x_ = pcgSolver(Hessian_, b_, pcg_iter_num); //0.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nin solveLinearSystem solve equation cost %f ms, pcg_iter_num: %d", t_solve_equation.toc(), pcg_iter_num);//15ms
memcpy(delta_x_array_, delta_x_.data(), sizeof(double) * (int)delta_x_.size());//转为数组,供状态更新使用
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhere3 solve complete, delta_x_.size()=" << delta_x_.size() << ", delta_x_.norm()= "<< delta_x_.norm()
<< ", delta_x_.squaredNorm()=" << delta_x_.squaredNorm() );
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_:" << delta_x_.transpose());
#endif
}
double Solver::dlComputeDenom(const Eigen::VectorXd& h_dl, const Eigen::VectorXd& h_gn,
const double dl_alpha, const double dl_beta) const {
if(h_dl == h_gn)
return currentChi_;
else if(h_dl == b_ / b_.norm() * radius_)
return ( radius_ * (2.0 * (dl_alpha * b_).norm() - radius_) ) / (2 * dl_alpha); //由于取norm(),所以b_符号不变
else
return 0.5 * dl_alpha * pow(1 - dl_beta, 2) * b_.squaredNorm() + dl_beta * (2 - dl_beta) * currentChi_;
}
//求解器相关函数
bool Solver::solve() {
if(method_==kLM) {
// ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)", linearized_jacobians.rows(), linearized_jacobians.cols());
TicToc t_LM_init;
// LM 初始化
computeLambdaInitLM();
ROS_DEBUG("\nsolver computeLambdaInitLM %f ms", t_LM_init.toc());
// LM 算法迭代求解
bool stop = false;
int iter = 0;
//尝试的lambda次数
try_iter_ = 0;
if(strategy_==1) {
false_theshold_ = 10;
} else if(strategy_==2) {
false_theshold_ = 10;
} else if (strategy_==3) {
false_theshold_ = 6;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nstrategy: %d, false_theshold_: %d", strategy_, false_theshold_);
//保存LM阻尼阻尼系数lambda
/* file_name_ = "./lambda.csv";
FILE *tmp_fp = fopen(file_name_.data(), "a");
fprintf(tmp_fp, "iter, lambda\n");
fflush(tmp_fp);
fclose(tmp_fp);*/
TicToc t_LM_iter;
while (!stop && (iter < iterations_)) {
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\niter: " << iter << " , chi= " << currentChi_ << " , Lambda= " << currentLambda_ << "\n");
bool oneStepSuccess = false;
int false_cnt = 0;
while (!oneStepSuccess) // 不断尝试 Lambda, 直到成功迭代一步
{
++try_iter_;
// setLambda
TicToc t_addLambdatoHessianLM;
addLambdatoHessianLM();//0.01ms
ROS_DEBUG("\naddLambdatoHessianLM cost %f ms", t_addLambdatoHessianLM.toc());
// 第四步,解线性方程 H X = B
TicToc t_solveLinearSystem;
solveLinearSystem();//8ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nsolveLinearSystem cost %f ms", t_solveLinearSystem.toc());
TicToc t_removeLambdaHessianLM;
removeLambdaHessianLM();//0.005ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nremoveLambdaHessianLM cost %f ms", t_removeLambdaHessianLM.toc());
// 优化退出条件1: delta_x_ 很小则退出 原来是1e-6
if (delta_x_.squaredNorm() <= 1e-10 || false_cnt > false_theshold_) {
stop = true;
ROS_DEBUG("\ndelta_x too small: %e, or false_cnt=%d > 10 break", delta_x_.squaredNorm(), false_cnt);//都是在这出去的
break;
} else {
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_ squaredNorm matched: " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_ size: " <<delta_x_.size()
<< ", delta_x: " << delta_x_.transpose() );
}
TicToc t_updateStates;
updateStates(-1.0);//0.08ms 1.更新状态 2.preMakeHessian()计算新的residual
ROS_DEBUG("\nupdateStates cost %f ms", t_updateStates.toc());
// 判断当前步是否可行以及 LM 的 lambda 怎么更新
oneStepSuccess = isGoodStepInLM();//误差是否下降
// 后续处理
if (oneStepSuccess) {
TicToc t_backupStates;
backupStates();//若求解成功则备份当前更新的状态量 0.03ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nbackupStates cost %f ms", t_backupStates.toc());
// 在新线性化点 构建 hessian
TicToc t_makeHessian;
makeHessian();
double makeHessian_finish_time = t_makeHessian.toc();
*makeHessian_time_sum_ += makeHessian_finish_time;
++(*makeHessian_times_);
ROS_DEBUG("\nmakeHessian cost: %f ms, avg_makeHessian_time: %f ms, makeHessian_time_sum_: %f, makeHessian_times_: %f",
makeHessian_finish_time, (*makeHessian_time_sum_)/(*makeHessian_times_), *makeHessian_time_sum_, *makeHessian_times_);
// TODO:: 这个判断条件可以丢掉,条件 b_max <= 1e-12 很难达到,这里的阈值条件不应该用绝对值,而是相对值
// double b_max = 0.0;
// for (int i = 0; i < b_.size(); ++i) {
// b_max = max(fabs(b_(i)), b_max);
// }
// // 优化退出条件2: 如果残差 b_max 已经很小了,那就退出
// stop = (b_max <= 1e-12);
false_cnt = 0;
} else {
false_cnt++;
TicToc t_rollbackStates;
rollbackStates(); // 误差没下降,回滚 0.05ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nrollbackStates cost %f ms", t_rollbackStates.toc());
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nfalse_cnt: %d", false_cnt);
}
iter++;
// 优化退出条件3: currentChi_ 跟第一次的chi2相比,下降了 1e6 倍则退出
if (sqrt(currentChi_) <= stopThresholdLM_) {
ROS_DEBUG("\ncurrentChi_ decrease matched break condition");
stop = true;
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nLM iterate %f ms", t_LM_iter.toc());
/* std::cout << "problem solve cost: " << t_solve.toc() << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << " makeHessian cost: " << t_hessian_cost_ << " ms" << std::endl;*/
} else if(method_==kDOGLEG) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nDL iter num: %d", iterations_);
//1.初始化 radius,g=b=J^Te
radius_ = 1;
epsilon_1_ = 1e-10;
//向量无穷范数:cwiseAbs:"coordinate-wise"(逐元素)取绝对值,colwise().sum()计算每行的绝对值之和,maxCoeff()得最大值
bool use_last_hessian = true;
bool stop = (linearized_residuals.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() < epsilon_3_) ||
(b_.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() <= epsilon_1_);
int iter = 0;
double rho, tempChi;
double rho_numerator, rho_denominator;
bool stop_cond_1;
currentChi_ = computeChi();
//2.循环 stop=||e||无穷范数<=阈值3 或 ||g||无穷范数<=阈值1
while (!stop && (iter < iterations_)) {
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\niter: " << iter << " , chi= " << currentChi_ << " , radius_= " << radius_ << "\n");
// if(!use_last_hessian)
// makeHessian();
double dl_alpha = b_.squaredNorm() / (linearized_jacobians * b_).squaredNorm();//都是取二范数平方,就不区分b的符号了
//3.计算h_sd
Eigen::VectorXd h_sd = dl_alpha * b_;
//4.计算g_gn
solveLinearSystem();//比较耗时
Eigen::VectorXd h_gn = delta_x_;
//5.计算h_dl
Eigen::VectorXd h_dl;
Eigen::VectorXd a = dl_alpha * h_sd;
Eigen::VectorXd b = h_gn;
double c = a.transpose() * (b - a);
double dl_beta;
if(c<=0) {
double tmp_1 = (b-a).squaredNorm();
dl_beta = (-c + sqrt(pow(c,2) + tmp_1 * (pow(radius_, 2) - a.squaredNorm()))) / tmp_1;
} else {
double tmp_1 = pow(radius_, 2) - a.squaredNorm();
dl_beta = tmp_1 / (c + sqrt(pow(c, 2) + (b-a).squaredNorm() * tmp_1));
}
if(b.norm() <= radius_)
h_dl = h_gn;
else if(a.norm() >= radius_)
h_dl = h_sd / h_sd.norm() * radius_;
else {
h_dl = a + dl_beta * (h_gn - a);
}
//判断是否需要继续迭代
get_cur_parameter(cur_x_array_);
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> x{cur_x_array_, x_size_};
double tmp_1 = h_dl.norm();
double tmp_2 = epsilon_2_*(x.norm() + epsilon_2_);
stop_cond_1 = tmp_1 <= tmp_2;
ROS_DEBUG("\ntmp_1: %f, tmp_2: %f, stop_cond_1: %d", tmp_1, tmp_2, stop_cond_1);
if(stop_cond_1) {//设为1e-12
stop = true;
} else {
//更新
updateStates(-1.0);
tempChi = computeChi();
rho = 0.0;
rho_numerator = currentChi_ - tempChi;
rho_denominator = dlComputeDenom(h_dl, h_gn, dl_alpha, dl_beta);
rho = rho_numerator / rho_denominator;
if(rho > 0) {
//执行更新,即保存备份
backupStates();
preMakeHessian();
TicToc t_makeHessian;
makeHessian();
double makeHessian_finish_time = t_makeHessian.toc();
makeHessian_time_sum_ += makeHessian_finish_time;
++makeHessian_times_;
ROS_DEBUG("\nmakeHessian cost: %f ms, avg_makeHessian_time: %f ms, makeHessian_time_sum_: %f, makeHessian_times_: %f",
makeHessian_finish_time, makeHessian_time_sum_/makeHessian_times_, makeHessian_time_sum_, makeHessian_times_);
use_last_hessian = false;
} else {
rollbackStates();
use_last_hessian = true;
}
get_cur_parameter(cur_x_array_);
if(rho > 0.75) {
radius_ = std::max(radius_, 3*h_dl.norm());
} else {
radius_ = 0.5 * radius_;
stop = radius_ < epsilon_2_*(x.norm() + epsilon_2_);
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nDL: radius_: %e, rho: %f, rho>0 = %d, currentChi_: %e, tempChi: %e, rho_numerator: %e, rho_denominator: %e",
radius_, rho, rho>0, currentChi_, tempChi, rho_numerator, rho_denominator);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ndelta_x_.squaredNorm(): " << delta_x_.squaredNorm() << ", delta_x_: " << delta_x_.transpose()
<< "\nb_.norm(): " << b_.norm() << ", b_: " << b_.transpose());
++iter;
}
ROS_DEBUG("\n finish DL iter, stop: %d or iter: %d >= %d", stop, iter, iterations_);
//6.根据h_dl.norm()判断是否迭代
// 若迭代则更新x(涉及状态更新,residual计算),计算rho,根据rho来更新x和raidus
}
return true;
}
}
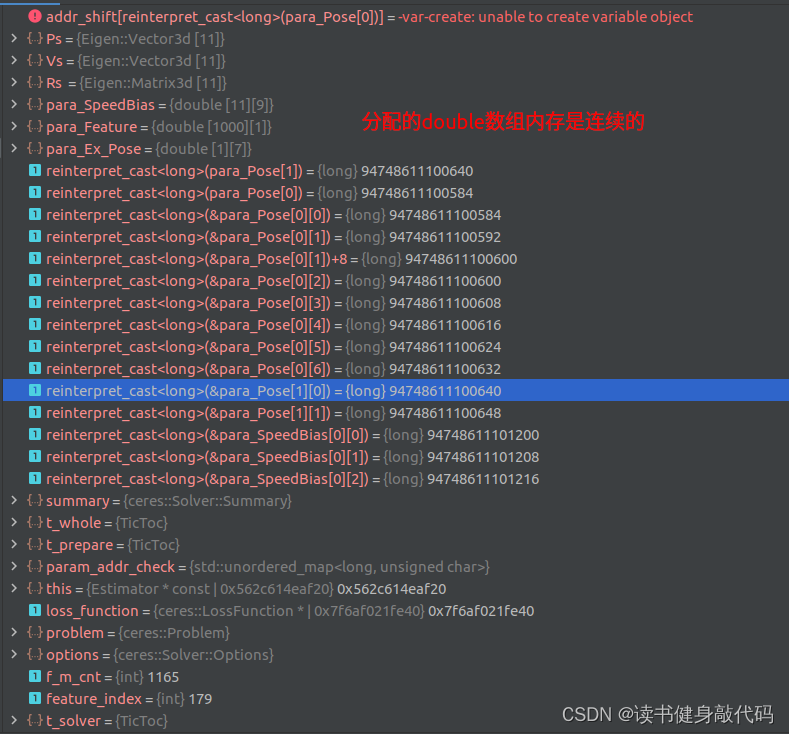
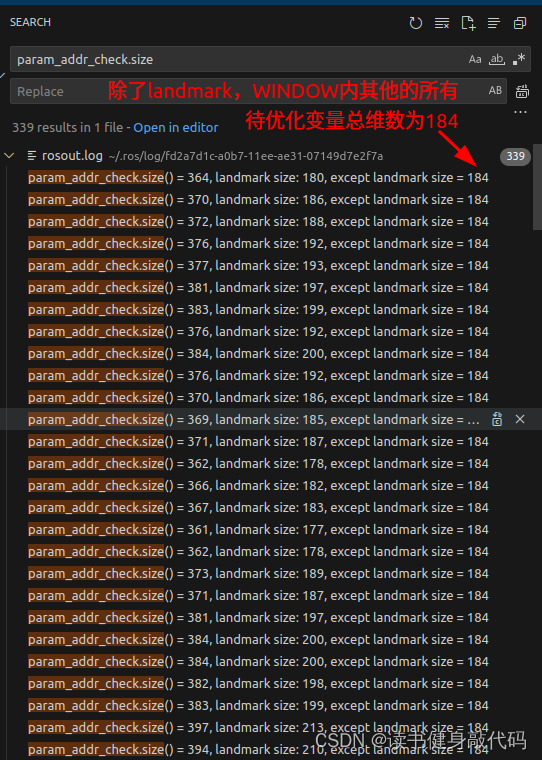
WINDOW内所有待优化变量维度统计,估计 t d t_d td?,无快速重定位时共 172 + L 172+L 172+L,其中 L L L为WINDOW内的landmark数量
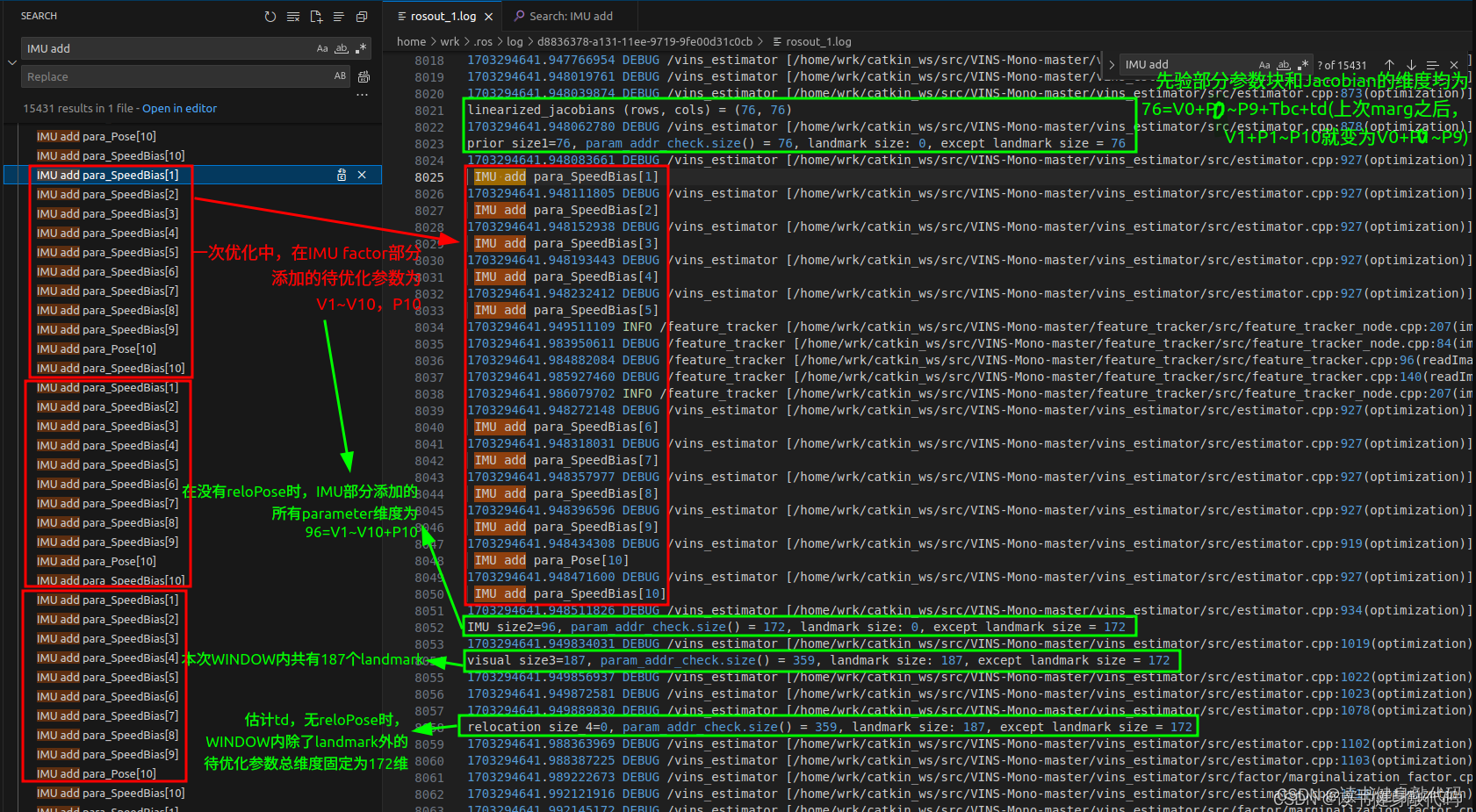
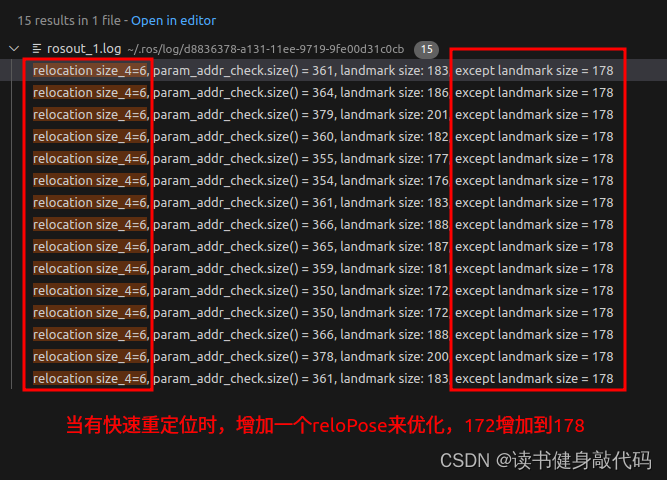
debug代码,定义两个unordered_map容器param_addr_check,landmark_addr_check,注意SIZE_POSE要-1去除冗余来统计:
//用于check维度
std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> param_addr_check;//所有param维度
std::unordered_map<long, uint8_t> landmark_addr_check;//landmark维度
//1.添加边缘化残差(先验部分)
size_t size_1=0;
if (last_marginalization_info)
{
// construct new marginlization_factor
MarginalizationFactor *marginalization_factor = new MarginalizationFactor(last_marginalization_info);//里面设置了上次先验的什么size,现在还不懂
problem.AddResidualBlock(marginalization_factor, NULL,
last_marginalization_parameter_blocks);
// /*用于check维度是否正确*/
// parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(addr)] = size;
for(int i=0; i<last_marginalization_parameter_blocks.size(); ++i) {
if(last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])]==1) {
ROS_DEBUG("here have 1 dimend");
// landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])] = 1;
}
size_t tmp_size = last_marginalization_info->parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i])];
tmp_size = tmp_size==7 ? 6: tmp_size;
//这个double*的地址代表的待优化变量的local_size,把每个地址都记录在map中,分配给待优化变量的地址都是连续的
for(int j=0; j<tmp_size; ++j) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(last_marginalization_parameter_blocks[i]) + (double)j * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
//打印prior的Jacobian维度
ROS_DEBUG("\nlinearized_jacobians (rows, cols) = (%lu, %lu)",
last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.rows(), last_marginalization_info->linearized_jacobians.cols());
size_1 = param_addr_check.size();//应该是76 实际87
ROS_DEBUG("\nprior size1=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_1, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
//2.添加IMU残差
for (int i = 0; i < WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
{
int j = i + 1;
//两帧KF之间IMU积分时间过长的不进行优化(可能lost?)
if (pre_integrations[j]->sum_dt > 10.0)
continue;
IMUFactor* imu_factor = new IMUFactor(pre_integrations[j]);//这里的factor就是残差residual,ceres里面叫factor
problem.AddResidualBlock(imu_factor, NULL, para_Pose[i], para_SpeedBias[i], para_Pose[j], para_SpeedBias[j]);
//check维度
long addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[i]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_Pose[%d]", i);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[i]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", i);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[j]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_Pose[%d]", j);
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
addr = reinterpret_cast<long>(para_SpeedBias[j]);
if(param_addr_check.find(addr) == param_addr_check.end()) {
ROS_DEBUG("\n IMU add para_SpeedBias[%d]", j);
for (int k = 0; k < SIZE_SPEEDBIAS; ++k) {
param_addr_check[addr + (long) k * (long) sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
}
}
size_t size_2 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1;//应该是81 V2~V10 实际97为啥???
ROS_DEBUG("\nIMU size2=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_2, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
//3.添加视觉残差
int f_m_cnt = 0;
int feature_index = -1;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
//!(至少两次tracking,且最新帧1st的tracking不能算(因为1st可能被marg掉),start_frame最大是[7])
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
++feature_index;
int imu_i = it_per_id.start_frame, imu_j = imu_i - 1;
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;
//这个id的feature的第一帧和后面所有的帧分别构建residual block
for (auto &it_per_frame : it_per_id.feature_per_frame)
{
imu_j++;
if (imu_i == imu_j)
{
continue;
}
Vector3d pts_j = it_per_frame.point;
//是否要time offset
if (ESTIMATE_TD)
{
//对于一个feature,都跟[it_per_id.start_frame]帧进行优化
ProjectionTdFactor *f_td = new ProjectionTdFactor(pts_i, pts_j, it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].velocity, it_per_frame.velocity,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].cur_td, it_per_frame.cur_td,
it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].uv.y(), it_per_frame.uv.y());
problem.AddResidualBlock(f_td, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index], para_Td[0]);
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Td[0])] = 1;
/*
double **para = new double *[5];
para[0] = para_Pose[imu_i];
para[1] = para_Pose[imu_j];
para[2] = para_Ex_Pose[0];
para[3] = para_Feature[feature_index];
para[4] = para_Td[0];
f_td->check(para);
*/
}
else
{
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[imu_i], para_Pose[imu_j], para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_i]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[imu_j]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
}
f_m_cnt++;
}
}
size_t size_3 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2;//应该和landmark_addr_check.size一样
ROS_DEBUG("\nvisual size3=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_3, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
ROS_DEBUG("visual measurement count: %d", f_m_cnt);//总的视觉观测个数,观测可能是在不同帧对同一个landmark进行观测,所以可能查过1000,注意与landmark个数进行区分
ROS_DEBUG("prepare for ceres: %f", t_prepare.toc());
//4.添加闭环检测残差,计算滑动窗口中与每一个闭环关键帧的相对位姿,这个相对位置是为后面的图优化(pose graph)准备 或者是 快速重定位(崔华坤PDF7.2节)
//这里注意relo_pose是Tw2_bi = Tw2_w1 * Tw1_bi
if(relocalization_info)
{
//printf("set relocalization factor! \n");
ceres::LocalParameterization *local_parameterization = new PoseLocalParameterization();
problem.AddParameterBlock(relo_Pose, SIZE_POSE, local_parameterization);
int retrive_feature_index = 0;
int feature_index = -1;
for (auto &it_per_id : f_manager.feature)
{
it_per_id.used_num = it_per_id.feature_per_frame.size();
if (!(it_per_id.used_num >= 2 && it_per_id.start_frame < WINDOW_SIZE - 2))
continue;
++feature_index;
int start = it_per_id.start_frame;
if(start <= relo_frame_local_index)//必须之前看到过
{
//1.先在i中match的点中找到可能是现在这个feature的id的index
while((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() < it_per_id.feature_id)//.z()存的是i,j两帧match上的feature的id
{
retrive_feature_index++;
}
//2.如果是,则WINDOW内的it_per_id.feature_id这个id的landmark就是被loop上的landmark,取归一化坐标,
if((int)match_points[retrive_feature_index].z() == it_per_id.feature_id)
{
//pts_j是i帧的归一化平面上的点,这里理解relo_Pose及其重要,relo_Pose实际上是Tw2_bi,视觉重投影是从WINDOW内的start帧的camera(在w2系下),投影到i帧(在w1系下),耦合了Tw1_w2
Vector3d pts_j = Vector3d(match_points[retrive_feature_index].x(), match_points[retrive_feature_index].y(), 1.0);
Vector3d pts_i = it_per_id.feature_per_frame[0].point;//start中的点
ProjectionFactor *f = new ProjectionFactor(pts_i, pts_j);
//relo_Pose是Tw2_bi
problem.AddResidualBlock(f, loss_function, para_Pose[start], relo_Pose, para_Ex_Pose[0], para_Feature[feature_index]);
retrive_feature_index++;
//check维度
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Pose[start]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(relo_Pose) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
for(int k=0; k<SIZE_POSE-1; ++k) {
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Ex_Pose[0]) + (long)k * (long)sizeof(long)] = 1;
}
param_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
landmark_addr_check[reinterpret_cast<long>(para_Feature[feature_index])] = 1;
ROS_DEBUG("\nhas relocation blocks\n");
}
}
}
}
size_t size_4 = param_addr_check.size() - size_1 - size_2 - size_3;//没有loop时应该为0
ROS_DEBUG("\nrelocation size_4=%lu, param_addr_check.size() = %lu, landmark size: %lu, except landmark size = %lu",
size_4, param_addr_check.size(), landmark_addr_check.size(), param_addr_check.size()-landmark_addr_check.size());//landmark_addr_check中多加了个td
9.3 solve.h
//
// Created by wrk on 2023/12/22.
//
#ifndef CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H
#define CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/console.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "eigen_types.h"
#include "../utility/tic_toc.h"
#include "../parameters.h"
namespace solve {
/*定义factor管理类
* */
const int NUM_THREADS = 4;
struct ResidualBlockInfo
{
ResidualBlockInfo(ceres::CostFunction *_cost_function, ceres::LossFunction *_loss_function, std::vector<double *> _parameter_blocks, std::vector<int> _drop_set)
: cost_function(_cost_function), loss_function(_loss_function), parameter_blocks(_parameter_blocks), drop_set(_drop_set) {}
void Evaluate();
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function;
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;
std::vector<double *> parameter_blocks;//优化变量数据的地址,sizes每个优化变量块的变量大小,以IMU残差为例,为[7,9,7,9]
std::vector<int> drop_set;//待边缘化的优化变量id
double **raw_jacobians;//二重指针,是为了配合ceres的形参 double** jacobians
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix<double, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::RowMajor>> jacobians;//这个数据结构看不懂,
Eigen::VectorXd residuals;//残差 IMU:15X1 视觉:2X1
int localSize(int size)
{
return size == 7 ? 6 : size;
}
};
struct ThreadsStruct
{
std::vector<ResidualBlockInfo *> sub_factors;
Eigen::MatrixXd A;
Eigen::VectorXd b;
std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_size; //global size
std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_idx; //local size
};
class Solver
{
public:
Solver(uint8_t strategy): method_(kLM), iterations_(1), strategy_(strategy), lm_alpha_(1), mem_allocated_(false){};
~Solver();
int localSize(int size) const;
int globalSize(int size) const;
void addResidualBlockInfo(ResidualBlockInfo *residual_block_info);//加残差块相关信息(优化变量、待marg的变量)
void preMakeHessian();//计算每个残差对应的Jacobian,并更新parameter_block_data
void makeHessian();//pos为所有变量维度,m为需要marg掉的变量,n为需要保留的变量
std::vector<double *> getParameterBlocks(std::unordered_map<long, double *> &addr_shift);
std::vector<ResidualBlockInfo *> factors;//所有观测项
int m, n;//m为要边缘化的变量个数(也就是parameter_block_idx的总localSize,以double为单位,VBias为9,PQ为6,),n为要保留下来的变量个数
//parameter_block_size 和 parameter_block_data分别对应block的大小和实际数据
std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_size; //global size <优化变量内存地址,localSize>
int sum_block_size;
std::unordered_map<long, int> parameter_block_idx; //local size 排序前是<待边缘化的优化变量内存地址,在parameter_block_size中的id>,排序后是<marg, id>m维 <remain, id>n维
std::unordered_map<long, double *> parameter_block_data;//<优化变量内存地址,数据>
std::unordered_map<long, double *> parameter_block_data_backup;//<优化变量内存地址,数据>
std::vector<int> keep_block_size; //global size
std::vector<int> keep_block_idx; //local size
std::vector<double *> keep_block_data;//之前看到的帖子说这是在marg过程中反解出的线性化点的参数值x0
Eigen::MatrixXd linearized_jacobians;//线性化点处的Jacobian
Eigen::VectorXd linearized_residuals;//线性化点处的residual
const double eps = 1e-8;
bool solve();
void solveLinearSystem();/// 解线性方程
bool updateStates(double weight) ;/// 更新状态变量
bool backupStates();//回滚状态变量
bool rollbackStates(); // 有时候 update 后残差会变大,需要退回去,重来
double computeChi() const;
void computeLambdaInitLM();/// 计算LM算法的初始Lambda
void addLambdatoHessianLM();/// Hessian 对角线加上或者减去 Lambda
void removeLambdaHessianLM();
bool isGoodStepInLM();/// LM 算法中用于判断 Lambda 在上次迭代中是否可以,以及Lambda怎么缩放
Eigen::MatrixXd pcgSolver(const MatXX &A, const VecX &b, int maxIter);/// PCG 迭代线性求解器
enum SolveMethod
{
kLM = 0,
kDOGLEG = 1
};
SolveMethod method_;
int iterations_;//迭代轮数
double currentChi_;
//LM参数
double currentLambda_;//LM中的阻尼因子,DOGLEG中的radius
double stopThresholdLM_; // LM 迭代退出阈值条件
std::string file_name_;
int try_iter_;
int false_theshold_;//每轮迭代允许的最大失败次数
double ni_; //strategy3控制 Lambda 缩放大小
double lm_alpha_; //strategy2更新使用的alpha
//求解结果
// VecX delta_x_rr_;
// VecX delta_x_mm_;
//DL参数
double radius_;
double epsilon_1_, epsilon_2_, epsilon_3_;
// double dl_alpha_;
/// 整个信息矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd Hessian_;
Eigen::VectorXd b_;
Eigen::VectorXd delta_x_;
//多留100的余量,这个是成员变量,在程序中是局部变量,放在栈区,不需要手动释放内存,因为它会在其作用域结束时自动被销毁
const int x_size_ = 1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100;
double cur_x_array_[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];
double delta_x_array_[1000 + (WINDOW_SIZE + 1) * (SIZE_POSE + SIZE_SPEEDBIAS) + SIZE_POSE + 1 + 100];
//是否已调用preMakeHessian分配过内存
bool mem_allocated_;
uint8_t strategy_;
double *makeHessian_time_sum_;//这个需要手撸才能统计时间,ceres无法统计
double *makeHessian_times_;
private:
bool get_cur_parameter(double* cur_x_array);
double dlComputeDenom(const Eigen::VectorXd& h_dl, const Eigen::VectorXd& h_gn,
const double dl_alpha, const double dl_beta) const;
};
}
#endif //CATKIN_WS_SOLVE_H
后面这些是在debug时的一些记录,可以略过不看。
9.4 LM的 λ \lambda λ初始化中的 τ \tau τ取值是否合适?

上面给的
τ
\tau
τ在
[
1
e
?
8
,
1
]
[1e-8,1]
[1e?8,1] 这个范围内不是绝对的,要根据实际的情况来设定:
- 太大可能导致 λ \lambda λ过大,步长过小,求出的 Δ x \Delta x Δx过小,更新不动 x x x;
- 太小可能导致 λ \lambda λ过大,步长过大, ρ \rho ρ一直 < 0 <0 <0,无法找到正确的迭代方向, x x x一直无法更新。
比如VINS-MONO中,如果使用strategy3,则 τ \tau τ大概为 1 e ? 15 1e^{-15} 1e?15数量级左右。
9.5 Schur消元求解之后更新先验的residual
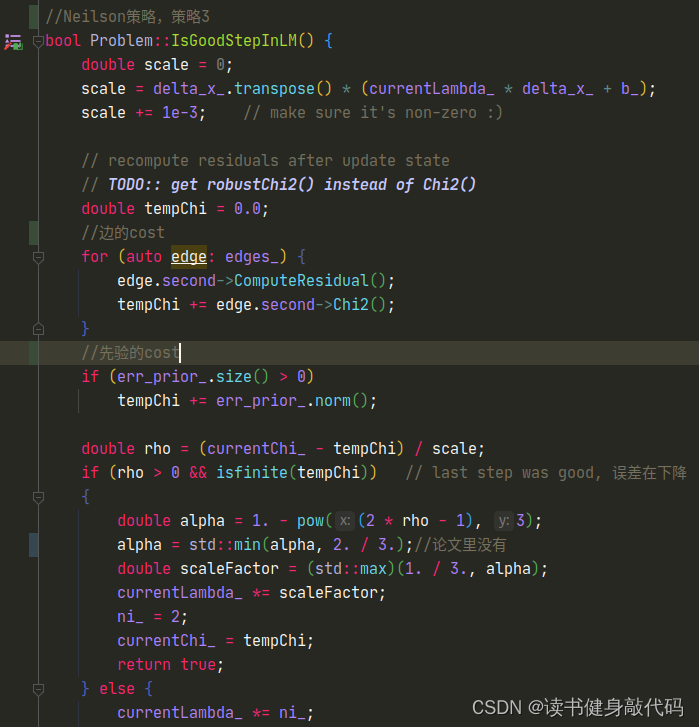
χ
\chi
χ实际上就是
e
T
W
e
e^TWe
eTWe
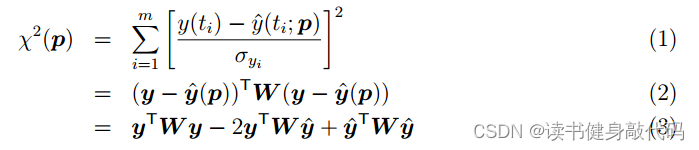
线性化点再挖一个坑:
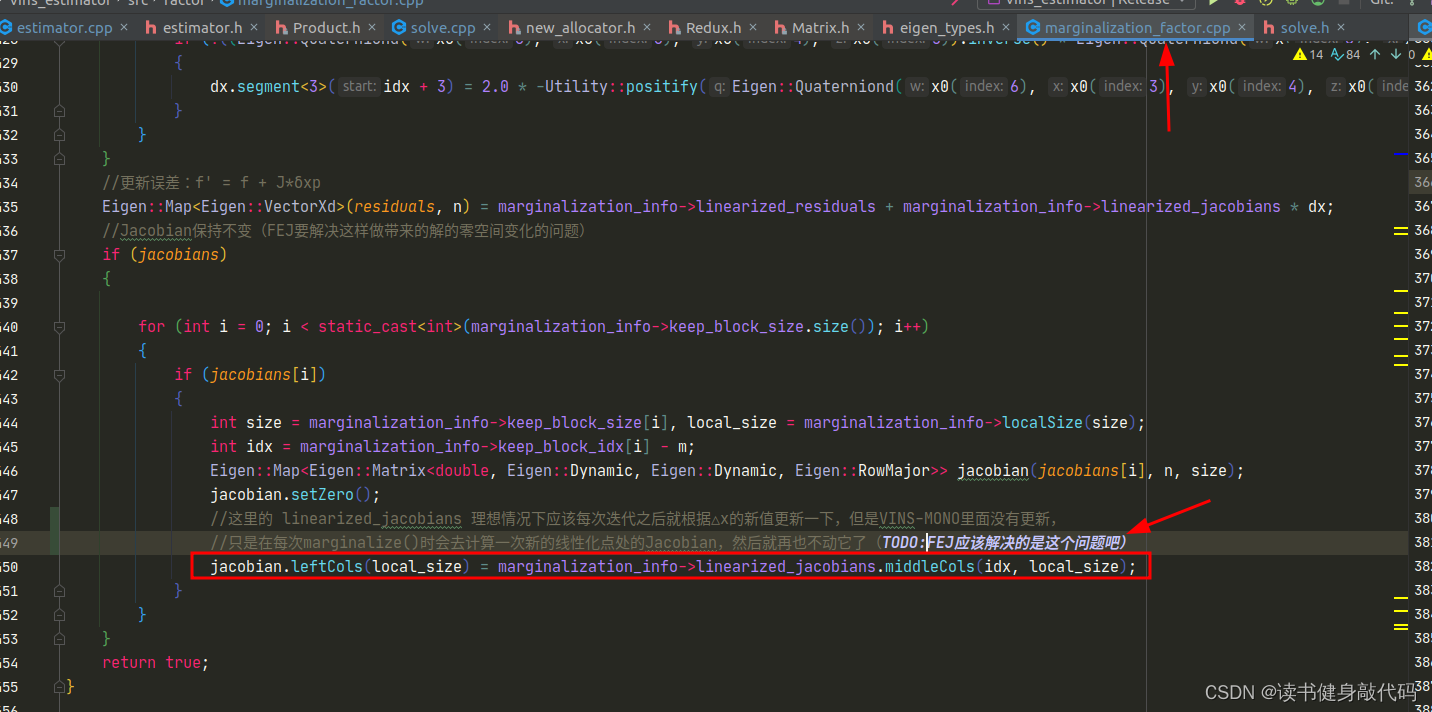
恍然大悟的evaluate()函数得Jacobian
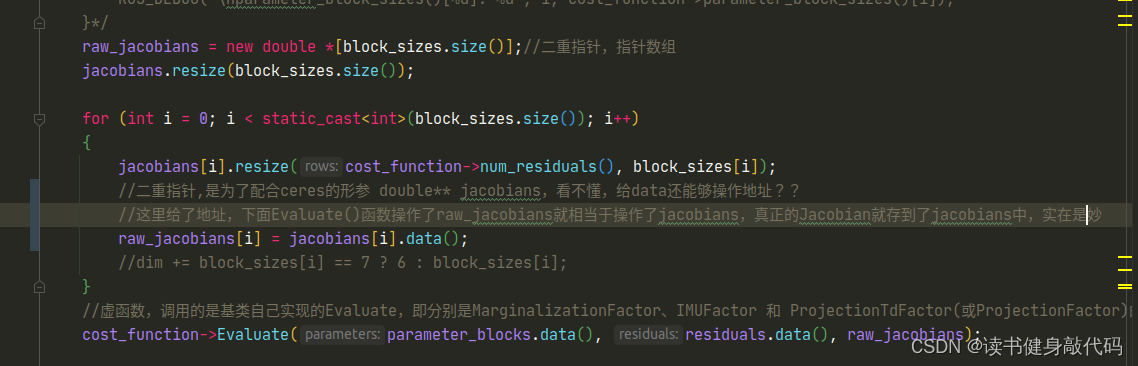
在preMarginalize()中调用的,因为marg不用ceres,不会在内部维护jacobian,所以需要手动调用计算Jacobian,多态调用evaluate(),根据上面,二重指针从raw_jacobians传给jacobians,所以在ThreadsConstructA中可以拿到Jacobian,实在是妙。
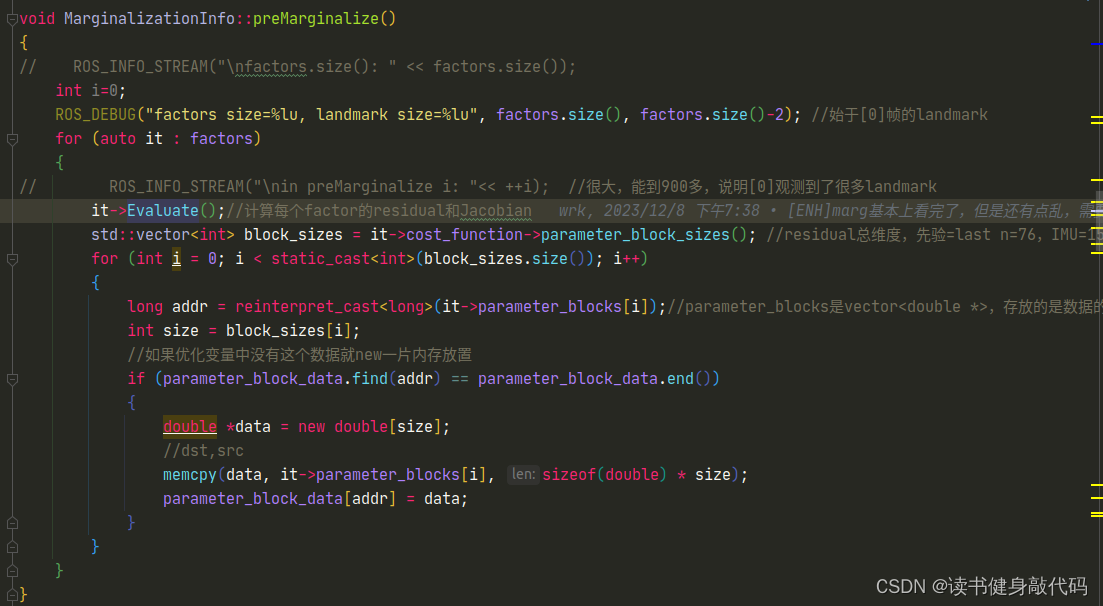
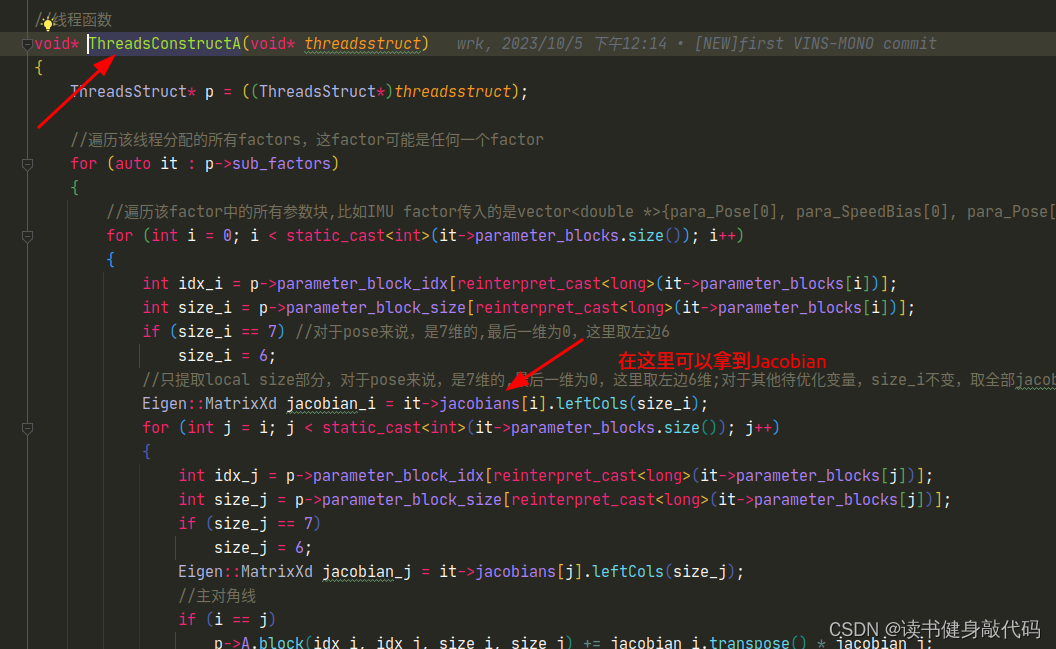
根据以上理解,在LM中每次更新完 x = x + Δ x x=x+\Delta x x=x+Δx后,就需要重新计算一下Jacobian和residual,下次evaluate时就会用到新的residual,
对于prior的residual,和VINS-MONO保持一样,不动Jacobian的值。
9.6 计算 χ = e T W e \chi=e^TWe χ=eTWe时需要考虑loss_function
在ResidualBlockInfo::Evaluate()中调用的多态Evaluate()函数后已经考虑了loss_function对Jacobian和residual的加权
9.7 先验的参数实际上就是V0,P0~P10,Tbc,td,而不是一个单独的特殊量
9.8 Hessian可视化
之前Debug b的时候曾经反解出J并打印出来过,可以看到
J
T
J
J^TJ
JTJ还是非常稀疏的:
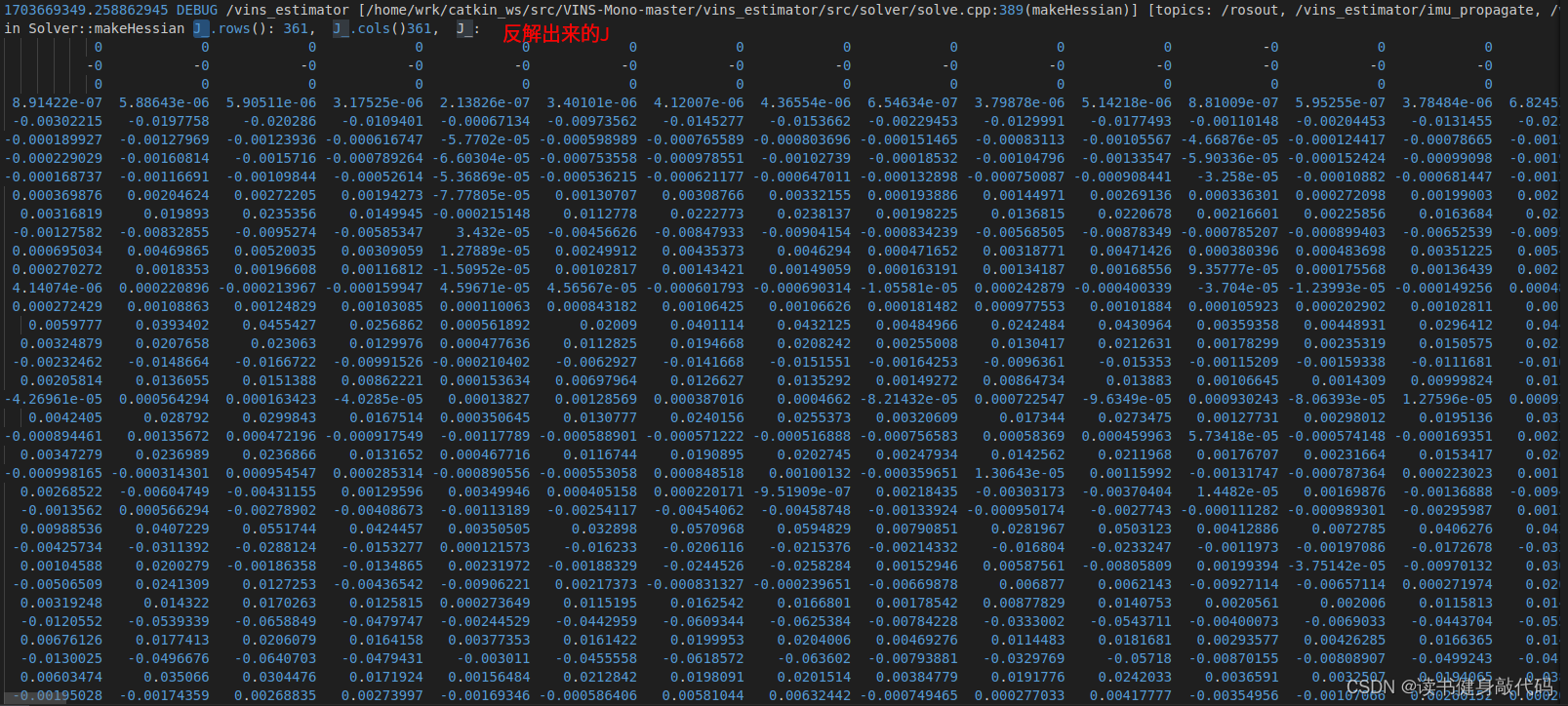

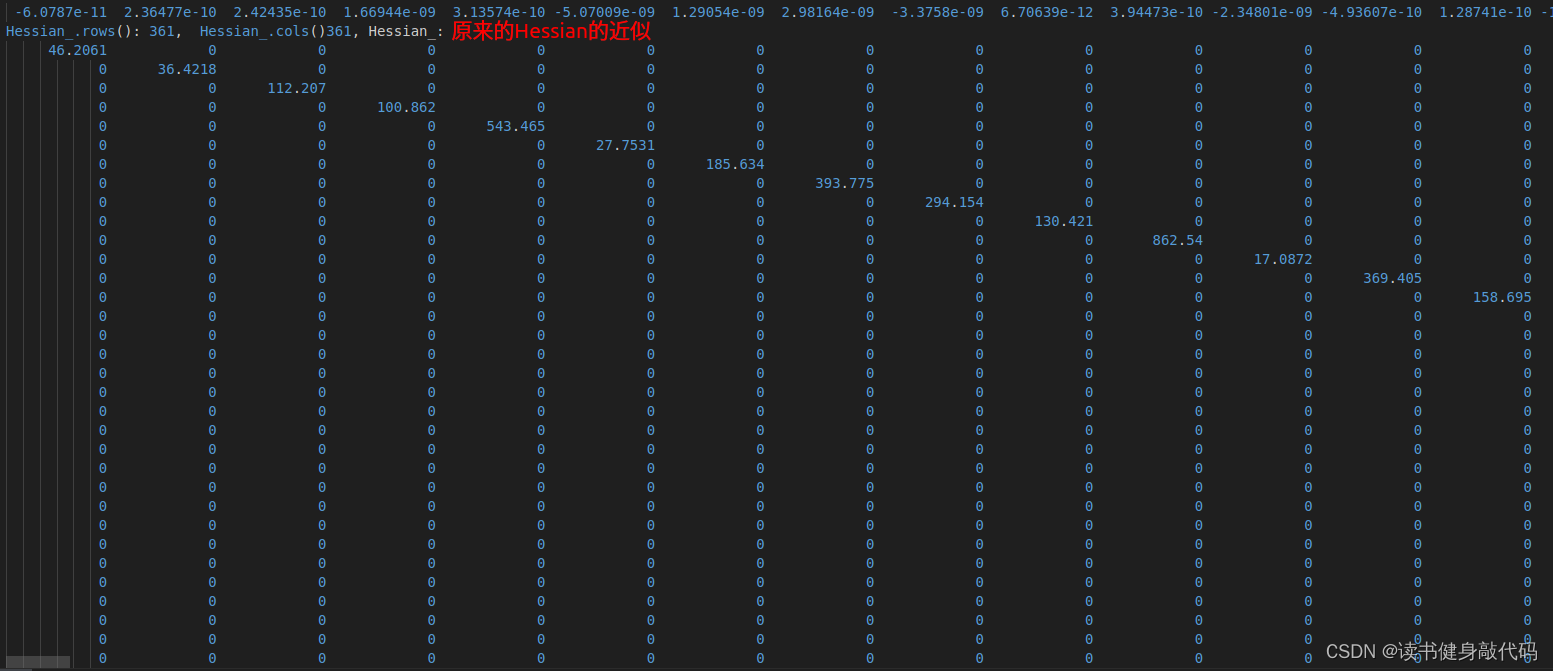
反解之后再算
J
T
?
J
J^T*J
JT?J,有些为0的已经不为0了,但是数值很小,大概是1e-10数量级,但主对角线可以看出还是正确的,所以反解总体上没问题。实际上J的rows()应该是观测的总维度(包括11个P,11个V,1个Tbc,1个td,L个landmark所有观测,注意不是L,观测道一次就有二维的reidual,参考《14讲》P247理解),但是从Hessian中只能反解出相同维度的
J
J
J,此处为
316
=
172
+
L
316=172+L
316=172+L,所以不知道观测的总维度为多少。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!